Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment of Hurdle Technology
Uploaded by
Jatinder KumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment of Hurdle Technology
Uploaded by
Jatinder KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT
OF
HURDLE TECHNOLOGY
SUBJECT:- FOOD PROCESSING
SUBMITTED BY:
JATINDERKUMAR
M.SC. FOOD TECHNOLOGY
INDEX
S.NO. CONTENTS PAGE No.
1 Definition of hurdle technology 3
2 Barrier during postharvest handling 3-4
3 Homeostasis and hurdle technology 5
4 Stresses in the multi-target hurdle technology 5-6
5 Application of hurdle technology to microbial
stability
7
6 Potential safety and quality hurdles 8
7 Conclusion 9
Hurdle Technology
Hurdle technology is also called combined methods or barrier technology. It is the
combination of the existing and novel techniques in order to establish a series of preservative
factors (hurdles or barriers) that any pathogens present should not be able to overcome. The
higher the hurdle, the greater will be effort.
Hurdle technology is used for gentle but effective preservation of foods.
It is not productive from the quality standpoint to provide extreme treatment
conditions to inhibit the growth of microorganisms in refrigerated food. Suitable
combinations of growth limiting factors can be used.
Sometimes individual hurdles may be set at lower intensities may show more
synergistic effect than would be required if only a single hurdle were used at the
preservation techniques.
Need of Hurdle technology
Pathogens are main cause of spoilage of foods which cannot be controlled by present
preservation techniques such as refrigeration, controlled atmosphere, modified atmosphere,
modified atmospheric packaging, etc. Moreover, the current consumer demand for natural
and fresh foods necessitates the use of only mild preservation techniques e.g. refrigeration,
controlled atmosphere, modified atmosphere packaging and bio- conservation. There is
strong need for improved mild preservation methods.
Example of Hurdles
A food product is microbiologically stable and safe because of the presence of set of
hurdles that is specific for the particular product in terms of nature and strength of this effect.
These hurdles together keep spoilage or pathogen under control and they cannot jump over
these hurdles.
Barriers during postharvest handling
The individual hurdles may encounter simultaneously or sequentially depending on
the type of hurdle and overall processing. The initial microbial load is important:-
If there are only few pathogens at the start then hurdles are enough to achieve the
microbial stability
If too many pathogens are present initially then more hurdles or higher intensities are
needed for microbial stability
Hygienic conditions are important for microbial load
Resistance to infections
Natural barriers:
1. Fruit skin (cuticle, epidermis, natural wax
2. Preformed inhibitors (phenolic compounds)
3. Induced inhibitors by wounding cork cells, phytoalexins
4. Natural volatiles (essential oils)
Post-harvest barriers
1. Low temperature in the storage
2. Controlled atmosphere (CO
2
/O
2
)
3. Waxing (chemical)
4. Modified atmosphere
5. Chemical inhibitors (Pesticides)
6. SO
2
fumigation
Alternative barriers
1. High temperature during pH handling
2. Natural volatiles (amino acids, ethanol, essential oils, etc.
3. Modified atmosphere packaging
4. Edible coating
5. Competitive micro-organisms
Homeostasis and Hurdle technology
Homeostasis of pathogens is the tendency to uniformity or stability in the normal
status e.g. maintenance of the pH within narrow range. The homeostasis is disturbed by
hurdles in foods, they will not multiply. They remain in lag phase or even die before they are
repaired. Thus, food preservation is achieved by disturbing the homeostasis of the pathogens.
Multi- targeted approach
Multi- targeted approach is that any hurdles affect the pathogens in several different
ways, e.g. affecting cell membranes, DNA, enzymes, pH, etc.
This approach is often more effective than single targeting and enables the use of
hurdles of lower intensity and thereby has less effect on product quality. In practical terms, it
is more effective to use combination of hurdles with low intensities affect microbial systems
or act synergistically than to use single hurdle with high intensity. The objective is to inhibit
the growth than to kill it.
