Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current and Capital Account Guide
Uploaded by
dhiwaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Current and Capital Account Guide
Uploaded by
dhiwaCopyright:
Available Formats
www.mrunal patel .co.
nr
(BASIC STUFF FROM EXAM POINT OF VIEW)
MRUNAL PATEL
QUESTI ONS
1. Current account & capital account.
2. Current & capital account convertibility.
3. Which account is permanent & which is reversible & why?
4. Full capital account convertibility : Pros and cons
5. On which account government needs to keep close eye?
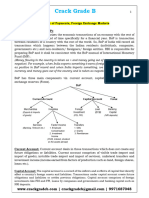
WHAT IS CURRENT AND CAPITAL ACCOUNT?
In an open economy, we buy stuff from abroad (Export), we sell stuff to abroad.(export)
Similarly Indian companies invest abroad, foreign companies invest in India.
So lot of money incoming and outgoing.
Current and Capital accounts are nothing but method of classifying that incoming and
outgoing money.
As you know, Balance of Payment (bop) = Import Export.
This BoP is calculated under two heads: Current Account and Capital Account.
Means money
(Rupees/Dollars/any
currency) sent and
received during
Money sent & received in Export/Import
in goods and services goes here.
Since the money we spend importing
crude oil, is quite larger than the money
we make while exporting stuff.
So for India, Import >> Export
So money going out >> Money coming
in So weve DEFICIT in Current account.
In short Money inflow and outflow via
import-export is classified in Current
Account.
NRIs sending $$ from Dubai and America
(Remittance from abroad)
Loans taken from IMF, World Bank
Tata buys British company; some Japanese
company buys Indian companythat kind
of money is also counted in here.
ONGC buys some Oil reserve in Russia,
Some French co. Buys thorium mine in
India, the kind of money also counted here
(rights over natural resources)
In short Investment and borrowing goes
here In Capital account
NOW WHAT THE HELL IS CURRENT AND CAPITAL ACCOUNT CONVERTIBILITY ???
Convertibility = converting one currency into another. Like rupee to dollar, yen to
poundanything.
Since money is incoming and outgoing. People will need to convert the money into different
currencies based on their requirements.
We classified the incoming and outgoing money into Current and Capital account.
Similarly we classify the procedure involved in converting that money. In brief..
CONVERTABILITY: CURRENT ACCOUNT VS. CAPITAL ACCOUNT
Youve a big mobile store, import 5000 i-
phones a month from America, but the
American supplier accepts payment only in
$$. So you get your rupee converted into $
at forex market at anytime, nobody
prevents you from this.
Again, some of those iphones, you sell to
Bangladesh and Nepal, and get their
currency, and you convert it into Rupees.
Again nobody prevents you from this.
Nobody prevents you from doing it.
A Japanese businessman buys some
building in India, after 5 years, price of that
building is increase 5x times. So he sells It
and wants to convert those Rupees into
Yen so that he can use those Yen back
home in Japan.
He cannot do this easily; he has to stick to
RBI guidelines. Eg. He can only transfer this
money after 5 years lock-in period.
Because this money is classified under
CAPITAL account.So, Money under Capital
Money classified under
Current account can be
easily converted into
dollar,yen, pound, rupee
anything.
Money classified under
Capital account CANNOT be
easily converted into
different currency. RBI has
strict guidelines.
= we donot have
full capital account
convertability !
www.mrunal patel .co.nr
Because the money is classified in
CURRENT ACCOUNT
This is Current account convertibility. I.e. It
allows residents to make and receive
trade-related payments receives dollars
(or any other foreign currency) for export
of goods and services and pay dollars for
import of goods and services, make sundry
remittances, access foreign currency for
travel, studies abroad, medical treatment
and gifts etc.
In India, current account convertibility was
established with the acceptance of the
obligations under IMF Agreement in 1994
account is harder to get converted (into
different currency)
It means we dont have Full CAPITAL
account convertibility.
WHICH ACCOUNT IS PERMANENT AND WHICH ACCOUNT IS REVERSIBLE? AND WHY?
