Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Industrial Analog Controllers
Uploaded by
Ahmed NahrawyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Industrial Analog Controllers
Uploaded by
Ahmed NahrawyCopyright:
Available Formats
Alexandria University
Faculty of Engineering
Automatic Control
Basic control Actions and
Industrial Automatic
Controllers
By:
Ahmed Mohammed Kamel
Sec:
!o: "#$
Introduction
An automatic controller compares
the actual value of the plant output
with the reference input(desired
value) , determines the deviation
,and produces a control signal that
will reduce the deviation to zero or
to a small value. The manner in the
automatic controller produces the
signal is called the control action
Classification of industrial analog
controllers
1. Two-position or on-off controllers
2. Proportional controllers
3. Integral controllers
4. Proportional - plus Integral controllers
5. Proportional - plus -derivative controllers
6. Proportional - plus Integral - plus -derivative
controllers .
Most industrial analog controllers use electricit or
pressuri!ed fluid suc" as oil or air as power sources .
#nalog controllers $a%e also classified according to
t"e &ind of power e$ploed in t"e operation 'suc" as
pneu$atic ' "draulic 'or electronic controllers .
T"e &ind of controller to use $ust %e decided %ased
on t"e nature of t"e plant and t"e operation
condition ' including suc" consideration as safet '
cost 'availa%ilit 'relia%ilit ' accurac ' weig"t 'and
si!e.
Automatic controller ,actuator ,and sensor :
T"e controller detects t"e actuating error signal w"ic"
is usuall at a ver low power level ' and a$plifies it
to a sufficientl "ig" level .
T"e actuator is a power device t"at produces t"e input
to t"e plant according to t"e control signal so t"at t"e
output signal will approac" t"e reference input signal .
T"e sensor or t"e $easuring ele$ent is a device t"at
converts t"e output varia%le into anot"er suita%le
varia%le 'suc" as a displace$ent 'pressure or voltage
t"at can %e used to co$pare t"e output to t"e reference
input signal . T"is ele$ent is in t"e pat" of t"e
feed%ac& of t"e closed loop sste$ .
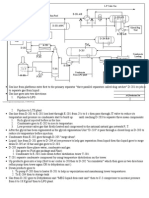
Pneumatic controllers :
(i$pl it is a controller t"at its wor&ing fluid is gas or speciall air
Kind of Pneumatic controllers :
1 )o!!le flapper a$plifier *
T"e power source is air and it convert t"e s$all
c"ange in position into large c"ange in t"e %ac& pressure
in t"e no!!le +Proportional controller .
2 Pneu$atic relas *
It is t"e second stage after nozzle flapper amplifier .
3 Pneu$atic Proportional controllers *
T"ere are two $ean tpes one called t"e force-distance and
t"e force-%alance .T"e %asic principle of operation does not
differ fro$ force-distance and t"e force-%alance %ut force-
%alance "as advantage t"at it eli$inate $an $ec"anical
lin&ages and pivot ,oints 't"ere% reducing t"e effects of friction
.
Hydraulic controller :
T"e widespread use of "draulic circuitr in $ac"ine tool
application' aircraft control sste$s' and si$ilar operations
occur of suc" factors as positiveness 'accurac '
fle-i%ilit '"ig" "orsepower to weig"t ratio 'fast starting
'stopping and reversal wit" s$oot"ness and precision ' and
si$plicit of operations.
Attention :
Particular attention is necessar to ensure t"at t"e
"draulic sste$ is sta%le and satisfactor under all
operation conditions . (ince viscosit of "draulic fluid
can greatl affect t"e da$ping and friction effects of t"e
"draulic circuits' sta%ilit tests $ust %e carried out at t"e
"ig"est possi%le operating te$perature .
)ote t"at $ost of "draulic sste$ are nonlinear so we
need to lineari!e it .
Kinds of hydraulic controllers
a. .draulic Proportional controllers .
%. .draulic Integral controllers .
c. .draulic Proportional - plus Integral controllers
figure /a0 .
d. .draulic Proportional - plus -derivative controllers
figure /%0.
