Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differential Equations Chapter1 - Exercise 1
Uploaded by
Muhammad Farhan GulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differential Equations Chapter1 - Exercise 1
Uploaded by
Muhammad Farhan GulCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 1.
1 (Introduction to differential equations):
State the order and linearity:
4
3
3
2
2
2
2) 0 (order 3, non-linear)
5) 1 (order 2, non-linear)
7) ( sin ) (cos ) 2 (order 3, lin
d y dy
x y
dx dx
d y dy
dx dx
y y
| |
+ =
|
\
| |
= +
|
\
= ear)
Determine the linearity of the differential equation:
10) ( ) 0
u
udv v uv ue du + + =
If v is the dependent variable:
( ) 0 (1 )
u u
dv dv
u v uv ue u u v ue
du du
+ + = + + =
(linear in v)
If u is the dependent variable:
( ) 0
u
du
u v uv ue
dv
+ + = (non-linear in u)
Verify that the indicated function is a solution of the given DE:
3
3
3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3
13) 6 13 0 ; cos 2
Let: cos 2
3 cos 2 2 sin 2
9 cos 2 6 sin 2 6 sin 2 4 cos 2
5 cos 2 12 sin 2
x
x
x x
x x x x
x x
y y y y e x
y e x
y e x e x
y e x e x e x e x
e x e x
+ = =
=
=
=
=
3 3 3 3 3
substitute , , into the DE:
6 13 0
5 cos 2 12 sin 2 6(3 cos 2 2 sin 2 ) 13( cos 2 ) 0
x x x x x
y y y
y y y
e x e x e x e x e x
+ =
+ =
3
0 0 (verified)
Therefore cos 2 is a solution to the DE: 6 13 0
x
y e x y y y
=
= + =
2
14) tan ; (cos ) ln(sec tan )
Let: (cos ) ln(sec tan )
cos
sin ln(sec tan ) (sec tan sec )
sec tan
sin ln(sec tan ) 1
y y x y x x x
y x x x
x
y x x x x c x
x x
x x x
+ = = +
= +
= + +
+
= +
2
sin
cos ln(sec tan ) (sec tan sec )
sec tan
cos ln(sec tan ) tan
substitute , , into the DE:
tan
cos ln(sec tan ) tan (cos ) ln(sec
x
y x x x x c x
x x
x x x x
y y y
y y x
x x x x x
= + + +
+
= + +
+ =
+ + tan ) tan
tan tan (verified)
Therefore (cos ) ln(sec tan ) is a solution to the DE: tan
x x x
x x
y x x x y y x
+ =
=
= + + =
3 1/2
1/2
3/2
3
3/2
18) 2 cos ; (1 sin )
Let: (1 sin )
1
(1 sin ) ( cos )
2
substitute , into the DE:
2 cos
1
2( (1 sin ) ( cos )) (
2
y y x y x
y x
y x x
y y
y y x
x x
= =
=
=
=
=
1/2 3
3/2 3/2
1/2 3
(1 sin ) ) cos
(1 sin ) cos (1 sin ) cos (verified)
Therefore (1 sin ) is a solution to the DE: 2 cos
x x
x x x x
y x y y x
=
= =
2 2 2
2 2
2
2
20) 2 ( ) 0; 2 1
From: 2 1
differentiate form: 4 2 2 0
4 2( ) 0
xydx x y dy x y y
x y y
xydx x dy ydy
xydx x y dy
+ = + =
+ =
+ =
=
2
2 2 2
( 2) : 2 ( ) 0 (verified)
Therefore 2 1 is a solution to the DE: 2 ( ) 0
xydx x y dy
x y y xydx x y dy
+ =
+ = + =
2 1
19) =( 1)(1 2 ); ln
1
2 1
From: ln ln(2 1) ln( 1)
1
2 1
differentiate wrt to : 1
(2 1) ( 1)
dX X
X X t
dt X
X
t X X t
X
dX dX
t
X dt X dt
| |
=
|
\
| |
= =
|
\
=
2 1
1
(2 1) ( 1)
2( 1) (2 1)
1
(2 1)( 1)
1
(2 1)( 1)
dX
dt X X
dX X X
dt X X
dX
dt X X
(
=
(
(
=
(
(
1
( 1)(2 1) or =( 1)(1 2 ) (verified)
2 1
Therefore ln is a solution to the DE: =( 1)(1 2 )
1
dX dX
X X X X
dt dt
X dX
t X X
X dt
=
(
=
| |
=
|
\
2 2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2
0 1
0 1
0 1
0 0 1
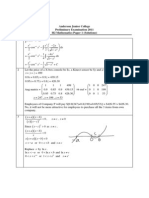
22) 2 1;
From:
( ) ( )
2 2
2
x t x x
x t x x
x t x x
x t x t x x x
x x x
dy
xy y e e dt c e
dx
y e e dt c e
d d
y e e dt c e
dx dx
d
e e dt xe e dt c xe
dx
e e xe
+ = = +
= +
= +
=
=
2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
