Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dctoac: DT T DV C T I
Uploaded by
Michael LeinerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dctoac: DT T DV C T I
Uploaded by
Michael LeinerCopyright:
Available Formats
DC to AC
You already know about transistors as switches. Now you need to know the transient behavior of
resistor-capacitor circuits. RC circuits can be used as timers. We will use them to control the
timing of transistor switching.
Capacitors store charge: ! C"Cap. #ere is the charge stored$ "Cap is the voltage drop across
the capacitor plates and C is the capacitance. %he energy stored in the capacitor is C"Cap
&
'&.
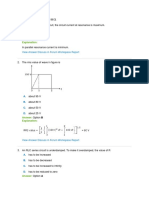
%hese euations describe the static properties. (uring the charging and discharging of a
capacitor we have
dt
t dV
C t I
Cap
) *
) * =
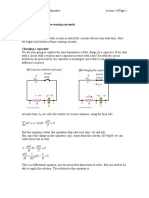
Now consider the circuit shown below.
+t time t ! , the open switch is closed and the capacitor begins to charge. %he current through
the resistor is the voltage drop across the resistor divided by the resistance:
%hus
a first-order linear differential euation with the initial condition "*,) ! ,.
%he solution is
=
RC
t
V V t V
Cap
e-p ) *
, ,
./m sure at some point in your education you came across this result. 0or our purposes let us
calculate the voltage at the point +:
R
t V V
t I
Cap
)) * *
) *
,
=
dt
t dV
C
R
t V V
Cap Cap
) * )) * *
,
=
%hus at the point + the voltage starts at ", and decays e-ponentially to 1ero with a time constant
of RC. We can use "+ to switch a pnp transistor: it would start 2off/ since "+ is large but then
switch to 2on/ as "+ got close enough to 1ero.
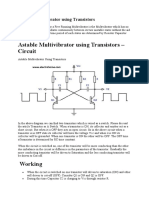
A free-running multivibrator:
3 Y
= =
RC
t
V t V V t V
Cap A
e-p ) * ) *
, ,
pnp transistor-4 switches on when the base approaches ground. %he 2on/ state of transistor-4 is
used to charge up a resistor-capacitor on the base of transistor-&$ & will turn off and then after
some time turn on5 then transistor-& will do the same to transistor-4. %hen end result is that the
transistors 2take turns/ switching on and off. %he figure below shows an oscilloscope image of
the voltage at points 3 and Y. We did much the same with the 666 timer chip but here the
waveform is not suare.
The top and bottom curves are the voltages at X and Y. The middle curve is the difference.
+s we shall see below this waveform can produce an +C signal.
.n a transformer a variable current through the primary coil creates a variable magnetic field
which in turn induces a variable current to flow in the secondary coil. .f we send the output of
the multivibrator to a transformer we obtain an alternating current in the transformer/s secondary
coil.
Transformer output.
