Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differences Between Mri and CT Scan
Uploaded by
Paavni SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differences Between Mri and CT Scan
Uploaded by
Paavni SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
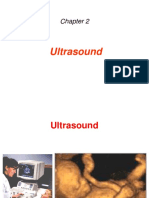
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MRI ,X-RAY ,CT SCAN,ULTRASOUND
1. PRINCIPLE:
CT scan uses an x-ray beam that slices through the patient.
MRI uses a magnetic field with radio frequencies introduced into it. When your body is placed
inside the magnetic field, the molecules of water in your body (hydrogen molecules) will start to
spin like a kid's top when he spins it. The top will begin to wobble as it slows down. Your
hydrogen molecules will start to wobble just like the top does at a certain rate of speed; the
stronger the magnetic field, the faster they will wobble and the weaker the magnetic field, the
slower they will wobble; it depends on the strength of the magnetic field. Then a radio
frequency is introduced into the magnetic field at the same rate of speed at which the "tops
wobble" causing the wobbling tops and radio frequency to sing out together sharing the same
signal frequency. (Thus the term resonance) That signal is used by the MRI computer to produce
the image.
Medical ultrasound or sonography is a medical-imaging technique based on exposing the
affected area to high frequency sound waves that produce pictures of organs and tissues inside
the body.
X-Rays make use of radiation to get an internal view of the body.
2. APPLICATIONS:
CT Scan does not show you tendons and ligaments very well at all. CT scans provide better
images for bones structures,inner ear as it can easily detect tumors in the auditory canal and
cochlea.CTscans help diagnose bone tumors,bone fractures,internal injuries, internal bleeding &
blood clot and to monitor cancer and heart diseases. CT Scanning is useful for
screening diseases such as colon cancer, detecting injuries and abnormalities in the head, chest,
heart, abdomen and extremities. This technique is often combined with other techniques such
as MRI, and ultrasonography. CT is the preferred modality for cancer, pneumonia, and abnormal
chest x-rays. Bleeding in the brain, especially from injury, is better seen on CT than MRI. But a
tumor in the brain is better seen on MRI. CT shows organ tear and organ injury quickly and
efficiently. Broken bones and vertebral bodies of the spine are better seen on CT CT is far
superior at visualizing the lungs and organs in the chest cavity between the lungs. MRI is not a
good tool for visualizing the chest or lungs at all. Some patients who have received certain types
of surgical clips, metallic fragments, cardiac monitors or pacemakers cannot receive an MRI. MRI
cannot be done in patients who are claustrophobic as the patient has to remain inside the noisy
machine for about 20-45 minutes.
Tendons and ligaments around the shoulder and knee are best seen by the physics used in MRI.
This is due to the density of the tissues that compose the tendons and ligaments. Spinal cord is
best seen by MRI for the same reason. The density of the spinal cord and the composition of it is
such that MRI physics can show it to us much better than CT.
X-Rays are largely used to examine broken bones. X-ray demonstrates the difference
between bone density and soft tissue.
Ultrasound applications are used for diagnostic applications such as visualizing muscles,
tendons, internal organs, to determine its size, structures, any lesions or other abnormalities.
Obstetric sonography is used to visualize fetuses during pregnancy. Other applications
of ultrasound include removing kidney and gall stones, lipectomy and other applications
3. Radiation exposure:
In ct and X-ray moderate to high radiation and in MRI none. No radiation exposure in US
4. Cost:
CT scans and X-rays, usually cost less than MRIs (with contrast). X-Ray is relatively cheaper than
MRI. Ultrasound is less expensive and comparatively safer technique than CT scans.
5. Acronym for :
CT-Computer tomography, MRI- Magnetic Resonance Imaging. X-radiation or Rontgen
radiation
6. Effects on the body:
Despite being small, CT can pose the risk of irradiation. CT scans are associated with the risk of
causing cancers, such as lung cancer, colon cancer and leukemia. This is mainly due to the use of
X-rays. No biological hazards have been reported with the use of the MRI. There are other
safety concerns associated with the use of contrast agents which are administered
intravenously. However, these disadvantages can be reduced with the use of lower doses.