Current account Capital account
Permanent Not Permanent
Irreversible Reversible
WHY?
Current account =Money sent and received during import and export
You sold something (exported) and received the money, so that money is yours forever (until
you spend it on something else!) So Current account is permanent and irreversible.
Capital account = Money sent and received during investment and borrowing.
Suppose Japanese guy buys factory in India (capital account), sells it after 5 years and takes
back the money. So Capital account inflow is NOT PERMANENT and hence reversible (because
he took back the money he invested in India).
FULL CAPITAL ACCOUNT CONVERTIBILITY PRO AND CONS
As we saw above, we dont have full capital account convertibility in India.
ARGUMENT IN FAVOR OF FULL CAPITAL ACCOUNT CONVERTIBILITY
It facilitates foreign investments and borrowing. So competition is increased = more factories =
more jobs = more product choices for consumers = good for economy. :)
ARGUMENTS AGAINST OF FULL CAPITAL ACCOUNT CONVERTIBILITY
Local producers have to compete with International giants. So they lose market. :(
o (Counter-argument: Ultimately business is about survival of the fittest, so perform or
perish, aint no need to get sentimental about swadeshi. Why should consumer pay for
not-so-good quality yet expensive product from a local man, if a foreigner is offering
better stuff at cheaper quality?)
What if foreigners buy lot of factories in India and suddenly they find that investing money in
France is better than in India. So they immediately sell all those factories, get their Rupees
converted into Euro and run away! Thatll lead to huge job loss and collapse in Indian market!
o (Counter argument: Its a two way street if Foreigners can do that, Indians can also do it
while investing abroad.)
o Sudden outflow of money happens only when governing institutions have weak
foundations and policies. [For example, when Government is busy firefighting
Sugar,onion prices without any long-term vision, it makes cronies get involved in
speculative business] If every country has sound economic policies, then itll be
attractive to invest in every country. Then there would be no sudden outflow or
inflow of money.
ON WHICH ACCOUNT GOVERNMENT NEEDS TO KEEP CLOSE EYE?
Sorry I dont know that exact answer. Government needs to keep an eye on both accounts to make
changes in trade policies, tax rates etc. But since Capital account inflows come with a risk (of sudden
outflow collapsing the economy), so Government should keep a close eye on Capital account.
FOR THE CURIOUS SOULS: EXAMPLE OF CURRENT AND CAPITAL ACCOUNT FOR 2009
APPENDIX TABLE 51 : INDIAS OVERALL BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
Item Rupees crore US $ million
2006-
07
2007-08
PR
2008-09
P
2006-
07
2007-
08 PR
2008-
09 P
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
A. CURRENT ACCOUNT
1 Exports, f.o.b. 5,82,871 6,67,757 7,98,956 1,28,888 1,66,163 1,75,184
