Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework 5 Solution Circuit Analysis
Uploaded by
Umit GudenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework 5 Solution Circuit Analysis
Uploaded by
Umit GudenCopyright:
Available Formats
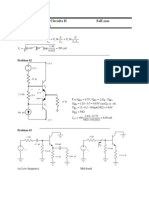
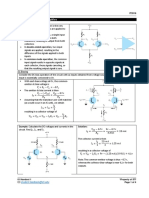
EEE481&EEE581 Homework 5 Solution due on 5-12-2007
Q1.
a) Find v
C
in terms of v
A
and v
B
if R = 47 K.
b) Find v
C
in terms of v
A
and v
B
if R = 47 K + 0.001*47 K
c) For case b) find A
dm
and A
cm
for this amplifier.
Assume opamps are ideal.
SOLUTION:
+
+
+
-
-
-
v
A
v
B
22
22
10
10
10
47
R
v
C
All
resistances
are in K
10000
10000
1
1 1
2 1
1 2
1 2
10
22 22
22 22 (1 ) 3.2 2.2
10 10 10
22 22
22 22 (1 ) 2.2 3.2
10 10 10
3.2 2.2 2.2 3.2 5.4( )
3.2 2.2 2.2 3.2
A B
A B
A A A B A B
A B
B B A B A B
A B A B A B
A B A B A B
v v
i
v v
v v i v v v v v
v v
v v i v v v v v
v v v v v v v v
v v v v v v v v
= + = + = + =
= = = + + = +
= + =
+ = + = +
1 1
2
1 2 2
1
2 2
1
1 2 2 2
2 1
2 1
10
10
1
10 10 10
1
47 47( )
10 10 10 10
47 47
(1 )
10 10 10
10 47 47
( )
10 10 10
C
e v
i
R
e e v
R
v R
i v
R
v R R
v e i v v
R R
R
v v
R
R
v v
R
=
= =
+
=
+
= + = +
+ +
= +
+
+
=
+
(a)
+
+
+
-
-
-
v
A
v
B
22
22
10
10
10
47
R
v
C
All
resistances
are in K
10000
10000
v
1
v
2
e
1
e
2
i
1
i
2
If R = 47 then
2 1
1 2
47 10 47 47
( )
47 10 10 10
47
( )
10
47
5.4( )
10
25.38( )
C
A B
A B
v v v
v v
v v
v v
+
=
+
=
=
=
(b)
If R = 47 + 0.0001*47 = 47.047 then
2 1
2 1
47.047 57 47
( )
57.047 10 10
4.7008238 4.7
4.7008238( 2.2 3.2 ) 4.7(3.2 2.2 )
25.381812 25.382636
C
A B A B
A B
v v v
v v
v v v v
v v
=
=
= +
= +
(c)
( )
2
( ) ( )
2 2
25.381812 25.382636
25.381812
2
25.382636
2
25.38
1
0.000824
1214
A B
C dm A B cm
cm cm
dm A dm B
A B
cm
dm
cm
dm
dm
cm
v v
v A v v A
A A
A v A v
v v
A
A
A
A
A
A
+
= +
= +
= +
+ =
=
=
= =
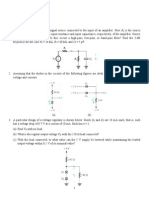
Q2.
Suppose the following filter-amplifier section is cascaded to the output of the amplifier
given above.
Assume opamps are ideal.
Find A
dm
and A
cm
for the overall amplifier if R = 47 K + 0.001*47 K. Also find the
passband of the amplifier.