0 0 1 1
0 0 1 1
2 1 2 2
substitute into the DE:
2 1 1 2 2 2 ( ) 1
t x x t x x x
x t x x t x x x
e dt c xe xe e dt c xe
y
dy
xy xe e dt c xe x e e dt c e
dx
=
+ = + + =
2 2 2
0 1
1 1 (verified)
Therefore is a solution to the DE: 2 1
x t x x
dy
y e e dt c e xy
dx
=
= + + =
Exercise 1.2 (Initial Value Problems)
Given
1
1
(1 )
x
y
c e
=
+
is a one-parameter family of solutions of the DE:
2
y y y = , find a
solution of the first-order IVP consisting this DE and the given initial condition:
1
(0)
1
1 1
1) (0) 1/ 3 0, 1/ 3
1
substitute into the general solution
(1 )
1 1
3 (1 )
(1 ) 3 4
1
solution for the IVP is:
(1 4 )
2) ( 1) 2
x
x
y x y
y
c e
c e
c c
y
e
y x
= = =
=
+
=
+
+ = =
=
=
1
1 1
( 1)
1
(1 )
1, 2
1
substitute into the general solution
(1 )
1 1 1
2 1
2 2 (1 )
1
solution for the IVP is:
[1 0.5 ]
x
x
y
y
c e
c e c
e c e
y
e
+
= =
=
+
= + = =
+
=
Given
1 2
cos sin x c t c t = + is a two-parameter family of solutions of the DE: 0 x x + = , find a
solution of the second-order IVP consisting this DE and the given initial conditions:
1 2 1 2
1 2 1 2
9) ( / 6) 1/ 2, ( / 6) 0
Given: cos sin , sin cos
( / 6) 1/ 2 / 6, 1/ 2
1 1 3 1
cos sin ..... (i)
2 6 6 2 2 2
( / 6) 0 / 6, 0
x x
x c t c t x c t c t
x t x
c c c c
x t x
= =
= + = +
= = =
= + = +
= = =
1 2 1 2
1 2
1 3
0 sin cos 0 ..... (ii)
6 6 2 2
solve (i) and (ii): 3 / 4, 1/ 4
3 1
solution for the IVP is: cos sin
4 4
c c c c
c c
x t t
= + = +
= =
= +
1 2 1 2
1 2 1 2
10) ( / 4) 2, ( / 4) 2 2
Given: cos sin , sin cos
( / 4) 2 / 4, 2
1 1
2 cos sin 2 ..... (i)
4 4 2 2
( / 4) 2 2 / 4, 2 2
x x
x c t c t x c t c t
x t x
c c c c
x t x
= =
= + = +
= = =
= + = +
= = =
1 2 1 2
1 2
1 1
2 2 sin cos 2 2 ..... (ii)
4 4 2 2
solve (i) and (ii): 3, 1
solution for the IVP is: 3cos sin
c c c c
c c
x t t
= + = +
= =
=
Given
1 2
x x
y c e c e
= + is a two-parameter family of solutions of the DE: 0 y y = , find a
solution of the second-order IVP consisting this DE and the given initial conditions:
1 2 1 2
1 1
1 2
1 1
1 2
2
1 2
12) (1) 0, (1)
Given: ,
(1) 0 0 ..... (i)
(1) ..... (ii)
1 1
solve (i) and (ii): ,
2 2
sol
x x x x
y y e
y c e c e y c e c e
y c e c e
y e e c e c e
c c e
= =
= + =
= = +
= =
= =
2
1
ution for the IVP is: ( )
2
x x
y e e
=
1 2 1 2
1
1 2
1
1 2
1 2
13) ( 1) 5, ( 1) 5
Given: ,
( 1) 5 5 ..... (i)
( 1) 5 5 ..... (ii)
solve (i) and (ii): 0, 5 /
x x x x
y y
y c e c e y c e c e
y c e c e
y c e c e
c c e
= =
= + =
= = +
= =
= =
(1 )
solution for the IVP is: 5
x
y e
+
=
You might also like
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Calculus SummaryDocument3 pagesCalculus SummaryJay JayNo ratings yet
- 2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsDocument21 pages2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsNicholas ChoyNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MSMA Chapter 6 - Rainwater HarvestingDocument20 pagesMSMA Chapter 6 - Rainwater HarvestingFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Math 221 Solution To ProblemsDocument16 pagesMath 221 Solution To ProblemsRyan Kristoffer NuñezNo ratings yet
- Bill No.1-Preliminaries - SwgsaDocument4 pagesBill No.1-Preliminaries - SwgsaFaraa Bella0% (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Theories of FailureDocument31 pagesTheories of FailureAnkon MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- D.E 6rd EditionDocument33 pagesD.E 6rd EditionkenNo ratings yet
- Discretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXDocument6 pagesDiscretization-Finite Difference, Finite Element Methods: D Dy Ax BX DX DX Dy DX Dy Ax A DXratchagar aNo ratings yet
- Tema 03 - Derivadas Parciales (Soluciones)Document5 pagesTema 03 - Derivadas Parciales (Soluciones)Javi GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Successive Differentiation and Leibnitz's TheoremDocument14 pagesSuccessive Differentiation and Leibnitz's TheoremNafi AhmedNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document12 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Linear Second (Higher) Order Linear Second (Higher) Order Equations With Constant CoefficientsDocument29 pagesLinear Second (Higher) Order Linear Second (Higher) Order Equations With Constant CoefficientsJean ChanNo ratings yet
- Solving a Quadratic Equation with Complex SolutionsDocument18 pagesSolving a Quadratic Equation with Complex SolutionsispiracNo ratings yet
- II Sem (Csvtu) Mathematics Unit 2 (Linear Differential Equation) SolustionsDocument31 pagesII Sem (Csvtu) Mathematics Unit 2 (Linear Differential Equation) SolustionsMrityunjoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Linear Differential Equations of Order One: The General Solution The General SolutionDocument8 pagesLinear Differential Equations of Order One: The General Solution The General SolutionMarielle Lucas GabrielNo ratings yet
- MillNotes MithrilDocument2 pagesMillNotes MithrilChristopher MillerNo ratings yet
- BT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)Document111 pagesBT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)gerwynngNo ratings yet
- MA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Document6 pagesMA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Bilguun BatboldNo ratings yet
- 2013 Ui Mock Putnam Exam September 25, 2013, 5 PM - 7 PM SolutionsDocument4 pages2013 Ui Mock Putnam Exam September 25, 2013, 5 PM - 7 PM SolutionsGag PafNo ratings yet
- Punto 2 Calculo Eje 2Document2 pagesPunto 2 Calculo Eje 2William Steven Gavilan TovarNo ratings yet
- Dif FormulDocument1 pageDif FormulHüseyin AyazNo ratings yet
- Math54 Teleman Final 2011spring SolnDocument3 pagesMath54 Teleman Final 2011spring SolntehkronosNo ratings yet
- Matek KepletekDocument2 pagesMatek KepletekblackjackkNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform BertoDocument28 pagesLaplace Transform BertoJee RollsNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations and AdmathDocument20 pagesDifferential Equations and AdmathmemeNo ratings yet
- Kombinatorika - ZadaciDocument7 pagesKombinatorika - ZadacirakivanNo ratings yet
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDocument12 pagesHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNo ratings yet
- DRM SolutionsDocument116 pagesDRM SolutionsCésar TapiaNo ratings yet
- Four Step Rule and Formulas For DifferentiationDocument7 pagesFour Step Rule and Formulas For DifferentiationRosanna RosalesNo ratings yet
