Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pressure Ans
Uploaded by
Hansraj Rahul0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
276 views2 pagesPHYSICS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPHYSICS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
276 views2 pagesPressure Ans
Uploaded by
Hansraj RahulPHYSICS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Pressure & Density
Compiled by: Sir Sumair
May 02
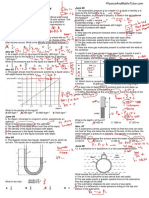
1. A cylindrical block of wood has a cross-sectional area A and
weight W. It is totally immersed in water with its axis vertical. The
block experiences pressures pt and pb at its top and bottom
surfaces respectively. Which of the following expressions is
equal to the upthrust on the block?
2. A mass of a liquid of density is thoroughly mixed with an
equal mass of another liquid of density 2. No change of the
total volume occurs. What is the density of the liquid mixture?
Nov 02
3. At a depth of 20 cm in a liquid of density 1800 kgm
3
, the
pressure due to the liquid is p. Another liquid has a density of
1200 kgm
3
.
What is the pressure due to this liquid at a depth of 60 cm?
Nov 03
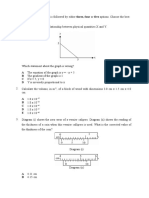
4. The graph shows how the pressure exerted by a liquid varies
with depth below the surface.
What is the density of the liquid?
A 600 kgm
3
B 760 kgm
3
C 5900 kgm
3
D 7500 kgm
3
June 04
5. An object, immersed in a liquid in a tank, experiences an
upthrust.
What is the physical reason for this upthrust?
A The density of the body differs from that of the liquid.
B The density of the liquid increases with depth.
C The pressure in the liquid increases with depth.
D The value of g in the liquid increases with depth.
Nov 04
6. The diagram shows two liquids, labelled P and Q, which do
not mix. The liquids are in equilibrium in an open U-tube.
What is the ratio
June 05
7. The hydrostatic pressure p at a depth h in a liquid of density is
given by the formula p = h g.
Which equation, or principle of physics, is used in the derivation of
this formula?
A density = mass volume
B potential energy = mgh
C atmospheric pressure decreases with height
D density increases with depth
Nov 05
8. Why does the pressure increase when a sealed container of gas
is heated?
A The gas molecules collide more often with each other.
B The gas molecules expand when they are heated.
C The gas molecules travel faster and hit the walls of the container
more often.
D There are more gas molecules present to collide with the walls of
the container.
9. Liquids X and Y are stored in large open tanks. Liquids X and Y
have densities of 800 kg m
3
and 1200 kg m
3
respectively.
At what depths are the pressures equal?
Nov 06
10. Which force is caused by a pressure difference?
A friction B upthrust C viscous force D weight
11. A bore hole of depth 2000 m contains both oil and water as
shown. The pressure at the bottom is
17.5 MPa. The density of the oil is 830 kg m
3
and the density of the
water is 1000 kg m
3
.
What is the depth x of the oil?
A 907 m B 1000 m C 1090 m D 1270 m
Nov. 07
12. A submarine carries a pressure meter so that the crew can work
out how far they are below the surface of the sea. At the surface, the
meter indicates a pressure of 100 kPa. The density of seawater is
1030 kg m
3
.
What is the depth below the surface when the meter reads 450 kPa?
A 34.6 m B 44.5 m C 340 m D 437 m
June 08
13. A submarine is in equilibrium in a fully submerged position.
What causes the upthrust on the submarine?
A The air in the submarine is less dense than sea water.
B The sea water exerts a greater upward force on the submarine
than the weight of the steel.
C The submarine displaces its own volume of sea water.
D There is a difference in water pressure acting on the top and
bottom of the submarine
Nov 08
14. Why does an ideal gas exert pressure on its container?
A The molecules of the gas collide continually with each other.
B The molecules of the gas collide continually with the walls of
the container.
C The molecules of the gas collide inelastically with the walls of
the container.
D The weight of the molecules exerts a force on the walls of the
container.
June 07
15. The density of mercury is 13.6 10
3
kg m
3
.
The pressure difference between the bottom and the top of a
column of mercury is 100 kPa.
What is the height of the column?
A 0.75 m B 1.3 m C 7.4 m D 72 m
June 09
16. The diagram represents a sphere under water. P, Q, R, and
S are forces acting on the sphere, due to the pressure of the
water.
Each force acts perpendicularly to the spheres surface. P and R
act in opposite directions vertically. Q and S act in opposite
directions horizontally.
Which information about the magnitudes of the forces is correct?
A P < R ; S = Q B P > R ; S = Q
C P = R ; S = Q D P = R = S = Q
17. The diagram shows a flask connected to a U-tube containing
liquid. The flask contains air at atmospheric pressure.
The flask is now gently heated and the liquid level in the right-
hand side of the U-tube rises through a distance h. The density
of the liquid is .
