Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Auditing Information Systems Process
Uploaded by
yasir_sameemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Auditing Information Systems Process
Uploaded by
yasir_sameemCopyright:
Available Formats
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
MohammadTohidurRahmanBhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,MCSD,A+,CSCF
TheProcessofAuditing
InformationSystems
Outof05Domains,it
covers14%
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Introduction
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
CourseAgenda
LearningObjectives
DiscussTaskandKnowledgeStatements
Discussspecifictopicswithinthechapter
Casestudies(individualPracticefollowCRM)
Samplequestions(individualPracticefollowCRM)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ExamRelevance
Ensurethat theCISA candidate
Provide audit services in accordance with IT audit standards to
assist theorganizationinprotectingandcontrollinginformationsystems.
The content area in this chapter will represent approximately
14%of theCISA examination(approximately28questions).
(CRM Pages: XX
Up to 2010 From 2011
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Task& KnowledgeStatements
Task and knowledge statements represent the basis
fromwhichexamitemsarewritten.
Tasks: Tasks are the learning objectives that IS
auditors/CISA candidates are expected to know to
performtheir jobduties.
knowledge statements: In order to performall of the
tasks, theISauditor/CISA candidateshouldhaveafirm
graspof all theknowledgestatements containedwithin
theCISA ReviewManual Chapter 1.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Tasks/ Objectives
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ProcessAreaTasks
FiveTasks:
1.1 Develop and implement a riskbased IT audit strategy in
compliance with IT audit standards to ensure that key areas are
included.
1.2 Plan specific audits to determine whether information systems
are protected, controlled and provide value to the organization.
1.3 Conduct audits in accordance with IS audit standards, guidelines
and best practices to meet planned audit objectives.
1.4 Communicate emerging issues, potential risks, and audit results
to key stakeholders.
1.5 Advise on the implementation of risk management and control
practices within the organization, while maintaining independence.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Knowledge Statements
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ProcessAreaKnowledgeStatements
TenKnowledgeStatements(contd.):
1.1 Knowledge of ISACA IT Audit and Assurance Standards,
Guidelines and Tools and Techniques, Code of Professional Ethics
and other applicable standards
1.2 Knowledge of risk assessment concepts, tools and techniques
in an audit context
1.3 Knowledge of control objectives and controls related to
information systems
1.4 Knowledge of audit planning and audit project management
techniques, including followup
1.5 Knowledge of fundamental business processes (e.g.,
purchasing, payroll, accounts payable, accounts receivable)
including relevant IT
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ProcessAreaKnowledgeStatements.
Ten Knowledge Statements
1.6 Knowledge of applicable laws and regulations which affect the
scope, evidence collection and preservation, and frequency of
audits
1.7 Knowledge of evidence collection techniques (e.g.,
observation, inquiry, inspection, interview, data analysis) used to
gather, protect and preserve audit evidence
1.8 Knowledge of different sampling methodologies
1.9 Knowledge of reporting and communication techniques (e.g.,
facilitation, negotiation, conflict resolution, audit report
Structure)
1.10 Knowledge of audit quality assurance systems and
frameworks
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
OrganizationofISAuditFunction
Audit charter (or engagement letter)
Stating managements responsibility and objectives for, and
delegation of authority to, the IS audit function
Outlining the overall authority, scope and responsibilities of
the audit function
Approval of the audit charter
Change in the audit charter
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditPlanning
Audit planning
Shorttermplanning
Longtermplanning
Thingstoconsider
Newcontrol issues
Changingtechnologies
Changingbusinessprocesses
Enhancedevaluationtechniques
Individual audit planning
Understandingofoverallenvironment
Businesspracticesandfunctions
Informationsystemsandtechnology
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditPlanning
Audit Planning Steps
1. Gain an understanding of the businesss mission, objectives,
purpose and processes.
2. Identify stated contents (policies, standards, guidelines,
procedures, and organization structure)
3. Evaluate risk assessment and privacy impact analysis
4. Performa risk analysis.
5. Conduct an internal control review.
6. Set the audit scope and audit objectives.
7. Develop the audit approach or audit strategy.
8. Assign personnel resources to audit and address engagement
logistics.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
EffectofLawsandRegulations(continued)
Regulatoryrequirements
Establishment
Organization
Responsibilities
Correlationtofinancial,operationalandIT
auditfunctions
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
EffectofLawsandRegulations
Stepstodeterminecompliancewithexternal
requirements:
Identify external requirements
Document pertinent laws and regulations
Assess whether management and the IS function have considered the
relevant external requirements
Review internal IS department documents that address adherence to
applicable laws
Determine adherence to established procedures
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ISACAISAuditingStandardsandGuidelines
FrameworkfortheISACAISAuditingStandards
asof1March2010
Standards(16)
Guidelines41(G19iscancelled)
Procedures(11)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Definition:Standards,Guidelines&Procedure
Standards define mandatory requirements for IT audit
and assurance.
Guidelines provide guidance in applying IT Audit and
Assurance Standards. The objective of the IT Audit and
Assurance Guidelines is to provide further information on
how to comply with the IT Audit and Assurance Standards.