Several studies have highlighted the harmful effects of ultrasound on pregnant mammals such
as mice though this effect has not yet been shown in humans. Also, increased exposure
to ultrasound waves leads to heating up of tissues, changes in pressure and other mechanical
disturbances. The powerful rays have the ability to create birth defects and diseases and can
also alter the DNA. The imaging effects or biological effects of x-rays can cause tissue cell injured
or even celldeath.So X-ray is doubled edged sword; in x-ray therapy it can help kill cancerous
cells,at the same time it can damage normal body cells.Thus we mmust use x-rays in aproper
way and pay attention to protect patient as well as ourselves from high doses of x-rays
exposure. X-Rays used in CT scans usually have no harms.
7. Ability to change the imaging plane without moving the patient:
Not present in CT scan. MRI machines can produce images in any plane. Ability to change the
imaging plane without moving the patient is present in US. While MRI and X-ray are both
imaging techniques for organs of the body, the difference is that MRI images provide a 3D
representation of organs, which X-Rays usually cannot.
8. Details of soft tissues:
Less detailed compared to MRI. MRI is much higher detail in the soft tissues. US is detailed with
advanced technology
9. Details of bony structures:
CT Provides good details about bony structures. MRI is less detailed compared to CT scan.
US is usually not used for bony structures. Instead they are used for internal organs of the body
10. Time taken for complete scan:
CT scan is usually completed within 5 minutes. MRI Scanning typically run for about 30 minutes.
Ultrasound usually takes about 10-15 minutes. Time taken for complete X-ray scan is a
few seconds.
11. Contrast agents:
One of the greatest advantages of MRI is the ability to change the contrast of the images. Small
changes in the radio waves and the magnetic fields can completely change the contrast of the
image. Different contrast settings will highlight different types of tissue Contrast agents are also
used in MRI but they are not made of iodine. There are fewer documented cases of reactions to
MRI contrast and it is considered to be safer than X-ray dye. Contrast agents for MRI are those
which have paramagnetic properties. One example is gadolinium. Iodine use may be associated
with allergic reactions. CT may be enhanced by use of contrast agents containing elements of a
higher atomic number than the surrounding flesh (iodine, barium). Contrast agents for MRI have
paramagnetic properties, e.g., gadolinium and manganese. Due to the high contrast resolution
of CT scanning, differences between the tissues are more apparent compared to other
techniques.
You might also like
- Atlas of Hybrid Imaging Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CT Vol. 2: Thorax Abdomen and Pelvis: Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CTFrom EverandAtlas of Hybrid Imaging Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CT Vol. 2: Thorax Abdomen and Pelvis: Sectional Anatomy for PET/CT, PET/MRI and SPECT/CTNo ratings yet
- Liver Imaging: MRI with CT CorrelationFrom EverandLiver Imaging: MRI with CT CorrelationErsan AltunNo ratings yet
- Radiology Notes (1-36)Document83 pagesRadiology Notes (1-36)el spin artifactNo ratings yet
- CT ScanDocument5 pagesCT ScanAsdur KhanNo ratings yet
- Chest RadiographyDocument39 pagesChest RadiographyBikram PaulNo ratings yet
- Probe Selection Machine Controls Equipment MGHillDocument14 pagesProbe Selection Machine Controls Equipment MGHilljohnalanNo ratings yet
- Mammography - Procedure, Test, Pain, Time, Types, Risk, Cancer, RateDocument4 pagesMammography - Procedure, Test, Pain, Time, Types, Risk, Cancer, RateMassimo RiserboNo ratings yet
- CT ScanDocument7 pagesCT Scanankithns102No ratings yet
- P8-9 CoverStory CT-HistoryDocument2 pagesP8-9 CoverStory CT-Historyalem87No ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - UltrasoundDocument62 pagesLesson 10 - UltrasoundDesignNo ratings yet
