Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio 5.2
Uploaded by
zwindows123456789Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio 5.2
Uploaded by
zwindows123456789Copyright:
Available Formats
105
1. 1990/I/5b
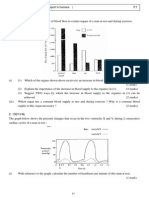
In an experiment to study the sensitivity of different parts of the skin touch, student X used a felt pen to
mark out an area on a certain part of the skin of student Y as shown in the diagram above. While student Y
was blindfolded, student X used a pin to touch gently every mark on the test region. Student Y would say
'yes' if he felt the touch. The percentage of positive responses (that is, when student Y could feel the touch)
was recorded. The experiment was then repeated on different regions of the skin and the results are
summarized as below :
(i) Which of the tested regions was most sensitive to touch ? (1 mark)
(ii) Why was student Y unable to feel the touch of the pin on some occasions during the experiment ?
(1 mark)
(iii) Describe the nervous pathway that enables student Y to feel the touch and to speak out. (4 marks)
(iv) At one point during the experiment, student X carelessly applied a strong force on the pin and student
Y withdrew his hand immediately.
(1) Name this type of response. (1 mark)
(2) This type of response usually occurs very rapidly. What is the significance of this characteristic ?
(1 mark)
(3) State ANOTHER characteristic of this type of response. (1 mark)
Region of skin Percentage of positive responses
back of hand
palm of hand
fingertip
forearm
50
85
100
75
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 5.2 Nervous coordination in humans | P.1
106
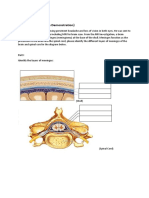
2. 1991/I/5ai(1),ii
The diagram below shows the cross section of a human spinal cord and the nervous supply to the arm :
(i) If the hand touches a hot object accidentally, the hand will withdraw from it immediately.
(1) What happens to the effector muscle in this response ? (1 mark)
(ii) Three men (X, Y and Z) were injured in a traffic accident. A doctor found out that their brains were
still functioning normally. He then conducted further test to check if there was any damage to other
parts of their nervous systems.
Man Test(s) conducted with the eyes of the patients
blindfolded
Observations
X Xs finger tip was pricked by a pin X felt the pain but he did not
withdraw his hand
Ys finger tip was pricked by a pin Y could not feel the pain and did not
withdraw his hand
Y
Y was asked to move his hand Y could move his hand
Z Zs finger tip was pricked by a pin Z withdrew his hand but he was
unaware of the touch and the
withdrawal of his hand
Which part of the nervous system was most likely damaged in X, Y and Z respectively ? Explain your
answer in each case. (8 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 5.2 Nervous coordination in humans | P.2
107
3. 1993/I/3ai,iii
Two patterns of response shown by the human body towards stimuli of different nature are outlined below :
(i) Referring to the specific cell types involved, describe the sequence of events that leads to the
withdrawal of the foot. (4 marks)
(iii) With reference to the mechanisms involved, explain why the response in pattern A occurs much
faster than that in pattern B. (2 marks)
4. 1995/I/3b
The diagram below shows the arrangement of some neurones in man:
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 5.2 Nervous coordination in humans | P.3
108
(i) Using numbers in the diagram, indicate the pathways of nerve impulses that bring about
(1) the withdrawal reflex of the arm. (1 mark)
(2) the voluntary action of the arm. (1 mark)
(ii) State two differences between reflex actions and voluntary actions. (2 marks)
(iii) For parts A, B and C of the brain, state and explain one role that each plays when a man is riding a
bicycle. (6 marks)
5. 2000/I/2biii
The pupil response to light intensity is a reflex action coordinated by the brain. By means of a flowchart,
show the nervous pathway involved.
