Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Methods in Power Systems
Uploaded by
suhrudkumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Methods in Power Systems
Uploaded by
suhrudkumarCopyright:
Available Formats
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code No: 09A60203 R09 Set No. 2
III B.Tech II Semester Examinations,April/May 2012
COMPUTER METHODS IN POWER SYSTEMS
Electrical And Electronics Engineering
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Distinguish between steady state and dynamic stability of a power system
network.
(b) What is meant by power angle curve and write its signicance.
(c) How can the steady state stability of power system be increased? [5+5+5]
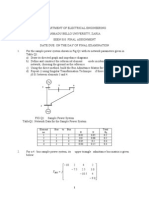
2. (a) For the power system network shown in gure 1, draw
i. Graph
ii. Tree
iii. Co-Tree
iv. Basic loops
v. Basic cut-sets.
(b) Write the network performance equations. [7+8]
Figure 1:
3. Explain the p.u. system of analyzing power system problems. Discuss the advan-
tages of this method over the absolute method of analysis. [15]
4. A synchronous generator is operating at an innite bus and supplying 45% of its
peak power capacity. As soon as a fault occurs, the reactance between the generator
and the line becomes four times its value before the fault. The peak power that
can be delivered after the fault is cleared is 70% of the original maximum value.
Determine the critical clearing angle. [15]
5. A 65-MVA star-connected 16 kV synchronous generator is connected to 20kV/120
kV, 75 MVA /Y transformer. The sub-transient reactance of the machine is 0.32
p.u. and the reactance of transformer is 0.1 p. u. When the machine is unloaded,
a 3-phase fault takes place on the HT side of the transformer. Determine:
1
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code No: 09A60203 R09 Set No. 2
(a) the sub transient symmetrical fault current on both sides of the transformer,
(b) the maximum possible value of the d.c. current. Assume 1 p.u. generator
voltage. [15]
6. (a) Write the algorithm for FDLF method.
(b) Compare G-S method and N-R methods. [8+7]
7. Consider the 3-bus system shown in gure 2. The PU line reactances are indicated
on the g. The line resistances are negligible. The magnitudes of all the three bus
voltages are specied to be |V
1
| = 1.00 pu, |V
2
| = 1.04 pu, |V
3
| = 0.96 pu. The
bus powers are specied in below table .
Bus Real demand Reactive demand Real generation Reactive generation
1 Pd1=1.0 Qd1=0.6 Pg1=0.7 Qg1 (unspecied)
2 Pd2=0 Qd2=0 Pg2=1.4 Qg2 (unspecied)
3 Pd3=1.0 Qd3=1.0 Pg4=0 Qg3 (unspecied)
Carry out the complete approximate load ow solution. Take bus-1 as slack bus.
[15]
Figure 2:
8. The bus impedance matrix for a 3-bus system is
j 0.3 j 0.2 j 0.275
Z
bus
= j 0.2 j 0.4 j 0.25
j 0.275 j 0.25 j 0.418
There is a line outage and the line from 1 to 2 is removed. Using the method of
building algorithm, determine the new bus impedance matrix. [15]
2
]
[
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code No: 09A60203 R09 Set No. 4
III B.Tech II Semester Examinations,April/May 2012
COMPUTER METHODS IN POWER SYSTEMS
Electrical And Electronics Engineering
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Wat is the load ow study and explain the need for load ow solution.
(b) What are the assumptions in SLFE(static load ow equations) and derive the
approximate load ow equations. [6+9]
2. Four bus bar sections have each a generator of 40 MVA 10% reactance and a bus
bar reactor of 8% reactance. Determine the maximum MVA fed into a fault on any
bus bar section and also the maximum MVA if the number of similar bus bars in
sections is very large. [15]
3. (a) What are the assumptions in FDLF method?
(b) Compare the dierent methods of load ow techniques. [3+12]
4. (a) Derive the formula for power transfer through a transmission line.