SOLUTION:
In the passband
1 2 3
150 32.9
4.7
C
C
out C C
e v e e
v
v v v
= = =
= + =
Therefore passband gain is 32.9
In general
1 2 3
6
1
6
6
3.3 10 3.3
1
1 3.3
3.3 10
10
C C
e e e
jw
e v v
jw
jw
= =
= =
+
+
+
-
4.7
3300
v
C
All
resistances
are in K
1F
0.01
3300
v
out
150
e
1
e
2
e
3
3 1
1 8 3
3
3 8
3
8
3
3
8
3
3 5
1
(150 10 // )
10 4.7 10
1 1 3.3
(1 (150 10 // ))
4.7 10 10 1 3.3
1
150 10
1 3.3 10
(1 ( )
1
4.7 10 1 3.3
150 10
10
1 150 10 3.3
(1 ( )
4.7 10 150 10 1 1 3.3
31.92
(1
15
out
C
C
C
e
v e
jw
jw
v
jw jw
jw jw
v
jw
jw
jw
v
jw jw
= +
= +
+
= +
+
+
= +
+ +
= +
5
5
5
5
5
3.3
)
0 10 1 1 3.3
32.92 150 10 3.3
150 10 1 1 3.3
1 4.5565 10 3.3
32.92
1 150 10 1 3.3
C
C
C
jw
v
jw jw
jw jw
v
jw jw
jw jw
v
jw jw
+ +
+
=
+ +
+
=
+ +
The high cutoff frequency is
5
1
2
150 10
H H
w f
= =
and
5
10
106.1
300
H
f Hz
= = .
The low cutoff frequency is
1
2
3.3
L L
w f = = and
1
0.048
6.6
L
f Hz
= = .
The passband gain is 32.9.
The overall gains of the whole amplifier are
25.38 32.9 835
0.000824 32.9 0.027
dm
cm
A
A
= =
= =
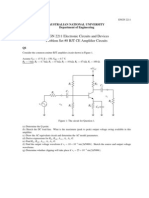
Q3.
Consider the three electrode isolated
ECG amplifier configuration on the
right. Assume that the instrumentation
amplifier has A
dm
and A
cm
as you have
found above in Q2.
The equivalent circuit is drawn below.
Assume that
2 1
10
in in
Z Z M = = ,
1
100
s
C pF = ,
2
100
s
C pF = ,
Z
e1
=20 K, Z
e2
=25 K,
ZRL=20K,
Z
iso
= 1/jwCiso
Ciso = 30 pF.
Find the output voltage due to the 220
V power line and also the output due
to the ecg signal.
Do not make any approximations.
a) Write the time waveform of the
output voltage in terms of a
cosinusoidal at 50 Hz and v.
How is 50 Hz interference comparable with v?
b) Write the time waveform of the output voltage in terms of a cosinusoidal at 50 Hz and
v if Z
e2
= 20 K also. How is 50 Hz interference comparable with v?
Earth
v
/2
1 s
C
2 s
C
220 V, 50 Hz
B
V
-
+
v
/2
Z
e1
Z
e2
Z
RL
+
-
+
-
+
-
out
v
Z
in1
Z
in2
v
1
v
2
A
dm
(v
1
-v
2
)+ A
cm
(v
1
+v
2
)/2
v is the
ecg signal
Instrumentation amplifier
Z
iso
Earth
1 s
C
2 s
C
220 V, 50 Hz
out
v
+
-
Assume that v is at frequency 10 Hz. This is necessary to find the impedances of the isolation
and stray capacitances when there is v only.