(Hint : This nervous pathway is similar to that of a spinal reflex arc.) (3 marks)
6. 2003/I/1av
Which part of the brain controls the breathing rate ? (1 mark)
7. 2003/I/3aii(2-3)with Q
The diagram below shows a section of the human eye :
(ii) (2) State the type of response illustrated by the constriction of B. (1 mark)
(3) The person also puts on his glasses. With regard to the nature of the response, state two ways in
which this action is different from the constriction of B. (2 marks)
8. 2004/I/2c
Irritability is the ability of an organism to respond to an external stimulus. Most cases of irritability work in
the following pattern :
Below are three examples of irritability in humans :
(I) Secretion of saliva when food is ingested
(II) Constriction of pupil under bright light
(III) Running out of the classroom upon hearing the fire alarm
(i) For case I, state the receptor and effector involved. (2 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 5.2 Nervous coordination in humans | P.4
109
(ii) Based on the above pattern, use a flowchart to show the nervous pathway for case II, including the
types of neurones involved. (3 marks)
(iii) (1) Name the region of the brain where the coordinating centre for case III is located. (1 mark)
(2) State two features of the responses controlled by this region. (2 marks)
9. 2006/I/3
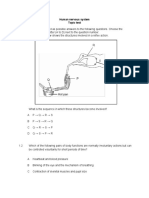
The figure below shows a magnetic resonance image of the lateral side of the upper body of a person:
(a) Name structure X and state its function. (2 marks)
(b) What is the importance of structure Z to structure Y? (1 mark)
(c) The diagram below shows the transverse section of structure Y and an outline of the arm:
On the above diagram, draw the reflex arc for the withdrawal reflex of the arm and label the different
components of the reflex arc. (4 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 5.2 Nervous coordination in humans | P.5
110
10. 2008/I/2
The photograph below shows the lateral view of a human brain.
(a) The surface of structure X is highly folded. What is the significance of this feature? (1 mark)
(b) Name structure Y and state one of its functions. (2 marks)
(c) A patient who suffered from a stroke was diagnosed to have part of area A damaged. After the stroke, it
was found that he had difficulty in moving his arm. What is area A? (1 mark)
(d) Area B is located behind area A. What is area B? (1 mark)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 5.2 Nervous coordination in humans | P.6
You might also like
- Instant Healing Meditation (Basic) - David Alan RamsdaleDocument31 pagesInstant Healing Meditation (Basic) - David Alan Ramsdaledeichem88% (8)
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesMyocardial InfarctionLetecia MooreNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Anatomy PastDocument21 pages1st Year Anatomy PastNaveed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response - M.C.Q Worksheet 1 - Grade 9Document3 pagesCoordination and Response - M.C.Q Worksheet 1 - Grade 9Minahil Javed100% (1)
- D.P.M. & M.D. Psychiatry PapersDocument11 pagesD.P.M. & M.D. Psychiatry PapersRamashanker YadavNo ratings yet
- Emergency Response Drill Scenarios 1Document10 pagesEmergency Response Drill Scenarios 1Arfiyunanto Malika50% (4)
- 1st Year MBBS Question Papers RGUHS 2021Document10 pages1st Year MBBS Question Papers RGUHS 2021Gaurav parashar100% (1)
- Anatomy 2009-2018 PastPapers PDFDocument32 pagesAnatomy 2009-2018 PastPapers PDFYasif AbbasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Anchorage in OrthodonticsDocument8 pagesSkeletal Anchorage in OrthodonticsNingombam Robinson SinghNo ratings yet
- IVD Medical Device V2Document44 pagesIVD Medical Device V2Vadi VelanNo ratings yet
- Kansas Foodborne Illness ManualDocument186 pagesKansas Foodborne Illness ManualLeo M. Pedro Jr.No ratings yet
- Coordiantion in Humans LQ - Q&ADocument15 pagesCoordiantion in Humans LQ - Q&AChan Chun YanNo ratings yet
- CoordinationDocument5 pagesCoordinationKin Sana HlaingNo ratings yet
- Bio5 2Document10 pagesBio5 2HarmonyChuiNo ratings yet
- MBM1101201301 Anatomy - Paper 1Document5 pagesMBM1101201301 Anatomy - Paper 1fyi fyiNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1Document8 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1Arokia RajNo ratings yet
