Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrinology I
Uploaded by
13un3915430 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views45 pagesEndocrinology I
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEndocrinology I
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views45 pagesEndocrinology I
Uploaded by
13un391543Endocrinology I
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 45
2/6/2009
-Notes by: Islamiat Olaribigbe
-olaribs14@hotmail.com
-A lot of the endocrine disorders do not have specific symptoms! J ust a
warning.
1
2/6/2009
-Read Slide
-Endocrine disorders affect a lot of organ systems.
2
2/6/2009
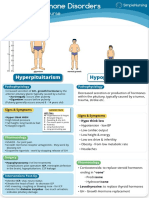
-This is a form of hyperthyroidism.
-It affects the eyes Exophthalmus; the neck Goiter; the skin pretibial
myxedema; heart Tachycardia; GI diarrhea; muscles weakness.
-You can see that all endocrine disorders affect a lot of organs systems
-Diagnosis is made by putting all of these signs and symptoms together.
3
2/6/2009
- Read Slide.
4
2/6/2009
-This is just a review of the endocrine system.
-For example: Let us take Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH).
-Stimulates the anterior pituitary (AP) to produce and release ACTH
-ACTH acts on the Adrenal gland to produce Cortisol.
-There are a lot of negative feedback loops in the endocrine system.
Increase in cortisol will negative feedback to decrease ACTH (in the
AP) and CRH (in the hypothalamus.)
-GHRF stimulates the AP to release GH, which then goes to the
target organs.
-TRH TSH Thyroid Hormones (T3 and T4)
-The posterior pituitary hormones are: ADH and Oxytocin (involved in
milk ejection)
-A special hormone is Prolactin (it is involved in lactation). It can give
you a clue of a CNS dysfunction.
-Not part of the hypothalamic-pituitary pathway is the: Parathyroid
gland; Insulin from the pancreas.
-Gonadal Hormones: They are part of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis;
Important for secondary characteristics in males and females.
5
2/6/2009
-Read Slide.
-E.g. Hypothyroidism due to a thyroid problem negative feedback to the
AP to release TSH try to correct the pathology.
6
2/6/2009
-A pituitary tumor may enlarge and compress the optic chiasm visual
defects (Bitemporal Hemianopsia).
-Read Slide.
-If the thyroid is affected, it may compress the esophagus dysphagia
-Depending on the hormone secreted by the mass, you can get feminization
in the males and virilization in the females.
7
2/6/2009
-Read Slide.
-Hyperthyroidism/Hypothyroidism Problems with Basal Metabolic Rate
-Insulin is necessary to maintain glucose. If there isnt enough insulin, you
may start to break protein and fats to compensate.
-ADH affects your water and electolytes (indirectly)
-Calcium metabolism can be affected by PTH, Vit D and other misc. causes
8
2/6/2009
-Heat/Cold Intolerance thyroid problem
-Polyphagia (eating a lot) and PolydipsiaDiabetes
-Puffiness thyroid problem
-Salt Craving due to loss of salt in the urine.
9
2/6/2009
-Gain weight rapidly clue to Hypercortisolism (Cushings) or
Hypothyroidism
-Decrease in weight Hyperthyroidism or Adrenal Insufficiency.
-Increase in height Excess GH
-Decrease in height may be due to vertebral fractures from osteoporosis
(Vit D probs.)
Neck SwellingThyroid Condition -Neck Swelling Thyroid Condition
10
2/6/2009
-Hair growth in females on the face or on the back sign of virilization (inc.
testosterone)
-Inc Sweating GH excess or hyperthyroidism
-Dec Sweating Hypothyroidism
-Pigmentation (especially on the palms of hands or oral mucosa) Adrenal
Insufficiency
Lowcortisol increaseACTH via the negative feedback loop -Low cortisol increase ACTH via the negative feedback loop
-Increased ACTH Increase melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
-Leads to hyperpigmentation.
11
2/6/2009
-Bone pains and tenderness Calcium metabolism disorders (can be Vit D
or PTH)
-Muscle pain Thyroid problem (may be either hyper- or hypo-)
-Periodic Paralysis generally associated with thyroid dysfunction.
