Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Signals and Instruments
Uploaded by
Alexandru DamocOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Signals and Instruments
Uploaded by
Alexandru DamocCopyright:
Available Formats
MEASUREMENTS FOR ELECTRONICS
AND
TELECOMMUNICATION AREA
. l. dr. ing. Ioana Marcu
Email: imarcu@radio.pub.ro
Grades Rules:
40% Lab
40% Final exam
20% Lab examination
10% Written test paper
Promovability conditions:
Lab >=5
Final exam > 16 din 40
Lab examination >=5
Written test paper >=5
Msurri n Electronic i Telecomunicaii
GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT METC
1. First specialized course VERY IMPORTANT!!!
2. The information very useful for the following years.
3. Course atendance: not mandatory but strongly encouraged!
4. Exam grade depends on the degree to understand this course
not on its memorization!
5. All the necessary explications are presented throughout this
course.
6. Problems similar to those solved at course are possible
subjects for final exam.
Msurri n Electronic i Telecomunicaii
COURSE CONTENT
1. Signals and instruments for signals generation/measurement
2. Oscilloscope (scope)
3. Voltage and electrical currents measurement
4. Impedances measurement
5. Frequency and time measurement
Course support:
ham.elcom.pub.ro/Metc
Measurements for Electronics and
Telecommunication Area
1. Signals and instruments for
signals measurements
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS
Measurements imply connection between signal
generators and acquisition equipment.
Generated signals can be classified:
analog signals;
digital signals;
modulated signals;
noisy signals or intentionally distorted.
Examples of acquisition instruments:
scopes
spectrum analyzers, etc.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS
SIGNALS
DEFINITION + CLASSIFICATION
physical quantity used for:
messages transmission or storage;
systems tests.
mathematically = time dependency;
Signals used for systems tests are described by
time-depended functions.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
Classification:
Deterministic signals
Random signals
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SIGNALS
DEFINITION + CLASSIFICATION
SIGNALS USED IN ELECTRONICS AREA
cover a large frequency domain:
Audio-frequency signals (AF)
frequency range between a couple of Hz and
approx. 20 kHz;
can be heard by human ear.
Radio-frequency signals (RF)
frequencies over 100kHz;
used for information transmission through radio
methods broadcasted with different antennas;
upper limit: a couple of GHz.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PERIODIC SIGNALS
T = repetition period of the signal
EXAMPLE:
Sine wave
( ) ( )
, x t kT x t k Z + = e
+A
0
A
T
t
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PERIODIC SIGNALS
One-way rectified sine wave
REDRESOR
MONO-
ALTERNAN
ONE-WAVE
RECTIFIER
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PERIODIC SIGNALS
Full-wave rectified sine wave
REDRESOR
DUBL-
ALTERNAN
FULL-WAVE
RECTIFIER
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PERIODIC SIGNALS
Square wave
two levels;
representation in binary form
of digital signals;
two logical values: 0 and 1.
Symmetric square:
amplitude: A
+
= A
;
period: equal periods for both states.
t
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PERIODIC SIGNALS
Triangular and saw-tooth signals:
Periodic square impulses:
t t
t
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PARAMETERS OF PERIODIC SIGNALS
T [s] signals repetition period;
A
+
[V] positive peak amplitude;
A
[V] negative peak amplitude;
A
vv
[V] peak-peak amplitude:
vv
A A A
+
=
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PARAMETERS OF PERIODIC SIGNALS
RMS root mean square:
= effective voltage = continuous voltage that produces
the same average power through a 1 resistance with
the corresponding period signal.
= for sine wave:
( )
2
1
t T
ef
t
A x t dt
T
+
=
}
2
ef
A
A =
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PARAMETERS OF PERIODIC SIGNALS
Average value (mean value):
( )
0
1
t T
t
A x t dt
T
+
=
}
A
0
mean
t
A
+
A
0
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
PARAMETERS OF PERIODIC SIGNALS
Square impulses:
= [s] - duty
= t
c
[s] rise time.
t
c
rise time
t
c
A
0.9A
0.1A
0
t
T
A
T
t
q =
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SINE WAVE - PARAMETERS
A amplitude
- pulsation
[rad./sec.]