- St. Paul's Convent School F.4 IGCSE Chapter 6 &12 QuizDocument5 pagesSt. Paul's Convent School F.4 IGCSE Chapter 6 &12 Quizonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly 23-24 Grade 5 - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly 23-24 Grade 5 - Answer KeyshamshadNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Specialist Biology Practice TestDocument7 pagesYear 10 Specialist Biology Practice TestSahana MEENACHISUNDARAMNo ratings yet
- Mini-Presentation 2 - Student Version (2021-2022 Revised)Document7 pagesMini-Presentation 2 - Student Version (2021-2022 Revised)陳憬熹No ratings yet
- 09 Sci GEP 1 EYEDocument4 pages09 Sci GEP 1 EYEprameetaNo ratings yet
- LXER - Gr12LifeSciences - The Human Eye and Ear - Nov2014Document10 pagesLXER - Gr12LifeSciences - The Human Eye and Ear - Nov2014Nicole Paul100% (1)
- Biology Nervous System Worksheet 1 and SolutionsDocument4 pagesBiology Nervous System Worksheet 1 and SolutionsNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Biology Tutorial Sheet g12 PDFDocument7 pagesBiology Tutorial Sheet g12 PDFSomebodyNo ratings yet
- 14.4 Coordination - and - Response - Igcse Cie Biology - Ext Theory QPDocument11 pages14.4 Coordination - and - Response - Igcse Cie Biology - Ext Theory QPBk FazalNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Causes of Vertical Diplopia - Red Flag or Muscle WeaknessDocument15 pagesUnderstanding The Causes of Vertical Diplopia - Red Flag or Muscle WeaknessdwongNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDocument7 pagesBiology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedoyooNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDocument7 pagesBiology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedOchieng WilberforceNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemKin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Assgt Biology-Form-1-End-Term-1-2020 PDFDocument8 pagesAssgt Biology-Form-1-End-Term-1-2020 PDFAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Transport in Mammals: 1989 Paper 2 Question 6Document21 pagesTransport in Mammals: 1989 Paper 2 Question 6Kin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Biology TheoryDocument13 pagesBiology TheoryZaw Linn PhyoNo ratings yet
- File 1676991736Document1 pageFile 1676991736anshag631No ratings yet
- Chapter 24. Sense Organs: ObjectivesDocument25 pagesChapter 24. Sense Organs: ObjectivesFrancisco GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Suprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Document7 pagesSuprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Yumna Sa'diyyahNo ratings yet
- Reflex Activities PART I. Reflexes and Reflex Arcs (Exercise 17, P. 309)Document9 pagesReflex Activities PART I. Reflexes and Reflex Arcs (Exercise 17, P. 309)shanoiapowelllNo ratings yet
- NSSBIO3E Cross Topic Ex III eDocument22 pagesNSSBIO3E Cross Topic Ex III ekatie yuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination PYQsDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Control and Coordination PYQsrohanmurali8No ratings yet
- II Sessional Q Paper MangaluruDocument2 pagesII Sessional Q Paper MangaluruAditya SahNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-FORM-1 AbubaydaDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY-FORM-1 AbubaydaHaron HB WritersNo ratings yet
- Ch-7 Control and Coordination (40marks)Document1 pageCh-7 Control and Coordination (40marks)sha.pratibha2016No ratings yet
- 10 - Coordination NotesDocument3 pages10 - Coordination NotesAlfred MwayutaNo ratings yet
- Bio F2 MSDocument8 pagesBio F2 MSsolutiongrandtechNo ratings yet
- Form 1 The Cell Questions Teacher - Co .KeDocument3 pagesForm 1 The Cell Questions Teacher - Co .Kelydiaciru01No ratings yet
- 8th Biology Paper FinalDocument4 pages8th Biology Paper FinalNimbusNo ratings yet
- 1ST Proff MBBS Papers (2021-11)Document66 pages1ST Proff MBBS Papers (2021-11)drbishalchowdhury13No ratings yet
- F1 Endterm 2 AssignmentDocument75 pagesF1 Endterm 2 AssignmentDavid AdikaNo ratings yet
- Bio F2 QSDocument9 pagesBio F2 QSsolutiongrandtechNo ratings yet
