Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCNP Interview Questions
Uploaded by
Naeem Shahzad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
530 views4 pagesCCNP interview question......... Most wanted
Original Title
Ccnp Interview Questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCCNP interview question......... Most wanted
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
530 views4 pagesCCNP Interview Questions
Uploaded by
Naeem ShahzadCCNP interview question......... Most wanted
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CCNP Job Interview Questions and Answers........
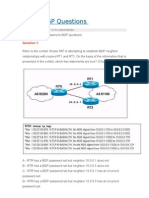
1 :: What is the purpose of a default route?
A default route is used if there is not a specific entry in the routing table for the
destination.
2 :: Explain the difference between a classful and a classless routing protocol.
Classless routing protocols advertise subnet mask information along with the network
prefixes. Classful routing protocols do not. Therefore, for a classful protocol, all subnets
for the major network number being used must be the same length. Also, classful
protocol cannot support discontiguous networks prefixes.
3 :: What are the states that an EIGRP route can be in and what do these states mean?
The passive state means that a router has a successor for a route. The active state means
that a router does not have a successor or feasible successor for a route and is actively
sending queries to neighbors to get information about the route.
4 :: What are the purposes of areas in an OSPF network?
Areas allow the design of a hierarchical network. Routes can be summarized or blocked
in an area to reduce the amount of routing information on internal OSPF routers.
5 :: Why are intra-area summary routes not allowed?
OSPF databases on routers in the same area must be identical. If route summarization
was allowed within an area, some routers would have specific routes and some routers
would have summary routes for routes in the area. If this were allowed, the databases for
the area would never agree.
6 :: What types of routes are allowed into a stub area?
OSPF intra-area and interarea routes, and a default route. External routes are not
advertised into a stub area.
7 :: What types of routes are allowed into a totally stubby area?
OSPF intra-area routes and a default route. OSPF interarea and external routes are not
advertised into a totally stubby area.
8 :: What types of routes are allowed into a NSSA?
OSPF intra-area and interarea routes, and possibly a default route. External routes from
ABRs are blocked, and external routes from ASBRs are converted to N1 or N2 routes.
9 :: What types of routes are allowed into a totally NSSA?
OSPF intra-area routes and a default route. External routes from ABRs are blocked, and
external routes from ASBRs are converted to N1 or N2 routes.
10 :: What is the difference between an E1 and E2 OSPF route?
An E1 route contains the OSPF cost to reach the ASBR plus the cost from the ASBR to
the external route. An E2 route contains only the cost from the ASBR to the external
route.
11 :: What are the three types of OSPF routers?
ABR, internal router, and ASBR.
12 :: What are the six OSPF route types?
: Intra-area, interarea, E1, E2, N1, and N2.
13 :: Where can routes be summarized in an OSPF network?
OSPF routes are summarized on an ABR. External routes are summarized on an ASBR
14 :: How is the OSPF router ID determined?
If physical interfaces are only used, the OSPF router ID is the highest IP address assigned
to an active physical interface. If loopback interfaces are used, the OSPF router ID is the
highest IP address assigned to a loopback interface. If the router-id command is used with
the OSPF configuration, the address used with this command will be the router ID.
15 :: How does OSPF determine the DR on a multi-access network?
The router with the highest interface priority will be the router ID. If all the interface
priorities on the multi-access network are the same, the router with the highest router ID
will be the DR.
16 :: How does OSPF determine an interarea shortest path?
First, calculate the shortest path to an ABR.
Second, calculate the shortest path across area 0 to an ABR that is attached to the
destination area.
Third, calculate the shortest path across the destination area from the ABR to the
destination network.
17 :: What is the purpose of an OSPF virtual link?
To connect a nonzero area to the backbone if the nonzero area becomes disconnected
from the backbone. A virtual link can also be used if the backbone, or area 0, becomes
discontiguous.
18 ::Which command in OSPF shows the network LSA information?
The command show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database network displays the network
link-state information.
19 :: What is the purpose of the AS_PATH attribute?
If a router has more than one route to the same IP prefix, the best path is the one with the
shortest AS_PATH (assuming other BGP attributes are equal).
20 :: What is the purpose of the WEIGHT attribute?
If a router has more than one route to the same IP prefix, the best path is the one with the
highest WEIGHT value.
21 :: What is the scope of the WEIGHT attribute?