What is the increase in pressure of the heated air in the flask?
A h B hg C hg D 2hg
Nov 09
18. In the kinetic model of gases, what is pressure equal to?
A the number of atoms hitting and rebounding from a surface of
the gas container
B the number of atoms hitting and rebounding from a unit area
of the gas container surface
C the force exerted by the atoms hitting and rebounding from a
surface of the gas container
D the force exerted by the atoms hitting and rebounding from a
unit area of the gas container surface
19. A rectangular metal bar exerts a pressure of 15 200 Pa on the
horizontal surface on which it rests.
If the height of the metal bar is 80 cm, what is the density of the
metal?
A 190 kg m
3
B 1900 kg m
3
C 19 000 kg m
3
D 190 000 kg m
3
June 10
20. An object, immersed in a liquid in a tank, experiences an
upthrust.
What is the physical reason for this upthrust?
A The density of the body differs from that of the liquid.
B The density of the liquid increases with depth.
C The pressure in the liquid increases with depth.
D The value of g in the liquid increases with depth.
21. Atmospheric pressure at sea level has a value of 100 kPa.
The density of sea water is 1020 kg m
3
.
At what depth in the sea would the total pressure be 110 kPa?
A 1.0m B 9.8 m C 10 m D 11 m
Answers
1 c 16 a
2 a 17 d
3 c 18 d
4 b 19 b
5 c 20 c
6 a 21 a
7 a
8 c
9 c
10 b
11 d
12 a
13 d
14 b
15 a
You might also like
- CPP FiitjeeDocument18 pagesCPP FiitjeeAmey Kale0% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics - Unit 4 - Justine T. SaldivarDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics - Unit 4 - Justine T. SaldivarJustine Tizon SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document9 pagesPaper 1Neural Spark Physics CieNo ratings yet
- Pressure & DensityDocument2 pagesPressure & DensityIffi AkramNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics MCDocument5 pagesIgcse Physics MCayeayeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3.2 Understanding Pressure in Liquids: Example 1Document4 pagesLESSON 3.2 Understanding Pressure in Liquids: Example 1Joseph TingNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Properties of Matter AllDocument8 pages9702 p1 Properties of Matter AllNushanKhanNo ratings yet
- Pressure & DensityDocument2 pagesPressure & DensityYoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Pressure ...Document2 pagesPressure ...riznailham7No ratings yet
- 3.2 Pressure in LiquidDocument12 pages3.2 Pressure in LiquidNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- Fluids SubjectiveDocument11 pagesFluids SubjectiveSayantan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Physic's Paper 1 Form4-08Document15 pagesPhysic's Paper 1 Form4-08Salmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- Objective Worksheet For Final Term 2023Document18 pagesObjective Worksheet For Final Term 2023SnowYTNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Fluid MechanicsDocument23 pagesIIT JEE Fluid MechanicsSherin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFmohapatramugdha99No ratings yet
- Midterm Examination in Fluid MechanicsDocument11 pagesMidterm Examination in Fluid MechanicsJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Practice TestDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Practice TestSung ParkNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument19 pagesMultiple ChoiceRamanujam O S100% (1)
- TB Chapter15Document14 pagesTB Chapter15Brey KeltonNo ratings yet
- Physics Work Sheet 2Document6 pagesPhysics Work Sheet 2Debela mendaraNo ratings yet
- 3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012Document12 pages3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012ZaoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Pressure:Lesson 3.2Document7 pagesChapter Pressure:Lesson 3.2Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Liquid Pressure 2012Document12 pages3.2 Liquid Pressure 2012cikgusuriyati100% (1)
- Supplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Document7 pagesSupplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Tanuj Gupta0% (2)
- ProblemsDocument3 pagesProblemsimPERFECTme09No ratings yet
- Pressure, Cambridge O LDocument5 pagesPressure, Cambridge O LSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Dodl Past Exam Questions - 240417 - 095612Document22 pagesDodl Past Exam Questions - 240417 - 095612omtyson72No ratings yet
- 8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsDocument8 pages8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsUpeka WeerasinghaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 1Document20 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 1haikukkkNo ratings yet
- Mech. Properties of FluidsDocument18 pagesMech. Properties of FluidsRakesh SNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument288 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties of FluidsProcurement OfficerNo ratings yet
- The Vertical Limbs of A U Shaped Tube Are Filled With A Liquid of DensityDocument14 pagesThe Vertical Limbs of A U Shaped Tube Are Filled With A Liquid of DensityUdeshaWickramaraachchi100% (1)
- DPP - Solids & FluidsDocument6 pagesDPP - Solids & FluidsMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- HidrostaticDocument42 pagesHidrostaticasdfgbugmenotNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument18 pagesRevisionelizabethNo ratings yet