(b) A 4-pole ,50 Hz, 22 kV turbo alternator has a rating of 100 MVA,p.f 0.8
lag.The moment of inertia of rotor is 9000 kg-m
2
. Determine M and H. [7+8]
5. A 50 Hz, three-phase synchronous generator delivers 1.00 p.u. power to an innite
busbar through a network in which resistance is negligible. A fault occurs which
reduces the maximum power transferable to 0.40 p.u. whereas, before the fault,
this power was 1.8 p.u. and, after the clearance of the fault 1.30 p.u. By the use
of equal area criterion, determine the critical angle. [15]
6. (a) Prove that when there is no mutual coupling, the diagonal and o-diagonal
elements of Y
Bus
can be computed from Y
ii
= y
ij
and Y
ij
= y
ij
.
(b) Dene the terms graph, tree, co-tree, tree branches, and links.
Write the relation between branches, links & no. of nodes. [7+8]
7. A three-phase transmission line operating at 33 kV and having a resistance and
reactance of 5 ohms and 20 ohms respectively is connected to the generating station
bus bar through a 5,000 kVA step-up transformer which has a reactance of 6 per
cent, which is connected to the bus bar being supplied by two alternators, one
10,000 kVA having 10% reactance, and another 5,000 kVA having 7.5% reactance.
Calculate the kVA at a short-circuit fault between phases occurring
(a) at the high voltage terminals of the transformers
(b) at load end of transmission line. [15]
8. Explain the algorithm for the addition and removal of lines in power system. [15]
3
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code No: 09A60203 R09 Set No. 1
III B.Tech II Semester Examinations,April/May 2012
COMPUTER METHODS IN POWER SYSTEMS
Electrical And Electronics Engineering
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
1. Three generators are rated as follows: Generator 1:100 MVA, 33 kV, reactance
10%, Generator 2:150 MVA, 32 kV, reactance 8% and Generator 3:110 MVA, 30
kV, reactance 12%. Determine the reactance of the generators corresponding to
base values of 200 MVA and 35 kV. [15]
2. (a) Dene the following terms with suitable example.
i. Graph
ii. Tree
iii. Co-Tree
iv. Cut-set
v. Basic Loop.
(b) Explain the incidence matrices:
A
, A, B and C. [7+8]
3. Dierentiate between steady state stability and transient stability of a power sys-
tem. Discuss the factors that aect:
(a) steady state stability, and
(b) transient state stability of the system. [15]
4. Develop load ow equations suitable for solution by N-R method using rectangular
coordinates when only PQ buses are present. [15]
5. The following is the system data for load ow solution. The line admittances are
given in table 1 and active and reactive powers are given in table 2.
Bus Code P, pu Q, pu V, pu Remarks
1 - - 1+j0 Slack bus
2 1 0.1 - PQ bus
3 3.5 0.3 - PQ bus
Bus Code Impedance
1-2 -j5
1-3 -j5
2-3 -j10
Find the voltages at the end of rst iteration by using G-S method. [15]
4
Table 1:
Table 2:
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code No: 09A60203 R09 Set No. 1
6. A power plant has two generators of 10 MVA. 15% reactance each and two 5 MVA
generators of 10% reactance paralleled at a common bus bar from which load is
taken through a number of 4 MVA step up transformers each having a reactance
of 5%. Determine the short circuit capacity of the breakers on the:
(a) low voltage, and
(b) high voltage side of the transformer. [15]
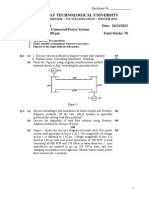
7. For the 3-bus system shown in gure 3 obtain Zbus. [15]
Figure 3:
8. (a) Explain breifly the two forms of instability in power system.
(b) Does over compensation of a transmission line aects the stability of a power
sytem? Justify the answer. [7+8]
5
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code No: 09A60203 R09 Set No. 3
III B.Tech II Semester Examinations,April/May 2012
COMPUTER METHODS IN POWER SYSTEMS
Electrical And Electronics Engineering
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
1. Two generators rated at 10 MVA 13.2 kV and 15 MVA 13.2kV are connected in
parallel to a bus bar. They feed supply to two motors of inputs 8 MVA and 12 MVA
respectively. The operating voltage of motors is 12.5 kV. Assuming base quantities
as 50 MVA and 13.8 kV draw the reactance diagram. The percent reactance for
generators is 15% and that for motors is 20%. [15]
2. (a) Derive the static load ow equations of a n-bus system.