2 Imports, c.i.f. 8,62,833 10,36,289 13,41,069 1,90,670 2,57,789 2,94,587
3 Trade Balance -
2,79,962
-3,68,532 -5,42,113 -61,782 -91,626 -
1,19,403
4 Invisibles, Net 2,35,579 2,99,618 4,09,842 52,217 74,592 89,586
A) Non-Factor
Services
1,33,064 1,51,059 2,28,778 29,469 37,565 49,818
Of which:
www.mrunal patel .co.nr
Software
Services
1,41,356 1,62,020 2,15,588 31,300 40,300 47,000
B) Income -33,234 -19,888 -21,116 -7,331 -4,917 -4,511
C) Private
Transfers
1,34,608 1,67,495 2,01,050 29,825 41,705 44,047
D) Official
Transfers
1,141 952 1,130 254 239 232
5 Current Account
Balance
-44,383 -68,914 -1,32,271 -9,565 -17,034 -29,817
B. CAPITAL ACCOUNT
1 Foreign
Investment, Net
(a+b)
66,791 1,80,788 11,760 14,753 44,957 3,462
A) Direct
Investment
Of which: 34,910 61,793 76,822 7,693 15,401 17,496
I) In India 1,02,652 1,37,434 1,58,579 22,739 34,236 34,982
Equity 73,969 1,07,320 1,25,362 16,394 26,758 27,809
Re-invested
Earnings
26,371 28,859 29,705 5,828 7,168 6,426
Other
Capital
2,312 1,255 3,512 517 310 747
Ii) Abroad -67,742 -75,641 -81,757 -15,046 -18,835 -17,486
Equity -56,711 -57,936 -63,478 -12,604 -14,421 -13,558
Re-invested
Earnings
-4,868 -4,363 -4,985 -1,076 -1,084 -1,084
Other
Capital
-6,163 -13,342 -13,294 -1,366 -3,330 -2,844
B) Portfolio
Investment
31,881 1,18,995 -65,062 7,060 29,556 -14,034
In India 31,630 1,18,348 -64,206 7,004 29,394 -13,855
Abroad 251 647 -856 56 162 -179
2 External
Assistance, Net
7,973 8,465 12,435 1,775 2,114 2,638
Disbursements 16,978 17,022 23,535 3,767 4,241 5,042
Amortisation -9,005 -8,557 -11,100 -1,992 -2,127 -2,404
3 Commercial
Borrowings, Net
72,365 91,180 38,009 16,103 22,633 8,158
Disbursements 93,932 1,22,270 71,626 20,883 30,376 15,382
Amortisation -21,567 -31,090 -33,617 -4,780 -7,743 -7,224
4 Short Term Credit,
Net
30,096 68,878 -31,160 6,612 17,183 -5,795
5 Banking Capital
Of which: 8,477 47,148 -19,868 1,913 11,757 -3,397
NRI Deposits, Net 19,574 706 20,431 4,321 179 4,290
6 Rupee Debt
Service
-725 -488 -476 -162 -121 -101
7 Other Capital, Net
@
18,696 37,802 21,681 4,209 9,470 4,181
8 Total Capital
Account
2,03,673 4,33,773 32,381 45,203 1,07,993 9,146
C. Errors & Omissions 4,344 4,830 2,775 968 1,205 591
D. Overall Balance
[A(5)+B(8)+C]
1,63,634 3,69,689 -97,115 36,606 92,164 -20,080
E. Monetary
Movements (F+G)
-
1,63,634
-3,69,689 97,115 -36,606 -92,164 20,080
F. IMF, Net 0 0 0 0 0 0
G. Reserves and
Monetary Gold
(Increase -, Decrease
+)
-
1,63,634
-3,69,689 97,115 -36,606 -92,164 20,080
P : Provisional. PR : Partially Revised.
@ : Includes delayed export receipts, advance payments against imports, net funds
held abroad and advances received pending issue of shares under FDI.
Note : 1. Gold and silver brought by returning Indians have been included under imports,
with a contra entry in private transfer receipts.
2. Data on exports and imports differ from those given by DGCI&S on account of
differences in coverage, valuation and timing.