Solution:
We can use superposition:
If there is no ECG but only 220V input is present then the circuit is
If there is no 220V input but only ECG is present then the circuit is
Earth
1 s
C
2 s
C
220 V, 50 Hz
B
V
-
+
Z
e1
Z
e2
Z
RL
+
-
out
v
Z
in1
Z
in2
v
1
v
2
A
dm
(v
1
-v
2
)+ A
cm
(v
1
+v
2
)/2
v is the
ecg signal
Instrumentation amplifier
Z
iso
Call
1 2 in in in
Z Z Z = =
220 only
(a)
Define
1 2
//( ) //( )
RL e in e in
Z Z Z Z Z Z = + + (which is actually
RL
Z )
2
1 2
1
//( )
220 95.65
1 1
//( )
s
B
s s
Z Ziso
jwC
V V
Z Ziso
jwC jwC
+
= =
+ +
18
cm B
iso
Z
v V j mV
Z Z
= =
+
1
1
2
2
1 2
1 2
1 2
( ) 8.94
17.9
2
in
cm
e in
in
cm
e in
in in
cm
e in e in
cm
Z
v v
Z Z
Z
v v
Z Z
Z Z
v v v j V
Z Z Z Z
v v
v j mV
=
+
=
+
= =
+ +
+
=
Earth
v
/2
1 s
C
2 s
C
B
V
-
+
v
/2
Z
e1
Z
e2
Z
RL
+
-
+
-
+
-
out
v
Z
in1
Z
in2
v
1
v
2
A
dm
(v
1
-v
2
)+ A
cm
(v
1
+v
2
)/2
Instrumentation amplifier
Z
iso
( 8.94 ) ( 17.9 )
835 8.94 0.027 17.9
7.4649 0.4833
6.98
out dm cm
v A j V A j mV
j V j mV
j mV j
j mV
= +
= +
= +
=
(b)
0.48
out
v j V =
Ecg only
Solution with approximation:
(a)
835
out dm ecg ecg
v A v v =
(b)
835
out dm ecg ecg
v A v v =
Solution without approximation:
(a)
833.1
out ecg
v v =
(b)
833.3
out ecg
v v =
%Exact analysis of isolated ECG amplifier (loop analysis)
clear all;
close all;
A=zeros(4,4);
B=zeros(4,1);
Z=zeros(4,2);
for j=1:2
Adm=-835;
Acm=0.027;
if j==1
v=1;
vline=0;
Zs1=-i/(2*pi*10*100e-12);
Zs2=-i/(2*pi*10*100e-12);
Ziso=-i/(2*pi*10*30e-12);
else
v=0;
vline=220;
Zs1=-i/(2*pi*50*100e-12);
Zs2=-i/(2*pi*50*100e-12);
Ziso=-i/(2*pi*50*30e-12);
end;
Ze1=20e3;
Ze2=25e3;
Zin1=10e6;
Zin2=10e6;
ZRL=20e3;
A(1,1)=Ze1+Zin1+ZRL;A(1,2)=-ZRL;A(1,3)=0;A(1,4)=0;
A(2,1)=-ZRL;A(2,2)=Ze2+Zin2+ZRL;A(2,3)=-Ze2-Zin2;A(2,4)=0;
A(3,1)=0;A(3,2)=-Ze2-Zin2;A(3,3)=Ze2+Zin2+Ziso+Zs2;A(3,4)=-Zs2;
A(4,1)=0;A(4,2)=0;A(4,3)=-Zs2;A(4,4)=Zs1+Zs2;
B(1)=v/2;
B(2)=v/2;
B(3)=0;
B(4)=vline-v;
Y=inv(A)*B;
Z(:,j)=Y;
end
for j=1:2
e1(j)=Z(1,j)*Zin1;
e2(j)=(Z(3,j)-Z(2,j))*Zin2;
vout(j)=Adm*(e1(j)-e2(j))+Acm*(e1(j)+e2(j))/2;
end;
Conclusion:
We see that when there is no electrode impedance imbalance the interference is negligible
which is 0.48 V compared to 835 mV assuming that ecg is 1 mV.
However when there is electrode impedance imbalance the interference is 6.98mV which is
about 0.8% of ecg.