- MPT Sports RevisionDocument15 pagesMPT Sports RevisionShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Human Biology Question Paper Igcse 9-1Document61 pagesHuman Biology Question Paper Igcse 9-1naduniNo ratings yet
- Biology PaperDocument6 pagesBiology PaperSuvadip SanyalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Lab) SRN To BSC Nursing Students Instruction: Answer All Questions Lecturer: MR Abdulai Bangura Time: 1hour 30minutesDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (Lab) SRN To BSC Nursing Students Instruction: Answer All Questions Lecturer: MR Abdulai Bangura Time: 1hour 30minutesBangso AbubakarrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MUHS PAPERSDocument26 pagesAnatomy MUHS PAPERSJayesh PawarNo ratings yet
- B10. CoordinationDocument8 pagesB10. CoordinationnienaNo ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1Document10 pagesHkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- 1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Document23 pages1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Kin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology (Theory)Document4 pages11 Biology (Theory)Rudrangshu OjhaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya SangathanDocument4 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya SangathanAdi KumarNo ratings yet
- S1 Science Rev Ex Unit 5 - EnergyDocument3 pagesS1 Science Rev Ex Unit 5 - Energy7pn22drrqxNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2011 PDFDocument9 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2011 PDFmohammedNo ratings yet
- Class XI Annual - 2022-23Document6 pagesClass XI Annual - 2022-23Farhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Control and Coordination Test 05Document1 page10 Science Control and Coordination Test 05Abhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- 1st Internals 21-22 BatchDocument3 pages1st Internals 21-22 BatchnarayanjarvisNo ratings yet
- Ch.17 Movements in Humans (Stud Version)Document25 pagesCh.17 Movements in Humans (Stud Version)吴昊No ratings yet
- Human Nervous System Topic TestDocument5 pagesHuman Nervous System Topic TestSthockzin EntNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IDocument36 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - Izwindows123456789No ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IIDocument21 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IIFelix YueNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IIDocument20 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IISabrina WongNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry + Coordinate Geometry - QDocument11 pagesPlane Geometry + Coordinate Geometry - Qzwindows123456789No ratings yet
- As & GS - Q PDFDocument12 pagesAs & GS - Q PDFPeter ChanNo ratings yet
- 2005 AL Chemistry Paper 2Document10 pages2005 AL Chemistry Paper 2zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Econ 1.2Document1 pageEcon 1.2zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1Document10 pagesHkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- Bio 5.3Document3 pagesBio 5.3Michelle ChanNo ratings yet
- Econ 1.1Document4 pagesEcon 1.1zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 8.2Document10 pagesBio 8.2zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 8.1Document2 pagesBio 8.1zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 8.3Document3 pagesBio 8.3zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 8.4 Genetic Engineering - P.1Document1 pageHkcee Biology - 8.4 Genetic Engineering - P.1zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 7.4Document4 pagesBio 7.4zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1Document1 pageHkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- HKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1Document6 pagesHKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- Bio 6.1Document6 pagesBio 6.1zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 6.4Document3 pagesBio 6.4zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1Document13 pagesHkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- Bio 5.4Document3 pagesBio 5.4zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 6.2Document3 pagesBio 