References:
You might also like
- Lab 7 RC Time ConstantDocument8 pagesLab 7 RC Time ConstantMalith Madushan100% (1)
- RC Circuit Lab ReportDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Lab ReportTedRamli50% (2)
- Voltage Controlled OscillatorDocument7 pagesVoltage Controlled Oscillatorjonesy5000No ratings yet
- 1/16 Din Microbased Controller: Operators ManualDocument69 pages1/16 Din Microbased Controller: Operators ManualJosue Camacho100% (2)
- RC Circuits: PHYS 2211L Lab 5Document10 pagesRC Circuits: PHYS 2211L Lab 5Angelica CanoNo ratings yet
- PHYS 2426 Lab 7 - The RC Circuit - ManualDocument6 pagesPHYS 2426 Lab 7 - The RC Circuit - Manualwhatis you nameNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current CircuitsDocument8 pagesAlternating Current CircuitsShafiq HafizullahNo ratings yet
- Eee Lab Report 07Document11 pagesEee Lab Report 07Sayeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Exponential FuntionDocument9 pagesLab 01 Exponential FuntionfarhanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C - RC CircuitsDocument20 pagesAP Physics C - RC CircuitsnalinigeeNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument146 pagesAstable Multivibratorsantovaron123No ratings yet
- Ee102 Lab 5Document12 pagesEe102 Lab 5Khuresh ShahNo ratings yet
- Kirchoffs Law & RC CircuitsDocument7 pagesKirchoffs Law & RC Circuitsrajput1287No ratings yet
- Experiment: Transient Response of An RC CircuitDocument7 pagesExperiment: Transient Response of An RC CircuitSalah Uddin MridhaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance in A RC CircuitDocument5 pagesCapacitance in A RC CircuitkanchankonwarNo ratings yet
- Parallel R, L, C Circuits: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesParallel R, L, C Circuits: ObjectiveSeHa HassanNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Time Constant of RC CircuitsDocument4 pagesLab 5 - Time Constant of RC CircuitshamzaNo ratings yet
- RC Circuits - George Ricarrson 2501987261Document9 pagesRC Circuits - George Ricarrson 2501987261George RYNo ratings yet
- Capacitors in Series and Parallel and The Time Constant RC: 1 Purpose of Experiment 10Document0 pagesCapacitors in Series and Parallel and The Time Constant RC: 1 Purpose of Experiment 10Jaiprasad ReddyNo ratings yet
- RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope: ObjectiveDocument13 pagesRC Circuits and The Oscilloscope: Objectiveআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরানNo ratings yet
- LabReport 3 FinaleDocument16 pagesLabReport 3 FinaleChiara CalvoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingDocument2 pagesExperiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingAlicia AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Daycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsDocument5 pagesDaycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsLaercio Marques100% (1)
- RC RL RLC 3.0 PDFDocument13 pagesRC RL RLC 3.0 PDFlp_blackoutNo ratings yet
- Today:: QT V Itr CDocument8 pagesToday:: QT V Itr CAbdul MuhaiminNo ratings yet
- The Transistor Astable Multi VibratorDocument6 pagesThe Transistor Astable Multi VibratorTavleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument10 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using TransistorsGangireddy SanjeevNo ratings yet
- The RC Circuit: TheoryDocument4 pagesThe RC Circuit: TheoryCanh LuongtienNo ratings yet
- The Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesDocument9 pagesThe Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesyashsviNo ratings yet
- P Iv P I ( - Ir)Document19 pagesP Iv P I ( - Ir)John Angelo ManaloNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument38 pagesAstable MultivibratorSherry Sher0% (1)
- Experiment Guide For RC Circuits 1. CapacitorsDocument9 pagesExperiment Guide For RC Circuits 1. CapacitorsShafiqul Islam ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Physics PraticalDocument12 pagesPhysics PraticalRohit MishraNo ratings yet
- Bistable Mono StableDocument30 pagesBistable Mono StableTurkish GatxyNo ratings yet
- The Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesDocument9 pagesThe Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesSGSNo ratings yet
- The RC Circuit: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocument8 pagesThe RC Circuit: Pre-Lab QuestionsMd. Sazidul Haque SazzadNo ratings yet
- The RC CircuitDocument8 pagesThe RC CircuitNadineNo ratings yet
- Electrical HerrmannDocument14 pagesElectrical HerrmannMauro Ferreira De LimaNo ratings yet