T - period
+A
0
A
T
t
( ) cos( ) x t A t = e +
2 f e= t
1
f
T
=
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SINE WAVE - PARAMETERS
initial phase;
Comparing two sine waves with the same
frequency:
=
1
2
= phase difference.
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
1 1 1
2 2 2
cos
cos
x t A t
x t A t
= e +
= e +
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SINE WAVE - PARAMETERS
RMS (Root Mean Square):
Peak-peak
amplitude:
2
ef
A
A =
2
vv
A A =
T
t
A
VV
A
A
ef
= 0,707 A
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
CIRCUIT BEHAVIOR FOR SINE WAVE
Linear circuits
LINEAR
CIRCUIT
y(x) = ax + b
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
CIRCUIT BEHAVIOR FOR SINE WAVE
Non-linear circuits
NON-LINEAR
CIRCUIT
- limitation -
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
CIRCUIT BEHAVIOR FOR SINE WAVE
Non-linear circuits
NON-LINEAR
CIRCUIT
2
( ) 1, 2 0, 6 0,1 y x x x = +
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
CIRCUIT BEHAVIOR FOR SINE WAVE
Modulators circuits
to transmit a signal by radio means a low-
frequency signal (modulator signal) will modify
one parameter of a much high-frequency sine
wave (carrier signal) modulation process.
Achieved signal has high frequency and carries
the useful information this signal is called
modulated signal.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
MODULATED SIGNALS
Modulation types:
Amplitude modulation (MA);
Frequency modulation (MF);
Phase modulation (MP).
Frequency-modulated signal
Amplitude-modulated signal
Modulator signal
Carrier signal
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SINE WAVE GENERATORS
A. Audio-frequency generators
larger frequency domain than audio range;
from 0,1 Hz up to 1MHz (even 10MHz);
rather simple generators with two adjusting
elements (decade and continuous steps):
frequency
amplitude.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
Audio-frequency generators
Quality parameters:
Distorsion factor:
- gives a degree for similarities between generated
signal and a pure sine wave.
Precision and resolution for frequency range;
Stability of generated frequency;
Control of generated amplitude;
Output impedance (thousand, hundred ohms).
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
Radio-frequency generators
B. Radio-frequency generators
100kHz - 100MHz;
maximum limit can be extended;
AM and FM capabilities;
have low-frequency generator for modulator
signal;
a digital frequency measurement equipment
can be used for exact control over carrier
frequency.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR - PARAMETERS
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR - PARAMETERS
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR - PARAMETERS
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR - PARAMETERS
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR - PARAMETERS
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR - PARAMETERS
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
FUNCTION GENERATOR - PARAMETERS
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SCOPE DISPLAY
Sine wave with 1V amplitude
Cy = 0.1V/div 10 divisions (out of graticule)
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SCOPE DISPLAY
Sine wave with 1V amplitude
Cy = 0.2V/div 5 divisions (out of graticule)
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SCOPE DISPLAY
Sine wave with 1V amplitude
Cy = 0.5V/div 2 divisions
A=2div
=1V
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SCOPE DISPLAY
Signals frequency measurement
Turn Cx [s/div] until one period of the signal appears.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SCOPE DISPLAY
Signals frequency measurement
Turn Cx [s/div] until one period of the signal appears.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SCOPE DISPLAY
Signals frequency measurement
Turn Cx [s/div] until one period of the signal appears.
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
SCOPE DISPLAY
Signals frequency measurement
Turn Cx [s/div] until one period of the signal appears.
T=5,6 div
.