Procedure/ Tools and Techniques provide examples of
procedures an IT audit and assurance professional might
follow. The objective of the IT Audit and Assurance Tools
and Techniques is to provide further information on how
to comply with the IT Audit and Assurance Standards.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ISACAISAuditingStandardsandGuidelines
ISAuditing Standards:16
1. Audit charter
2. Independence
3. Professional Ethics and
Standards
4. Competence
5. Planning
6. Performance of audit work
7. Reporting
8. Follow-up activities
9. Irregularities and illegal acts
10.IT governance
11.Use of risk assessment in audit
planning
12.Audit Materiality
13.Using the Work of Other Experts
14.Audit Evidence
15.IT Controls
16.E-commerce
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ISACAISAuditingStandardsandGuidelines(continued)
G1UsingtheWorkof OtherAuditors
G2Audit EvidenceRequirement
G3Useof Computer AssistedAudit Techniques(CAATs)
G4Outsourcingof ISActivitiestoOther Organizations
G5Audit Charter
G6MaterialityConceptsforAuditingInformationSystems1September
G7DueProfessional Care
G8Audit Documentation
G9Audit Considerationsfor IrregularitiesandIllegal Acts
G10Audit Sampling
G11Effect of PervasiveISControls
G12Organizational RelationshipandIndependence
G13Useof RiskAssessment inAudit Planning
G14ApplicationSystemsReview
G15Audit PlanningRevised
ISAuditing Guidelines:41(421=41, G19is cancelled)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
G16Effect of ThirdPartiesonanOrganization'sIT Controls
G17 Effect of Non-audit Role on the IT Audit and Assurance
ProfessionalsIndependence
G18IT Governance
G19 Irregularities and Illegal Acts 1 J uly 2002. Withdrawn 1 September
2008
G20Reporting
G21EnterpriseResourcePlanning(ERP) SystemsReview
G22Business-to-consumer (B2C) E-commerceReview
G23SystemDevelopment LifeCycle(SDLC) ReviewReviews
G24Internet Banking
G25Reviewof Virtual PrivateNetworks
G26BusinessProcessReengineering(BPR) Project Reviews
G27MobileComputing
G28Computer Forensics
G29Post-implementationReview
G30Competence
ISACAISAuditingStandardsandGuidelines(continued)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ISACAISAuditingStandardsandGuidelines(continued)
G31Privacy
G32 Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Review From It
Perspective
G33General ConsiderationsontheUseof theInternet
G34Responsibility, AuthorityandAccountability
G35Follow-upActivities
G36BiometricControls
G37ConfigurationManagement Process
G38AccessControls
G39IT Organization
G40Reviewof SecurityManagement Practices
G41ReturnonSecurityInvestment (ROSI)
G42ContinuousAssurance <<<
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ISACAISAuditingStandardsandGuidelines
ITAuditandAssuranceToolsandTechniques:11
P1 IS Risk Assessment
P2 Digital Signatures
P3 Intrusion Detection
P4 Viruses and other Malicious Code
P5 Control Risk Self-assessment
P6 Firewalls
P7 Irregularities and Illegal Acts
P8 Security AssessmentPenetration Testing and Vulnerability
Analysis
P9 Evaluation of Management Controls Over Encryption
Methodologies
P10 Business Application Change Control
P11 Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
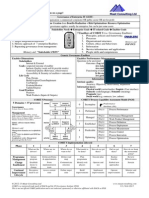
ITRiskAssessmentQuadrants
Quadrant I (High Risk)
Suggested Action(s):
Mitigate
S
e
n
s
i
t
i
v
i
t
y
R
a
t
i
n
g
Vulnerability Assessment Rating
100%
0%
100%
Quadrant II (Medium Risk)
Suggested Action(s):
Accept
Mitigate
Transfer
Quadrant III (Medium Risk)
Suggested Action(s):
Accept
Mitigate
Transfer
Quadrant IV (Low Risk)
Suggested Action(s):
Accept
Example Risk
Level Assignment
50%
50%
0%
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ISACAISAuditingStandardsandGuidelines
ISACA Auditing Procedures
Procedures developed by the ISACA Standards
Board provide examples.
The IS auditor should apply their own professional
judgment to the specific circumstances.
(Index of Procedures)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InternalControl(continued)
InternalControls
Policies, procedures, practices and
organizational structures implemented to
reduce risks
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ComponentsofInternalControlSystem
Internalaccountingcontrols
Operationalcontrols
Administrativecontrols
InternalControl(continued)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InternalControlObjectives
Safeguardingofinformationtechnologyassets
Compliancetocorporatepoliciesorlegalrequirements
Authorization/input
Accuracyandcompletenessofprocessingoftransactions
Output
Reliabilityofprocess
Backup/recovery
Efficiencyandeconomyofoperations
InternalControl(continued)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Classification ofInternalControls
Preventive controls
Detective controls
Corrective controls
InternalControl(continued)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
IS ControlObjectives
Control objectives in an information
systems environment remain unchanged
from those of a manual environment.
However, control features may be different.