12
2/6/2009
-Loss of Libido Low sex hormones
-Amenorrhea can be primary (never had menses) or secondary
(cessation of menses) Gonadal dysfunction
-Lack of secondary characteristics Hypothalamic-Pituitary Dysfunction or
Primary gonadal problems where the gonads never developed e.g. Turners,
etc
-Galactorrhea (outside of childbirth) Sign of increasedprolactin Galactorrhea (outside of childbirth) Sign of increased prolactin
-Failure of Lactation (after childbirth) Hypopituitarism
-Gynecomastia too much female hormones in a male.
13
2/6/2009
- Protrusion of Eyes Exophthalmos Graves disease
14
2/6/2009
-Past history is important especially in children.
-Read Slide.
-Watch to see if children have fallen out of their growth curves.
-Failure to enter puberty Endocrinal or Genetic (e.g. Kallmann Syndrome
Hypogonadism/lack of secondary sex characteristics and Anosmia)
15
2/6/2009
-Read Slide.
-There are some genetic causes of hormonal problems (very rare)
-Hirsutism Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (usually overweight with secondary
amenorrhea)
16
2/6/2009
-Read Slide.
-Medications can mimic endocrine dysfunction.
-Cocaine can mimic hyperthryroidism (e.g. palpitations)
-Lithium may cause endocrine problem Hypothyroidism becauses it
interferes with iodine trapping in the thyroid.
-Hormonal Replacement Therapy can present as endocrine disorders (may
be too much or too little) be too much or too little)
17
2/6/2009
-Read Slide.
-Diet Pills Tachycardia
-Exogenous Steroids Cushing-like Syndrome
-Estrogen May increase TBG
-Iodide May cause either hyper- or hypothyroidism
18
2/6/2009
- Endocrine disorders covers all of the organ systems.
19
2/6/2009
Lassitude Fatigue or Lethargy
-Combination of these signs and symptoms will help with diagnosis
-Growth Rateespecially in kids. The main culprits in kids that interfere
with growth are: GH deficiency, Thyroid Hormone deficiency and Cortisol
excess.
-Temperature Intolerance Thyroid problems
Cause of the most significant weight gain Hypercortisolism -Cause of the most significant weight gain Hypercortisolism.
20
2/6/2009
-Read Slide.
-She repeated what she had said before.
-Poor Healing and Bruising Hypercortisolism
-Flushing secondary to Carcinoidor may be due to Pheochromocytoma.
-Look at next slide.
21
2/6/2009
- ReadSlide
22
2/6/2009
Read Slide.
23
2/6/2009
-Headaches Pituitary dysfunction
-Coarsening of appearance may be due to excess GH
-Voice change hypothyroidism
-Pain, Swelling or Pressure on neck Thyroid problems
24
2/6/2009
-Palpitations can be severe enough to cause High output cardiac failure esp.
Hyperthyroidism
-Hypertension Hyperaldosteronism(with an associated hypokalemia),
Pheochromocytoma (associated with episodic headaches and palpitations)
25
2/6/2009
-Read Slide.
-Addisons Disease also presents with low BP.
-Hyperthyroidism doesnt cause true diarrhea (i.e. loose stools) but may be
more of hyper-defecation (frequent small stool, not necessarily loose).
26
2/6/2009
- Read Slide
27
2/6/2009
-Read Slide
-DI usually want COLD ICE WATER, compared to DM. DM patients do not
have a special need for ice water (they will drink anything).
-Hypercalcemia may be cause by hyperparathroidismor Vit D toxicity.
-Hypokalemia Hyperaldosteronismwith resistant HTN.
28
2/6/2009
-Hypogonadismwill have no interest in sex.
-Obstretrical Hx Blood loss during delivery may cause Sheehans
Syndrome
-Menstrual Hx early menopause, amenorrhea, etc
-Fertility has to do with H-P axis
29
2/6/2009
- Read Slide.
30
2/6/2009
- ReadSlide.
31
2/6/2009
- Endocrine disorder usually has to do with too something.
32
2/6/2009
-Read slide.
-IncreasedRR DKA (Kussmauls Breathing)
33
2/6/2009
- Eunuchoidism sign of hypogonadism. Long extremities with small trunk.
34
2/6/2009
-They may complain that the shoe or glove size does not fit.