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- Problem 2) 2000 Cos (10) ( : T AvgDocument8 pagesProblem 2) 2000 Cos (10) ( : T AvgSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- Bee332 HW8S 2011Document2 pagesBee332 HW8S 2011hooj08No ratings yet
- Answer Key AnalysisDocument7 pagesAnswer Key AnalysisSarath BabuNo ratings yet
- Brilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012Document11 pagesBrilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012sanskarid94No ratings yet
- College of Engineering Midterm Test Answer: Subject Code: Course Title: Date: Time AllowedDocument8 pagesCollege of Engineering Midterm Test Answer: Subject Code: Course Title: Date: Time AllowedMohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- In Gate 2012Document24 pagesIn Gate 2012Anish GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Ac CircuitDocument26 pagesEe602 Ac CircuitArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetChika OfiliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesDocument21 pagesChapter 3 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesRajesh PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Triangular Wave Applied to Op-Amp Inverting Input Generates Oscillating Output Between -15V and +15VDocument16 pagesTriangular Wave Applied to Op-Amp Inverting Input Generates Oscillating Output Between -15V and +15VAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- EEE 241 EEE 241 Analog Electronics 1 Tutorial Tutorial DR Norlaili Mohd NohDocument42 pagesEEE 241 EEE 241 Analog Electronics 1 Tutorial Tutorial DR Norlaili Mohd NohMd Anwar HossainNo ratings yet
- Solution - Tutorial 3Document11 pagesSolution - Tutorial 3zgalionoooNo ratings yet
- ECC364 LC Oscillator StabilityDocument21 pagesECC364 LC Oscillator StabilityAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- ANU ENGN 2211 BJT CE Amplifier CircuitsDocument9 pagesANU ENGN 2211 BJT CE Amplifier CircuitsAristotle Atijera AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Physics 9 HW9 SolnsDocument10 pagesPhysics 9 HW9 SolnsAditya Narayan SwainNo ratings yet
- Transistor OsicllatorsDocument47 pagesTransistor OsicllatorsMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : NPN PNPDocument44 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : NPN PNPAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument25 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsHariPonnanaNo ratings yet
- (2012) MEIII (Midterm) PDFDocument8 pages(2012) MEIII (Midterm) PDFTai-Yuan HsuNo ratings yet
- Solutions All MOCK Tests - EEDocument64 pagesSolutions All MOCK Tests - EEsamg27No ratings yet
- Ispitni Zadaci - ElektrotehnikaDocument14 pagesIspitni Zadaci - ElektrotehnikaAleksandar KrčuljNo ratings yet
- Ap2011 Solutions 03Document10 pagesAp2011 Solutions 03soniaxNo ratings yet
- Solns 2cmosDocument18 pagesSolns 2cmosramprakash_rampelliNo ratings yet
- N-R BasicsDocument46 pagesN-R BasicsHossain 'Soroosh' MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Repeater Wt-20 Key SolutionDocument8 pagesRepeater Wt-20 Key Solutionboominaathan18No ratings yet
- GATE EC 2012 MCQ Questions 1-15Document50 pagesGATE EC 2012 MCQ Questions 1-15Gautam KunalNo ratings yet
- Multistage AmplifiersDocument9 pagesMultistage AmplifiersjaganmohanrsNo ratings yet
- Targate'15: Ec Test Id: 151262Document11 pagesTargate'15: Ec Test Id: 151262Ancil CleetusNo ratings yet
- EC 2012 With SolutionsDocument50 pagesEC 2012 With Solutionsprabhjot singh1No ratings yet
- EE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionDocument6 pagesEE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionKL ChiangNo ratings yet
- Common Drain Amplifier or Source Follower: 1. Low Frequency Small Signal Equivalent CircuitDocument16 pagesCommon Drain Amplifier or Source Follower: 1. Low Frequency Small Signal Equivalent CircuitPadaliya ShreyaNo ratings yet
- Problem Slide1Document49 pagesProblem Slide1Bharavi K SNo ratings yet
- Analog CircuitsDocument18 pagesAnalog CircuitsSAMIT KARMAKARNo ratings yet
- New EM4Document28 pagesNew EM4Srinivasagopalan MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Analog Lect 21 17032012Document17 pagesAnalog Lect 21 17032012Angad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 Astable Multivibrators: T RC F TDocument8 pagesChapter-7 Astable Multivibrators: T RC F TredberryyesNo ratings yet