The internal control objectives, thus need,
to be addressed in a manner specific to IS
related processes
InternalControl(continued)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InternalControl(continued)
IS Control Objectives (contd)
Safeguarding assets
Assuring the integrity of general operating system
environments
Assuring the integrity of sensitive and critical
application systemenvironments through:
Authorization of the input
Accuracy and completeness of processing of
transactions
Reliability of overall information processing activities
Accuracy, completeness and security of the output
Database integrity
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InternalControl(continued)
IS Control Objectives (contd)
Ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of operations
Complying with requirements, policies and procedures, and
applicable laws
Developing business continuity and disaster recovery plans
Developing an incident response plan
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InternalControl(continued)
IS Control Objectives (contd)
COBIT
Aframeworkwith 34highlevelcontrolobjectives
Planningandorganization
Acquisitionandimplementation
Deliveryandsupport
Monitoringandevaluation
Useof36majorITrelatedstandardsandregulations
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InternalControl(continued)
General ControlProcedures(continued)
apply to all areas of an organization and include
policies and practices established by management to
provide reasonable assurance that specific objectives
will be achieved.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InternalControl(continued)
General ControlProcedures(continued)
Internal accounting controls directed at accounting
operations
Operational controls concerned with the daytoday
operations
Administrative controls concerned with operational
efficiency and adherence to management policies
Organizational logical security policies and procedures
Overall policies for the design and use of documents and
records
Procedures and features to ensure authorized access to
assets
Physical security policies for all data centers
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ISControlProcedures
Strategy and direction
General organization and management
Access to data and programs
Systems development methodologies and change control
Data processing operations
Systems programming and technical support functions
Data processing quality assurance procedures
Physical access controls
Business continuity/disaster recovery planning
Networks and communications
Database administration
Internal Control (continued)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
MohammadTohidurRahmanBhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,MCSD,A+,CSCF
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
DefinitionofAuditing
Systematic process by which a competent,
independent person objectively obtains and
evaluates evidence regarding assertions about an
economic entity or event for the purpose of forming
an opinion about and reporting on the degree to
which the assertion conforms to an identified set of
standards.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
DefinitionofISAuditing
Any audit that encompasses review and
evaluation (wholly or partly) of automated
information processing systems, related non
automated processes and the interfaces
between them.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Classificationofaudits:
Financialaudits
Operationalaudits
Integratedaudits
Administrativeaudits
Informationsystemsaudits
Specializedaudits
Forensicaudits
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditPrograms
Basedonthescopeandtheobjectiveofthe
particularassignment
ISauditorsperspectives
Security(confidentiality,integrityandavailability)
Quality(effectiveness,efficiency)
Fiduciary(compliance,reliability)
ServiceandCapacity
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Generalauditprocedures
Understandingoftheauditarea/subject
Riskassessmentandgeneralauditplan
Detailedauditplanning
Preliminaryreviewofauditarea/subject
Evaluatingauditarea/subject
Compliancetesting
Substantivetesting
Reporting(communicatingresults)
Followup
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Proceduresfortesting& evaluatingIS controls
Use of generalized audit software to survey the contents of
data files
Use of specialized software to assess the contents of
operating system parameter files
Flowcharting techniques for documenting automated
applications and business process
Use of audit reports available in operation systems
Documentation review
Observation
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditMethodology
Asetofdocumentedauditproceduresdesignedto
achieveplannedauditobjectives
Composedof
Statementofscope
Statementofauditobjectives
Statementofworkprograms
Setupandapprovedbytheauditmanagement
Communicatedtoallauditstaff
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Typical audit phases
1. Audit subject
Identify the area to be audited
2. Audit objective
Identify the purpose of the audit
3. Audit scope
Identify the specific systems, function or unit of the
organization
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Typical audit phases (Contd)
4. Pre-audit planning
Identify technical skills and resources needed
Identify the sources of information for test or
review
Identify locations or facilities to be audited
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Typicalauditphases (Contd)
5. Audit procedures and steps for data gathering
Identify and select the audit approach
Identify a list of individuals to interview
Identify and obtain departmental policies, standards
and guidelines
Develop audit tools and methodology
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Typicalauditphases (Contd)
6.Proceduresforevaluatingtest/review result
7.Proceduresfor communication
8.Auditreportpreparation
Identifyfollowupreviewprocedures
Identifyprocedurestoevaluate/testoperational efficiencyand
effectiveness
Identifyprocedurestotestcontrols
Reviewandevaluatethesoundnessofdocuments,policiesand
procedures.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Typical Audit Phases Summary
Identify
the area to be audited
the purpose of the audit
the specific systems, function or unit of
the organization to be included in the
review.
technical skills and resources needed
the sources of information for tests or
review such as functional flowcharts,
policies, standards, procedures and prior
audit work papers.
locations or facilities to be audited.
select the audit approach to verify and test
the controls
list of individuals to interview
obtain departmental policies, standards
and guidelines for review
Develop
audit tools and methodology to test and
verifycontrol
procedures for evaluating the test or
reviewresults
procedures for communication with
management
Identify
follow-upreviewprocedures
procedures to evaluate/test operational
efficiencyandeffectiveness
procedurestotest controls
Review and evaluate the soundness of
documents, policies and procedures
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
WorkPapers(WPs)(Contd)
What are documented in WPs?
Audit plans
Audit programs
Audit activities
Audit tests
Audit findings and incidents
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
WorkPapers
Donothavetobeonpaper
Mustbe
Dated
Initialized
Pagenumbered
Relevant
Complete
Clear
Selfcontainedandproperlylabeled
Filedandkeptincustody
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
FraudDetection
Managements responsibility
Benefits of a welldesigned internal control system
Deterring frauds at the first instance
Detecting frauds in a timely manner
Fraud detection and disclosure
Auditors role in fraud prevention and detection
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditRisk
Audit risk is the risk that the
information/financial report may
contain material error that may go
undetected during the audit.