Stresses in the multi-target Hurdle technology
Sequential or simultaneous exposure to different stresses may become the micro-
organisms to be exhausted. Therefore, multi-targeted preservation of products could be the
key to differentiate the pathogen reactions in favour of safety and quality preservation.
Hurdles used in the preservation (low and high temperature, fumigation, high CO
2
,
low O
2
, etc.) are in fact stresses and they tend to disrupt, restrict or accelerate the
physiological processes of product and pathogens in a different way.
The hurdle approach is based on the different response of product and pathogen to the
hurdle stress imposed. The combination of different hurdles offers the potential of issuing
less injury to product tissues.
Stress reactions and Hurdle technology
A stress is an external factor of such magnitude that it tends to disrupt the
physiological processes of the organism (host product or metabolic processes and does so in
adverse conditions. The extent of injury sustained is determined by the severity of the length
of time the organism is exposed and the resistance to stress.
Stress can produce an injurious effect (direct, indirect or secondary stress). The
injurious effects for the pathogen come primarily from the inhibition of growth and less
related to survival and death of micro-organisms. The injurious effects for the product are
related with the maintenance of quality characteristics.
Synergy
It is the interaction of two or more agents such as that the combined effect is greater
than the expected sum of the individual effects (23=6).
Additive
The interaction where the combined effect is exactly the sum (2+3=5).
Antagonism
It is the interaction where the combined effect is less than the sum (2+35).
Concept of combining Hurdles
The hurdles provided must at minimum be additive in action preferably synergistic and not
antagonistic.
Potential of using hurdle technology in the preservation of horticulture
products
Examples:
The pathogen present in the packing house overcomes or jumps over all the hurdles
and the commodity deteriorates.
The pathogen present in the packing house overcomes or jump over all the hurdles but
is not able to pass the modified atmosphere packaging hurdle
The pathogen present in the packing house does not overcome or jump over the heat
hurdle. Secondary growth of pathogen will be inhibited by the MAP hurdle
The pathogen present in the packing house does not jump over the heat hurdle and
MAP and storage hurdles
Applications of Hurdle technology to microbial stability (food safety)
and quality of food
The hurdles influence the safety as well as quality of foods (positive or negative
effects) depending on its intensity.
Example:- Low temperature (e.g.0C) may improve storage quality of apples but the
same hurdle (0C) may induce chilling injury of peppers, tomatoes.
High temperature(50C): In order to secure the total quality of food, the safety and
the quality hurdles should be kept in the optimal range.
If the intensity of a particular hurdle is too small, it should be increased to secure the
safety target.
If the intensity (height and exposure) is detrimental to the food quality, it should be
lowered.
Potential safety and quality Hurdles
The most important hurdles used in fresh fruits and vegetables are low storage or high short
term exposure temperature
Controllled atmosphere/ modified atmosphere
Modified atmosphere packaging
Preservatives
Conclusion
Hurdle technology is used for gentle but effective preservation of foods. The
disturbance of the homeostasis of micro-organisms is the key phenomenon of food
preservation. The multi target approach is more effective than single targeting and enables the
use of hurdles of lower intensity and thereby has less of an effect on the product quality. The
novel and ambitious goal for optimal food preservation is the multi target preservation of
foods in which intelligently applied the gentle hurdles will have a synergistic effect. There is
an increasing interest to implement the hurdle technology approach in the preservation of
fresh fruits and vegetables by selecting mild alternative hurdles which are required for
sustainable agricultural production.