- Hw2ans 2013 PDFDocument5 pagesHw2ans 2013 PDFAnthony AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12 The RC Series Circuit: RC T o CDocument5 pagesExperiment 12 The RC Series Circuit: RC T o CUddipta K. SaikiaNo ratings yet
- NE555 Astable MultivibratorDocument6 pagesNE555 Astable Multivibratorbhanuka2009No ratings yet
- CaoacitanceDocument6 pagesCaoacitanceHassan KenjrawyNo ratings yet
- Eeng200-Exp1 3Document7 pagesEeng200-Exp1 3What's new ?No ratings yet
- Experiment Physic RC CircuitDocument7 pagesExperiment Physic RC CircuitLia XeraNo ratings yet
- IC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsDocument11 pagesIC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- PAG 09.1 - Investigating Charging and Discharging of CapacitorsDocument4 pagesPAG 09.1 - Investigating Charging and Discharging of CapacitorsjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Physics II Lab ReportDocument11 pagesPhysics II Lab ReportThịnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoffs Rules RL RC NotesDocument4 pagesKirchhoffs Rules RL RC Notesniravgandhi93No ratings yet
- Lab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Document11 pagesLab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Ece KayaNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Lab Virtual Rev1.docx 1 1 PDFDocument7 pagesRC Circuit Lab Virtual Rev1.docx 1 1 PDFPrisalNo ratings yet
- RCSeries S09Document6 pagesRCSeries S09Anonymous tTLGacyhZ2No ratings yet
- Objective: RequirementsDocument5 pagesObjective: RequirementssnehasishNo ratings yet
- Home Published Books Courses Taught Matlab, Gui Pspice Useful Links PersonalDocument8 pagesHome Published Books Courses Taught Matlab, Gui Pspice Useful Links PersonaldialauchennaNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument28 pagesCourse OutlineIdrisa Mussa ChubwaNo ratings yet
- Spice Ii: Prepared by Dr. Wagih GirgisDocument30 pagesSpice Ii: Prepared by Dr. Wagih GirgisMostafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- ECE 53: Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesECE 53: Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringMd Rasheduzzaman Al-AminNo ratings yet
- Capacitors: The Impedance of A CapacitorDocument4 pagesCapacitors: The Impedance of A Capacitornavinchopra1986No ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- SWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Document13 pagesSWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Table of Roadway JurisdictionDocument8 pagesTable of Roadway JurisdictionMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- 3.19.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting With Cameron OfficeDocument1 page3.19.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting With Cameron OfficeMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- 3.23.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting 3TCDocument1 page3.23.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting 3TCMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- 3.12.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting With Cameron OfficeDocument1 page3.12.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting With Cameron OfficeMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- 3.26.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting With Cameron OfficeDocument1 page3.26.18 - 3rd Track - Meeting With Cameron OfficeMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-5 Shop Drawing - Phase 3Document1 pageMPT-5 Shop Drawing - Phase 3Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-3 A-37305 Phase 3Document1 pageMPT-3 A-37305 Phase 3Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Mpt-3 Shop Drawing - Phase 1Document1 pageMpt-3 Shop Drawing - Phase 1Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-3 A-37305 Phase 3Document1 pageMPT-3 A-37305 Phase 3Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-2 A-37305 Phase 2Document1 pageMPT-2 A-37305 Phase 2Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFDocument1 pageMPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Mpt-2 Shop Drawing - TableDocument1 pageMpt-2 Shop Drawing - TableMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFDocument1 pageMPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFDocument1 pageMPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-4 A-37305 Phase 4Document1 pageMPT-4 A-37305 Phase 4Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-3 Shop Drawing - Phase 1Document1 pageMPT-3 Shop Drawing - Phase 1Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFDocument1 pageMPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-3 A-37305 Phase 3Document1 pageMPT-3 A-37305 