6.2zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 5.1Document5 pagesBio 5.1zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1Document5 pagesHkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- Bio 3.1Document7 pagesBio 3.1zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1Document7 pagesHkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- Bio 4.4Document8 pagesBio 4.4zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio 4.2Document13 pagesBio 4.2zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Bio Past PaperDocument6 pagesBio Past Paperzwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Perbedaan Kadar Hbsag Sampel Serum Dan Plasma Metode Clia Pada PendonorDocument7 pagesPerbedaan Kadar Hbsag Sampel Serum Dan Plasma Metode Clia Pada PendonorAAK DHGRiski MaulanaNo ratings yet
- DSWD Guidelines For Residential FacilitiesDocument12 pagesDSWD Guidelines For Residential FacilitiesCharlene Ordoñez Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PG Regulations AmendmentsDocument29 pagesPG Regulations Amendmentsdrtpk100% (1)
- Drugs Study ER LEAD Drug (Yntig)Document5 pagesDrugs Study ER LEAD Drug (Yntig)Herbert Almendras HuyoNo ratings yet
- FD PDFDocument580 pagesFD PDFAinul LuthfiNo ratings yet
- Lab Scientist Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesLab Scientist Job DescriptionRajeev PareekNo ratings yet
- PhilHealth Circular 35 S. 2013 PDFDocument17 pagesPhilHealth Circular 35 S. 2013 PDFNomad's CastleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Marketing Department: Company 1-Apollo Hospitals Enterprises LTD (Apollo)Document20 pagesChapter 4 Marketing Department: Company 1-Apollo Hospitals Enterprises LTD (Apollo)TYB92BINDRA GURSHEEN KAUR R.No ratings yet
- Republic of Kenya: Application For Registration of A Health InstitutionDocument13 pagesRepublic of Kenya: Application For Registration of A Health InstitutionianNo ratings yet
- Mediware Information Systems, Inc. (MEDW) - Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare - Deals and Alliances ProfileDocument34 pagesMediware Information Systems, Inc. (MEDW) - Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare - Deals and Alliances ProfileFithriani SaragihNo ratings yet
- 香港脊醫 Hong Kong Chiropractors Dec 2017Document10 pages香港脊醫 Hong Kong Chiropractors Dec 2017CDAHKNo ratings yet
- PR Ke-2Document2 pagesPR Ke-2Maulia IsnainiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Test Science 5Document7 pages2nd Grading Test Science 5LeonorBagnisonNo ratings yet
- Hemophilia: Factor IX (Hemophilia B)Document38 pagesHemophilia: Factor IX (Hemophilia B)Jhvhjgj JhhgtyNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank GuidelinesDocument10 pagesBlood Bank Guidelinesmanjinder singhNo ratings yet
- Alcoholnew 120916093616 Phpapp02 PDFDocument82 pagesAlcoholnew 120916093616 Phpapp02 PDFNihal S KiranNo ratings yet
- Best Evidence Statement (Best)Document6 pagesBest Evidence Statement (Best)AleCsss123No ratings yet
- AOS Injury Classification Systems Poster THORACOLUMBARDocument1 pageAOS Injury Classification Systems Poster THORACOLUMBARWilliams Maita GallardoNo ratings yet
- 4th Regional Pneumococcal Symposium - DownloadableDocument64 pages4th Regional Pneumococcal Symposium - DownloadablesabinvaccineNo ratings yet
- Research Sa Chem Trabaho'a Na!Document14 pagesResearch Sa Chem Trabaho'a Na!NoellhaJeanetteGabeLiwagonNo ratings yet
- Mendiguchia 2012 Rectus Femoris Muscle Injuries in Football-A Clinically Relevant Review of Mechanisms of Injury, Risk Factors and Preventive Strategies PDFDocument11 pagesMendiguchia 2012 Rectus Femoris Muscle Injuries in Football-A Clinically Relevant Review of Mechanisms of Injury, Risk Factors and Preventive Strategies PDFJuan PalomoNo ratings yet
- List of Instruments For 2nd Year BDSDocument17 pagesList of Instruments For 2nd Year BDSMohammad ShoebNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument47 pagesHistoryRajesh IthaNo ratings yet
- عملیات شفاء امراض Amliyat Shifa Amraz 0091-33-23607502 - DIL KE AMRAZ KA RUHANI ELAJ (Spiritual Treatment of Heart Diseases)Document4 pagesعملیات شفاء امراض Amliyat Shifa Amraz 0091-33-23607502 - DIL KE AMRAZ KA RUHANI ELAJ (Spiritual Treatment of Heart Diseases)msmpaki@yahoo.comNo ratings yet