Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bearing Capacity of Rock
Uploaded by
fruitplus.epalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bearing Capacity of Rock
Uploaded by
fruitplus.epalCopyright:
Available Formats
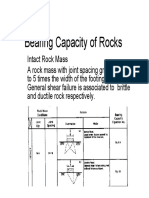
Bearing Capacity of Rocks
Intact Rock Mass Intact Rock Mass
A rock mass with joint spacing greater than 4
to 5 times the width of the footing. Local and
General shear failure is associated to brittle General shear failure is associated to brittle
and ductile rock respectively.
Jointed Rock Mass Jointed Rock Mass
General Shear Failure
Local Shear Failure Local Shear Failure
Compressive Failure:
A h t i d b l t i d A case characterized by poorly constrained
columns of poor rock.
Splitting Failure
For widely spaced and vertically oriented For widely spaced and vertically oriented
discontinuities, failure generally initiates by
splitting beneath the foundation.
The ultimate bearing capacity is given by:
Guideline properties of Rock Mass
Cl Classes
Allowable Bearing Stresses on Rock
Masses
Foundat i ons on Fr act ur ed Rock For mat i on
30
M
P
a
)
Not e: Use maxi mum q
a
< q
u
wher e q
u
= compr essi ve st r engt h
20
25
r
e
s
s
q
a
(
M
wher e q
u
compr essi ve st r engt h
of i nt act r ock speci mens
15
e
a
r
i
n
g
S
t
r
) 130 / ( 1
) 16 / (
1 ) (
RQD
RQD
MPa q
ALLOWABLE
+
NOTE: 1 MPa = 10 t sf
5
10
o
w
a
b
l
e
B
e
Peck, et al . (1974)
NOTE: 1 MPa = 10 t sf
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
A
l
l
o
( )
Appr oxi mat i on
Rock Quality Designation, RQD
In case of rock mass with favorable discontinuities, the net allowable
bearing pressure may be estimated from:
q
a
= q
c
* N
j
Where q
c
= average uniaxial compressive strength of rock cores Where q
c
average uniaxial compressive strength of rock cores
N
j
= empirical coefficient depending on the spacing of the discontinuities
/ 3 B S +
[ ] ) / ( 300 1 10 S +
=
= thickness of discontinuity = thickness of discontinuity
S = spacing of discontinuities
B = width of footing
The above relationship is valid for a rock mass with spacing of
continuities > 0.3 m, < 10 mm (15 mm if filled with soil) and
B >0 3 m B >0.3 m.
Pile Foundations:
The allowable bearing capacity of socketed piles is given by:
q
a
= q
c
* N
j
* N
d
Where Where
N
d
= 0.8 + 0.2 h/d
h = depth of socket in rock
d = diameter of socket
Determination of Net Allowable Bearing Pressure from
P t T t Pressuremeter Test:
[ ] ) (
3
1
f l d f a
D P K D q + =
Where q
a
= allowable bearing pressure in t/m
2
P
l
= limit pressure determined by the Pressuremeter in t/m
2
D
f
= overburden pressure in t/m
2
Values of K
d
Values of K
d
Depth of footing K
d
Depth of footing K
d
Load at rock surface 0.8
Load at radius/width of foundation 2.0
unit
Load at 4 times radius/width of 3.6
foundation unit
Load at 10 times radius/width of
f d ti it
5.0
foundation unit
Plate Load Test Plate Load Test
Correction Factors : (Not required for RMR) Co ect o acto s ( ot equ ed o )
Ground Water Table:
(a) Rock with discontinuous joints with opening less (a) Rock with discontinuous joints with opening less
than 1mm wide 0.75
(b) Rock with continuous joints with opening 1 to 5
id fill d ith 0 7 t 0 5 mm wide filled with gouge 0.7 to 0.5
(c) Limestone/ Dolomite deposit with major cavities
filled with soil 0.66 to 0.5.
Cavities: Major cavities inside limestone - 0.5
Slope and orientation of joints:
( ) F i i t ti f ti j i t i th l (a) Fair orientation of continuous joints in the slope
1 to 0.5
(b) Unfavorable orientation of continuous joints in (b) Unfavorable orientation of continuous joints in
slope 0.5 to 0.33.