A riskbased audit approach is used to
assess risk and assist with an IS auditors
decision to perform either compliance
or substantive testing.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditRisks
Inherentrisk
Controlrisk
Detectionrisk
Overallauditrisk
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
RiskbasedApproach Overview
GatherInformationandPlan
ObtainUnderstandingofInternalControl
PerformComplianceTests
PerformSubstantiveTests
ConcludetheAudit
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Materiality
An auditing concept regarding the importance of an
item of information with regard to its impact or
effect on the functioning of the entity being audited
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
RiskAssessmentTechniques
Enables management to effectively allocate limited
audit resources
Ensures that relevant information has been obtained
Establishes a basis for effectively managing the audit
department
Provides a summary of how the individual audit
subject is related to the overall organization and to
business plans
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditObjectives
ItistheSpecificgoalsoftheaudit
Compliancewithlegal®ulatory
requirements
Confidentiality
Integrity
Reliability
Availability
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Compliancevs.SubstantiveTesting
Compliance test
determines whether controls are in compliance with
management policies and procedures
Substantive test
tests the integrity of actual processing
Correlation between the level of internal controls and
substantive testing required
Relationship between compliance and substantive
tests
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Evidence
It is a requirement that the auditors
conclusions must be based on sufficient,
competent evidence.
Independence of the provider of the
evidence
Qualification of the individual providing the
information or evidence
Objectivity of the evidence
Timing of evidence
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Techniquesforgatheringevidence:
ReviewISorganizationstructures
ReviewISpolicies andprocedures
ReviewISstandards
ReviewISdocumentation
Interviewappropriatepersonnel
Observeprocessesandemployeeperformance
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
InterviewingandObservingPersonnel
Actualfunctions
Actualprocesses/procedures
Securityawareness
Reportingrelationships
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Sampling(continued)
General approaches to audit sampling:
Statistical sampling
Nonstatistical sampling
Methods of sampling used by auditors:
Attribute sampling
Variable sampling
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Sampling(continued)
Attributesampling
Stoporgosampling
Discoverysampling
Variablesampling
Stratifiedmeanperunit
Unstratified meanperunit
Differenceestimation
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Confidentcoefficient
Levelofrisk
Precision
Expectederrorrate
Samplemean
Samplestandarddeviation
Tolerableerrorrate
Populationstandarddeviation
Statistical sampling terms:
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Keystepsinchoosingasample
Determinetheobjectivesofthetest
Definethepopulationtobesampled
Determinethesamplingmethod,suchasattribute
versusvariablesampling.
Calculatethesamplesize
Selectthesample
Evaluatingthesamplefromanauditperspective.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ComputerAssistedAuditTechniques.Contd.
CAATs enable IS auditors to gather
information independently
CAATs include:
Generalized audit software (GAS)
Utility software
Test data
Application software for continuous online
audits
Audit expert systems
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
NeedforCAATs
Evidencecollection
Functionalcapabilities
Functionssupported
Areasofconcern
ComputerAssistedAuditTechniques.Contd.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ExamplesofCAATsusedtocollectevidence
CAATSasacontinuousonlineapproach
ComputerAssistedAuditTechniques.Contd.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AdvantagesofCAATs
Cost/benefitsofCAATs
ComputerAssistedAuditTechniques.Contd.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
DevelopmentofCAATs
Documentationretention
Accesstoproductiondata
Datamanipulation
ComputerAssistedAuditTechniques.Contd.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Evaluation of Strengths and Weaknesses
Assessevidence
Evaluateoverallcontrolstructure
Evaluatecontrolprocedures
Assesscontrolstrengthsandweaknesses
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
JudgingMaterialityofFindings
Materialityisakeyissue
Assessmentrequiresjudgmentofthe
potential effectofthefindingifcorrective
actionisnot taken
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
CommunicatingAuditResults
Exitinterview
Correctfacts
Realisticrecommendations
Implementationdatesforagreedrecommendations
Presentationtechniques
Executivesummary
Visualpresentation
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Auditreportstructureandcontents
An introduction to the report
The IS auditors overall conclusion and opinion
The IS auditors reservations with respect to the audit
Detailed audit findings and recommendations
A variety of findings
Limitations to audit
Statement on the IS audit guidelines followed
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ManagementActionstoImplementRecommendations
Auditingisanongoingprocess
Timingoffollowup
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AuditDocumentation
Contentsofauditdocumentation
Custodyofauditdocumentation
Supportoffindingsandconclusions
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ConstraintsontheConductoftheAudit
Availabilityofauditstaff
Auditee constraints
ProjectManagementTechniques
Developadetailedplan
Reportprojectactivityagainsttheplan
Adjusttheplan
Takecorrectiveaction
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ControlSelfAssessment(CSA),Contd.