- Chap 11 and Intro To CourseDocument44 pagesChap 11 and Intro To CourseAtpNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 FluidDocument5 pagesSheet 3 Fluidabdomoshref9No ratings yet
- Problems - Introduction and Fluid Statics - 1Document5 pagesProblems - Introduction and Fluid Statics - 1Asjad khanNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSS0% (1)
- Baro Mano WorksheetDocument12 pagesBaro Mano WorksheetashokNo ratings yet
- Q 1Document4 pagesQ 1Manu K VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Pressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsDocument14 pagesPressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsLai Kee Kong100% (1)
- UP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024Document9 pagesUP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024erumriaz.1995No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Class TestDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Class TestshamshadNo ratings yet
- AnnieDocument6 pagesAnnieAnnie Glorina LumauigNo ratings yet
- HW-1 2Document4 pagesHW-1 2Ozan YakarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (4th Year)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics (4th Year)Jaypee Calamba100% (1)
- Chapter 7Document3 pagesChapter 7Aadar NNo ratings yet
- Practice Fluids - 3Document7 pagesPractice Fluids - 3jayNo ratings yet
- CQZ1 Solutions ExplanationsDocument11 pagesCQZ1 Solutions Explanationsricardo lopezNo ratings yet
- Section e Solids Gases Liquids Revision GuideDocument10 pagesSection e Solids Gases Liquids Revision GuideCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument1 pageFluid MechanicsEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument6 pagesFluids PDFccbcorcoles0% (2)
- Compilation of Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesCompilation of Solved ProblemsyslovillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Physics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1 EditedDocument10 pagesPhysics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1 EditedEzra Loganathan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- The Chemical Engineer - Issue 942 - 943 - December 2019 - January 2020 PDFDocument68 pagesThe Chemical Engineer - Issue 942 - 943 - December 2019 - January 2020 PDFMichael WiseNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Timetable 1617 v3Document3 pages2nd Year Timetable 1617 v3Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Engineer - Consultants & Contractors Guide 2020 - December 2019Document24 pagesThe Chemical Engineer - Consultants & Contractors Guide 2020 - December 2019Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Assessment of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Beverage Bottles Consumed in The State of CaliforniaDocument102 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Beverage Bottles Consumed in The State of CaliforniaHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- TRDocument1 pageTRHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Engineer - Issue 946 - April 2020 PDFDocument68 pagesThe Chemical Engineer - Issue 946 - April 2020 PDFHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Travefy Free Itinerary Template - XSLXDocument70 pagesTravefy Free Itinerary Template - XSLXHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Travefy Free Itinerary Template - XSLXDocument7 pagesTravefy Free Itinerary Template - XSLXMarcus J. ValdezNo ratings yet
- Travefy Free Itinerary TemplateDocument8 pagesTravefy Free Itinerary TemplateMarcus J. ValdezNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena Exam, January 2011, With Model AnswersDocument11 pagesTransport Phenomena Exam, January 2011, With Model AnswersHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- L2 - Reactors - CresswellDocument18 pagesL2 - Reactors - CresswellHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- 01 First Order Model AG 2012Document56 pages01 First Order Model AG 2012Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Additional Material Energy BalancesDocument32 pagesAdditional Material Energy BalancesHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Optimization Models For Heat Integration-I. Area AND Energy Targeting AND Modeling of Multi-Stream ExchangersDocument14 pagesSimultaneous Optimization Models For Heat Integration-I. Area AND Energy Targeting AND Modeling of Multi-Stream ExchangersHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- UOP PSA Systems For Hydrogen Recovery and Purificatio From Refinery Off GasDocument2 pagesUOP PSA Systems For Hydrogen Recovery and Purificatio From Refinery Off GasHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Design of Integrated Refrigeration Systems: G. Wu and X. X. ZhuDocument19 pagesDesign of Integrated Refrigeration Systems: G. Wu and X. X. ZhuHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- UG Handbook 2016 - FinalDocument58 pagesUG Handbook 2016 - FinalHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Cogeneration 03 04 2014Document125 pagesCogeneration 03 04 2014Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Control Simulink Tutorial PART ADocument5 pagesControl Simulink Tutorial PART AHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Additional Material Energy BalancesDocument32 pagesAdditional Material Energy BalancesHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Timetable 1617 v3Document3 pages2nd Year Timetable 1617 v3Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Cooling Water Systems: August 2011Document23 pagesOptimal Design of Cooling Water Systems: August 2011Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- NTU MethodDocument15 pagesNTU MethodVenkatesh KandalamNo ratings yet