- I.7 by SubstitutionDocument16 pagesI.7 by SubstitutionRheina VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Quardatic Equation-02-Solved ExamDocument14 pagesQuardatic Equation-02-Solved ExamRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2012 JC2 Preliminary Exam H2 Math Paper 1 SolutionsDocument10 pages2012 JC2 Preliminary Exam H2 Math Paper 1 SolutionsHuixin LimNo ratings yet
- 2010 TJC SolDocument12 pages2010 TJC SolPooja KapurNo ratings yet
- Solving a differential equation using parametrizationDocument1 pageSolving a differential equation using parametrizationAmália EirezNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers Additional Notes 1Document11 pagesComplex Numbers Additional Notes 1Jade GurtizaNo ratings yet
- Special FunctionsDocument39 pagesSpecial FunctionsAakash NairNo ratings yet
- Resolucao 2008-2009 - s2-t2Document11 pagesResolucao 2008-2009 - s2-t2ChevronelleNo ratings yet
- Coordination Transformations For Strain & Stress RatesDocument4 pagesCoordination Transformations For Strain & Stress RatesJey SinghNo ratings yet
- Primera Parte Trabajo ColaborativoDocument4 pagesPrimera Parte Trabajo Colaborativojose trujilloNo ratings yet
- Chap11 - Alpha Chiang SolucionesDocument13 pagesChap11 - Alpha Chiang Solucionesnecroteck1No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 4 SolutionsAkshay NarasimhaNo ratings yet
- Math Challenge Problem SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath Challenge Problem Solutions72 Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Junior College Math Paper SolutionsDocument15 pagesJunior College Math Paper SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- EE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008Document26 pagesEE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008doomachaleyNo ratings yet
- SOV ConductionDocument47 pagesSOV ConductionRanadip AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Worked Examples CH 13Document16 pagesWorked Examples CH 13ajithNo ratings yet
- MATH 121 - MIDTERM 1 Solutions and PropositionsDocument3 pagesMATH 121 - MIDTERM 1 Solutions and PropositionsmahiruserNo ratings yet
- Honsanalworkshop5sols CMPLT PDFDocument5 pagesHonsanalworkshop5sols CMPLT PDFSomeoneNo ratings yet
- RRRRDocument2 pagesRRRRLeo SaitamaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1B: Se Hace Un Cambio de VariableDocument9 pagesEjercicio 1B: Se Hace Un Cambio de VariableEnzon Eduardo Porras MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Sydney Boys High School Mathematics Trial HSC SolutionsDocument19 pagesSydney Boys High School Mathematics Trial HSC SolutionsFrankydayNo ratings yet
- Essential Oil GuidelineDocument39 pagesEssential Oil GuidelineFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- Eat Well, LoveDocument70 pagesEat Well, LoveFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Report 2-PRELIMDocument5 pagesConceptual Report 2-PRELIMFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Linear EquationsDocument2 pages2.3 Linear EquationsFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- 1) Contractual Arrangements (2nd Sem 2014-15)Document6 pages1) Contractual Arrangements (2nd Sem 2014-15)Faraa BellaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Exact EquationsDocument6 pages2.4 Exact EquationsFaraa BellaNo ratings yet