Cx
f=1/T
Measurements for Electronics and Telecommunication Area
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Honeywell Ky 97a PDFDocument237 pagesHoneywell Ky 97a PDFJEFFREY DEE MAURY NORIEGANo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationadibNo ratings yet
- EE 179 Digital and Analog Communication Systems Homework SolutionsDocument6 pagesEE 179 Digital and Analog Communication Systems Homework SolutionsAnthony KwoNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication - IntroductionDocument111 pagesDigital Communication - Introductionsushilkumar_0681100% (4)
- MATLAB & Simulink For Digital CommunicationDocument115 pagesMATLAB & Simulink For Digital CommunicationKy Phan40% (5)
- Tle/Epas: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document28 pagesTle/Epas: Quarter 1 - Module 1Doone Heart Santander CabuguasNo ratings yet
- Electronics Circuits for CommunicationsDocument46 pagesElectronics Circuits for CommunicationsLee RitzNo ratings yet
- OsiloskopDocument89 pagesOsiloskopSazali HusinNo ratings yet
- TransmittersDocument9 pagesTransmittersDavid van TeeselingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document53 pagesChapter 1Renz Benhar Ocon BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Electronic CommunicationDocument62 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Electronic Communicationmcruz_1919360% (1)
- M F E A T: Easurements OR Lectronics ND ElecommunicationsDocument13 pagesM F E A T: Easurements OR Lectronics ND Elecommunicationscarmen777No ratings yet
- Analog Communication SystemsDocument169 pagesAnalog Communication SystemsVenkateswara RajuNo ratings yet
- Elements of Communication System:: Communication: It Is The Process of Conveying orDocument168 pagesElements of Communication System:: Communication: It Is The Process of Conveying orsakthiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 & 2Document69 pagesUnit 1 & 2Saiyma Fatima RazaNo ratings yet
- Communication Theory Lecture NotesDocument120 pagesCommunication Theory Lecture NotesAnup KumarNo ratings yet
- LAB 1.cDocument13 pagesLAB 1.cMUHAMMAD AMMARNo ratings yet
- Comsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication SystemsDocument35 pagesComsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication Systemsali_rehman87No ratings yet
- Lecture02 Spring04Document56 pagesLecture02 Spring04Jonathan F. CardinalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics Communications SystemsDocument32 pagesFundamentals of Electronics Communications SystemsRonilloyd SantosNo ratings yet
- Modullation PPT NewDocument58 pagesModullation PPT NewMayank TripathiNo ratings yet
- Comsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication SystemsDocument44 pagesComsats Institute of Information Technology: EEE 352 Analog Communication SystemsUsman Ullah AsifNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electronics Chapter 1Document36 pagesIntroduction to Electronics Chapter 1詹勳智No ratings yet
- TransducersDocument36 pagesTransducersAnurag JoshiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lecture 1Document40 pagesWeek 1 Lecture 1athomeNo ratings yet
- Communication PPT AM FMDocument105 pagesCommunication PPT AM FMDum BoiNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2272A Satellite Communication Uplink Transmitter Downlink Receiver TransponderDocument2 pagesScientech 2272A Satellite Communication Uplink Transmitter Downlink Receiver TransponderRaghu RamNo ratings yet
- EENG 3810 INTRODocument35 pagesEENG 3810 INTROSyed Ariful Islam EmonNo ratings yet
- Measure AC Signals with CRODocument57 pagesMeasure AC Signals with CRODhamu DharanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To CommDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To CommhaftamunigusNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Measurement and InstrumentationDocument16 pagesLecture 2: Measurement and InstrumentationDeepali KundnaniNo ratings yet
- Module 5 NewDocument43 pagesModule 5 NewMythri RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Data Acquisition Systems May 21 PMRDocument51 pagesChapter 5 - Data Acquisition Systems May 21 PMRGeleta BekeleNo ratings yet