- Viner 2005 Forensic Radiography in South AfricaDocument24 pagesViner 2005 Forensic Radiography in South Africah8517No ratings yet
- Rtog 0813 Marina CousinsDocument22 pagesRtog 0813 Marina Cousinsapi-426094285No ratings yet
- Detecting and Measuring Radiation Lect 4Document22 pagesDetecting and Measuring Radiation Lect 4Tonyo LinaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Practice & Patient CareDocument14 pagesHospital Practice & Patient CareAkinsola Ayomidotun100% (1)
- Ultrasonography of The Hepatobiliary TractDocument9 pagesUltrasonography of The Hepatobiliary TractPaola Méndez NeciosupNo ratings yet
- RT For General PublicDocument24 pagesRT For General Publicraheel252100% (1)
- Protection From RadiationDocument8 pagesProtection From Radiationapi-270822363No ratings yet
- Biological Effects of UltrasoundDocument3 pagesBiological Effects of UltrasoundSaravjeet Singh100% (1)
- UZVDocument56 pagesUZVGoran MaliNo ratings yet
- Radio BiologyDocument26 pagesRadio BiologyMAN MedanNo ratings yet
- Radiology ServicesDocument5 pagesRadiology Servicesshah007zaadNo ratings yet
- Mri SequencesDocument13 pagesMri SequencesNorma RamirezNo ratings yet
- Mammography MachineDocument17 pagesMammography MachineGaurav Molankar100% (1)
- Introduction To Imaging and Radiologic ScienceDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Imaging and Radiologic ScienceminayokiNo ratings yet
- Contrast Media ExtravasationDocument4 pagesContrast Media ExtravasationmanishbabuNo ratings yet
- AAPM-TG53 (Quality Assurance For Clinical RTP)Document57 pagesAAPM-TG53 (Quality Assurance For Clinical RTP)ΜΡ_No ratings yet
- Policies and Procedures Radiology DepartmentDocument6 pagesPolicies and Procedures Radiology DepartmentRalph Gerard Saldajeno ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- MRI PhysicsDocument113 pagesMRI PhysicsSaeed Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Made EasyDocument7 pagesUltrasound Made EasyAnonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- Radiology Physics: WWW - Krest.inDocument12 pagesRadiology Physics: WWW - Krest.inSivakumar SadasivamNo ratings yet
- ULTRASOUNDDocument14 pagesULTRASOUNDpriyadharshini100% (1)
- Diagnostic Exam For Bones, Joints and Muscles: 1. Bone Density Test For Osteoporosis BackgroundDocument14 pagesDiagnostic Exam For Bones, Joints and Muscles: 1. Bone Density Test For Osteoporosis BackgroundRoel MarañoNo ratings yet
- Intervention Radiology ProceduresDocument58 pagesIntervention Radiology Proceduresjusttesting10No ratings yet
- 103manual QAP Radiologi Pindaan Januari 2019Document115 pages103manual QAP Radiologi Pindaan Januari 2019UMGC Sri RampaiNo ratings yet
- Contrast MediaDocument94 pagesContrast MediaJustin JoseNo ratings yet
- Oncology Scope of ServicesDocument2 pagesOncology Scope of ServicesJaisurya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound ImagingDocument20 pagesUltrasound ImagingSitanshu SatpathyNo ratings yet
- QUANTEC RT ConstraintsDocument41 pagesQUANTEC RT ConstraintsNika Topuria100% (2)
- MRI Physics Ch12Document53 pagesMRI Physics Ch12麥宗敬No ratings yet
- Radiology ReviewDocument52 pagesRadiology ReviewFourthMolar.com50% (2)
- Calibration of Ionisation ChamberDocument76 pagesCalibration of Ionisation ChamberArmin DurakovićNo ratings yet
- Principles of Oncology and Outline of ManagementDocument78 pagesPrinciples of Oncology and Outline of ManagementPavan JonnadaNo ratings yet
- Philips Learning Center Enewsletter Issue 3Document1 pagePhilips Learning Center Enewsletter Issue 3Suresh NarayanaswamyNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles of UtzDocument44 pagesPhysical Principles of UtzRalph RichardNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound ImagingDocument103 pagesUltrasound Imagingsolomong100% (1)
- Treatment Planning I Isodose DistributionsDocument58 pagesTreatment Planning I Isodose DistributionsqazwsxsasaNo ratings yet
- Contrast Media and Adverse Effects - Vijay KumarDocument41 pagesContrast Media and Adverse Effects - Vijay KumarTapshi SohalNo ratings yet