You might also like
- MATH8-Relations and Functions Worksheet AnswersDocument15 pagesMATH8-Relations and Functions Worksheet AnswersRhealyn Joy Narciso100% (2)
- r32 - Rb26dett Ecu PinoutDocument1 pager32 - Rb26dett Ecu PinouttospotNo ratings yet
- FAQ: Capital A/c Convertibility and How It Affects You: Print This Page CloseDocument2 pagesFAQ: Capital A/c Convertibility and How It Affects You: Print This Page CloseAmol MahajanNo ratings yet
- So What Is Capital Account Convertibility?Document4 pagesSo What Is Capital Account Convertibility?nick21_347No ratings yet
- Meaning of Convertibility of Rupee by YashuDocument4 pagesMeaning of Convertibility of Rupee by YashuVishal ModiNo ratings yet
- Capital Account ConvertabilityDocument3 pagesCapital Account Convertabilitydisha_11_89No ratings yet
- Factors to Consider in FDI and Balance of Payments ExplainedDocument10 pagesFactors to Consider in FDI and Balance of Payments ExplainedRajesh DmNo ratings yet
- Causes Behind Falling RupeeDocument441 pagesCauses Behind Falling RupeeSahil KapoorNo ratings yet
- Mrunal (Economic Survey Ch6) Balance of Payments, Forex Reserves, Currency Exchange, NEER, REER PrintDocument14 pagesMrunal (Economic Survey Ch6) Balance of Payments, Forex Reserves, Currency Exchange, NEER, REER PrintAnil CletusNo ratings yet
- 5 MacroeconomicsDocument22 pages5 MacroeconomicsSai harshaNo ratings yet
- Capital Account Convertibility - A Way Ahead For India: Project Report OnDocument12 pagesCapital Account Convertibility - A Way Ahead For India: Project Report OnKeta KurkuteNo ratings yet
- CC SunilDocument33 pagesCC SunilDilip ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- Capital Account Convertibilty: By: Preeti N (766) Sumit H (803) Vinay NDocument13 pagesCapital Account Convertibilty: By: Preeti N (766) Sumit H (803) Vinay NVinay NaikNo ratings yet
- Know The Difference Between NRE and NRO AccountDocument5 pagesKnow The Difference Between NRE and NRO AccountSanjeet MohantyNo ratings yet
- Bank Tokyo Financial Statements 2010Document45 pagesBank Tokyo Financial Statements 2010Mahmood KhanNo ratings yet
- Indian Depository RecieptDocument24 pagesIndian Depository Recieptadilfahim_siddiqi100% (1)
- Balance of Payment (Lect - 19210180Document33 pagesBalance of Payment (Lect - 19210180aamirzbhatt31No ratings yet
- Bartronics LTD (BARLTD) : Domestic Revenues Take A HitDocument4 pagesBartronics LTD (BARLTD) : Domestic Revenues Take A HitvaluelettersNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Hirapara Kaushal, Sojitra ParagDocument20 pagesPresented By:-Hirapara Kaushal, Sojitra ParagKaushal HiraparaNo ratings yet
- 2010 05 Alternative Investment Options in IndiaDocument3 pages2010 05 Alternative Investment Options in IndiasatishcreativeNo ratings yet
- Market Outlook 16th April 2012Document5 pagesMarket Outlook 16th April 2012Angel BrokingNo ratings yet
- The Financial Plan: Arya Kumar Chief ED & IPR Unit BITS, PilaniDocument20 pagesThe Financial Plan: Arya Kumar Chief ED & IPR Unit BITS, Pilanirock_worldNo ratings yet
- What is CAD? Understanding India's Current Account Deficit and Recommendations for ReductionDocument2 pagesWhat is CAD? Understanding India's Current Account Deficit and Recommendations for ReductionDipen PataniNo ratings yet
- BoP and ForexDocument33 pagesBoP and ForexNeha RathoreNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Balance of Payments in India For Last 5 YearsDocument15 pagesAnalysis On Balance of Payments in India For Last 5 YearsRoopavathy Mani100% (2)
- Indian Forex ReservesDocument3 pagesIndian Forex Reserves00758ganeshNo ratings yet
- Balance of PaymentsDocument15 pagesBalance of PaymentsBalavarshini Rajasekar0% (2)
- Bop ProjectDocument36 pagesBop ProjectArun Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payment BoP Via DiagramsDocument7 pagesBalance of Payment BoP Via Diagramsvicky60702000No ratings yet
