Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Kinetics CBSE Class XII Notes
Uploaded by
Rahul SharmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Kinetics CBSE Class XII Notes
Uploaded by
Rahul SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Kinetics
1. Chemical reaction : - Fast ionic NaOH + HCl ---> NaCl + H2 Rate cannot be calculated
Slow Rusting of iron
(reversible) Moderate rate reaction
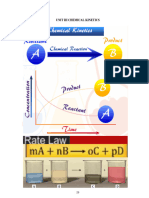
2. For chemical reaction aA + bB cC + dD
Average Rate r= = mol L
-1
S
-1
for A ------> B r = [ -ve sign for decrease in concentration ]
3. Reaction life time: - Time to complete 98% reaction.
4. Instantaneous rate: - Rate at given instant of time is called instantaneous rate and found
graphically. Represented by slope of graph.
For Reactant For Product
5. Homogeneous Reaction : - Reactant and catalyst in same phase.
SO2(g) + O2(g) ---[NO]-----> SO3(g)
6. Heterogenous Reaction : - Reaction and catalyst in different phase.
SO2(g) + O2(g) -------V2O5(s)-----> SO3
7. Effective collision : - Collision of reactant molecules which bring chemical change
8. Threshold energy: - Minimum energy to bring chemical change.
9. Activation Energy (Ea) : - Minimum energy to be supplied externally to start a reaction.
Ea = Eth - ER
ER Energy required to form intermediate [ activated complex]
10. Law of mass action : - r = k [A]
a
[B]
b
[a, b are coefficient in balanced chemical reaction].
11. Rate law expression : - Rate of chemical reaction determined experimentally i.e dependence of
rate on concentration of reaction raised to power determined experimentally.
r = K [A]
x
[B]
y
x = order of reaction with respect to [A] x, y may or may not be
y= order of reaction with respect to [B] equal to stoichiometric
x + y = overall order of reaction coefficient
12. Rate constant :- If [A] = [B] = 1mol L
-1
r = K i.e rate constant is equal to rate of reaction
when conc. of reactants = 1mol L
-1
13. Unit of rate constant : - K = r/[R]
n
= mol L
-1
S
-1
/ [mol L
-1
]
n
for zero order = mol L
-1
S
-1
for I order = S
-1
S
-1
always comes
for II order = mil L S
-1
14. Zero order reaction :- Rate does not depend on conc. of reactant.
H2 + Cl2 ---hv---> 2HCl
15. Negative order reaction : - Rate decreases on increasing conc.
2O3 ----> 3O2
16. Fraction order reaction : - H2 + Br2 ------> 2HBr r = k [H2] [Br]
1/2
17. Molecularity: - No of [R] collide simultaneously to bring chemical change in elementary
reaction is called molecularity.
Uni molecular NH4NO2 ----> N2 + 2H2O
Bi molecular 2HI --------> H2 + I2
18. Complex reaction: - Reaction which has molecularity more than 2 and proceed through more
than one step. Slowest step is rate determination step.
e.g. 2NO2 + F2 ---> 2NO2F
Rate law given r = K [NO2] [F2]
Mechanism NO2 + F2 ----slow----> NO2F + F Given, NO2 + F2 ----slow----> NO2F + F
NO2 + F ------fast----> NO2F NO2 + F ------fast----> NO2F
2NO2 + F2 ------> 2NO2F
r = K [NO2] [F2]
19. Integrated rate equation: - Equation give relation b/w rate constant, time and conc. of [R]
calculated by integration is called integrated rate equation.
r = K [A]
n
equate for zero order K = ([R]o [R])/t , t
= [R]o/2K
r = - dA/dt & integrate, const. = c for Ist order K = (2.303/t)log[R]o/[R]t
at t = 0 [R] = [R]o t
= 0.693/K, not depend on conc. of R
20.
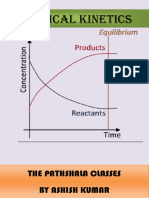
Graph b/w ln[R] and t Graph b/w log [R]0/[R]
21. Pseudo first order reaction : - Chemical reaction has two [R] but rate depend on only one [R],
since other is in excess is called pseudo first order reaction.
e.g. CH3COOC2H5 + H2O ----H+------> CH3COOH + C2H5OH
r = K
I
[CH3COOC2H5] [H2O] = K [CH3COOC2H5] i.e K = K
I
[H2O]
22. Half life of a n
th
order reaction : -
t
1/ [R]0
n-1
Therefore, for zero order t
[R]0
n-1
for first order t
independent of conc.
for second order t
1/[R]o
23. Arrhenius Equation : - Give relation b/w rate constant and temp.
On increasing temperature by 10
0
[10K] rate constant becomes double.