WEIGHT has only local significance and is not advertised to BGP peers.
22 :: What is the purpose of the LOCAL_PREF attribute?
If a router has more than one route to the same IP prefix, the best path is the one with the
highest LOCAL_PREF (assuming the WEIGHT attribute for the routes is equal).
23 :: What is the scope of the LOCAL_PREF attribute?
The LOCAL_PREF attribute is advertised throughout the autonomous system.
24 :: What is the purpose of the metric or MULTI_EXIT_DISC attribute?
MED is used to prefer a path into an autonomous system. A lower MED value is
preferred.
25 :: What is the order of preference for the BGP attributes AS_PATH, LOCAL_PREF,
MED, and WEIGHT?
WEIGHT, LOACL_PREF, AS_PATH, MED
26 :: How is the OSPF cost of an interface calculated?
By default, the cost of an OSPF interface is 100,000,000/(Interface Bandwidth). The
constant 100,000,000 can be changed using the auto-cost reference-bandwidth command.
27 :: Describe the operation of Anycast RP.
Two or more RPs are configured with the same IP address. The IP addresses of the RPs
are advertised using a unicast IP routing protocol. Each multicast router chooses the
closest RP. If an RP fails, the routers switch to the next nearest RP after the unicast IP
routing protocol converges. The MSDP is used between RPs to exchange active multicast
source information.
28 :: What is the range of IP multicast addresses?
224.0.0.0239.255.255.255
29 :: What is the purpose of the interface command ip multicast spares-dense-mode?
Used with PIMSM Auto-RP and version 2. If the RPs fail, the router reverts to dense
mode.
30 :: Explain the function of a rendezvous point?
A RP is the focal point for multicast traffic. Traffic is forwarded to the RP from multicast
sources. The RP then forwards traffic to multicast receiver
You might also like
- Answer:: Networking Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesAnswer:: Networking Interview QuestionsnaeemNo ratings yet
- CCNP Route NotesDocument7 pagesCCNP Route NotesunikdipNo ratings yet
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- IPv6 Fundamentals: Learn the Basics of How IPv6 Works, IPv6 Addresses and IPv6 Subnetting: Computer Networking, #2From EverandIPv6 Fundamentals: Learn the Basics of How IPv6 Works, IPv6 Addresses and IPv6 Subnetting: Computer Networking, #2Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- BGP QuestionsDocument8 pagesBGP Questionsstorm2010No ratings yet
- CCNP Job Interview Questions - Networkingnews PDFDocument12 pagesCCNP Job Interview Questions - Networkingnews PDFmanishathfcl100% (2)
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsFrom EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Routing Basic Interview Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesRouting Basic Interview Questions and AnswersLokesh ShanjeevNo ratings yet
- Interview Guide - TOP 300+ CCNA Interview Questions - NetorksDocument19 pagesInterview Guide - TOP 300+ CCNA Interview Questions - Netorksmonisha0% (1)
- My Best Questions For An Interview of Network EngineerDocument3 pagesMy Best Questions For An Interview of Network EngineerAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Network Engineer Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesNetwork Engineer Interview Questionsnatrix029No ratings yet
- BGP ScenarioDocument1 pageBGP ScenarioSmite100% (1)
- BGP Questions and Answers Vol 1.0Document25 pagesBGP Questions and Answers Vol 1.0Eduardo AguilarNo ratings yet
- BGP Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewDocument4 pagesBGP Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewBhanu Saini100% (1)
- 1.overview and Traffic FlowDocument9 pages1.overview and Traffic FlowRamon Pirbux100% (1)
- CCNP Interview Questions Answers Guide PDFDocument14 pagesCCNP Interview Questions Answers Guide PDFEslam Hassan Ali100% (2)
- OSPF QuestionsDocument31 pagesOSPF QuestionsArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- BGP CommunityDocument20 pagesBGP CommunityRANJITHNo ratings yet