Amanagementtechnique
Amethodology
Inpractice,aseriesoftools
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ImplementationofCSA
Facilitatedworkshops
Hybridapproach
ControlSelfAssessment(CSA),Contd.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ControlSelfAssessment
Benefits of CSA
Disadvantages of CSA
Objectives of CSA
Enhancement of audit responsibilities (not a
replacement)
Education for line management in control
responsibility and monitoring
Empowerment of workers to assess the control
environment
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ControlSelfAssessment
ISAuditorsRoleinCSAs
TechnologyDrivers forCSAProgram
Traditionalvs.CSAApproach
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
MohammadTohidurRahmanBhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,MCSD,A+,CSCF
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
EmergingChangesinISAuditProcess
NewTopics:
AutomatedWorkPapers
IntegratedAuditing
ContinuousAuditing
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AutomatedWorkPapers
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Riskanalysis
Auditprograms
Results
Testevidences,
Conclusions
Reportsandothercomplementaryinformation
Automated Work Papers(Contd)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
AutomatedWorkPapers
Controlsoverautomatedworkpapers:
Accesstoworkpapers
Audittrails
Approvalsofauditphases
Securityandintegritycontrols
Backupandrestoration
Encryptionforconfidentiality
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
IntegratedAuditing
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
IntegratedAuditing
process whereby appropriate audit disciplines are
combined to assess key internal controls over an operation,
process or entity
Focuses on risk to the organization (for an internal
auditor)
Focuses on the risk of providing an incorrect or
misleading audit opinion (for external auditor
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
IntegratedAuditing Typicalprocess:
Identification of relevant key controls
Reviewand understanding of the design of key controls
Testing that key controls are supported by the IT
system
Testing that management controls operate effectively
A combined report or opinion on control risks, design
and weaknesses
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ContinuousAuditing
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ContinuousAuditing
Continuous Auditing: A methodology that
enables independent auditors to provide written
assurance on a subject matter using a series of
auditors reports issued simultaneously with, or a
short period of time after, the occurrence of events
underlying the subject matter
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Distinctive character
short time lapse between the facts to be audited and
the collection of evidence and audit reporting
Drivers
better monitoring of financial issues
allowing realtime transactions to benefit from real
time monitoring
preventing financial fiascoes and audit scandals
using software to determine proper financial controls
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ContinuousAuditingvs.ContinuousMonitoring
ContinuousMonitoring
Managementdriven
Basedonautomatedproceduresto meetfiduciary
responsibilities
ContinuousAuditing
Auditdriven
Doneusingautomatedauditprocedures
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
ContinuousAuditingEnablerfortheApplication
ofContinuousAuditing
New information technology developments
Increased processing capabilities
Standards
Artificial intelligence tools
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Transactionlogging
Querytools
Statisticsanddataanalysis(CAAT)
Databasemanagementsystems(DBMS)
Datawarehouses,datamarts,datamining.
Artificialintelligence(AI)
Embeddedauditmodules(EAM)
Neuralnetworktechnology
StandardssuchasExtensibleBusinessReporting
Language
IT Techniques in a Continuous Auditing Environment
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
A high degree of automation
An automated and reliable informationproducing process
Alarm triggers to report control failures
Implementation of automated audit tools
Quickly informing IS auditors of anomalies/errors
Timely issuance of automated audit reports
Technically proficient IS auditors
Availability of reliable sources of evidence
Adherence to materiality guidelines
Change of IS auditors mindset
Evaluation of cost factors
ContinuousAuditing Prerequisites
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
(ContinuousAuditing)
Advantages
Instant capture of internal control problems
Reduction of intrinsic audit inefficiencies
Disadvantages
Difficulty in implementation
High cost
Elimination of auditors personal judgment and
evaluation
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Practice Question
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
11 Which of the following BEST describes the early
stages of an IS audit?
A. Observing key organizational facilities
B. Assessing the IS environment
C. Understanding the business process and environment applicable to
the review
D. Reviewing prior IS audit reports
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
11C: Understanding the business process
and environment applicable to the review is
most representative of what occurs early on
in the course of an audit. The other choices
relate to activities actually occurring within
this process.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
12 In performing a riskbased audit, which risk
assessment is completed initially by the IS auditor?
A.Detectionriskassessment
B.Controlriskassessment
C.Inherentriskassessment
D.Fraudriskassessment
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
12C: Inherent risks exist independently of
an audit and can occur because of the nature
of the business. To successfully conduct an
audit, it is important to be aware of the
related business processes. To perform the
audit the IS auditor needs to understand the
business process, and by understanding the
business process, the IS auditor better
understands the inherent risks.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
13 While developing a riskbased audit program, on
which of the following would the IS auditor MOST likely
focus?
A. Business processes
B. Critical IT applications
C. Operational controls
D. Business strategies
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
13A: A riskbased audit approach focuses
on the understanding of the nature of the
business and being able to identify and
categorize risk. Business risks impact the
longterm viability of a specific business.
Thus, an IS auditor using a riskbased audit
approach must be able to understand
business processes.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
14 Which of the following types of audit risk assumes
an absence of compensating controls in the area being
reviewed?
A. Control risk
B. Detection risk
C. Inherent risk
D. Sampling risk
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
14C: The risk of an error existing that could be
material or significant when combined with other
errors encountered during the audit, there being no
related compensating controls, is the inherent risk.
Control risk is the risk that a material error exists that
will not be prevented or detected in a timely manner by
the system of internal controls. Detection risk is the
risk of an IS auditor using an inadequate test procedure
that concludes that material errors do not exist, when
they do. Sampling risk is the risk that incorrect
assumptions are made about the characteristics of a
population fromwhich a sample is taken.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
15 An IS auditor performing a review of an application's controls
finds a weakness in system software that could materially impact
the application. The IS auditor should:
A. disregard these control weaknesses since a system software review is
beyond the scope of this review.