a
%
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Misalignment of The Exhaust Manifold and BellowsDocument5 pagesMisalignment of The Exhaust Manifold and BellowsAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Fuel Metering Valve Problem: TroubleshootingDocument2 pagesFuel Metering Valve Problem: TroubleshootingAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- Failures of Cylinder Head Valves On G3500C and G3500E Generator Set Engines (1100, 1105, 1121)Document5 pagesFailures of Cylinder Head Valves On G3500C and G3500E Generator Set Engines (1100, 1105, 1121)Ahmed Nahrawy100% (1)
- AutomotiveDocument124 pagesAutomotiveAhmed Nahrawy100% (9)
- ASME Pressure Transient Flow Forces (Manring and Zhang)Document5 pagesASME Pressure Transient Flow Forces (Manring and Zhang)Ahmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- 966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemDocument2 pages966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemAhmed Nahrawy82% (11)
- 966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemDocument2 pages966F Wheel Loader Electrical SystemAhmed Nahrawy82% (11)
- Pipeline Construction PDFDocument3 pagesPipeline Construction PDFAhmed Nahrawy100% (1)
- Pitch Diameter, DDocument2 pagesPitch Diameter, DAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- 966F & 966F Series II Wheel Loaders Hydraulic SystemDocument2 pages966F & 966F Series II Wheel Loaders Hydraulic SystemAhmed Nahrawy100% (7)
- LTS PlantDocument2 pagesLTS PlantAhmed NahrawyNo ratings yet
- K Value of FittingsDocument4 pagesK Value of FittingsJoydip Misra100% (6)
- Well TestingDocument25 pagesWell TestingAhmed Nahrawy100% (3)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- HX75S OmDocument147 pagesHX75S OmINGENIERIA H&C SASNo ratings yet
- Intel® Desktop Board DH61HO: Technical Product SpecificationDocument82 pagesIntel® Desktop Board DH61HO: Technical Product Specificationkoplo2010No ratings yet
- Ah Hydraulic Setting ToolDocument12 pagesAh Hydraulic Setting ToolCarlos HolguinNo ratings yet
- Differential LockDocument24 pagesDifferential LockJeevan Landge PatilNo ratings yet
- LG Digital SignageDocument21 pagesLG Digital SignageYazan RamezNo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar University Technology of Institute: School of Computing and Electrical EngineeringDocument55 pagesBahir Dar University Technology of Institute: School of Computing and Electrical Engineeringkrishnareddy_chintala0% (1)
- Rack 760082479 Product SpecificationsDocument2 pagesRack 760082479 Product SpecificationsJose ViquezNo ratings yet
- Manuel Technique MicroLab Mk8 PDFDocument29 pagesManuel Technique MicroLab Mk8 PDFkaiwan mohammedNo ratings yet
- Electrical TWD-ModelDocument1 pageElectrical TWD-ModelzeshanjamilNo ratings yet
- Haz Repair&MaintDocument29 pagesHaz Repair&MaintSANJAY PANDYANo ratings yet
- 3BSE020923R5001 CIO S800 InstallDocument284 pages3BSE020923R5001 CIO S800 InstallFabian SolanoNo ratings yet
- CZ XGZP6857a100kpg 0001Document7 pagesCZ XGZP6857a100kpg 0001RolandoIgorLeivaNo ratings yet
- Movacolor MC-24 Users ManualDocument69 pagesMovacolor MC-24 Users ManualZachary FedorchukNo ratings yet
- Megane F7R710 ECU Pinout PDFDocument5 pagesMegane F7R710 ECU Pinout PDFAlberto Martiniere100% (1)
- Vetus Diesel EngineDocument80 pagesVetus Diesel EnginestartaxisNo ratings yet
- Advantech Protocol Bundle SolutionsDocument5 pagesAdvantech Protocol Bundle SolutionsBiswjit DeyNo ratings yet
- Frances Juris B. Natino 7-STE 1 ICT Quarter 2-Module 1: Activity 1 ADocument3 pagesFrances Juris B. Natino 7-STE 1 ICT Quarter 2-Module 1: Activity 1 ALjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Specifications: Refrigerators and FreezersDocument2 pagesSpecifications: Refrigerators and Freezersdwinanto100% (1)
- Instructions: Dx100 OptionsDocument80 pagesInstructions: Dx100 OptionsDuvan TamayoNo ratings yet
- 722 800 PDFDocument4 pages722 800 PDFMAQUISAN0% (1)
- 45e PPB 246Document16 pages45e PPB 246HOMERO NOGUEDANo ratings yet
- Yale g807 Erp18vt Lift Truck (Europe) Service Repair ManualDocument32 pagesYale g807 Erp18vt Lift Truck (Europe) Service Repair ManualSARAMQR50% (2)
- Power Distribution Network Design For VlsiDocument211 pagesPower Distribution Network Design For VlsiAvas RoyNo ratings yet
- Ics Manual PDFDocument47 pagesIcs Manual PDFSurya RawNo ratings yet
- 2004 Element Online Reference Owner's ManualDocument233 pages2004 Element Online Reference Owner's ManualAnton ShinelevNo ratings yet
- Shop Manual Pc2000-8 Sen01607-00pdDocument567 pagesShop Manual Pc2000-8 Sen01607-00pdSurya Gunawan100% (3)
- Daily Vehicle Checklist Ver1Document1 pageDaily Vehicle Checklist Ver1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Head Actuator: Gabriel MbuguaDocument6 pagesHead Actuator: Gabriel MbuguaGaby MbuguaNo ratings yet
- Underground Cable Temperature Monitoring in The Real WorldDocument28 pagesUnderground Cable Temperature Monitoring in The Real World¡Santa Comida ECNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Transportation Aids and Vehicle Storage: ActivityDocument2 pagesVehicle Transportation Aids and Vehicle Storage: Activityaiman dotsawalNo ratings yet