Phase 3Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Mpt-2 Shop Drawing - TableDocument1 pageMpt-2 Shop Drawing - TableMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Mpt-0 Shop Drawing - Table 22Document1 pageMpt-0 Shop Drawing - Table 22Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFDocument1 pageMPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Mpt-0 Shop Drawing - TableDocument1 pageMpt-0 Shop Drawing - TableMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- MPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFDocument1 pageMPT-2 SHOP DRAWING - Phase 2 PDFMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Mpt-1 Shop Drawing - Phase 122Document1 pageMpt-1 Shop Drawing - Phase 122Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Wedding ChartDocument1 pageWedding ChartMichael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Mpt-1 Shop Drawing - Phase 1Document1 pageMpt-1 Shop Drawing - Phase 1Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- SWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Document13 pagesSWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- SWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Document13 pagesSWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- SWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Document13 pagesSWP 2019-XXX Temporary Water Service Connections r4Michael LeinerNo ratings yet
- Iec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24Document8 pagesIec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24rakibulislamakash40No ratings yet
- Sec1-Network Analysis and Syn (Indiabix)Document20 pagesSec1-Network Analysis and Syn (Indiabix)xaiiNo ratings yet
- Yang-Circuit Systems With MATLAB and PSpice-2007Document538 pagesYang-Circuit Systems With MATLAB and PSpice-2007nelsonNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Experimental Methods NET-JRF June 2011-Dec 2014Document16 pagesElectronics and Experimental Methods NET-JRF June 2011-Dec 2014morganNo ratings yet
- Electrical Damping of A Piezoelectric PlateDocument17 pagesElectrical Damping of A Piezoelectric PlatestaedtlerpNo ratings yet
- Me 360 Pid ImplementationDocument3 pagesMe 360 Pid ImplementationJarfoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 D. C. Circuit: - SyllabusDocument32 pagesUnit - 1 D. C. Circuit: - SyllabusAnas AnsariNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C - RC CircuitsDocument20 pagesAP Physics C - RC CircuitsnalinigeeNo ratings yet
- Electronics Q2 M5Document37 pagesElectronics Q2 M5James Zander Ignacio100% (1)
- Voltage RegulatorDocument23 pagesVoltage RegulatorJulio Gabriel AseronNo ratings yet
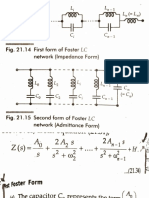
- Ques 4 Foster CauerDocument15 pagesQues 4 Foster CauerSwastik koulNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument17 pagesLab ManualSatyam Govila100% (1)
- MITRES 6-010S13 ComchaptrsDocument678 pagesMITRES 6-010S13 ComchaptrsMarko MackicNo ratings yet
- TS19503CB10H: Taiwan SemiconductorDocument13 pagesTS19503CB10H: Taiwan Semiconductorn tanevarNo ratings yet
- SPM Module Design Guide Overview PDFDocument2 pagesSPM Module Design Guide Overview PDFlookb6No ratings yet
- EC8462-Linear Integrated Circuits Lab ManualDocument85 pagesEC8462-Linear Integrated Circuits Lab ManualArul Perumal85% (13)
- Exercise Chapter 2Document7 pagesExercise Chapter 2DonkeyTank67% (3)
- High PassDocument2 pagesHigh PassMamoon BarbhuyanNo ratings yet
- Tda7000 For Narrowband FM ReceptionDocument13 pagesTda7000 For Narrowband FM ReceptionPeter KrabawaziNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge Oscillator:: RC Phase Shift Network (Lead Lag Network)Document6 pagesWien Bridge Oscillator:: RC Phase Shift Network (Lead Lag Network)Rashid ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits - MLinhDocument40 pagesLecture 01 - Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits - MLinhTran Quoc PhongNo ratings yet
- Med Instrumentation Lab ManualDocument96 pagesMed Instrumentation Lab ManualRula BastoniNo ratings yet
- Ecx3231 Lab01 2015-2016Document6 pagesEcx3231 Lab01 2015-2016Lackith Chandimal HettiarachchiNo ratings yet
- Tpa 1517Document21 pagesTpa 1517enriqueNo ratings yet
- DAC Utilizing ADCDocument3 pagesDAC Utilizing ADCelfrichNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NI ELVISDocument136 pagesIntroduction To NI ELVISchrsolvegNo ratings yet
- 107 ManualDocument69 pages107 ManualhaimiryazNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Noise Analysis Guide For Your Signal ChainDocument7 pagesStep by Step Noise Analysis Guide For Your Signal Chainnemarc08No ratings yet