K = A . e
-Ea/RT
lnK = lnA (Ea/RT) lne , where ln = loge
lnK = lnA (Ea/RT) / logK = logA Ea/2.303RT
logK2/K1 = Ea/2.303R[1/T1 1/T2]
24. Effect of catalyst : -
(i) Lower Ea by providing alternate path
(ii) Do not change Kc since rf = rb
(iii) Do not change G
(iv) Work for only spontaneous reaction
25. Fraction of molecule having E equal to or greater than Ea
x = e
-Ea/RT
/ ln x = -Ea/RT / log x = -Ea/2.303RT
26. Collision theory for reaction rate : -
(i) A reaction occur on proper collision of two molecules if posses E >= Ea i.e if they have no
proper orientation reaction not take place.
e.g. CH3Br + OH- ------> CH3OH + Br
-
(ii) If improper orientation
(iii) According to collision theory expression for rate of a reaction
r = PZABe
-Eo/RT
, P = Probability of orientation factor ZAB = frequency factor
Ea = activation energy, R = 8.314 , T = temperature
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-3Document17 pagesChemical Kinetics-3Ashutosh KunwarNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate .2Document35 pagesReaction Rate .2ClosuNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesChemical Kineticsworkup366No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-12Document18 pagesChemical Kinetics-12Manas ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Document10 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Gaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry: Course No.: CH 101Document14 pagesDepartment of Chemistry: Course No.: CH 101liz_hobbs79No ratings yet
- Kinetika KimiaDocument35 pagesKinetika Kimiablank-56No ratings yet
- Document From JenDocument51 pagesDocument From JenAksh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument41 pagesChemical Kineticskishangopi1230% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics: Rate of Reaction MechanismDocument60 pagesChemical Kinetics: Rate of Reaction MechanismAneudis Javier BritoNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Reaction KineticsDocument142 pages1.0 Reaction KineticsKhairul Aswari Ab RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 - Chemical - Kinetics (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocument40 pagesChapter - 13 - Chemical - Kinetics (Compatibility Mode) PDFLel Lailiy100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics: Chung (Peter) Chieh Professor of Chemistry University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, CanadaDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics: Chung (Peter) Chieh Professor of Chemistry University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canadadescar84No ratings yet
- Chem Kine SulDocument4 pagesChem Kine SulChutvinder LanduliyaNo ratings yet
- Chem Chapt13 PractiseDocument5 pagesChem Chapt13 PractiseqwerNo ratings yet
- Chapt05 Lecture SsDocument48 pagesChapt05 Lecture SsLiky LeeNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument27 pagesChemical KineticsRoshen RonyNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument20 pagesDefinitionsudipta chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticszzDocument29 pagesChemical KineticszzfailurewasteworthlessNo ratings yet
- MAXIMUM MARKS REVISION MODULEDocument26 pagesMAXIMUM MARKS REVISION MODULEKRITHIKA .MNo ratings yet
- DP Chemical KineticsDocument32 pagesDP Chemical KineticsAniket RayNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument22 pagesChemical Kineticspragun0507No ratings yet
- 13lectureppt 101122094708 Phpapp01Document41 pages13lectureppt 101122094708 Phpapp01Salim Ahmad Salim AlirajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 (Kinetics)Document9 pagesChapter 16 (Kinetics)Richard KimNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument23 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Chemical Kinetics PDFAshika D ChandavarkarNo ratings yet
- 22 00 14 11 12 2023 Doc-20220901-Wa0007.Document9 pages22 00 14 11 12 2023 Doc-20220901-Wa0007.hmegm123No ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Slides Kinetics Week 5-2 PDFDocument34 pagesLecture 14 Slides Kinetics Week 5-2 PDFSam YuritrevNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionsDocument51 pagesRate of ReactionsEisa IshaqzaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 KineticsDocument69 pagesChapter 5 KineticsexpertwritersNo ratings yet
- Feb2020-Chuong4-Toc Do Va Co Che Phan Ung Hoa HocDocument36 pagesFeb2020-Chuong4-Toc Do Va Co Che Phan Ung Hoa HocHồng NgọcNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Unit IDocument43 pagesChemical Kinetics: Unit IEanna Jullienne UyvicoNo ratings yet