You might also like
- International Society for Rock Mechanics: List of Members 1980From EverandInternational Society for Rock Mechanics: List of Members 1980Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Ground Freezing 1980: Selected Papers from the Second International Symposium on Ground Freezing, Trondheim, Norway, 24-26 June 1980From EverandGround Freezing 1980: Selected Papers from the Second International Symposium on Ground Freezing, Trondheim, Norway, 24-26 June 1980No ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of RockDocument19 pagesBearing Capacity of RockAhmad PooladiNo ratings yet
- The Bearing Capacity of Footings On Coarse SoilsDocument11 pagesThe Bearing Capacity of Footings On Coarse SoilsMattNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Soil and Calculation of Bearing CapacityDocument8 pagesBearing Capacity of Soil and Calculation of Bearing CapacityVincent OryangNo ratings yet
- Triaxial TestDocument21 pagesTriaxial TestTshepiso NthiteNo ratings yet
- Trench Stability in Cohesive SoilDocument6 pagesTrench Stability in Cohesive SoilShahab KhaledNo ratings yet
- Settlement Analysis of SoilsDocument22 pagesSettlement Analysis of SoilsMuhammad Hasham100% (1)
- Shear Strength of Soils Final (Complete)Document176 pagesShear Strength of Soils Final (Complete)lcblsc100% (3)
- Rock Socketed PilesDocument7 pagesRock Socketed PilesMohamedRaahimNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Soil Geotechnical InvestigationDocument4 pagesMethodology For Soil Geotechnical InvestigationShyama Prasad SamantaNo ratings yet
- Contact PressureDocument2 pagesContact PressurePrantik Adhar Samanta100% (1)
- Soil Nail - GNP - GoodDocument19 pagesSoil Nail - GNP - GoodgahsoonNo ratings yet
- Revised Geo Technical Reports of Trishuli River Bridge at NuwakotDocument35 pagesRevised Geo Technical Reports of Trishuli River Bridge at NuwakotHem Shahi100% (1)
- Interpretative ReportsDocument22 pagesInterpretative ReportsHéctor Nandar C.100% (1)
- Is.15736.2007 Electrical Resistivity MethodDocument19 pagesIs.15736.2007 Electrical Resistivity Methodrajeshji_000No ratings yet
- For Calculation of SBC From RMR VALUEDocument5 pagesFor Calculation of SBC From RMR VALUESrikalpa RajguruNo ratings yet
- 03-Slope Stability Analysis of Cut Slopes Using Rock and Slope MassDocument17 pages03-Slope Stability Analysis of Cut Slopes Using Rock and Slope MassArif KesumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Circular Secant Pile Walls in Soft ClaDocument11 pagesDesign and Construction of Circular Secant Pile Walls in Soft ClaHumza Mubarik100% (1)
- Pinhole Erosion Test For Identification of Dispersive ClaysDocument28 pagesPinhole Erosion Test For Identification of Dispersive ClaysAndyra Jaiz Baddu100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Lateral Earth PressureDocument45 pagesChapter 5 Lateral Earth PressureAdel JamalNo ratings yet
- Sonic Logging Test PresentationDocument21 pagesSonic Logging Test PresentationYip Ying MunNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Raft MethodDocument2 pagesEquivalent Raft Methodmrlee28100% (2)
- Shallow Foundations - Settlement and EC7Document18 pagesShallow Foundations - Settlement and EC7Ashik Rehmath ParambilNo ratings yet
- 14 3302013ShearStrengthDocument55 pages14 3302013ShearStrengthGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Plate Load TestDocument21 pagesPlate Load Tests shila devi100% (2)
- Case History of Osterberg Cell Testing of A - 1500mm Bored Pile AnDocument9 pagesCase History of Osterberg Cell Testing of A - 1500mm Bored Pile AnlingamkumarNo ratings yet
- Leads Institute of Technology & EngineeringDocument22 pagesLeads Institute of Technology & EngineeringAladdin Narzo100% (2)
- Table of Ultimate Friction Factors For Dissimilar MaterialsDocument1 pageTable of Ultimate Friction Factors For Dissimilar MaterialsJurie_sk3608No ratings yet
- Plaxis AsigmentDocument8 pagesPlaxis AsigmentzuluagagaNo ratings yet
- Groundimprovement SEMINARDocument29 pagesGroundimprovement SEMINARAkshayShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Worked Example 4 Tie BackDocument15 pagesWorked Example 4 Tie BackEverson BoyDayz PetersNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering: Site InvestigationsDocument62 pagesFoundation Engineering: Site InvestigationssstibisNo ratings yet