B. conduct a detailed system software review and report the control
weaknesses.
C. include in the report a statement that the audit was limited to a review
of the application's controls.
D. review the system software controls as relevant and recommend a
detailed system software review.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
15D: The IS auditor is not expected to ignore control
weaknesses just because they are outside the scope of a
current review. Further, the conduct of a detailed
systems software review may hamper the audit's
schedule and the IS auditor may not be technically
competent to do such a review at this time. If there are
control weaknesses that have been discovered by the IS
auditor, they should be disclosed. By issuing a
disclaimer, this responsibility would be waived. Hence,
the appropriate option would be to review the systems
software as relevant to the review and recommend a
detailed systems software review for which additional
resources may be recommended.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
16 The PRIMARY use of generalized audit
software (GAS) is to:
A. test controls embedded in programs.
B. test unauthorized access to data.
C. extract data of relevance to the audit.
D. reduce the need for transaction vouching.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
16C: Generalized audit software facilitates direct access to
and interrogation of the data by the IS auditor. The most
important advantage of using GAS is that it helps in
identifying data of interest to the IS auditor. GAS does not
involve testing of application software directly. Hence, GAS
indirectly helps in testing controls embedded in programs
by testing data. GAS cannot identify unauthorized access to
data if this information is not stored in the audit log file.
However, this information may not always be available.
Hence, this is not one of the primary reasons for using GAS.
Vouching involves verification of documents. GAS could
help in selecting transactions for vouching. Using GAS does
not reduce transaction vouching.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
17WhichofthefollowingisMOSTeffectivefor
implementingacontrolselfassessment(CSA)
withinbusinessunits?
A.Informalpeerreviews
B.Facilitatedworkshops
C.Processflownarratives
D.Dataflowdiagrams
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
17B: Facilitated workshops work well
within business units. Process flow
narratives and data flow diagrams would not
be as effective since they would not
necessarily identify and assess all control
issues. Informal peer reviews similarly would
be less effective for the same reason.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
18 The FIRST step in planning an audit is to:
A. define audit deliverables.
B. finalize the audit scope and audit objectives.
C. gain an understanding of the business'
objectives.
D. develop the audit approach or audit strategy.
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
18C: The first step in audit planning is to
gain an understanding of the business's
mission, objectives and purpose, which in
turn identifies the relevant policies,
standards, guidelines, procedures, and
organization structure. All other choices are
dependent upon having a thorough
understanding of the business's objectives
and purpose.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
19TheapproachanISauditorshouldusetoplanIS
auditcoverageshouldbebasedon:
A.risk.
B.materiality.
C.professionalskepticism.
D.sufficiencyofauditevidence.
PracticeQuestions(contd.)
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
19A: Standard S5, Planning, establishes
standards and provides guidance on
planning an audit. It requires a riskbased
approach.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
PracticeQuestions
IlO A company performs a daily backup of critical
data and software files, and stores the backup tapes at
an offsite location. The backup tapes are used to restore
the files in case of a disruption. This is a:
A. preventive control.
B. management control.
C. corrective control.
D. detective control.
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
110C: A corrective control helps to correct or minimize the
impact of a problem. Backup tapes can be used for restoring
the files in case of damage of files, thereby reducing the
impact of a disruption. Preventive controls are those that
prevent problems before they arise. Backup tapes cannot be
used to prevent damage to files and hence cannot be
classified as a preventive control. Management controls
modify processing systems to minimize a repeat occurrence
of the problem. Backup tapes do not modify processing
systems and hence do not fit the definition of a management
control. Detective controls help to detect and report
problems as they occur. Backup tapes do not aid in detecting
errors.
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Question
&
Answer
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
Mohammad Tohidur Rahman Bhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,A+,MCSD,ISMS,CSCF
MohammadTohidurRahmanBhuiyan
CGEIT,CISA,MCSD,A+,CSCF
You might also like
- Security AuditDocument31 pagesSecurity AuditTarang Shah100% (2)
- Intrusion Detection System (Ids) ReviewDocument7 pagesIntrusion Detection System (Ids) Reviewcgarcias76No ratings yet
