Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Outline Statistics
Uploaded by
Nurin IzadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Outline Statistics
Uploaded by
Nurin IzadCopyright:
Available Formats
1
TEACHERS
John Taylor
Rod Air
Jeremy Exelby
AIM
To provide students with a general introduction to the study of statistics in English.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
This course will
Introduce students to the language of mathematics and statistics in English.
Provide students with the mathematical and statistical background for further study in
Commerce, Social Sciences and other disciplines.
GENERAL LEARNING OUTCOMES
On successful completion of this course students will:
Understand and be able to use the language of mathematics and statistics in English.
Be secure in the mathematical and statistical skills required within each topic area.
Be able to apply mathematical and statistical skills and procedures to solve problems
and explain solutions.
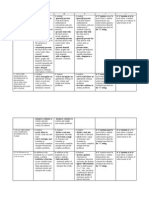
ASSESSMENT SCHEDULE
Assessment
Task
Time Due Content Length Weighting
Assignment 1 Week 3
Descriptive
statistics
5%
Test 1 Week 7
Probability, (covers
work taught in
weeks 3,4,5,6,)
1.5 hours 20%
Test 2 Week 9
Binomial and
Normal
distributions
1.5 hours 20%
Assignment 2 Week 11
Confidence
Intervals
5%
Final
examination
Exam week
Whole course 2 hours 50%
Foundation Studies Programme
FNDN 006 Statistics
Trimester One, 2014
2
MANDATORY COURSE REQUIREMENTS
Students must attend at least 80% of all classes in this course.
Students must achieve a minimum of 40% in the final two hour examination.
RESOURCES
Set Text
( Note : This a new textbook and replaces the older version)
Sigma Statistics NCEA Level 3
David Barton and Claire Laverty
ISBN9781442556980
Approximate price $69.99
Copies can be bought at the VUW bookshop
Or the Sigma Statistics eText Vital Source: Digital access
code- 1 year lease for $17.99. This can be used on a touch
pad or computer.
ISBN 9781486009930
http://www.pearsoned.co.nz/9781442556980
Scientific calculator e.g. Casio fx-82 or similar
Additional Reference
Barton, D. Theta mathematics. (Available in WJ Scott Library)
COURSE CONTENT
Week 1
Introducing Statistics What a Statistician does; problem, plan, data, analysis,
conclusion.
sample statistics (mean, median. mode, range, inter-quartile range, standard
deviation, variance),
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand the concepts of a statistical investigation.
understand, calculate and interpret measures of central tendency and spread
including the use of calculators and spreadsheets.
apply measures of central tendency and spread in problem situations.
References: Sigma Chapter 10 p230
Week 2
Statistics understand different types of graphs
Display of data (box and whisker, stem and leaf, bar graphs, histograms).
Analyse data and interpret what it means
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
draw and interpret statistical graphs including the use of spreadsheets.
Analyse data in graphs and tables, justify inferences and write a conclusion
3
References: Sigma Chapter 6 p127
Week 3 Assignment 1 due
Basic probability, equally likely outcomes, independent events, mutually
exclusive events, discrete and continuous variables.
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand the language of probability
calculate probabilities using a variety of techniques Venn diagrams,
contingency tables, probability trees
understand the basic probability rules including the rules for complementary,
mutually exclusive and independent events
solve problems involving probabilities
References: Sigma Chapter 15 p336
Week 4
Expected value
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
calculate the mean, variance and standard deviation of a random variable.