- Finding Mutual Inductance Bridge MethodDocument25 pagesFinding Mutual Inductance Bridge MethodMohammed Shafi AhmedNo ratings yet
- SSM Chapter 01Document16 pagesSSM Chapter 01Jao Wei KuangNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit and FieldsDocument24 pagesElectric Circuit and Fieldssamg27No ratings yet
- ECSE 353 FormulasDocument6 pagesECSE 353 FormulasEileen FuNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolDocument9 pagesHW 1 Sol張量凱No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (2)
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator Full DerivationDocument12 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator Full DerivationPranav Itraj0% (1)
- ECE 410 Homework 6 - Solution Spring 2008Document4 pagesECE 410 Homework 6 - Solution Spring 2008murthyNo ratings yet
- CL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014Document7 pagesCL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014saurabhdabas7No ratings yet
- L N I NBS I NS I NI R NS R L M M MH e L Di DT A S V MVDocument18 pagesL N I NBS I NS I NI R NS R L M M MH e L Di DT A S V MVAnxo Do ForteNo ratings yet
- Formulas and properties of functionsDocument3 pagesFormulas and properties of functionsYessikhita Salomon LaraNo ratings yet
- UEEA2333 Analog Electronics Tutorial SolutionsDocument3 pagesUEEA2333 Analog Electronics Tutorial SolutionssadyehclenNo ratings yet
- 15.1 (A) For Example:: Problem SolutionsDocument46 pages15.1 (A) For Example:: Problem SolutionsLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- GATEDocument45 pagesGATESaideep NarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Class-A Source Follower With External Resistor Output StageDocument23 pagesClass-A Source Follower With External Resistor Output StagelaksologinNo ratings yet
- EC-GATE-2012 KeyDocument31 pagesEC-GATE-2012 KeypnrgoudNo ratings yet
- EEE3405Tut1 5QSDocument10 pagesEEE3405Tut1 5QSArjunneNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 - Q. 25 Carry One Mark Each.: X A X AADocument14 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 25 Carry One Mark Each.: X A X AAGauravArjariaNo ratings yet
- Force vector along a lineDocument7 pagesForce vector along a linebalakaleesNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- UMTS EVB Kit Document List - 20140315Document2 pagesUMTS EVB Kit Document List - 20140315Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- PS MPU 9250A 01 v1.1Document42 pagesPS MPU 9250A 01 v1.1maadidNo ratings yet
- Justin Romberg Lecture 4Document74 pagesJustin Romberg Lecture 4Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- Eece253 01 IntroDocument81 pagesEece253 01 IntrosudhacseNo ratings yet
- 01 Basis ExpansionsDocument28 pages01 Basis ExpansionsUmit GudenNo ratings yet
- Cs 421: Computer Networks Fall 2010Document9 pagesCs 421: Computer Networks Fall 2010Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Probability Review Chapter 1Document7 pagesProbability Review Chapter 1Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- VHDL Memory Models: EL 310 Erkay Savaş Sabancı UniversityDocument24 pagesVHDL Memory Models: EL 310 Erkay Savaş Sabancı UniversityUmit GudenNo ratings yet
- EE 342 Lab1 Preliminary WorkDocument2 pagesEE 342 Lab1 Preliminary WorkUmit GudenNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document3 pagesHW 1Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- Ee 501 Lecture Notes 1Document5 pagesEe 501 Lecture Notes 1Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- ECE382 s05 Hw4solnDocument16 pagesECE382 s05 Hw4solnUmit Guden100% (1)
- Oral Presentation Criteria For Proposal Presentation and Report PresentationDocument1 pageOral Presentation Criteria For Proposal Presentation and Report PresentationUmit GudenNo ratings yet
- Table of Fourier Transform PairsDocument8 pagesTable of Fourier Transform PairsmayankfirstNo ratings yet
- 3 The Wiener FilterDocument15 pages3 The Wiener FilterManish VohraNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - Theodore VoronovDocument49 pagesVector Calculus - Theodore VoronovUgras SEVGEN100% (2)