- IT Risk Management Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandIT Risk Management Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Planning ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Planning ProcessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Follow-up ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Follow-up ProcessRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Auditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlFrom EverandAuditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlNo ratings yet
- IRCA Technical Review Briefing Note ISO 27001 PDFDocument16 pagesIRCA Technical Review Briefing Note ISO 27001 PDFtstehNo ratings yet
- Google Cloud Platform GCP Audit ProgramDocument31 pagesGoogle Cloud Platform GCP Audit ProgramjohnNo ratings yet
- COBIT 5 For Risk Laminate Res Eng 0913Document8 pagesCOBIT 5 For Risk Laminate Res Eng 0913dandisdandisNo ratings yet
- Training IT Audit CHP 1Document56 pagesTraining IT Audit CHP 1billy_ea7323100% (1)
- Developing The IT Audit Plan Using COBIT 2019Document11 pagesDeveloping The IT Audit Plan Using COBIT 2019吴rua歌No ratings yet
- IT Audit - FrameworkDocument20 pagesIT Audit - FrameworkAbi SyukriNo ratings yet
- How To Derive An IT Audit UniverseDocument4 pagesHow To Derive An IT Audit UniversekolocokroNo ratings yet
- Application Sys. ReviewDocument4 pagesApplication Sys. ReviewadiltsaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Information Risk Management - GRC COBITDocument11 pagesWeek 2 - Information Risk Management - GRC COBITJayath GayanNo ratings yet
- IT Security Audit: Prepared by Mbabazi SylviaDocument36 pagesIT Security Audit: Prepared by Mbabazi SylviaMicheal BixNo ratings yet
- InfoSystemsAuditChecklist (Version 1)Document44 pagesInfoSystemsAuditChecklist (Version 1)Merrick Martin100% (1)
- DCSS enDocument36 pagesDCSS enashvar9No ratings yet
- Voice-Over Internet Protocol (Voip) Audit/Assurance ProgramDocument45 pagesVoice-Over Internet Protocol (Voip) Audit/Assurance ProgramElisha MushaijaNo ratings yet
- About The CRISC Exam PDFDocument7 pagesAbout The CRISC Exam PDFBumbhole RaoNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Audit Methodology:: Planning PhaseDocument4 pagesInformation Technology Audit Methodology:: Planning PhaseshakawathNo ratings yet
- ISO27701 EU Sep 19Document9 pagesISO27701 EU Sep 19Viko0% (1)
- Iso/Iec: Group 3Document37 pagesIso/Iec: Group 3Abdunnajar MahamudNo ratings yet
- Service Organization Control (SOC) Reports Overview: Technology Risk ServicesDocument15 pagesService Organization Control (SOC) Reports Overview: Technology Risk ServicesHemant DusaneNo ratings yet
- ASI - IT Risk and ControlsDocument19 pagesASI - IT Risk and ControlsArthia RuthNo ratings yet
- 1 - Risk Starter Kit Introduction and Getting StartedDocument6 pages1 - Risk Starter Kit Introduction and Getting StartedSuleyman S. GulcanNo ratings yet
- Handout - IsAE 3402Document9 pagesHandout - IsAE 3402professional.ca728No ratings yet
- CRISC Certification TrainingDocument5 pagesCRISC Certification Trainingmankrish6314No ratings yet
- 2022 Ultimate Guide To SOC 2 EbookDocument20 pages2022 Ultimate Guide To SOC 2 EbookMark Starmin100% (1)
- ISO 27001 Gap Analysis Service DescriptionDocument4 pagesISO 27001 Gap Analysis Service DescriptionBlanche AlmondNo ratings yet
- IT Control Objectives For Sarbanes-OxleyDocument12 pagesIT Control Objectives For Sarbanes-OxleyDiego VergaraNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam 100 Practice QuestionDocument22 pagesCISA Exam 100 Practice Questionharsh100% (1)
- COBIT-5-Assurance Res Eng 1213Document17 pagesCOBIT-5-Assurance Res Eng 1213sheryhanNo ratings yet
- COBIT Overview for IT Processes and ControlsDocument19 pagesCOBIT Overview for IT Processes and ControlsAshraf Abdel HamidNo ratings yet
- Information Risks: Whose Business Are They?: Itgovernance DomainpracticesandcompetenciesDocument23 pagesInformation Risks: Whose Business Are They?: Itgovernance DomainpracticesandcompetenciesNegrito de JesusNo ratings yet
- Iso 27001Document6 pagesIso 27001許宏任No ratings yet
- Cyber EthicsDocument16 pagesCyber Ethicsnavinnaithani100% (2)
- ISO 27000 Series Information Security StandardsDocument4 pagesISO 27000 Series Information Security Standardswahid100% (1)
- Aligning COSO and Privacy Frameworks - Joa - Eng - 0320Document10 pagesAligning COSO and Privacy Frameworks - Joa - Eng - 0320chavez.tel9No ratings yet
- IS Auditing Tools and Tech - Res - Eng - 0215 PDFDocument46 pagesIS Auditing Tools and Tech - Res - Eng - 0215 PDFcecil_jrNo ratings yet
- Audit WorkprogramDocument29 pagesAudit WorkprogramMakarand LonkarNo ratings yet
- Cag It AuditDocument90 pagesCag It AuditRana SarkarNo ratings yet
- 30 Whitepapers Iso 29100 How Can Organizations Secure Its Privacy NetworkDocument9 pages30 Whitepapers Iso 29100 How Can Organizations Secure Its Privacy Networkmafun249No ratings yet
- Cybercrime-Audit-Assurance-Program Icq Eng 1012Document54 pagesCybercrime-Audit-Assurance-Program Icq Eng 1012ssglcnNo ratings yet
- Section 4: System Infrastructure and ControlDocument72 pagesSection 4: System Infrastructure and ControlAbdullah AlrimawiNo ratings yet
- Governance, Architecture and IT StrategyDocument16 pagesGovernance, Architecture and IT StrategyBiswajit DuttaNo ratings yet