You might also like
- Shading PrinciplesDocument5 pagesShading PrinciplesNisa Ann100% (1)
- Syllabus Vet Lic ExamDocument41 pagesSyllabus Vet Lic ExamNielB06No ratings yet
- Food Poisoning Presentation FinalDocument20 pagesFood Poisoning Presentation Finalwazeela malikNo ratings yet
- Coil SelectionDocument5 pagesCoil SelectionMohsin Shaikh100% (1)
- Topic 1.2 Analytical ProcessDocument52 pagesTopic 1.2 Analytical ProcessEyzah75% (8)
- 3.ADP-hurdle Tech FinalDocument15 pages3.ADP-hurdle Tech FinalhardikNo ratings yet
- Hematology Lab Manual IllustrationsDocument9 pagesHematology Lab Manual IllustrationsPojangNo ratings yet
- Hurdle Technology PresentationDocument28 pagesHurdle Technology PresentationUTPALAKSHYA DASNo ratings yet
- Food Preservation by Hurdle TechnologyDocument6 pagesFood Preservation by Hurdle TechnologyAndrea Atréju ArdidicoreNo ratings yet
- Food SpoilageDocument20 pagesFood SpoilageMinas Salah100% (1)
- Manual PDFDocument149 pagesManual PDFCoria AndresNo ratings yet
- Canvas SHS Pe 3 Week 1Document6 pagesCanvas SHS Pe 3 Week 1Gizelle ANo ratings yet
- Hurdle Technology GuideDocument7 pagesHurdle Technology GuideKeerthi PNo ratings yet
- Food SafetyDocument108 pagesFood Safetysham ibrahimNo ratings yet
- SLFT 05201: Food Analysis and InstrumentationDocument55 pagesSLFT 05201: Food Analysis and Instrumentationsalim kisemileNo ratings yet
- Food PreservationDocument24 pagesFood PreservationMukeshChhawariNo ratings yet
- Food BasicsDocument30 pagesFood BasicsRupini SinnanPandian100% (1)
- Camel AnesthesiaDocument16 pagesCamel Anesthesiamuhammad zeeshan ansarNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms' Beneficial Role in Food IndustryDocument3 pagesMicroorganisms' Beneficial Role in Food IndustryLady Quinte MNo ratings yet
- Cell Adaptation, Injury, and DeathDocument48 pagesCell Adaptation, Injury, and DeathRizka SukmasariNo ratings yet
- Climacteric vs Non-Climacteric Fruits: Respiration and RipeningDocument1 pageClimacteric vs Non-Climacteric Fruits: Respiration and RipeningAadil Khan GandapurNo ratings yet
- 5536-Food Microbiology Lec.Document5 pages5536-Food Microbiology Lec.mmoradi55No ratings yet
- Bacteriocin Food PreservationDocument31 pagesBacteriocin Food PreservationAjidhaslin Dhass0% (1)
- Lec.3 Food Microbiology Intrinsic and Extrinsic Parameters of Foods That Affect Microbial GrowthDocument5 pagesLec.3 Food Microbiology Intrinsic and Extrinsic Parameters of Foods That Affect Microbial GrowthAlukoNo ratings yet
- SPIROCHAETES & MYCOPLASMA: MORPHOLOGY AND PATHOGENESISDocument28 pagesSPIROCHAETES & MYCOPLASMA: MORPHOLOGY AND PATHOGENESISSarah PavuNo ratings yet
- Postharvest Biochemistry ChangesDocument10 pagesPostharvest Biochemistry Changesrag.1607No ratings yet
- @impact of Food Processing On QualityDocument46 pages@impact of Food Processing On QualitywindasrihandayaniNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies For Fruits and VegetablesDocument19 pagesEmerging Technologies For Fruits and VegetablesRoushan100% (1)
- Food SpoilageDocument13 pagesFood SpoilageKrithishNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument2 pagesGenetic EngineeringMinal KantNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial ResistenceDocument23 pagesAntimicrobial Resistencelayal mrowehNo ratings yet
- Post Harvest LAB FinalDocument10 pagesPost Harvest LAB FinalMontasha AdilNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Culture Media TypesDocument28 pagesBacteria Culture Media TypesJendie BayanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Parental NutritionDocument11 pagesPeripheral Parental Nutritiontaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Principles of Aquaculture 2020 NotesDocument55 pagesPrinciples of Aquaculture 2020 NotesBolloju BabaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology-Specimens CollectionDocument31 pagesMicrobiology-Specimens Collectionapi-253201876100% (1)