- SCH 305Document34 pagesSCH 305Qwin NajyaNo ratings yet
- Unit-7 Chemical Kinetics 2023Document13 pagesUnit-7 Chemical Kinetics 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Chemical Kinetics NotesDocument6 pagesZumdahl Chemical Kinetics NotesMalletNjonkemNo ratings yet
- Notes Chemical KineticsDocument17 pagesNotes Chemical KineticsAMAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- Explain Reaction MechanismDocument5 pagesExplain Reaction MechanismQuynh NhuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Kineticsnadeemnagthan008No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document32 pagesChapter 4Nguyen NhatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry [PDF]Document13 pagesChemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry [PDF]shubhamgajraj5566No ratings yet
- 2.kinetics Homogenous ReactionsDocument33 pages2.kinetics Homogenous ReactionsArief Al Imam HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics: ConceptDocument23 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Kinetics: ConceptRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: General Chemistry 2Document27 pagesChemical Kinetics: General Chemistry 2France TurdaNo ratings yet
- Laju Reaksi PDFDocument9 pagesLaju Reaksi PDFHafsemi RapsanjaniNo ratings yet
- A2 Chemistry Unit 4 NotesDocument27 pagesA2 Chemistry Unit 4 NotesRebecca78% (9)
- Chapter 6Document46 pagesChapter 6Yahya Alhaddi KA201 18No ratings yet
- Chap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRADocument129 pagesChap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRA黄麒安No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Gist of The LessonDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics: Gist of The Lessonanshikahp1No ratings yet
- Kinetics ReactionDocument40 pagesKinetics ReactionSohila A. MabroukNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Rate EquationsDocument20 pagesChemical Kinetics Rate EquationsShimon LalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Level N Chapter 12 BQ-AK 2223Document19 pagesChemistry Level N Chapter 12 BQ-AK 2223Dema IhabNo ratings yet
- CHM096 1 Chem Kinetics RMDocument100 pagesCHM096 1 Chem Kinetics RMAinul AqilaNo ratings yet
- CHPR4406 Reactions Lecture 1Document16 pagesCHPR4406 Reactions Lecture 1xx_aleksa_hrvatska_xxNo ratings yet
- Content Marketed & Distributed By: Chemical KineticsDocument9 pagesContent Marketed & Distributed By: Chemical KineticsPrithviraj NetkeNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument8 pagesChemical KineticsSnehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- 11 Reaction KineticsDocument95 pages11 Reaction KineticsSyamil Adzman100% (1)
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- Boundary Value Problems: Dr. Suresh Kumar, BITS PilaniDocument11 pagesBoundary Value Problems: Dr. Suresh Kumar, BITS PilaniRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- C5 PDFDocument16 pagesC5 PDFRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Some Special Functions: Dr. Suresh Kumar, BITS PilaniDocument14 pagesSome Special Functions: Dr. Suresh Kumar, BITS PilaniRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Systems of First Order DE Solutions GuideDocument9 pagesSystems of First Order DE Solutions GuideRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- C4 PDFDocument8 pagesC4 PDFRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Second Order DE Solutions and MethodsDocument16 pagesSecond Order DE Solutions and MethodsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- C1 PDFDocument6 pagesC1 PDFRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- C9 PDFDocument14 pagesC9 PDFRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- C6 PDFDocument8 pagesC6 PDFRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument34 pagesThermodynamicsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solving First Order Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesSolving First Order Differential EquationsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Class 12 CbseDocument8 pagesAldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Class 12 CbseRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Xam Idea ChemDocument331 pagesXam Idea ChemLokesh Badpanda86% (7)