- A7bdb51b 1Document16 pagesA7bdb51b 1Ignacio MarínNo ratings yet
- 09coshh and ReachDocument23 pages09coshh and ReachHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- 10risk Assessment and ComahDocument25 pages10risk Assessment and ComahHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- HTandPI Problem2Document3 pagesHTandPI Problem2Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Group MM Agenda 050218Document2 pagesGroup MM Agenda 050218Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Year 3 MeetingDocument4 pagesYear 3 MeetingHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- Introductory Context (Identifying Plant Item To Be Designed in Relation of The Whole Process) Equipment Selection (Specifying Design Objectives and Constraints and Justifying Choice of Equipment)Document1 pageIntroductory Context (Identifying Plant Item To Be Designed in Relation of The Whole Process) Equipment Selection (Specifying Design Objectives and Constraints and Justifying Choice of Equipment)Hansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- MAS4 Gas TurbineDocument38 pagesMAS4 Gas TurbineRajath ShettyNo ratings yet
- Xin Yang, Derek Ingham, Lin Ma, Hao Zhou, Mohamed PourkashanianDocument11 pagesXin Yang, Derek Ingham, Lin Ma, Hao Zhou, Mohamed Pourkashaniansattar aljabairNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Communications: To Cite This Article: Zhanyong Li, Noriyuki Kobayashi, Akira Nishimura & MasanobuDocument17 pagesChemical Engineering Communications: To Cite This Article: Zhanyong Li, Noriyuki Kobayashi, Akira Nishimura & MasanobuTerrence Terry BhengoeNo ratings yet
- EXcellent Acoustic Book 91843326-eBook-Physics-PDF-Engineering-Acoustics PDFDocument37 pagesEXcellent Acoustic Book 91843326-eBook-Physics-PDF-Engineering-Acoustics PDFconcord1103100% (1)
- Heat Practicals (EM) - 230613 - 001844Document17 pagesHeat Practicals (EM) - 230613 - 001844Dharsitth AshvinNo ratings yet
- 9702 s14 QP 21Document16 pages9702 s14 QP 21Jing WangNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Document173 pagesGas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Karim SalesNo ratings yet
- TSEE NoteDocument12 pagesTSEE NoteYogesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Compressed AirDocument4 pagesCompressed Airmdalt9180100% (1)
- Respond Areas in SpaceDocument277 pagesRespond Areas in SpaceArijit SharmaNo ratings yet
- CNG Base TrainingDocument74 pagesCNG Base TrainingInterogator5100% (1)
- 6.3 Pressure and Volume (Boyle's Law) : Chapter 6 GasesDocument19 pages6.3 Pressure and Volume (Boyle's Law) : Chapter 6 Gases.....No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3wallacec1017No ratings yet
- Unconsidered Emissions of Mercury From The Oil and Gas Industry (ICMGP Qa3 Poster Presentation)Document1 pageUnconsidered Emissions of Mercury From The Oil and Gas Industry (ICMGP Qa3 Poster Presentation)Lee Hunter JrNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter - Pretest Science 8Document4 pagesThird Quarter - Pretest Science 8Nathan Masilungan100% (3)
- Thermodynamics Questions MCqsDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Questions MCqsGoverdhan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Fire and Arson Investigation ReviewerDocument17 pagesFire and Arson Investigation ReviewerJohn Paul TanNo ratings yet
- Line Chart QuestionsDocument60 pagesLine Chart QuestionsArunNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5.3 Ideal Gas LawDocument6 pagesLesson 5.3 Ideal Gas LawAqshin BabaevNo ratings yet
- XI Chem Target Paper (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)Document9 pagesXI Chem Target Paper (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)MuhammadSultanNo ratings yet
- Full Exam Review #2Document14 pagesFull Exam Review #2ManmeetKalsiNo ratings yet
- Mini Mock Exam - QDocument9 pagesMini Mock Exam - QHana maeNo ratings yet
- Manual Ambient Oxygen MonitorDocument41 pagesManual Ambient Oxygen MonitorRobert BungalawanNo ratings yet
- s540 Flue Gas Analyser Maxilyzer NG PlusDocument2 pagess540 Flue Gas Analyser Maxilyzer NG Plusisraelnogueira3No ratings yet
- CHE1017 - Food Process Engineering: Dr. S. K. BeheraDocument55 pagesCHE1017 - Food Process Engineering: Dr. S. K. BeheraermiasNo ratings yet
- Kick Tolerance Paper 2Document8 pagesKick Tolerance Paper 2Diego AraqueNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science Midterm IVDocument5 pages8th Grade Science Midterm IVsebas aritaNo ratings yet
- MPP High Performance Multi Phase Pump E00601Document6 pagesMPP High Performance Multi Phase Pump E00601chijioke ekekeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial LU1-7 Sem 1Document38 pagesTutorial LU1-7 Sem 1Amir Asyraf ZainudinNo ratings yet
- Saipem Catalog SampleDocument6 pagesSaipem Catalog SampleSathishNo ratings yet