- Factors Causing Food SpoilageDocument6 pagesFactors Causing Food SpoilageAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADER100% (1)
- Isolation and Identification of Fungi From Fast Food Restaurants in Langa BazarDocument6 pagesIsolation and Identification of Fungi From Fast Food Restaurants in Langa BazarIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Food Preservation Methods for Long Shelf LifeDocument5 pagesFood Preservation Methods for Long Shelf LifeUmarani Mohanasundaram0% (1)
- Solids Determination MethodsDocument3 pagesSolids Determination MethodsrahoznawrozNo ratings yet
- Spoilage of Fresh and Processed Fish and Fishery ProductsDocument3 pagesSpoilage of Fresh and Processed Fish and Fishery ProductssimasNo ratings yet
- Anti Nutritional FactorsDocument3 pagesAnti Nutritional FactorsGokul DeviNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Food Analysis SamplingDocument52 pagesIntroduction to Food Analysis SamplingAndréa Stennie RaoelimahefaNo ratings yet
- Causative Factors For Food Quality DeteriorationDocument42 pagesCausative Factors For Food Quality DeteriorationMadhu ShaliniNo ratings yet
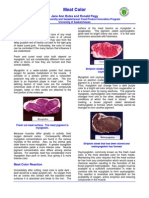
- Meat Color University of SaskatchewanDocument4 pagesMeat Color University of SaskatchewanLenin LeivaNo ratings yet
- Meat SpoilageDocument9 pagesMeat SpoilageMabookgm MaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HaccpDocument41 pagesChapter 4 HaccpSPMUSER9ANo ratings yet
- 16 Caffeine S Mechanisms of Action and Its Cosmetic UseDocument7 pages16 Caffeine S Mechanisms of Action and Its Cosmetic UseEduardo Damian Verde LeonNo ratings yet
- Food SpoilageDocument52 pagesFood SpoilageSatpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Principles of The Food Processing and PreservationDocument3 pagesPrinciples of The Food Processing and PreservationspidyNo ratings yet
- Role of Probiotics & Prebiotics in Gut HealthDocument5 pagesRole of Probiotics & Prebiotics in Gut HealthAq MwNo ratings yet
- 1 Slide Food SpoilageDocument23 pages1 Slide Food SpoilageIneke AuliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Sources of Microorganisms in FoodDocument23 pagesLecture 1. Sources of Microorganisms in FoodAnégria GahimbareNo ratings yet
- Contamination, Spoilage, PreservationDocument30 pagesContamination, Spoilage, PreservationAnkit ChaliseNo ratings yet
- APEDA India's agri export authorityDocument3 pagesAPEDA India's agri export authorityanon_183604043No ratings yet
- FOOD PRESERVATION METHODSDocument22 pagesFOOD PRESERVATION METHODSBadar MughairaNo ratings yet
- BNF Food Poisoning Tcm4-662860Document23 pagesBNF Food Poisoning Tcm4-662860clinical_pathologyNo ratings yet
- Preservation by Low TemperatureDocument8 pagesPreservation by Low TemperatureDr-Uadal SinghNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Endotoxins and ExotoxinsDocument6 pagesDifference Between Endotoxins and ExotoxinsJasna KNo ratings yet
- Page I135 Sunflower MealDocument1 pagePage I135 Sunflower MealPedro ZamarripaNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology ScopeDocument2 pagesFood Microbiology ScopeProbioticsAnywhere50% (2)
- Tropical Food: Chemistry and Nutrition V2From EverandTropical Food: Chemistry and Nutrition V2George InglettNo ratings yet
- Resource 680Document31 pagesResource 680Zirrus GlassNo ratings yet
- Prehensive Viva Test (Responses)Document80 pagesPrehensive Viva Test (Responses)Srikanth TanguduNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 5 PDF Elelments 3 1Document5 pagesInteractive Textbook 5 PDF Elelments 3 1api-240094705No ratings yet
- USP-NF Strong Ammonia SolutionDocument2 pagesUSP-NF Strong Ammonia SolutionyoussufNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Natural Gas Liquid MeasurementsDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Natural Gas Liquid Measurementsmakasad26No ratings yet