-Acromegaly.
35
2/6/2009
-This is Truncal Obesity. Characteristic of Cushings.
-If you were to examine the abdomen carefully, you might see purple striae.
36
2/6/2009
-ReadSlide.
-Thyroid Achropachy Clubbing-like effect.
-HypoparathyroidismMucocutaneous Candidiasis
37
2/6/2009
-These are identical twins. Which one has Addisons Disease?
-The one on the R (Hyperpigmentation, thinner)
38
2/6/2009
- ReadSlide
39
2/6/2009
40
2/6/2009
- When looking @ signs and symptoms of Goiter.
41
2/6/2009
- Read Slide.
42
2/6/2009
43
2/6/2009
- Hypogonadism check the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
44
2/6/2009
45
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Final Internalmed2Document1,788 pagesFinal Internalmed2Sharayu DhobleNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Short Stature and Pubertal DelayDocument27 pagesCase Presentation: Short Stature and Pubertal Delaydidu91No ratings yet
- Growth Hormone DisordersDocument1 pageGrowth Hormone DisordersVishalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 50Document79 pagesChapter 50latrishahollmonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DisordersDocument9 pagesEndocrine System DisordersYazn Amjad Mahmoud ElayanNo ratings yet
- Posterior Pituitary Disorder RomeoDocument19 pagesPosterior Pituitary Disorder RomeoSavin PetersNo ratings yet
- Pituitary DisordersDocument38 pagesPituitary DisordersJaspreet KangNo ratings yet
- Endo Lect-Ant Pituitary GlandDocument18 pagesEndo Lect-Ant Pituitary GlanddoctorrfarrukhNo ratings yet
- Sheehan's Syndrome: A Case Report: KeywordsDocument2 pagesSheehan's Syndrome: A Case Report: Keywordsnurul habibahNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypoglycemia in ChildrenDocument16 pagesTreatment of Hypoglycemia in ChildrenKamuiShirouNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders-1Document52 pagesEndocrine Disorders-1Nathaniel Mbiu TimNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Document172 pagesEndocrinology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Mohammed RisqNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument10 pagesEndocrinologyJohn Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- James Nelson and Elizabeth Varney V United States of America 2014 Damages Order PDFDocument38 pagesJames Nelson and Elizabeth Varney V United States of America 2014 Damages Order PDFMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- Hypopituitarism - ThomasDocument40 pagesHypopituitarism - ThomasguidanceNo ratings yet
- Hipoglicemia 2020 - Ingles PDFDocument18 pagesHipoglicemia 2020 - Ingles PDFMargaret MaggiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesEndocrine SystemYary MayorNo ratings yet
- Cs 19 SolvedDocument4 pagesCs 19 SolvedgogoNo ratings yet
- Paper IX MCQ Set ADocument3 pagesPaper IX MCQ Set AHimanshu KarmacharyaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary DisordersDocument4 pagesAnterior Pituitary DisordersJe LynNo ratings yet
- Hypopituitarism: Dr. Rasikapriya First Year PaediatricsDocument34 pagesHypopituitarism: Dr. Rasikapriya First Year PaediatricsReshu ThakuriNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)Document28 pagesEndocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)sarguss14100% (2)
- Hypopituitarism: Group OneDocument22 pagesHypopituitarism: Group OneSAMMYNo ratings yet
- Jardine Jade Albert C. Valdez, RMTDocument48 pagesJardine Jade Albert C. Valdez, RMTEj BersalonaNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland DisordersDocument80 pagesPituitary Gland DisordersNang KhamNo ratings yet
- Primary Empty Sella 2005Document7 pagesPrimary Empty Sella 2005Paúl Otañez MolinaNo ratings yet
- (1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Endocrine Work-Up in ObesityDocument32 pages(1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Endocrine Work-Up in ObesityAbdiNo ratings yet
- Primary Tumors of The Posterior Pituitary: A Systematic ReviewDocument20 pagesPrimary Tumors of The Posterior Pituitary: A Systematic ReviewNicolás HenaoNo ratings yet
- Hypopituitarism PDFDocument2 pagesHypopituitarism PDFcedricNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders - NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine Disorders - NotesLLLJJJNo ratings yet