- ASDSO ShearStrength 2015 PDFDocument86 pagesASDSO ShearStrength 2015 PDFLuciano JuniorNo ratings yet
- Soil C and Phi ValuesDocument3 pagesSoil C and Phi ValuesthamiradNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Wall SpecificationDocument12 pagesDiaphragm Wall SpecificationLee Cw100% (3)
- Chapter 15 Shallow Foundations - 02242010Document8 pagesChapter 15 Shallow Foundations - 02242010Tolaz KoyiNo ratings yet
- In Situ Testing For Highways and Runways Shukla Sivakugan 2009Document6 pagesIn Situ Testing For Highways and Runways Shukla Sivakugan 2009Marcus Vinicius100% (1)
- SPT-Field Permeability TestDocument7 pagesSPT-Field Permeability TestkhemankarNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 Bearing Capacity of SoilDocument57 pagesLecture-2 Bearing Capacity of SoilolibiraNo ratings yet
- Termination Criteria of Piles Subjected To Axial Loading To Is StandardsDocument15 pagesTermination Criteria of Piles Subjected To Axial Loading To Is Standardssongkk100% (1)
- Discharge Capacity of Prefabricated Vertical Drains and Their MeasurementDocument12 pagesDischarge Capacity of Prefabricated Vertical Drains and Their MeasurementHamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- Foundation Behaviour Below An Embankment On Soft SoilsDocument9 pagesFoundation Behaviour Below An Embankment On Soft SoilsLuca BrandiNo ratings yet
- Paper On Waler BeamDocument0 pagesPaper On Waler Beamharicv019No ratings yet
- Allowable Bearing Capacity Schmertmann MethodDocument13 pagesAllowable Bearing Capacity Schmertmann MethodMenan de LeonNo ratings yet
- Characterisation of Soil ESCI 16-2-2012Document102 pagesCharacterisation of Soil ESCI 16-2-2012Divya Tadepalli100% (1)
- Pile Design To BS EN 1997-1:2004 (EC7) and The National AnnexDocument68 pagesPile Design To BS EN 1997-1:2004 (EC7) and The National AnnexSewGuanNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Layered Soilsweaker Soil Underlain by Stronger SoilDocument4 pagesBearing Capacity of Layered Soilsweaker Soil Underlain by Stronger Soilbunheng lonNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Shallow Foundations On Jointed Rock MassDocument89 pagesBehaviour of Shallow Foundations On Jointed Rock MasscenapNo ratings yet
- Delhi Metro Paper On MonitoringDocument8 pagesDelhi Metro Paper On MonitoringTarun Kant GoyalNo ratings yet
- Sheet Pile WallsDocument9 pagesSheet Pile WallsSiti Khadijah HubadillahNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Report GuidelinesDocument8 pagesGeotechnical Report GuidelinesCele Adu-wusuNo ratings yet
- Keynote D.V. KarandikarDocument47 pagesKeynote D.V. KarandikarlingamkumarNo ratings yet
- Strengthening of Marine Deposit by Deep Cement MixingDocument40 pagesStrengthening of Marine Deposit by Deep Cement MixingKai HoNo ratings yet
- Soilcrete Construction MaterialsDocument2 pagesSoilcrete Construction Materialsscelo buthelezi100% (1)
- Burland&Burbidge MethodDocument2 pagesBurland&Burbidge MethodShimant Gunjan100% (2)
- STRUT Load MonitoringDocument12 pagesSTRUT Load Monitoringtun20000No ratings yet
- Development and Evaluation of Some Empirical Methods of Correlation Between The Cone Penetration Test (CPT) and Standard Penetration Test (SPT)Document14 pagesDevelopment and Evaluation of Some Empirical Methods of Correlation Between The Cone Penetration Test (CPT) and Standard Penetration Test (SPT)KemoHNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation - PresentationDocument39 pagesPile Foundation - PresentationJimmy KalumataNo ratings yet
- Eh PdnguidelinesDocument14 pagesEh Pdnguidelinesfruitplus.epalNo ratings yet
- Eurocode 7 Geotechnical Design Worked ExamplesDocument172 pagesEurocode 7 Geotechnical Design Worked ExamplesJevgenijs Kolupajevs100% (1)
- SewerCAD Users Guide v5Document368 pagesSewerCAD Users Guide v5fruitplus.epalNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration TestDocument59 pagesStandard Penetration TestcuervohijoguachoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic and Static Load Tests PDFDocument6 pagesDynamic and Static Load Tests PDFKS LeeNo ratings yet
- Foundations Under Static LoadsDocument80 pagesFoundations Under Static Loadsfruitplus.epalNo ratings yet
- JKR Spec 2005Document188 pagesJKR Spec 2005rex79x98% (60)
- Guideline On Fabrication of Bore Pile ReinforcementDocument21 pagesGuideline On Fabrication of Bore Pile Reinforcementfruitplus.epalNo ratings yet