- SEBI Grade A 2020 Economics Balance of PaymentsDocument11 pagesSEBI Grade A 2020 Economics Balance of PaymentsThabarak ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Compliance India - Recurring Compliances for BusinessesDocument6 pagesRegulatory Compliance India - Recurring Compliances for BusinessesRajiv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: An Effort byDocument19 pagesBalance of Payments: An Effort bybuttasingh8039No ratings yet
- Capital and Current Account ConvertibilityDocument2 pagesCapital and Current Account ConvertibilityKhushi KaulNo ratings yet
- Share Market SeminarDocument65 pagesShare Market Seminarpritisimi100% (1)
- FSA Assignment III Group 4Document4 pagesFSA Assignment III Group 4Kristina Kitty100% (1)
- Research Paper On Balance of PaymentsDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Balance of Paymentsafmcqeqeq100% (1)
- NRI Banking: I) Foreign Currency (Non-Resident) AccountsDocument5 pagesNRI Banking: I) Foreign Currency (Non-Resident) AccountsPALAKNo ratings yet
- Understanding Balance of Payments and International TradeDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Balance of Payments and International TradeKrish PatilNo ratings yet
- Annual Report: Head Office & FactoryDocument6 pagesAnnual Report: Head Office & FactoryVenky PragadaNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet - Balance of Payments - FormattedDocument11 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet - Balance of Payments - FormattedAnshulNo ratings yet
- Economic and Social Issues (Esi) Balance of Payments Summary Sheet For Rbi Grade B and Nabard Grade A/B 2019Document11 pagesEconomic and Social Issues (Esi) Balance of Payments Summary Sheet For Rbi Grade B and Nabard Grade A/B 2019SaumyaNo ratings yet
- Bank of Tokyo Mitshubhishi LTD 2009Document46 pagesBank of Tokyo Mitshubhishi LTD 2009Mahmood KhanNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments-Final For KreaDocument25 pagesBalance of Payments-Final For KreaDhananjay SinghalNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement: Segregation of Cash FlowsDocument7 pagesCash Flow Statement: Segregation of Cash FlowsawedawedNo ratings yet
- C C C C CDocument5 pagesC C C C Cmrinmoy_nsuNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Lect 6 - BOP - Lec 2Document16 pagesModule 6 - Lect 6 - BOP - Lec 2BHAVYA GOPAL 18103096No ratings yet
- Zerodha Technical AnalysisDocument104 pagesZerodha Technical Analysisicecrack100% (1)
- Introduction to India's Income Tax ActDocument46 pagesIntroduction to India's Income Tax ActVikranthNo ratings yet
- ME Class 11-12Document25 pagesME Class 11-12Dixith GandheNo ratings yet
- State Bank of IndiaDocument5 pagesState Bank of IndiaBhavika GuptaNo ratings yet
- One From Everyone NEWDocument14 pagesOne From Everyone NEWPratik KathuriaNo ratings yet
- THOUFIKA SUMMER INTERNSHIP REPORT SDocument4 pagesTHOUFIKA SUMMER INTERNSHIP REPORT SKUMARAGURU PONRAJNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Statement of Cash FlowsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the Statement of Cash FlowsLouix LaneNo ratings yet
- IngvysyaDocument12 pagesIngvysyashashi1124No ratings yet
- CAC-Capital Account ConvertibilityDocument5 pagesCAC-Capital Account ConvertibilityShilpi JainNo ratings yet
- currency convertibilityDocument13 pagescurrency convertibilityTanvi ShahNo ratings yet
- Tally Erp9 EnglisheditionDocument31 pagesTally Erp9 Englisheditionapi-262072056No ratings yet
- FinalDocument144 pagesFinalsatyamehtaNo ratings yet
- Ptmail m1219 Ss Two Stock Special Report PDFDocument18 pagesPtmail m1219 Ss Two Stock Special Report PDFAaron MartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Fundamental AnalysisDocument37 pagesChapter 11 Fundamental AnalysisSamuel DwumfourNo ratings yet
- Guide to Management Accounting CCC (Cash Conversion Cycle) for managersFrom EverandGuide to Management Accounting CCC (Cash Conversion Cycle) for managersNo ratings yet
