Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Female Genital Tract Cancers
Uploaded by
Solomon Seth Sallfors0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views5 pagesFemale Genital Tract Cancers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFemale Genital Tract Cancers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views5 pagesFemale Genital Tract Cancers
Uploaded by
Solomon Seth SallforsFemale Genital Tract Cancers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
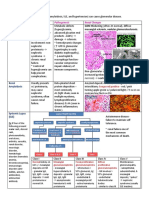
Female Genital Tract Cancers Wassons material
Vulva => Non-Neoplastic Epithelial Disorders
Leukoplakia => White plaques may present a variety of benign, pre malignant of malignant lesions
Lichen Sclerosus Squamous cell
hyperplasia/Lichen
simplex chronicus
Vulva => Non-Neoplastic Epithelial Disorders
Leukoplakia => White plaques may present a variety of benign, pre malignant of malignant lesions
Lichen Sclerosus Squamous cell hyperplasia/Lichen simplex chronicus
Age Most common in post-menopausal, but can
strike all ages
Gross Appear as smooth, white plaques or papules
that may extend and coalesce
Surface is smooth and resembles parchment
Labia becomes atrophic and stiffened when
entire vuvla is affected
- Vaginal orifice is constricted
White plaques - Leukoplakia
Histology Thinned epidermis and disappearance of rete
pegs
Hydropic degeneration non basal cells
Superficial hyperkeratosis
Dermal fibrosis with scant perivascular,
mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate
Sclerotic Stroma
Thickened epidermis (acanthosis), expansion of stratum
granulosum
Significant surface hyperkeratosis
Increased mitotic activity in stratum basalis and spinosum
Sometimes pronounced leukocytic infiltration
Hyperplastic cells have no atypia
Pathology Cause unknown
Maybe Auto-immune
Activated T cells in subepithelial inflammatory
infiltrate
Non-specific condition from rubbing or scratching the skin
Notes Not pre-malignant
Symptomatic disease = chance of SCC
No increased pre-disposition to cancer
o Often present at margins of established cancer of vulva
Tumors of the vulva
Benign exophytic lesions
Condyloma acuminatum HPV induced Fibroepithelial polyp/ Squamous papilloma
Sexually transmitted, benign lesions
Gross Verrucous = Multifocal Wart-like appearance
Numerous Condylomas cycle the Intoitus. (opening
to the vagina)
Histo Acanthosis = Thickened epidermis
Hyperkeratosis
Koilocytic atypia = viral cytopathic changes
o Enlarged, Atypical nuclei
o Cytoplastic vacuolation
o Cytoplasmic perinuclear halo
Path HPV Low oncogenic risk HPVs - 6,11
Productive viral infection
Replication in squamous cells.
Life cycle ends in mature superficial cells
Koilocytotic atypia
Notes Not a precancerous lesions.
Squamous Neoplastic Lesions
VIN HPV induced Carcinoma
VIN Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
o Uncommon malignant neploasm 3% of
genital cancers in chicks. 2/3 in chicks >
60 years.
Gross Multifocal
Histo Squamous cell carcinomas MC
Begin as classic VIN lesions
Marked Nuclear Atypia
Path HPV 16
Notes Synonymous with carcinoma in situ (Bowen
disease
Precedes invasive carcinoma
Cancer risk increase with age
Spontaneous regression in the young
Glandular neoplastic Lesions
Papillary Hidradenoma Extramammary Paget disease
o Vulva contains modified apocrine sweat
glands and ectopic breast.
o Rare lesion similar to Paget
disease of the breast
o Paget cells show apocrine, eccrine,
and keratinocyte differentiation
and come from progenitor cells
o
o Sharply circumscribed nodule on labia
majora or interlabial folds
o Tendency to ulcerate may be confused
with carcinoma
o Pruritic, red, crusted, sharply
demarcated, maplike area usu
occurring on labia.
o Tumor identical in appearance to
intraductal papilloma of the breast
Vulva contains tissue closely resembling
breast
o Tumor consists of tubular ducts lined by
nonciliated columnar cell layer and
myoepithelial layer underneath
o Diagnostic microscopic feature -
large tumor cells single or in
clusters surrounded by halos.
o Fine granular cytoplasm
containing mucopolysaccharide.