- MSMA2nd Web May2012Document800 pagesMSMA2nd Web May2012sallymazeera100% (1)
- ScatteringDocument25 pagesScatteringjestamilNo ratings yet
- Landinggear Assignment 1Document7 pagesLandinggear Assignment 1Gurvinderpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Acoustics2 KKDocument8 pagesAcoustics2 KKAanchal BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- CFD Study Heat PipeDocument8 pagesCFD Study Heat PipeSalman Chowdhury ShawonNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics MCQDocument3 pagesElectrostatics MCQSarabpreet Singh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Gearbox MaintenanceDocument14 pagesGearbox MaintenancemahdiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Laws of Motion (1) - 1Document1 pageCBSE Class 11 Physics Laws of Motion (1) - 1sherry louiseNo ratings yet
- Carrier 50tcq 3 12TRDocument118 pagesCarrier 50tcq 3 12TRjack-bcNo ratings yet
- Water Mist Systems WMS-01-Multi Zone: Fpe AsDocument5 pagesWater Mist Systems WMS-01-Multi Zone: Fpe AsReinard BadenhorstNo ratings yet
- The X-Ray BeamDocument26 pagesThe X-Ray Beamdanlen faye flojoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Hydrographic Surveying Part1Document44 pagesLecture 3 - Hydrographic Surveying Part1Ayi100% (8)
- Testing of The Mechanical Properties For 15mo3 SteelDocument2 pagesTesting of The Mechanical Properties For 15mo3 SteelavenclNo ratings yet
- Kodak Professional T-Max Films: Technical Data / Black-And-White FilmDocument30 pagesKodak Professional T-Max Films: Technical Data / Black-And-White Filmc64thorgalNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: DS-2000 Series Reflecting and Refracting TelescopesDocument44 pagesInstruction Manual: DS-2000 Series Reflecting and Refracting TelescopesBrandon BohannonNo ratings yet
- ME355 NotesDocument147 pagesME355 NotesrogerfisicaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To A Real-Time Weather ForecastingDocument20 pagesIntroduction To A Real-Time Weather ForecastingjjjdklcfjsdcfNo ratings yet
- Boiler Manual Umpp PDFDocument53 pagesBoiler Manual Umpp PDFRanjanaWajeNo ratings yet
- Study On The Diaphragm Fracture in A Diaphragm Compressor For A Hydrogen Refueling StationDocument10 pagesStudy On The Diaphragm Fracture in A Diaphragm Compressor For A Hydrogen Refueling StationMateusNo ratings yet
- Vertical Turbine PumpsDocument18 pagesVertical Turbine PumpsazkNo ratings yet
- Cond. Multiposicion Runway ROV-72HR1 (OnOff)Document2 pagesCond. Multiposicion Runway ROV-72HR1 (OnOff)ctaarielNo ratings yet
- 2021 Uzem Chemistry Ch09 - 2 Solubility and Complex-Ion EquilibriaDocument102 pages2021 Uzem Chemistry Ch09 - 2 Solubility and Complex-Ion EquilibriaErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument5 pagesAbstractkanzNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Complex and ERD Well PlanningDocument36 pagesModule 7 - Complex and ERD Well Planningchristianleal123No ratings yet
- Guidelines On The Design of Floor For Vibration Due To Walking LoadsDocument39 pagesGuidelines On The Design of Floor For Vibration Due To Walking LoadsLeung LiangNo ratings yet
- Production of 2-Ethylhexanol From Propylene and Synthesis GASDocument7 pagesProduction of 2-Ethylhexanol From Propylene and Synthesis GASTeliyah DurgiahNo ratings yet
- Steam Boiler Litt ReviewDocument4 pagesSteam Boiler Litt ReviewToMem33% (3)
- Best Practice in - Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (Hvac) Systems Management & Control Date: 6 To 7 March 2017 (2 Days) Venue: SingaporeDocument3 pagesBest Practice in - Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (Hvac) Systems Management & Control Date: 6 To 7 March 2017 (2 Days) Venue: Singaporegud-eng wannabeNo ratings yet
- (SPR Environmental Chemistry) H.J.M. Bowen - Environmental Chemistry Vol3 (2010, Royal Society of Chemistry) PDFDocument158 pages(SPR Environmental Chemistry) H.J.M. Bowen - Environmental Chemistry Vol3 (2010, Royal Society of Chemistry) PDFUmar JuttNo ratings yet
- Contact MechanicsDocument8 pagesContact MechanicsPourya NouryNo ratings yet
- Engineering Standards Manual ISD 341-2: Chapter 13, Welding & Joining Volume 2, Welding Fabrication ProcedureDocument9 pagesEngineering Standards Manual ISD 341-2: Chapter 13, Welding & Joining Volume 2, Welding Fabrication ProcedureJovanni RodriguezNo ratings yet