- HSRP Interview Questions - Network & Security ConsultantDocument11 pagesHSRP Interview Questions - Network & Security ConsultantRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Cisco Ipv6 Labs PDFDocument18 pagesCisco Ipv6 Labs PDFEugen BasarabNo ratings yet
- 106.quality of Service QoSDocument9 pages106.quality of Service QoSsanuNo ratings yet
- Notes To CcieDocument42 pagesNotes To CcieLeon DobrzinskyNo ratings yet
- Routing Process PictureDocument1 pageRouting Process Picturelefreak1979No ratings yet
- BGP AttributesDocument54 pagesBGP AttributesDaniel RicardoNo ratings yet
- MPLS - LabDocument221 pagesMPLS - LabmirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF TopologyDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF TopologyErid RocaNo ratings yet
- (MPLS) - Sysnet NotesDocument3 pages(MPLS) - Sysnet NotesNarendra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Switch Final Exam CCNP 6Document12 pagesSwitch Final Exam CCNP 6Tuấn Linh100% (2)
- BGP StudyDocument7 pagesBGP StudyReuben DanielNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNP OSPF Q & A - Tech Interview Prep QuestionsDocument5 pagesCisco CCNP OSPF Q & A - Tech Interview Prep QuestionsShaswat RajNo ratings yet
- BGP Short Note FileDocument60 pagesBGP Short Note FileTabarez AhmedNo ratings yet
- Point To Point Protocol Cisco Ccna Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePoint To Point Protocol Cisco Ccna Cheat SheetWalter ValverdeNo ratings yet
- 6.-Policy Based Routing (PBR)Document11 pages6.-Policy Based Routing (PBR)jaiimeandres100% (1)
- F5 LTM Lab GuideDocument7 pagesF5 LTM Lab GuideAman VermaNo ratings yet
- CCNP Interview QuestionDocument40 pagesCCNP Interview QuestionanuvindkrNo ratings yet
- CCNP Labs PDFDocument124 pagesCCNP Labs PDFUmer Aziz RanaNo ratings yet
- ASA Firewall Interview Questions and Answers (CCIE) - Networker InterviewDocument10 pagesASA Firewall Interview Questions and Answers (CCIE) - Networker InterviewRaj KaranNo ratings yet
- CCIE RS Quick Review KitDocument63 pagesCCIE RS Quick Review KitJaime LuqueNo ratings yet
- Cisco BGPDocument82 pagesCisco BGPMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Network Engineer Job Interview Technical Questions..: by pp2Document5 pagesNetwork Engineer Job Interview Technical Questions..: by pp2Vishnu PandeyNo ratings yet
- OSPF Interview QA (WK) Part1-3 v1Document19 pagesOSPF Interview QA (WK) Part1-3 v1Heera SinghNo ratings yet
- MPLS QAsDocument6 pagesMPLS QAsLaxman Shrestha100% (1)
- CCNP Routing WB PDFDocument207 pagesCCNP Routing WB PDFhaleem malikNo ratings yet
- BGP Next Hop SelfDocument9 pagesBGP Next Hop SelfNagendra SinghNo ratings yet
- 20 - Troubleshooting IP Routing Protocols (CCIE Professional Development Series) (Aziz, Liu, Martey, Shamim, IsBN 1587050196)Document1,145 pages20 - Troubleshooting IP Routing Protocols (CCIE Professional Development Series) (Aziz, Liu, Martey, Shamim, IsBN 1587050196)Eloy SimoesNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- Deploying Next Generation Multicast-enabled Applications: Label Switched Multicast for MPLS VPNs, VPLS, and Wholesale EthernetFrom EverandDeploying Next Generation Multicast-enabled Applications: Label Switched Multicast for MPLS VPNs, VPLS, and Wholesale EthernetNo ratings yet
- Administering Cisco QoS in IP Networks: Including CallManager 3.0, QoS, and uOneFrom EverandAdministering Cisco QoS in IP Networks: Including CallManager 3.0, QoS, and uOneNo ratings yet
- Rick Gallahers MPLS Training Guide: Building Multi Protocol Label Switching NetworksFrom EverandRick Gallahers MPLS Training Guide: Building Multi Protocol Label Switching NetworksRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 8: Expert Administration CookbookFrom EverandCisco Unified Communications Manager 8: Expert Administration CookbookNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy HandoutsDocument161 pagesDigital Literacy HandoutsNaeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- UnlDocument33 pagesUnlNaeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Primary Treatment Plan DiagramDocument1 pagePrimary Treatment Plan DiagramNaeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 3 Software Lifecycle Models: 1. Vision 