- IUCN Red List India – Critically Endangered SpeciesDocument76 pagesIUCN Red List India – Critically Endangered SpeciesdhiwaNo ratings yet
- Imp PersonalitiesDocument6 pagesImp PersonalitiesdhiwaNo ratings yet
- IUCN Important News-EnvironmentDocument14 pagesIUCN Important News-EnvironmentdhiwaNo ratings yet
- India (History) ChronologyDocument70 pagesIndia (History) ChronologyAngel Zyesha50% (2)
- UPSC Successful Candidate 2009-10 2Document8 pagesUPSC Successful Candidate 2009-10 2dhiwa100% (1)
- Currency System-M1 To M4Document4 pagesCurrency System-M1 To M4Tejashwi Aaryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Philip Rance EAH Philo of ByzantiumDocument3 pagesPhilip Rance EAH Philo of ByzantiumstoliNo ratings yet
- Tap Yourself FreeDocument134 pagesTap Yourself Freenguyenhavn100% (2)
- EM-CABLE Product CatalogDocument96 pagesEM-CABLE Product Catalogm00h00No ratings yet
- GERD – Definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology and diagnostic investigationsDocument132 pagesGERD – Definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology and diagnostic investigationsSorana VasilescuNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Cape Bio Unit 1 2023Document37 pagesLab Manual Cape Bio Unit 1 2023drug123addict25No ratings yet
- Mitchella Partridge Berry Materia Medica HerbsDocument3 pagesMitchella Partridge Berry Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Goat Milk Marketing Feasibility Study Report - Only For ReferenceDocument40 pagesGoat Milk Marketing Feasibility Study Report - Only For ReferenceSurajSinghalNo ratings yet
- CSC-1321 Gateway User Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument48 pagesCSC-1321 Gateway User Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineKislan MislaNo ratings yet
- Function and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQDocument4 pagesFunction and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxNo ratings yet
- Specifications Sheet ReddyDocument4 pagesSpecifications Sheet ReddyHenry CruzNo ratings yet
- Gerovital anti-aging skin care product guideDocument10 pagesGerovital anti-aging skin care product guideכרמן גאורגיהNo ratings yet
- P&id BoilerDocument1 pageP&id BoilerBagus AryowibowoNo ratings yet
- Tec Relay 52GDocument3 pagesTec Relay 52Gimmer nainggolanNo ratings yet
- Knowing Annelida: Earthworms, Leeches and Marine WormsDocument4 pagesKnowing Annelida: Earthworms, Leeches and Marine WormsCherry Mae AdlawonNo ratings yet
- Palm Wine SpecificationDocument10 pagesPalm Wine SpecificationUday ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 500 Important Spoken Tamil Situations Into Spoken English Sentences SampleDocument7 pages500 Important Spoken Tamil Situations Into Spoken English Sentences SamplerameshdurairajNo ratings yet
- 4608 Eed 01Document29 pages4608 Eed 01NickNo ratings yet
- 5s OfficeDocument10 pages5s OfficeTechie InblueNo ratings yet
- Sony HCD-GTX999 PDFDocument86 pagesSony HCD-GTX999 PDFMarcosAlves100% (1)
- Blood Group 3Document29 pagesBlood Group 3Hamirie JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Poultry DiseasesDocument5 pagesPoultry DiseasesAnjum IslamNo ratings yet
- Director's Report Highlights Record Wheat Production in IndiaDocument80 pagesDirector's Report Highlights Record Wheat Production in Indiakamlesh tiwariNo ratings yet
- SC Earthquake GuideDocument8 pagesSC Earthquake GuideNevin SmithNo ratings yet
- Vishwabhanu Oct '18 - Jan '19Document26 pagesVishwabhanu Oct '18 - Jan '19vedicvision99100% (3)
- Qualtrics Ebook Employee Lifecycle Feedback Apj - q8uL5iqE4wt2ReEuvbnIwfG4f5XuMyLtWvNFYuM5Document18 pagesQualtrics Ebook Employee Lifecycle Feedback Apj - q8uL5iqE4wt2ReEuvbnIwfG4f5XuMyLtWvNFYuM5RajNo ratings yet
- Arta Fridei Kahlo A Fost Intotdeauna o ReactieDocument13 pagesArta Fridei Kahlo A Fost Intotdeauna o ReactieAlta DaianNo ratings yet
- Fajar Secondary Sec 3 E Math EOY 2021Document16 pagesFajar Secondary Sec 3 E Math EOY 2021Jayden ChuaNo ratings yet