- KVS Junior Mathematics Olympiad (JMO) - 2002Document5 pagesKVS Junior Mathematics Olympiad (JMO) - 2002puneethnjnpNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes and ArenesDocument8 pagesHalo Alkanes and ArenesRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions1Document18 pagesRedox Reactions1Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument4 pagesRedox ReactionsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Classification and NomenclatureDocument20 pagesChemistry - Classification and NomenclatureDevesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- General Principles and Process of Isolation of ElementsDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles and Process of Isolation of ElementsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Surface ChemistryDocument4 pagesSurface ChemistryRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- The RC CircuitDocument2 pagesThe RC CircuitRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Complex Number MCQDocument7 pagesMathematics Complex Number MCQRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Fistful of BeerDocument30 pagesA Fistful of BeerSteven SchaefferNo ratings yet
- Ares Shrike 5 56 Manual Ver1 1Document50 pagesAres Shrike 5 56 Manual Ver1 1hodhodhodsribd50% (2)
- A320 Limitations Summary Aug 2012Document2 pagesA320 Limitations Summary Aug 2012Bobi Guau100% (14)
- ISTAR Facilities (5e) PDFDocument12 pagesISTAR Facilities (5e) PDFfrankling91No ratings yet
- IVERSEN RUNDOLMO - Driving and PersonalityDocument13 pagesIVERSEN RUNDOLMO - Driving and PersonalityNela Nevena AndjelkovićNo ratings yet
- AutoLink Instruction ManualDocument17 pagesAutoLink Instruction ManualtunghtdNo ratings yet
- Prezentacija en 1317Document25 pagesPrezentacija en 1317Amir HafizovićNo ratings yet
- Magazine 1Document25 pagesMagazine 1Bouw NummerNo ratings yet
- Atr 72-500 Pilot HandbookDocument27 pagesAtr 72-500 Pilot HandbookFredyRedDevilz88% (8)
- Design and Implementation of Smart Black Box System For Gathering The Safety Information in VehiclesDocument2 pagesDesign and Implementation of Smart Black Box System For Gathering The Safety Information in VehiclesAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Active Passive FarhanDocument17 pagesActive Passive Farhanmian saadNo ratings yet
- Probability Quiz Problems Coin Tosses Jobs TV Shows Poisson DistributionDocument3 pagesProbability Quiz Problems Coin Tosses Jobs TV Shows Poisson DistributionnaimNo ratings yet
- Offshore Helicopter SafetyDocument25 pagesOffshore Helicopter SafetyChirca FlorentinNo ratings yet
- Combine The Sentences To Form The Past, Unreal ConditionalDocument33 pagesCombine The Sentences To Form The Past, Unreal ConditionalMarco Aurelio Atencio MuñozNo ratings yet
- Willys Jeep GuideDocument13 pagesWillys Jeep GuideJonathan Javier Olivero Gomez100% (1)
- AC Explorac 220 RC SpecificationDocument94 pagesAC Explorac 220 RC Specificationவிமல் அந்தோணி83% (6)
- Aircraft Crash Site ProceduresDocument26 pagesAircraft Crash Site ProceduresCAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- The Railway ChildrenDocument5 pagesThe Railway ChildrenLove Purple100% (1)
- Three Injured in Crash Near Route 9Document5 pagesThree Injured in Crash Near Route 9Laura Peters ShapiroNo ratings yet
- DRIVER TRAINING KIYONDocument52 pagesDRIVER TRAINING KIYONRizwan Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Emergency Response ChecklistDocument5 pagesEmergency Response ChecklistNiel Brian VillarazoNo ratings yet
- Filamer v. IAC DigestDocument2 pagesFilamer v. IAC DigestFrancis Guinoo100% (1)
- Chandu AviationDocument37 pagesChandu Aviationsk_sahu88No ratings yet
- ComAir Flight 5191Document3 pagesComAir Flight 5191Rajat JainNo ratings yet
- Frano Selak 'World's Luckiest Man' Gives Away His Lottery FortuneDocument2 pagesFrano Selak 'World's Luckiest Man' Gives Away His Lottery FortuneAna MarijaNo ratings yet
- Art PractDocument2 pagesArt PractFeny Martina, M.PdNo ratings yet
- Disaster MX - Overview of Disaster Management and MCIDocument94 pagesDisaster MX - Overview of Disaster Management and MCIdrnikahmadNo ratings yet
- EnglishhhDocument4 pagesEnglishhhAlbar Muhammad Aziz50% (2)
- MH370 Search Effort Swings Towards Finding Black BoxesDocument4 pagesMH370 Search Effort Swings Towards Finding Black BoxesThavamNo ratings yet





































![Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry [PDF]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/722192383/149x198/88182f919d/1712866381?v=1)