- COBIT - A Key To Success As An IT AuditorDocument3 pagesCOBIT - A Key To Success As An IT AuditorkamuturiNo ratings yet
- Transforming Enterprise IT: Speaker Name/Title DateDocument17 pagesTransforming Enterprise IT: Speaker Name/Title DatebentojagoNo ratings yet
- ISO27k ISMS Gap Analysis and SoA - v1 - 02Document47 pagesISO27k ISMS Gap Analysis and SoA - v1 - 02Christen Castillo100% (1)
- COBIT Overview and ITIL V3 MappingDocument50 pagesCOBIT Overview and ITIL V3 Mappingdeadone09No ratings yet
- Systems Development Life Cycle PDFDocument92 pagesSystems Development Life Cycle PDFPatrick GoNo ratings yet
- ISO 27001 ISMS security managementDocument9 pagesISO 27001 ISMS security managementManinder SinghNo ratings yet
- COBIT 5 IntroductionDocument6 pagesCOBIT 5 Introductiondan27090% (1)
- CRMA Exam References GuideDocument1 pageCRMA Exam References GuideJoe FrostNo ratings yet
- COBIT 5 Foundation Exam Revision On A PageDocument1 pageCOBIT 5 Foundation Exam Revision On A PageSergiö Montoya100% (1)
- CSCF Assessment Template For Mandatory Controls (Version2022) v1.2Document179 pagesCSCF Assessment Template For Mandatory Controls (Version2022) v1.2PetrrNo ratings yet
- Iso/Iec 27001 and Cobit 5 Information Security Management and Data Classification ProgramDocument8 pagesIso/Iec 27001 and Cobit 5 Information Security Management and Data Classification Programstephen1004No ratings yet
- HS AgroDocument42 pagesHS AgroSHIVANSHUNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment Cafes Monte Bianco Final V2Document13 pagesGroup Assignment Cafes Monte Bianco Final V2Linh Chi Trịnh T.No ratings yet
- Higher Education Financing Agency BrochureDocument6 pagesHigher Education Financing Agency BrochuremidhunnobleNo ratings yet
- Sample Partnership AgreementDocument38 pagesSample Partnership AgreementAlex VolkovNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System Part 4Document26 pagesQuality Management System Part 4Bo DoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 10667Document5 pagesRepublic Act No. 10667orionsrulerNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of The IdeaDocument5 pagesSWOT Analysis of The IdeaSaim QadarNo ratings yet
- Evercore TearsheetDocument1 pageEvercore TearsheetJennifer KwonNo ratings yet
- How To Think Like A Marketing Genius - Table of ContentsDocument10 pagesHow To Think Like A Marketing Genius - Table of Contentsbuymenow2005No ratings yet
- Laporan Keuangan Triwulan III September 2020 PDFDocument176 pagesLaporan Keuangan Triwulan III September 2020 PDFSatria MegantaraNo ratings yet
- NMC GOLD FINANCE LIMITED - Forensic Report 1Document11 pagesNMC GOLD FINANCE LIMITED - Forensic Report 1Anand KhotNo ratings yet
- Planning Strategies: Production PlanningDocument22 pagesPlanning Strategies: Production Planningpprasad_g9358No ratings yet
- Costing for FDLC JDE and brightERP ProjectsDocument4 pagesCosting for FDLC JDE and brightERP ProjectsanoopNo ratings yet
- Foreign Capital As A Source of FinanaceDocument8 pagesForeign Capital As A Source of FinanaceD KNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Part 1 Lecture OutlineDocument17 pagesSupply Chain Management Part 1 Lecture OutlineEmmanuel Cocou kounouhoNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument5 pagesBangladesh Pharmaceutical IndustryMizanur Rahman0% (1)
- CPA-HSE Best Practice Guide For Crane Hire and Contract Lifting - ExtractDocument1 pageCPA-HSE Best Practice Guide For Crane Hire and Contract Lifting - ExtractWNo ratings yet
- Effective Talent Management & Succession Planning OptimizationDocument4 pagesEffective Talent Management & Succession Planning OptimizationdaabhiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Env403Document6 pagesAssignment - Env403Mahadi HasanNo ratings yet
- Ge Is Faced With Jack Welch S Impending Retirement and WhetherDocument1 pageGe Is Faced With Jack Welch S Impending Retirement and WhetherAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Journalizing Accounting TransactionsDocument19 pagesJournalizing Accounting TransactionsChristine Paola D. Lorenzo100% (1)
- Timex - Marketing MixDocument11 pagesTimex - Marketing MixHimanMohapatra100% (1)
- Problem Solving: A: What Is The Capital Balance of Bea On December 31, 2022?Document6 pagesProblem Solving: A: What Is The Capital Balance of Bea On December 31, 2022?Actg SolmanNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Enterprise Architecture Pada PT Vitapharm Menggunakan Framework TogafDocument13 pagesPerancangan Enterprise Architecture Pada PT Vitapharm Menggunakan Framework TogafJulianto SaputroNo ratings yet
- CM1 PAS1 Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument16 pagesCM1 PAS1 Presentation of Financial StatementsMark GerwinNo ratings yet
- 9 External Environment Factors That Affect BusinessDocument5 pages9 External Environment Factors That Affect BusinessHasan NaseemNo ratings yet
- BBA Viva Final Year PDFDocument70 pagesBBA Viva Final Year PDFPratikBhowmickNo ratings yet
- Asli Köseoğlu Billur Yümlü Onur Erdoğan Sibel Temürlenk Sarah UnterburgerDocument26 pagesAsli Köseoğlu Billur Yümlü Onur Erdoğan Sibel Temürlenk Sarah UnterburgerAslı Akkaş100% (1)
- Gold Plus Case StudyDocument11 pagesGold Plus Case StudymansiNo ratings yet
- Valeura Hse Management System PDFDocument19 pagesValeura Hse Management System PDFAbdelkarimNo ratings yet