(b) Explain the advantages and disadvantages of G-S method. [8+7]
3. A motor is receiving 25% of the power that it is capable of receiving from an innite
bus. If the load on the motor is doubled, calculate the maximum value of load angle
during the swinging of the rotor around its new equilibrium position. [15]
4. (a) Compare G-S method and N-R methods.
(b) Write the algorithm for N-R method using rectangular coordinates when PV
buses are absent. [7+8]
5. Derive the formulae for Z
bus
using building algorithm for the addition of link with
mutual coupling to other elements. [15]
6. A 50 Hz synchronous generator is connected an innite bus through a line. The
p.u. reactances of generator and the line are j0.2 p.u. and j0.4 p.u. respectively.
The generator no load voltage is 1.1 p.u. and that of innite bus is 1.0 p.u. The
inertia constant of the generator is 4 MW-sec/MVA. Determine the frequency of
natural oscillations if the generator is loaded to 80% of its maximum power transfer
capacity and small perturbation in power is given. [15]
7. A 3 phase, 30 MVA, 6.6kV alternator having 10% reactance is connected
through a 30 MVA, 6600/33,000 v delta-star connected transformer of 5% reac-
tance to a 33 kV transmission line having a negligible resistance and a reactance
of 4 ohms. At the receiving end of the line there is a 30 MVA, 33,000/6600 volt
delta-star connected transformer of 5% reactance stepping down the voltage to 6.6
kV. Both the transformers have their neutral solidly grounded. Draw the one-line
diagram and the positive, negative and zero sequence networks of this system and
determine the fault currents for single line grounded fault at the receiving station
L.V. bus bars.For generator assume -ve sequence reactance as 70% that of + ve
sequence. [15]
6
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code No: 09A60203 R09 Set No. 3
8. (a) For the 3-bus system shown in gure 4, let a new bus (bus no.4) be added
with bus no.2 through a transmission line of impedance (0.01+j0.3)p.u. Obtain
Y for the new system?
(b) Explain why Y is often used in load ow study. [15]
Figure 4:
7
bus
bus
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
You might also like
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Power Electrical Past PaperDocument5 pagesPower Electrical Past PaperNadeesha BandaraNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument10 pagesPower System AnalysisAlluri Appa RaoNo ratings yet
- Elx303 ExamDocument5 pagesElx303 ExamNadeesha BandaraNo ratings yet
- 9A02602 Power System AnalysisDocument4 pages9A02602 Power System Analysissivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- EE6501-Question BankDocument16 pagesEE6501-Question BankBelayneh TadesseNo ratings yet
- Eel301 2022Document2 pagesEel301 2022rraj09102002No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Anonymous MYbA037ikNo ratings yet
- Instructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesInstructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Nithiya MaharajanNo ratings yet
- Eee Iii Year 2017-2018Document48 pagesEee Iii Year 2017-2018J JulietNo ratings yet
- NHE2486-Main12-Power Year 4 Past PaperDocument7 pagesNHE2486-Main12-Power Year 4 Past Paperlynx101No ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument5 pagesPower System AnalysisVidyavihar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Inter Connected Power System - CombinedDocument11 pagesInter Connected Power System - CombinedPalak AriwalaNo ratings yet
- Part - B (2 X 15 30 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDocument2 pagesPart - B (2 X 15 30 Marks) Answer All QuestionsGokul ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Eeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Document5 pagesEeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Kabir MohammedNo ratings yet
- R5410204-Power System Operation and ControlDocument4 pagesR5410204-Power System Operation and ControlShakthi BoseNo ratings yet
- Psa Question Bank 2Document9 pagesPsa Question Bank 2Krishnakumar IesNo ratings yet