- Thyroid UltrasoundDocument62 pagesThyroid UltrasoundYoungFanjiens100% (1)
- Chapter 1-Contrast MediaDocument18 pagesChapter 1-Contrast MediaFisiha FikiruNo ratings yet
- Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument6 pagesBiliary Tract DiseaseRafael KameradNo ratings yet
- ESUR Guidelines On Contrast MediaDocument10 pagesESUR Guidelines On Contrast MediatsimitselisNo ratings yet
- Nuclear OncologyDocument33 pagesNuclear OncologyOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- Doppler Ultrasonography of The Lower Extremity ArteriesDocument34 pagesDoppler Ultrasonography of The Lower Extremity ArteriesNidaa MubarakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical ImagingDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Medical ImagingkylieverNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Diagnostic Imaging - Prof - dr.İsmetTAMERDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Diagnostic Imaging - Prof - dr.İsmetTAMERAly MssreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Physical Principles of Ultrasound Imaging and Doppler Peter N Burns PHDDocument26 pagesIntroduction To The Physical Principles of Ultrasound Imaging and Doppler Peter N Burns PHDCatarina Dos ReisNo ratings yet
- Medical X Ray Equipment Management System 2015 PDFDocument41 pagesMedical X Ray Equipment Management System 2015 PDFjariyarasheedNo ratings yet
- Resolution in Ultrasound ImagingDocument7 pagesResolution in Ultrasound ImagingVyshnavi EaswaranNo ratings yet
- Prerequisites For USGDocument23 pagesPrerequisites For USGIndera VyasNo ratings yet
- Women's Imaging: MRI with Multimodality CorrelationFrom EverandWomen's Imaging: MRI with Multimodality CorrelationMichele A. BrownRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- WP Content Uploads 2014 03 Practice Question Set On Reasoning For Ibps Probationary Officer Exam 2012 Freshers AddaDocument22 pagesWP Content Uploads 2014 03 Practice Question Set On Reasoning For Ibps Probationary Officer Exam 2012 Freshers AddaPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ibps Po Paper 32Document44 pagesIbps Po Paper 32Paavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ibps Po Paper 32Document44 pagesIbps Po Paper 32Paavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Paper 3Document14 pagesCbse Paper 3Paavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Joshi Classes Test (+2) : One Marks QuestionsDocument15 pagesJoshi Classes Test (+2) : One Marks QuestionsPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- IBPS RRB (Group A Officers) Exam 2012 Question Paper - Quantitative AptitudeDocument41 pagesIBPS RRB (Group A Officers) Exam 2012 Question Paper - Quantitative AptitudePaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Paper 3Document14 pagesCbse Paper 3Paavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial Service Mumbai Act of Parliament: IDBI Bank Limited Is An Indian Government-OwnedDocument1 pageFinancial Service Mumbai Act of Parliament: IDBI Bank Limited Is An Indian Government-OwnedPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Australian Open French Open Wimbledon US Open: TennisDocument1 pageAustralian Open French Open Wimbledon US Open: TennisPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Blue Economy: 2014 Women's Hockey World CupDocument9 pagesThe Blue Economy: 2014 Women's Hockey World CupPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Blue Economy: 2014 Women's Hockey World CupDocument9 pagesThe Blue Economy: 2014 Women's Hockey World CupPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Maha Navratna Psus: Maharatna StatusDocument7 pagesMaha Navratna Psus: Maharatna StatusPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sales and Finance Work Together in The Best-Run CompaniesDocument2 pagesSales and Finance Work Together in The Best-Run CompaniesPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- SidbiDocument3 pagesSidbiPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Definition of 'Gross Margin'Document1 pageDefinition of 'Gross Margin'Paavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanDocument3 pagesFinancial PlanPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lorraln - Corson, Solutions Manual For Electromagnetism - Principles and Applications PDFDocument93 pagesLorraln - Corson, Solutions Manual For Electromagnetism - Principles and Applications PDFc. sorasNo ratings yet