solve problems involving expected values
calculate the mean of a function of a random variable
References: Sigma Ch 19 p405
Week 5
Arrangements and selections
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand factorial numbers, permutations and combinations
solve problems involving arrangements and selections
References: Sigma Ch 18 p384
Week 6
Conditional Probability
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand the rule for calculating conditional probabilities
solve problems involving conditional probabilities
References: Sigma Ch 17 p370
Week 7 Test 1
Binomial distribution
Use of binomial tables and spreadsheets
Applications to binomial distribution problems
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand binomial distributions
calculate binomial probabilities using tables, calculators and spreadsheets
solve problems involving binomial distributions
References: Sigma Ch 21 p450
4
Week 8
Normal distribution
Standard normal distribution
Use of normal tables and spreadsheets
Application to normal distribution problems
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand normal distributions and the standard normal distribution
calculate normal probabilities using tables, calculators and spreadsheets
solve problems involving normal distributions
References: Sigma Ch 23 p492
Week 9 Test 2
Distribution of the sample mean Central Limit theorem
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand the distribution of the sample mean, X
understand the Central Limit Theorem
solve problems based on the Central Limit Theorem
References: Sigma Appendix 1 p543
Week 10
Confidence intervals for means
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
understand the concept of estimating population parameters from sample
statistics
calculate confidence intervals for means and the difference of two means
calculate required sample sizes
References: Sigma Appendix 1p543
Week 11 Assignment 2 due
Scatter diagrams and the correlation coefficient
Learning Outcomes: By the end of the week, students should be able to:
draw and interpret scatter diagrams
calculate and interpret correlation coefficients
solve problems involving correlations
References: Sigma Ch 4 p63
Week 12
Examination revision
You might also like
- Course Outline Math 2015Document2 pagesCourse Outline Math 2015api-210303377No ratings yet
- Chapter9 Mathlinks8 UnitplanDocument10 pagesChapter9 Mathlinks8 Unitplanapi-271785617No ratings yet
- UbD Lesson Plan Algebra IIDocument8 pagesUbD Lesson Plan Algebra IIunayNo ratings yet
- Belmont Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesBelmont Lesson Plan Templateapi-251950318No ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Final 2Document3 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Final 2api-400093008No ratings yet
- Intasc Standard 8 Instructional - KKDocument2 pagesIntasc Standard 8 Instructional - KKapi-541766753No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Primary 20 MinsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan-Primary 20 Minsapi-2946278220% (1)
- Social Skills Standards That Will Also Be Addressed in LessonDocument4 pagesSocial Skills Standards That Will Also Be Addressed in LessonAnonymous RnIiiQkrNo ratings yet
- SLK Grade 6 MathematicsDocument9 pagesSLK Grade 6 MathematicsRommel Yabis100% (1)
- Completeunitplan 1Document8 pagesCompleteunitplan 1api-355201738No ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Math Lesson 2Document3 pages3rd Grade Math Lesson 2api-5438212520% (1)
- Unit Plan 2Document32 pagesUnit Plan 2api-272192496No ratings yet
- Geometry Ubd Stages 1 2 3 - Edu 223 - 9 12 - Aurora TurmelleDocument7 pagesGeometry Ubd Stages 1 2 3 - Edu 223 - 9 12 - Aurora Turmelleapi-434662376No ratings yet
- Quadratics Lesson 4 Solving A Quadratic Equation by FactoringDocument3 pagesQuadratics Lesson 4 Solving A Quadratic Equation by Factoringapi-253132227No ratings yet
- Ubd Lesson Plan1Document3 pagesUbd Lesson Plan1api-317359280No ratings yet
- Circles Lesson Plan - MackenzieDocument3 pagesCircles Lesson Plan - Mackenzieapi-394649537No ratings yet
- Tws 4 CompleteDocument2 pagesTws 4 Completeapi-213553729No ratings yet
- Unit Overview and Lesson PlanDocument31 pagesUnit Overview and Lesson PlanKendall100% (1)
- Geng 5505 UWA Project ManagementDocument2 pagesGeng 5505 UWA Project ManagementSuman Saha0% (1)