- Ps 2 NewDocument7 pagesPs 2 NewAditya PatilNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument3 pagesPower SystemMogaka LucasNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Max. Marks: 30 Branch/Sem:En-Vi Time: 2 HrsDocument2 pagesPower System Analysis Max. Marks: 30 Branch/Sem:En-Vi Time: 2 HrsVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Psa All Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesPsa All Questions and AnswersMODERN TELUGAMMAYINo ratings yet
- Question Paper CodeDocument6 pagesQuestion Paper Codeprasad powerNo ratings yet
- Ee1351 PsaDocument16 pagesEe1351 PsaStephen Kenth La GuerreNo ratings yet
- Ee2404 Set1Document121 pagesEe2404 Set1Sachin Samy0% (1)
- (4958) - 1067 T.E. Electrical Power System - II (2012 Course) (Semester - II)Document3 pages(4958) - 1067 T.E. Electrical Power System - II (2012 Course) (Semester - II)Shubham KaklijNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperDocument2 pagesPower System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperKeyur PatelNo ratings yet
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Document11 pagesEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- Figure For Question No. 1Document4 pagesFigure For Question No. 1noybit mondalNo ratings yet
- Merged DocumentDocument25 pagesMerged DocumentAshokAbiNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis ImportantDocument8 pagesPower System Analysis Importantsparkle courageNo ratings yet
- Eee Sem 7 Ee2404lmDocument36 pagesEee Sem 7 Ee2404lmAnonymous gAVMpR0aNo ratings yet
- 2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankJeril joseNo ratings yet
- Power System Simulation Lab - QuestionsDocument13 pagesPower System Simulation Lab - QuestionsMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- PSADocument25 pagesPSAramyadspNo ratings yet
- Faculty of EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineeringavinashavi93No ratings yet
- Dynamic Improvement of Induction Generators Connected To Distribution Systems Using A DstatcomDocument5 pagesDynamic Improvement of Induction Generators Connected To Distribution Systems Using A DstatcomVinod Kumar VudathaNo ratings yet
- Psa ModelDocument2 pagesPsa ModelSyed MeerNo ratings yet
- EE2351-Power System Analysis PDFDocument15 pagesEE2351-Power System Analysis PDFRK K0% (1)
- Practical ExamDocument2 pagesPractical ExamIrfan AliNo ratings yet
- EDSDocument8 pagesEDSSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- 209 Power System - 3Document4 pages209 Power System - 3sukirajNo ratings yet
- Ee306 ADocument3 pagesEe306 AAparna JoseNo ratings yet
- Lab WorkDocument22 pagesLab WorkTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Assigment EPSD Lab PDFDocument5 pagesAssigment EPSD Lab PDFArjit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSrîkår SríNo ratings yet
- Ps IIDocument1 pagePs IIapi-279049687No ratings yet
- Power System Analysis (Jan-2014)Document10 pagesPower System Analysis (Jan-2014)Likhitha YerraNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWDocument13 pagesPower System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- 18-05 Power System Analysis (EL)Document2 pages18-05 Power System Analysis (EL)keerthanavijayaNo ratings yet
- 171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFDocument3 pages171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFPalak AriwalaNo ratings yet
- NR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocument6 pagesNR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Psa Solved May 2019Document18 pagesPsa Solved May 2019Bestowal Infotechs 2018No ratings yet
- United International University (Uiu)Document4 pagesUnited International University (Uiu)Masud SarkerNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis June 2022Document12 pagesPower System Analysis June 2022SuryaeswarNo ratings yet
- PSASghhggdvDocument6 pagesPSASghhggdvDarshan GowdaNo ratings yet
- 15-150902-Power System Analysis and SimulationDocument3 pages15-150902-Power System Analysis and SimulationBHARAT parmarNo ratings yet
- EE61 Power System AnalysisDocument3 pagesEE61 Power System AnalysisMartin De Boras PragashNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- WSM PDFDocument17 pagesWSM PDFSathish SelvaNo ratings yet