Stains w/PAS, Alcian blue or
mucicarmine
o Paget cells show apocrine, eccrine,
and keratinocyte differentiation
and come from progenitor cells
o Consists of papillary projection
covered with two layers of cells
Upper columnar, secretory cells
Lower flattened myoepithelial
cells
o Unlike Paget dz of the nipple
(which is always assoc with
underlying ductal breast
carcinoma), vulvar lesions are
most frequently confined to the
skin and adjacent hair follicles and
sweat glands
o Prone to recurrence
Malignant Melanoma
Malignant melanoma
o Peak in 6
th
or 7
th
decade; Rare
o Wide spread dissemination. 5 year
survival < 32%
o Prognosis linked to depth of invasion.
Lesions deeper than 1mm over half are
fatal.
o CEA and Mucoploysaccharide
negative(both are in Pagets). Anti S100
protein positive.
Vagina
Vaginal Adenosis / Clear Cell Carcinoma Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VAIN)
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
You might also like
- VulvaDocument7 pagesVulvaJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Midterm ChartDocument15 pagesMidterm Chartapi-26938624100% (1)
- Embryology Outline Pulmonary UAG Med Block 2Document4 pagesEmbryology Outline Pulmonary UAG Med Block 2AndreaSanchezNo ratings yet
- Liver & PancreasDocument3 pagesLiver & Pancreasameerabest100% (1)
- Robbins Ch. 18 Liver and Biliary Tract Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesRobbins Ch. 18 Liver and Biliary Tract Review QuestionsPA2014No ratings yet
- Patho Robbins Sumary Pereira MDDocument22 pagesPatho Robbins Sumary Pereira MDNicole SarcosNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Document9 pagesWeek 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Amber LeJeuneNo ratings yet
- (8!5!13) Cell Injury OutlineDocument9 pages(8!5!13) Cell Injury OutlineBhumiShahNo ratings yet
- Patho. Reviewer On Cellular InjuryDocument21 pagesPatho. Reviewer On Cellular InjurySeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Genetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesDocument1 pageGenetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesJ KPNo ratings yet
- 3-Ammar Notes (Ob - Gyn)Document6 pages3-Ammar Notes (Ob - Gyn)Dr-Hashem Al-ShareefNo ratings yet
- V V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageDocument1 pageV V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageCyndiNo ratings yet
- Pathology 5.05a CervixDocument6 pagesPathology 5.05a CervixDranreb Berylle MasangkayNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Conditions in Neonates: DR Hodan Ahmed, Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Amoud Medical School, AUDocument27 pagesHemorrhagic Conditions in Neonates: DR Hodan Ahmed, Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Amoud Medical School, AUAbdisalan hassanNo ratings yet
- Anemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDocument15 pagesAnemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 DiseasesDocument1 pageExam 1 DiseasesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine 01 PDFDocument9 pagesSmall Intestine 01 PDFfadoNo ratings yet
- Female Genital TractDocument5 pagesFemale Genital Tractsarguss14100% (1)
- Mnemonic of Some Rare Genetic Disease PDFDocument9 pagesMnemonic of Some Rare Genetic Disease PDFfaraz100% (1)
- Lec 2 - Blood VesselsDocument12 pagesLec 2 - Blood VesselsJeffrey LübbertNo ratings yet
- Parvo BacteriaDocument2 pagesParvo BacteriaErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument18 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageSanaNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Normal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)Document12 pagesNormal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)nmp274No ratings yet
- Dracunculus MedinensisDocument1 pageDracunculus MedinensisEm KayNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics SamplexDocument6 pagesPediatrics SamplexThea SansonNo ratings yet
- Oneliner All SubectsDocument265 pagesOneliner All SubectsSantosh Raja100% (1)
- Antifungal Agents: EchinocandinsDocument2 pagesAntifungal Agents: EchinocandinsCourtney TownsendNo ratings yet
- Accordion Sign-Appearance (C. Difficile)Document41 pagesAccordion Sign-Appearance (C. Difficile)Andra HijratulNo ratings yet
- Female PathologyDocument16 pagesFemale Pathologymiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Anti FungalsDocument5 pagesAnti FungalskakuNo ratings yet
- Hema Part 3 Final PDFDocument188 pagesHema Part 3 Final PDFH.B.ANo ratings yet
- 4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangDocument4 pages4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangMiel Raphael AranillaNo ratings yet
- Gyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesDocument8 pagesGyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Review For The 2° Semester Exam Alessandro Mo6a, UVVG, 3 YearDocument9 pagesReview For The 2° Semester Exam Alessandro Mo6a, UVVG, 3 Yeardjxela89No ratings yet
- Antivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSDocument3 pagesAntivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- Red Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenDocument3 pagesRed Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Patho Common Stuff - RobbinsDocument7 pagesPatho Common Stuff - RobbinsMaf BNo ratings yet
- Approach To Hematuria and Proteinuria in ChildrenDocument52 pagesApproach To Hematuria and Proteinuria in ChildrenMysheb SS100% (1)
- USMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewDocument767 pagesUSMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewMack LinfidioNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci Reviewer 1Document6 pagesGram Positive Cocci Reviewer 1alianaNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Quick TablesDocument276 pagesInternal Medicine Quick Tablesjoey plouffeNo ratings yet
- GI Anatomy & EmbryoDocument19 pagesGI Anatomy & EmbryoMaya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- Kidney AnatomyDocument2 pagesKidney Anatomyameerabest100% (1)
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 pagesTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- ID Bug chart-DKDocument92 pagesID Bug chart-DKNeil M D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- A Summary of The Chemical Mediators Involve in The Acute Inflammatory Response Is Shown in The Table BelowDocument30 pagesA Summary of The Chemical Mediators Involve in The Acute Inflammatory Response Is Shown in The Table Belowinny100% (1)
- Pathology 5.05b Vagina and Vulva - DR - Dy (Final Edit)Document11 pagesPathology 5.05b Vagina and Vulva - DR - Dy (Final Edit)Dranreb Berylle MasangkayNo ratings yet
- Alarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyDocument22 pagesAlarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneDocument5 pagesDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPENo ratings yet
- PDF Chapter 22 The Female Genital TractDocument59 pagesPDF Chapter 22 The Female Genital Tractsmian08No ratings yet
- B - Embyrology HomologuesDocument1 pageB - Embyrology HomologuesS ParekhNo ratings yet
- Oral Cases Study Guide - PediatricsDocument68 pagesOral Cases Study Guide - PediatricsJohn100% (1)
- Staph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusDocument5 pagesStaph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusTom PedersonNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Infections in HumansFrom EverandAnaerobic Infections in HumansSydney FinegoldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Vulva Vagina Uterus - MODIFIED PDFDocument141 pagesVulva Vagina Uterus - MODIFIED PDFBatool SherbiniNo ratings yet
- Cardio My Opa Thies ChartDocument2 pagesCardio My Opa Thies ChartSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Indications by ClassDocument1 pageIndications by ClassSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- AV Block ChartDocument1 pageAV Block ChartSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy Self StudyDocument3 pagesCardiomyopathy Self StudySolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Part of Aorta Main Branch: AscendingDocument5 pagesPart of Aorta Main Branch: AscendingSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment EndocarditisDocument1 pageEpidemiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment EndocarditisSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Book ListDocument3 pagesBook ListSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Neuro Practical I TablesDocument9 pagesNeuro Practical I TablesSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- Introduction To Cardiovascular Radiography: Spencer M. Smith, M.D. August 24, 2007Document49 pagesIntroduction To Cardiovascular Radiography: Spencer M. Smith, M.D. August 24, 2007Solomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written I TablesDocument6 pagesNeuro Written I TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written III TablesDocument5 pagesNeuro Written III TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- A6: Mild Suicidal Ideation of Limited Frequency, Intensity, andDocument1 pageA6: Mild Suicidal Ideation of Limited Frequency, Intensity, andSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Well