- Emf Measurements in The Bts Cellular Stations of Vodafone AlbaniaDocument6 pagesEmf Measurements in The Bts Cellular Stations of Vodafone AlbaniawormingNo ratings yet
- Ec 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesDocument120 pagesEc 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesAnonymous G4srxwO3jINo ratings yet
- MW-B-C/EV Microwave LaboratoryDocument3 pagesMW-B-C/EV Microwave LaboratoryJon Snow-Stark0% (1)
- Practicas de OsciloscopioDocument9 pagesPracticas de OsciloscopiokarolcoNo ratings yet
- Detector Camp Magnetic PDFDocument2 pagesDetector Camp Magnetic PDFClaudiu MirceaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document39 pagesChap 2Ainnina AdenaliaNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Electronics I Laboratory - EXPERIMENT 10 Common Emitter AmplifierDocument6 pagesObjectives:: Electronics I Laboratory - EXPERIMENT 10 Common Emitter AmplifierRabindraMaharanaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Enhancement: Correcting Magnitude and Phase Distortion in Wideband Piezoelectric Transducer SystemsDocument11 pagesBandwidth Enhancement: Correcting Magnitude and Phase Distortion in Wideband Piezoelectric Transducer Systemssundari_muraliNo ratings yet
- Transmitters: Presented by G Kiran Kumar (210115019) Mayank Shukla (210115020)Document29 pagesTransmitters: Presented by G Kiran Kumar (210115019) Mayank Shukla (210115020)Sunil GiriNo ratings yet
- Ec102: Electronics & Communication Laboratory List of ExperimentsDocument95 pagesEc102: Electronics & Communication Laboratory List of Experimentsaryan kumarNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFDocument41 pagesElectronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFtesterNo ratings yet
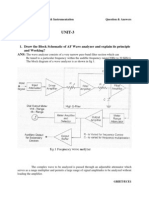
- UNIT-3: 1. Draw The Block Schematic of AF Wave Analyzer and Explain Its Principle and Working? AnsDocument17 pagesUNIT-3: 1. Draw The Block Schematic of AF Wave Analyzer and Explain Its Principle and Working? AnsriyazpashaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab ManualDocument246 pagesElectronics Lab ManualAji Vadakkedathu100% (1)
- Pengantar Teknik Elektro: Telekomunikasi IDocument51 pagesPengantar Teknik Elektro: Telekomunikasi Imario tiaraNo ratings yet
- SergeyYurish Tutorial SIGNAL 2017Document108 pagesSergeyYurish Tutorial SIGNAL 2017Chao-Shiun WangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemJon AbNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Telecommunication SystemsDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Telecommunication SystemsEditha KiwiaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering & Technology (Autonomous)Document51 pagesAnalog Communication: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering & Technology (Autonomous)HimaBindu ValivetiNo ratings yet
- Diagram" Add With Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDiagram" Add With Power SupplyJonathan F. CardinalNo ratings yet
- Modulation Schemes: EEE 352 Analog Communication Systems Mansoor Khan EE Dept. CIIT Islamabad CampusDocument22 pagesModulation Schemes: EEE 352 Analog Communication Systems Mansoor Khan EE Dept. CIIT Islamabad Campusali_rehman87No ratings yet
- UNIT-3: AF Wave AnalyzerDocument18 pagesUNIT-3: AF Wave AnalyzerbijalmehtaNo ratings yet
- Application of Wavelet Transform Technique For Extraction of Partial Discharge Signal in A TransformerDocument12 pagesApplication of Wavelet Transform Technique For Extraction of Partial Discharge Signal in A TransformerNguyen Quang ThangNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 AnalogDocument48 pagesChapter4 AnalogOsman AtamNo ratings yet