- TIP41 / TIP41C: FeaturesDocument2 pagesTIP41 / TIP41C: FeaturesCAMILA ROMINA LUCANANo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics and Foundations - (Chapter 10 Shear Strength of Soils) PDFDocument63 pagesSoil Mechanics and Foundations - (Chapter 10 Shear Strength of Soils) PDFFrancisco Reyes0% (1)
- Aerodynamic Investigation of Horizontal Axis Wind TurbineDocument4 pagesAerodynamic Investigation of Horizontal Axis Wind Turbineprabhat ranjan mishraNo ratings yet
- EEC Different Types of Electrical Wiring DiagramsDocument11 pagesEEC Different Types of Electrical Wiring Diagramsyash JadhaoNo ratings yet
- C020100 Model LPD - C020200 Model MSD: Intended Use UnpackingDocument2 pagesC020100 Model LPD - C020200 Model MSD: Intended Use UnpackingDoris Torres CabezasNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Iskra KNKDocument20 pagesCatalogue Iskra KNKSỹ TháiNo ratings yet
- B737-Flight Controls Systems SummaryDocument24 pagesB737-Flight Controls Systems SummaryTrailblazer487100% (1)
- Chemistry PYQSDocument71 pagesChemistry PYQSAYESHA HUSNANo ratings yet
- The Control of Flight Force by A Flapping Wing: Lift and Drag ProductionDocument21 pagesThe Control of Flight Force by A Flapping Wing: Lift and Drag ProductionRAJARATNANo ratings yet
- Internal Arc Testing of MV Switchgear-Experience With IEC 62271-200Document5 pagesInternal Arc Testing of MV Switchgear-Experience With IEC 62271-200Zineddine BENOUADAHNo ratings yet
- T BeamDocument17 pagesT BeamManojNo ratings yet
- Niloplast Niloplast: MineralDocument2 pagesNiloplast Niloplast: Mineralsr2011glassNo ratings yet
- ANFALDocument3 pagesANFALMr AchakzaiNo ratings yet
- Sem 1, Basic UltrasoundDocument95 pagesSem 1, Basic UltrasoundaghniajolandaNo ratings yet
- CLPAK628H Series Installation Manual 20150907 PDFDocument27 pagesCLPAK628H Series Installation Manual 20150907 PDFmauroschilling100% (6)
- Mahajan Et Al 2023 Three Dimensional Physical Modeling of Response of Existing Metro Tunnel To Pile Loading in DelhiDocument17 pagesMahajan Et Al 2023 Three Dimensional Physical Modeling of Response of Existing Metro Tunnel To Pile Loading in Delhibillkhandai007No ratings yet
- Class 12 Maths (Commerce) Summer Vacation HomeworkDocument7 pagesClass 12 Maths (Commerce) Summer Vacation HomeworkVridhi AroraNo ratings yet
- GLASSWARESDocument26 pagesGLASSWARESandie maxeyNo ratings yet
- Shanthi PavanDocument12 pagesShanthi PavanAasif HameedNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Muhd Haziq Sufi - F1128Document10 pagesLab 2 - Muhd Haziq Sufi - F1128Muhamad HaziqNo ratings yet
- Segura 2017 Seismic Performance Limitation of Slender Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsDocument268 pagesSegura 2017 Seismic Performance Limitation of Slender Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsDavid VallejoNo ratings yet
- Architect/Engineers: #117 Office of Facilities Management 100% Bid Documents For Construction Ground Floor Reflected Ceiling Plan 626A4-15-103 Renovate Emergency RoomDocument11 pagesArchitect/Engineers: #117 Office of Facilities Management 100% Bid Documents For Construction Ground Floor Reflected Ceiling Plan 626A4-15-103 Renovate Emergency RoomAlexNo ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document14 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768whmidi7331No ratings yet
- Fabric Brochure Letter Rev2 Web PDFDocument28 pagesFabric Brochure Letter Rev2 Web PDFMoamenNo ratings yet
- Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering: Nishant Sagar 1DS18EI033Document32 pagesDayananda Sagar College of Engineering: Nishant Sagar 1DS18EI033MELONo ratings yet
- Omed0104 2022 MayDocument4 pagesOmed0104 2022 MayIffa NooramNo ratings yet
- 3-D Theory & Solved Example Module-6-ADocument23 pages3-D Theory & Solved Example Module-6-ARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Price-List Polycab Industrial Flexible CablesDocument4 pagesPrice-List Polycab Industrial Flexible CablesKevin MaldeNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument19 pagesPhysicsapi-254985234No ratings yet