- RS232Document9 pagesRS232Shijumon KpNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Differential Topology (Brin M.G.) (Course Notes)Document59 pagesIntroduction To Differential Topology (Brin M.G.) (Course Notes)mederbilNo ratings yet
- Exam3 4Document1 pageExam3 4Umit GudenNo ratings yet
- HMC 1001 and HMC 1002Document15 pagesHMC 1001 and HMC 1002Không Có GìNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Amplifiers: Extended Temperature Low Noise CardsDocument2 pagesOptical Fiber Amplifiers: Extended Temperature Low Noise CardsAbdulrahman AdaaniNo ratings yet
- Injector PWM ModificationDocument6 pagesInjector PWM Modificationpablo j vargasNo ratings yet
- Warrior 8 Software FOM-61-150Document90 pagesWarrior 8 Software FOM-61-150Wualdir Vivas ChungaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Representation of Transistor CIrcuitsDocument5 pagesMatrix Representation of Transistor CIrcuitsMatthew HamerNo ratings yet
- EE301-Fall 2015: Laboratory #5: BJT AMPLIFIERDocument3 pagesEE301-Fall 2015: Laboratory #5: BJT AMPLIFIEROrhunNo ratings yet
- LCR-Meter ElektorDocument5 pagesLCR-Meter ElektorFernando VidalNo ratings yet
- Resident Physics Lectures on Attenuation MathDocument25 pagesResident Physics Lectures on Attenuation MathSebastian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- AmplifierDocument68 pagesAmplifierशुभम तिवारीNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mixed Signals and SensorsDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Mixed Signals and SensorsMaryjane PayaoNo ratings yet
- JFET Input Instrumentation Amplifier With Rail-to-Rail Output in MSOP PackageDocument28 pagesJFET Input Instrumentation Amplifier With Rail-to-Rail Output in MSOP Packagejunk junkNo ratings yet
- Korg Mde-X: Owner's ManualDocument27 pagesKorg Mde-X: Owner's ManualguyNo ratings yet
- 博士班資格考 電子學題庫Document15 pages博士班資格考 電子學題庫Adil KhanNo ratings yet
- Programmable Voltage Reference: DescriptionDocument9 pagesProgrammable Voltage Reference: DescriptionRamazan ÖzenNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering Unit - I Two Mark QuestionsDocument7 pagesBiomedical Engineering Unit - I Two Mark QuestionsMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Negative Feedback AmplifiersDocument33 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Negative Feedback AmplifiersKishore Reddy100% (2)
- B&K Short Form Catalog (1973)Document44 pagesB&K Short Form Catalog (1973)Francesco Violi100% (2)
- Differential and Common Mode Operation of Op-AmpsDocument8 pagesDifferential and Common Mode Operation of Op-AmpsRoxanne LazarteNo ratings yet
- Pro Audio Review January February 2014Document44 pagesPro Audio Review January February 2014dawsiekeysNo ratings yet
- Design of High-Performance Balanced Audio InterfacesDocument23 pagesDesign of High-Performance Balanced Audio InterfacesLucas RossoNo ratings yet
- EveryCircuit Tutorial: Circuit Analysis Made EasyDocument31 pagesEveryCircuit Tutorial: Circuit Analysis Made EasyMika Mikic100% (1)
- Digital Servo Motion ControlDocument25 pagesDigital Servo Motion ControlEdsonNo ratings yet
- Allgon System Ab: Compact Repeater With Adjustable Bandwidth 800 MHZ Version, Cdma, 15 MHZ Product Number: Alr4200/011Document2 pagesAllgon System Ab: Compact Repeater With Adjustable Bandwidth 800 MHZ Version, Cdma, 15 MHZ Product Number: Alr4200/011MUJTABA RASHID BHATNo ratings yet
- Modelling Equations with the Telecoms-Trainer 101Document8 pagesModelling Equations with the Telecoms-Trainer 101Claire AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- KAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Document18 pagesKAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Max TanNo ratings yet
- AD8314Document16 pagesAD8314Aparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- En 12668-1-2010 PDFDocument48 pagesEn 12668-1-2010 PDFJaulay100% (3)
- TEA7532 Monitor Amplifier: Programmable Gain IC for Loudspeaker TelephonesDocument17 pagesTEA7532 Monitor Amplifier: Programmable Gain IC for Loudspeaker TelephonesGiapy Phuc TranNo ratings yet
- Digitally-Controlled Analog Volume Control PDFDocument21 pagesDigitally-Controlled Analog Volume Control PDFBhadreshkumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifierDocument57 pagesFeedback AmplifierSUSHANTA BORDOLOINo ratings yet