2. Definition 3. Development 4. MaintenanceDocument13 pagesLecture No. 3 Software Lifecycle Models: 1. Vision 2. Definition 3. Development 4. MaintenanceKhurram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Breeder Management RevisedDocument28 pagesBreeder Management RevisedNaeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- CcnaDocument3 pagesCcnaNaeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Treasury Sub Treasury Chalan FormDocument1 pageTreasury Sub Treasury Chalan FormNaeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Class 3 General KnowledgeDocument2 pagesClass 3 General KnowledgeNaeem ShahzadNo ratings yet
- ARM7 LPC2148 User Manual v1.0Document20 pagesARM7 LPC2148 User Manual v1.0yadhu k.cNo ratings yet
- Sap Basis T CodesDocument3 pagesSap Basis T CodesVenkatesh Vykuntam100% (1)
- Model PaperDocument2 pagesModel PaperAbhi ShekNo ratings yet
- Ans B4Document4 pagesAns B4StudentNo ratings yet
- Individual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Enclosure No. 3 To Deped Order No. 011, S. 2020Document1 pageIndividual Daily Log and Accomplishment Report: Enclosure No. 3 To Deped Order No. 011, S. 2020DenMark Tuazon-RañolaNo ratings yet
- GPS 022-000019BDocument290 pagesGPS 022-000019BAshwini PradhanNo ratings yet
- Glencoe Mathematics - Online Study ToolsDocument4 pagesGlencoe Mathematics - Online Study ToolsShahzad AhmadNo ratings yet
- SagarRane (10 0) PDFDocument7 pagesSagarRane (10 0) PDFswaroopa RaniNo ratings yet
- Huda Haider: EducationDocument2 pagesHuda Haider: EducationAyisha PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Cache Management TechniqueDocument15 pagesDynamic Cache Management Technique185G1 Pragna KoneruNo ratings yet
- Installing OpenSceneGraphDocument9 pagesInstalling OpenSceneGraphfer89chopNo ratings yet
- Forwarder-7 2 1-ForwarderDocument144 pagesForwarder-7 2 1-ForwarderRaghavNo ratings yet
- How To Generate GSAK Stats and Automatically Upload To ProfileDocument11 pagesHow To Generate GSAK Stats and Automatically Upload To ProfileMiguelNo ratings yet
- Autonomous CarDocument28 pagesAutonomous CarNagabhushana0% (1)
- SecurityDocument11 pagesSecurityShilpi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- UI Design Report ExampleDocument3 pagesUI Design Report ExampleWei LeeNo ratings yet
- Lec7 - CS787 - Advanced AlgorithmsDocument7 pagesLec7 - CS787 - Advanced AlgorithmsSérgio Luiz PiresNo ratings yet
- Symbol LS2208 Programming - SerialDocument2 pagesSymbol LS2208 Programming - SerialAndrez ZiilvaNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument1 pagePythonvinodjamesNo ratings yet
- Lec#2 Software EngineeringDocument67 pagesLec#2 Software EngineeringHamza AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Exam 1st Periodical ExamDocument17 pagesExam 1st Periodical ExamEphraime Ricerra0% (2)
- Beckman Coulter Cellavision DM96Document166 pagesBeckman Coulter Cellavision DM96Al Joseph Malinay AndaNo ratings yet
- CSE313 - Final Exam Question - PC-A - TH - Fall20Document2 pagesCSE313 - Final Exam Question - PC-A - TH - Fall20Md Zahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- EEP-Arc Flash Hazard Calculation in 9 Steps Using IEEE 1584-AAADocument6 pagesEEP-Arc Flash Hazard Calculation in 9 Steps Using IEEE 1584-AAAJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Removing Undesired Periodic DataDocument10 pagesRemoving Undesired Periodic DataRatna Giridhar KavaliNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Testing & Commissioning of Disabled Toilet Alarm DTA SystemDocument3 pagesMethod Statement For Testing & Commissioning of Disabled Toilet Alarm DTA Systemvin ssNo ratings yet
- Features of Unix Shell?: LinkDocument21 pagesFeatures of Unix Shell?: LinkpujiptNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic Symbols Copy and Paste ̗̀ °Document1 pageAesthetic Symbols Copy and Paste ̗̀ °Ain NajwaNo ratings yet
- Image Compression: JPEG: Summary: SourcesDocument21 pagesImage Compression: JPEG: Summary: SourcesNgô Hiếu TrườngNo ratings yet
- Com - Upgadata.up7723 LogcatDocument4 pagesCom - Upgadata.up7723 Logcatxiaowangww0No ratings yet