- Grade Level: Subject: SDC, 3-6 Math, Measurements Title: Time Frame: Graph Paper Perimeters 40 MinutesDocument3 pagesGrade Level: Subject: SDC, 3-6 Math, Measurements Title: Time Frame: Graph Paper Perimeters 40 Minutesapi-253399358No ratings yet
- Iowa Core ArtifactDocument1 pageIowa Core Artifactapi-547747390No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Linear and Exponential FunctionsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Linear and Exponential Functionsapi-246371537No ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For cs2305.081 06u Taught by Sergey Bereg (sxb027100)Document2 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For cs2305.081 06u Taught by Sergey Bereg (sxb027100)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Mathematics: Welcome To 7 Grade. A Successful Year of Learning Math Lies Ahead!Document5 pages7th Grade Mathematics: Welcome To 7 Grade. A Successful Year of Learning Math Lies Ahead!api-283017841No ratings yet
- 2nd Grade Extreme Weather Unit Lesson PlanDocument3 pages2nd Grade Extreme Weather Unit Lesson Planapi-355088943No ratings yet
- Math Lesson Plan: Macey Conrad Kathryn BrashierDocument4 pagesMath Lesson Plan: Macey Conrad Kathryn Brashierapi-355875049No ratings yet
- Sample Dissertation OverviewDocument3 pagesSample Dissertation OverviewSherynhell Ann Perales100% (1)
- MSE2183Document11 pagesMSE2183MarkusNo ratings yet
- Subject Specific Pedagogy in MathematicsDocument8 pagesSubject Specific Pedagogy in MathematicsJohn TomsettNo ratings yet
- Pre-Observation Formkunakorn9oct18Document2 pagesPre-Observation Formkunakorn9oct18api-456126813No ratings yet
- 3rd Grade MP 1 Science RubricDocument1 page3rd Grade MP 1 Science RubrickathyadilaNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit Plan Representing DataDocument10 pagesMath 8 Unit Plan Representing Dataapi-266874931No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2api-338809879No ratings yet
- Algebra 1-2 Curriculum Map All UnitsDocument31 pagesAlgebra 1-2 Curriculum Map All Unitsapi-281539956No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template: Teacher Candidate: Kelly Willinger School: Promise Grade Level: 5 Room Number: 310Document12 pagesLesson Plan Template: Teacher Candidate: Kelly Willinger School: Promise Grade Level: 5 Room Number: 310api-341625641No ratings yet
- BPTs Basic Productivity Tools LESSON IDEA TemplateDocument3 pagesBPTs Basic Productivity Tools LESSON IDEA Templateaalaila collierNo ratings yet
- Ema200 Ass 2 Lesson SequenceDocument5 pagesEma200 Ass 2 Lesson Sequenceapi-317132930No ratings yet
- Criterion 1 2 3 6 RubricDocument2 pagesCriterion 1 2 3 6 Rubricapi-297764207No ratings yet
- CSCE 3513 Syllabus - Fall 2021Document5 pagesCSCE 3513 Syllabus - Fall 2021Nathan SmithNo ratings yet
- Math UnitDocument30 pagesMath Unitapi-250964578No ratings yet
- Adding Doubles Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAdding Doubles Lesson PlanstacierconleyNo ratings yet
- The Cornhole ProblemDocument14 pagesThe Cornhole Problemapi-352809637100% (1)
- Graduated Difficulty - Area LessonDocument13 pagesGraduated Difficulty - Area Lessonapi-287347463No ratings yet
- Math 10-3 Year PlanDocument2 pagesMath 10-3 Year Planapi-250169429100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Designing Bumper CarsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Designing Bumper CarsLauren NixonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan 1api-561417510No ratings yet
- 16-2 PerimeterDocument4 pages16-2 Perimeterapi-304585026No ratings yet
- Math 10c Long Range PlanDocument6 pagesMath 10c Long Range Planapi-266460789No ratings yet
- Project Base LearningDocument5 pagesProject Base LearningBARISHA MANNANo ratings yet
- Lessonplantemplate-Iste CordyDocument5 pagesLessonplantemplate-Iste Cordyapi-253462692No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Perimeter and Area in The Coordinate PlaneDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Perimeter and Area in The Coordinate Planeapi-283338157No ratings yet
- EDPM01 Blank Proposal Proforma (All Phases)Document4 pagesEDPM01 Blank Proposal Proforma (All Phases)Simon KanNo ratings yet
- AST201 Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesAST201 Course SyllabusacidburnaNo ratings yet