- 03 Amplitude ModulationDocument44 pages03 Amplitude ModulationVILLASECA, EDWARDNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 ELECTRONICSDocument38 pagesCHAPTER 1 ELECTRONICSRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Quantum PhysicsDocument11 pagesFoundations of Quantum PhysicsAlexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- Metc Part1Document19 pagesMetc Part1Alexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Quantum PhysicsDocument11 pagesFoundations of Quantum PhysicsAlexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- In This ProjectDocument1 pageIn This ProjectAlexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- Source CodeDocument6 pagesSource CodeAlexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- Organic Light Emitting Diodes - OLED-: What Is An OLED?Document2 pagesOrganic Light Emitting Diodes - OLED-: What Is An OLED?Alexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Activation EnergyDocument4 pagesDetermination of The Activation EnergyAlexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- The Spectroscope Determination of Emission and Absorption SpectrumDocument1 pageThe Spectroscope Determination of Emission and Absorption SpectrumAlexandru DamocNo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Ce Part ADocument13 pagesEc8395 Ce Part AmakNo ratings yet
- Divisions of The Tetrachord by John H. ChalmersDocument373 pagesDivisions of The Tetrachord by John H. ChalmersGerardo Meza GómezNo ratings yet
- Example 9.8 A 400 Watt Carrier Is Amplitude Modulated To A Depth of 80%. Calculate The Total Power in TheDocument6 pagesExample 9.8 A 400 Watt Carrier Is Amplitude Modulated To A Depth of 80%. Calculate The Total Power in TheDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- BSNL Tta (Je) Communication 200 Expected Questions (Wwwallexamreviewcom) Part TwoDocument20 pagesBSNL Tta (Je) Communication 200 Expected Questions (Wwwallexamreviewcom) Part TwodikeshNo ratings yet
- GATE Communications BookDocument12 pagesGATE Communications BookFaniAliNo ratings yet
- Bule Hora University: College of Engineering and Technology)Document43 pagesBule Hora University: College of Engineering and Technology)Befkadu BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Coms ElexDocument127 pagesComs ElexWasim Abbas0% (1)
- Pulse ModulationDocument12 pagesPulse ModulationhlrwNo ratings yet
- ACDocument26 pagesACNandu0% (1)
- Unit 3Document175 pagesUnit 3Bhadra V RajaNo ratings yet
- Electronics 100 Important MCQDocument23 pagesElectronics 100 Important MCQRaghu Veer KNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Important Graphs: 1. Field Lines Due To Some Simple Charge ConfigurationsDocument19 pagesPhysics 12th Important Graphs: 1. Field Lines Due To Some Simple Charge ConfigurationsArjun PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Glossary: - Device That Converts An Information Signal Into A Form Suitable For Propagation Along A ChannelDocument4 pagesGlossary: - Device That Converts An Information Signal Into A Form Suitable For Propagation Along A ChannelReivenNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Wireless Communication BasicsDocument21 pagesIntroduction to Wireless Communication Basicsashokyadav7390% (2)
- BECE Intro Lec-1 MO19Document40 pagesBECE Intro Lec-1 MO19SS TripathyNo ratings yet
- اتصالات لاسلكية مسعود الداقلDocument200 pagesاتصالات لاسلكية مسعود الداقلmarwan khalilNo ratings yet
- Communication Theory 2 MarksDocument24 pagesCommunication Theory 2 MarksabvajaNo ratings yet
- It2202 QBDocument3 pagesIt2202 QBavianbuNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems A Lecture Notes by Mahesh Lohith K. SDocument9 pagesCommunication Systems A Lecture Notes by Mahesh Lohith K. Sarjun poudelNo ratings yet
- 50 Top Modulation & Demodulation Objective Questions AnswersDocument11 pages50 Top Modulation & Demodulation Objective Questions Answersvigneshwarannn0% (2)
- TV BroadcastingDocument32 pagesTV BroadcastingChester Kyles ColitaNo ratings yet
- Btech1 PDFDocument29 pagesBtech1 PDFPOOJA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Communication Systems - I - EE 228Document2 pagesCommunication Systems - I - EE 228Asim AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic Concepts of ModulationDocument25 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Concepts of Modulationayu afNo ratings yet