- Niobium and Heat Affected Zone MythologyDocument42 pagesNiobium and Heat Affected Zone MythologyLayzza TardinNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil AnalysisDocument6 pagesFuel Oil AnalysisPawan BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Tissue Culture: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesTissue Culture: Very Short Answer QuestionskzrdurNo ratings yet
- Syllabus:-Biomolecules, Cell: The Unit of Life, Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument9 pagesSyllabus:-Biomolecules, Cell: The Unit of Life, Structural Organisation in AnimalsEXCEPTIONAL FOCUSNo ratings yet
- EOR Screening-TaberDocument14 pagesEOR Screening-TaberAjeng AyuNo ratings yet
- Material Properties of EPDM, NBR, and FPM Rubber Seals - Technical - Resources - BLUCHERDocument3 pagesMaterial Properties of EPDM, NBR, and FPM Rubber Seals - Technical - Resources - BLUCHERManish Pareek100% (1)
- 3-11-8 - Pressure Vessel Cs - UopDocument31 pages3-11-8 - Pressure Vessel Cs - UopSean Davis100% (1)
- Concrete Repair and Protection System1 - CeresitDocument12 pagesConcrete Repair and Protection System1 - CeresitJill Jim LivestockNo ratings yet
- Establishing Scientifically Justified Acceptance Criteria For The Cleaning Validation of Apis (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) (Le Blanc)Document6 pagesEstablishing Scientifically Justified Acceptance Criteria For The Cleaning Validation of Apis (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) (Le Blanc)jorgeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Properties, Viscosity and ApplicationsDocument77 pagesFluid Mechanics: Properties, Viscosity and ApplicationsvijaynieNo ratings yet
- Limit State Design Method: Chapter: Three Design of Reinforced Concrete StructureDocument8 pagesLimit State Design Method: Chapter: Three Design of Reinforced Concrete StructureNabin Chandra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motor Oil ENGDocument64 pagesMotor Oil ENGNicolai BelocosovNo ratings yet
- 17-Oil Centrifuge PDFDocument89 pages17-Oil Centrifuge PDFUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Inspect F50: Everything Needed For Conventional High Resolution Sample InvestigationDocument4 pagesInspect F50: Everything Needed For Conventional High Resolution Sample InvestigationMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Ans No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationDocument4 pagesAns No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationHimanshu TrivediNo ratings yet
- Device Fabrication Technology: Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (C. Hu) Slide 3-1Document40 pagesDevice Fabrication Technology: Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (C. Hu) Slide 3-1EASACOLLEGENo ratings yet
- MASTERY PHYSICS SPM EXPERIMENTSDocument12 pagesMASTERY PHYSICS SPM EXPERIMENTSSuhami IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Integrate Planck's Function Using Gamma FunctionDocument14 pagesIntegrate Planck's Function Using Gamma FunctionMaxtron Evelyn MoonNo ratings yet
- Phase Inversion of W/O Emulsions by Adding Hydrophilic Surfactant - A Technique For Making Cosmetics ProductsDocument8 pagesPhase Inversion of W/O Emulsions by Adding Hydrophilic Surfactant - A Technique For Making Cosmetics ProductsAsshole FuckerNo ratings yet
- An114 Hand Soldering Tutorial For The Fine Pitch QFP DevicesDocument22 pagesAn114 Hand Soldering Tutorial For The Fine Pitch QFP DevicesPat Jojo SadavongvivadNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Flanges - Pressure and Temperature Ratings - Group 1.1 - Carbon SteelDocument7 pagesCarbon Steel Flanges - Pressure and Temperature Ratings - Group 1.1 - Carbon Steelnoha azamaliNo ratings yet
- Nutritive Evaluation of Ammoniated Benggala GrassDocument2 pagesNutritive Evaluation of Ammoniated Benggala GrassRolan TuturoongNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Basics for ECW 211Document53 pagesFluid Mechanics Basics for ECW 211dixn__No ratings yet