- (If Applicable, If Not Explain Why) : (Demonstration of Learning)Document3 pages(If Applicable, If Not Explain Why) : (Demonstration of Learning)api-282904450No ratings yet
- m11 MultimediaDocument3 pagesm11 Multimediaapi-523795815No ratings yet
- Mystery Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMystery Lesson Planapi-348627392No ratings yet
- UbD Unit Elementary Algebra (To Be Submitted)Document5 pagesUbD Unit Elementary Algebra (To Be Submitted)Kirk Torregosa PañaresNo ratings yet
- Guided Reading Lesson PlanDocument1 pageGuided Reading Lesson Planapi-216705889No ratings yet
- Course Outline Grade 10-FunctionsDocument8 pagesCourse Outline Grade 10-FunctionsGeorge Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Courseoutline 12 Maths CDocument2 pagesCourseoutline 12 Maths CWinston BoonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONSDocument12 pagesLesson 5 - RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONSYvette Bayudan50% (2)
- ch4 - Counting PrincipleDocument23 pagesch4 - Counting PrincipleMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Randon Number GenerationDocument12 pagesRandon Number Generationatul211988No ratings yet
- Salkind Chapter 11Document26 pagesSalkind Chapter 11ishikaNo ratings yet
- ST2334 Notes (Probability and Statistics - NUS)Document55 pagesST2334 Notes (Probability and Statistics - NUS)Manmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bandits: (Some Slides Stolen From Csaba's AAAI Tutorial)Document16 pagesIntroduction To Bandits: (Some Slides Stolen From Csaba's AAAI Tutorial)Shaukat HussainNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment #2Document2 pagesHomework Assignment #2Snoop celevNo ratings yet
- Comaptibility Functions and Formulas - ExcelDocument8 pagesComaptibility Functions and Formulas - ExcelShohanNo ratings yet
- Additional Reading Material-Probability-2Document11 pagesAdditional Reading Material-Probability-2palanivelNo ratings yet
- Rec 8B - Discrete Random Variables Part 2-1-1Document5 pagesRec 8B - Discrete Random Variables Part 2-1-1Skylar HsuNo ratings yet
- MVN Packages RDocument9 pagesMVN Packages RRifki MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 8 Sampling and Sampling Distribution - EMBADocument24 pages8 Sampling and Sampling Distribution - EMBAjavedNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Book SolutionsDocument100 pagesProbability and Statistics Book SolutionsLieke Lokin50% (4)
- Probability and Random Processes: Lesson 4 Counting MethodsDocument35 pagesProbability and Random Processes: Lesson 4 Counting MethodsvrsafeNo ratings yet
- Ee342 Final Cheat SheetDocument1 pageEe342 Final Cheat SheetShane TakamuneNo ratings yet
- Spring 2006 Test 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesSpring 2006 Test 1 SolutionAndrew ZellerNo ratings yet
- Math FinanceDocument2 pagesMath FinanceimaniceguyNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Science, Technology, Engineering and MathematicsDocument142 pagesStatistics and Probability: Science, Technology, Engineering and MathematicsFelicity JulieNo ratings yet
- Capstone Research Powerpoint PresentationDocument38 pagesCapstone Research Powerpoint PresentationChris Tine PaceteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2Basel TahaNo ratings yet
- GSB 420 Daily ReturnsDocument5 pagesGSB 420 Daily ReturnsdadadashixiaoxiaoNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference For Two Samples PDFDocument16 pagesStatistical Inference For Two Samples PDFRaymond GonsalesNo ratings yet
- MATH 545, Stochastic Calculus Problem Set 2: January 24, 2019Document7 pagesMATH 545, Stochastic Calculus Problem Set 2: January 24, 2019patriciaNo ratings yet
- Parameter Theta in Lindley DistributionDocument7 pagesParameter Theta in Lindley DistributionLiban Ali MohamudNo ratings yet
- (Tutorial) Mid-Term ReviewDocument60 pages(Tutorial) Mid-Term ReviewCath BienNo ratings yet
- Penelope 2003Document253 pagesPenelope 2003jiar001No ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Abdul Hamid B. Hj. Mar ImanDocument49 pagesDescriptive Statistics: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Abdul Hamid B. Hj. Mar ImanAbhijeet MahajanNo ratings yet
- LAS 7 Mean of A Discrete Random VariableDocument1 pageLAS 7 Mean of A Discrete Random VariableLorelan CapistranoNo ratings yet
- The Assumptions of The CLRMDocument2 pagesThe Assumptions of The CLRMRustamzad GulNo ratings yet