- Mathsnacks05 InfiniteDocument1 pageMathsnacks05 Infiniteburkard.polsterNo ratings yet
- CU 8. Johnsons Roy NeumanDocument41 pagesCU 8. Johnsons Roy NeumanPatrick MatubayNo ratings yet
- Focus Charting of FDocument12 pagesFocus Charting of FRobert Rivas0% (2)
- 011 - Descriptive Writing - UpdatedDocument39 pages011 - Descriptive Writing - UpdatedLeroy ChengNo ratings yet
- Counselling Goes To The Movies: Antwone Fisher (2002)Document12 pagesCounselling Goes To The Movies: Antwone Fisher (2002)Azizul MohamadNo ratings yet
- Proto Saharan Precursor of Ancient CivilizationsDocument175 pagesProto Saharan Precursor of Ancient CivilizationsClyde Winters100% (4)
- The Training Toolbox: Forced Reps - The Real Strength SenseiDocument7 pagesThe Training Toolbox: Forced Reps - The Real Strength SenseiSean DrewNo ratings yet
- Predictive Tools For AccuracyDocument19 pagesPredictive Tools For AccuracyVinod Kumar Choudhry93% (15)
- Lesson Plan Pumpkin Moon SandDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Pumpkin Moon Sandapi-273177086No ratings yet
- RubricsDocument1 pageRubricsBeaMaeAntoniNo ratings yet
- Nielsen & Co., Inc. v. Lepanto Consolidated Mining Co., 34 Phil, 122 (1915)Document3 pagesNielsen & Co., Inc. v. Lepanto Consolidated Mining Co., 34 Phil, 122 (1915)Abby PajaronNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Transcendence in Transhumanism PDFDocument10 pagesSpiritual Transcendence in Transhumanism PDFZeljko SaricNo ratings yet
- Ergatividad Del Vasco, Teoría Del CasoDocument58 pagesErgatividad Del Vasco, Teoría Del CasoCristian David Urueña UribeNo ratings yet
- Information Theory Entropy Relative EntropyDocument60 pagesInformation Theory Entropy Relative EntropyJamesNo ratings yet
- K9G8G08B0B SamsungDocument43 pagesK9G8G08B0B SamsungThienNo ratings yet
- Describing LearnersDocument29 pagesDescribing LearnersSongül Kafa67% (3)
- Concentrating Partial Entanglement by Local OperationsDocument21 pagesConcentrating Partial Entanglement by Local OperationsbhpliaoNo ratings yet
- What Is Folate WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesWhat Is Folate WPS OfficeMerly Grael LigligenNo ratings yet
- Atul Bisht Research Project ReportDocument71 pagesAtul Bisht Research Project ReportAtul BishtNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Experience at Formaply Inustry in Brgy. de Ocampo, Trece Martires City, CaviteDocument34 pagesWork Immersion Experience at Formaply Inustry in Brgy. de Ocampo, Trece Martires City, CaviteKen AshleyNo ratings yet
- Aspects of The Language - Wintergirls Attached File 3Document17 pagesAspects of The Language - Wintergirls Attached File 3api-207233303No ratings yet
- Origin of "ERP"Document4 pagesOrigin of "ERP"kanika_bhardwaj_2No ratings yet
- Types of Numbers: SeriesDocument13 pagesTypes of Numbers: SeriesAnonymous NhQAPh5toNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease With PregnancyDocument115 pagesLiver Disease With PregnancyAmro Ahmed Abdelrhman100% (3)
- Technique Du Micro-Enseignement Une Approche PourDocument11 pagesTechnique Du Micro-Enseignement Une Approche PourMohamed NaciriNo ratings yet
- Nastran 2012 Superelements UgDocument974 pagesNastran 2012 Superelements Ugds_srinivasNo ratings yet
- Playwriting Pedagogy and The Myth of IntrinsicDocument17 pagesPlaywriting Pedagogy and The Myth of IntrinsicCaetano BarsoteliNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletan Problems in Soccer PlayersDocument5 pagesMusculoskeletan Problems in Soccer PlayersAlexandru ChivaranNo ratings yet
- Is 13779 1999 PDFDocument46 pagesIs 13779 1999 PDFchandranmuthuswamyNo ratings yet