Woman LabDocument2 pagesWell Woman LabSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- FOBS Test 2 Key SlidesDocument140 pagesFOBS Test 2 Key SlidesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Handout Cases, Childhood Disorders, PLMDocument12 pagesHandout Cases, Childhood Disorders, PLMSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written II TablesDocument10 pagesNeuro Written II TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders ChartDocument11 pagesPersonality Disorders ChartSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- OMT & The Workplace: Basic Ergonomics & Poor Postural HabitsDocument51 pagesOMT & The Workplace: Basic Ergonomics & Poor Postural HabitsSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- Feature Delirium Dementia CausesDocument9 pagesFeature Delirium Dementia CausesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- ReviewSheetExam2 (Pelvic)Document9 pagesReviewSheetExam2 (Pelvic)Solomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Primary Health Care - QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesPrimary Health Care - QuestionnaireMac DeconNo ratings yet
- Full List of PhobiaDocument15 pagesFull List of PhobiaDennisNguyễnNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorder PeadsDocument51 pagesEye Disorder PeadsGrashiaNo ratings yet
- Prevalence and Epidemiology: Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Meniére's DiseaseDocument2 pagesPrevalence and Epidemiology: Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Meniére's DiseaseShiela GutierrezNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Paleopathology: S. MaysDocument8 pagesInternational Journal of Paleopathology: S. MaysErna MiraniNo ratings yet
- Montana PDFDocument10 pagesMontana PDFNBC MontanaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Q&ADocument12 pagesPediatric Q&AMateen ShukriNo ratings yet
- Antitubercular DrugsDocument22 pagesAntitubercular DrugsApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- MLSP Midterm NotesDocument22 pagesMLSP Midterm NotesKat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Case Study CopdDocument7 pagesCase Study CopdIrveen Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- MalnutrionDocument15 pagesMalnutrionClare DucutNo ratings yet
- Insidious ScreenplayDocument104 pagesInsidious ScreenplayFaisal Hashmi100% (4)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionChiel MagnoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response (Pidsr) "PIDSR A Bedrock of Effective Disease Surveillance" - Secretary DuqueDocument4 pagesPhilippine Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response (Pidsr) "PIDSR A Bedrock of Effective Disease Surveillance" - Secretary DuqueRoel AbricaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Hydropericardium Syndrome in PoultryDocument20 pagesPresentation On: Hydropericardium Syndrome in PoultrySantosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiaDocument31 pagesArrhythmiaAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- Bruchko EditedDocument3 pagesBruchko EditedLeteni PicsNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument22 pagesLeprosyMary Saligan RatoNo ratings yet
- XXXXXDocument14 pagesXXXXXJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Unilever - LIFEBUOYDocument9 pagesUnilever - LIFEBUOYanon_839867152No ratings yet
- Moral Dilemma: Whether or Nor Extend The Enhanced Community QuarantineDocument3 pagesMoral Dilemma: Whether or Nor Extend The Enhanced Community QuarantineCharlton Benedict BernabeNo ratings yet
- BiographyDocument7 pagesBiographyapi-348852766No ratings yet
- Neuro Rehabilitation Principle and Practise PDFDocument292 pagesNeuro Rehabilitation Principle and Practise PDFIonela Arustei100% (1)
- Septic Arthritis 97-03Document20 pagesSeptic Arthritis 97-03john michael olivares100% (5)
- Occlusal AnalysisDocument14 pagesOcclusal AnalysisDavid DongNo ratings yet
- Atypical Pearly Penile Papules Mimicking Primary SyphilisDocument2 pagesAtypical Pearly Penile Papules Mimicking Primary Syphilismamal malikaNo ratings yet
- ENS Guide To Diagnosis & Management (v2 - 09.2016)Document37 pagesENS Guide To Diagnosis & Management (v2 - 09.2016)Renato Mondani0% (1)
- 3rd Mid CaseDocument32 pages3rd Mid CaseHarshini MakkenaNo ratings yet
- MGR Univ - PerioDocument8 pagesMGR Univ - PerioMohamed FaizalNo ratings yet
- STUDENT NUMBER: 1164231 Assignment 1 Word Count: 2871 MSC Restorative DentistryDocument19 pagesSTUDENT NUMBER: 1164231 Assignment 1 Word Count: 2871 MSC Restorative DentistryStefan MladenovNo ratings yet