Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Body Review
Uploaded by
api-2611727660 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
607 views4 pagesOriginal Title
human body review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
607 views4 pagesHuman Body Review
Uploaded by
api-261172766Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Human Body Study Guide
I. Body Systems - systems complete a task individually as well as work
with other systems to help the body function. You should know the main
functions of each body system listed, what systems work together and
how, and what each system looks like when given a photo.
A. skeletal - system made up of bones, cartilage and joints
1. Functions
a) protection - protects organs and other key body parts from
injury
b) movement - allows body parts to move
c) support - keeps the body upright
B. muscular - made up of 3 types of muscle tissue - smooth, cardiac,
and skeletal, also includes tendons and ligaments
1. Functions
a) movement - working with the skeletal system, the muscles help
move the body
b) protection - cover many bones and serve as limited protection
C. digestive - made up of mouth, esophagus, stomach, large intestines,
small intestines, pancreas and colon
1. Functions
a) to consume (eat) and digest food. Breaks food down and
provides body with nutrients from food.
D. circulatory - composed or arteries (take blood away from the heart),
veins (take blood to the heart), capillaries (oxygen is used, the place
where veins and arteries meet), blood cells (white- ght disease and
work with your immune system. red - carry nutrients and oxygen to
the body.)
1. Functions
a) designed to carry blood to and from all parts of the body. Also
aids in keeping the body healthy using white blood cells.
b) works with respiratory system to provide body with oxygen and
nutrients via the blood
E. respiratory - composed of the trachea (long tube that leads from
mouth to lungs) and lungs (two balloon like structures that bring air in
and out of the body)
1. Functions
a) to provide the body with oxygen
b) breathing in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide
c) works with the circulatory system to provide body with oxygen
and nutrients via the blood.
F. nervous - made up of the brain, spinal chord and nerves
1. Functions
a) responsible for sending messages to all parts of the body.
Below is a picture of what each system looks like independent of the others. You should
be able to identify each system based on the pictures provided. Focus only on the
systems listed above. The Nervous system may have tiny little branches that represent
nerves that are not listed on the drawing below.
I. Cells and Tissues - you should be able to identify what the basic
organelles of cells are. The difference between unicellular and
multicellular and examples of each type of organism.
II.
A. Organelles - simply put, this is a fancy name for parts of the cell
1. Nucleus - center of the cell, considered the cell brain
2. Cell Membrane or Cell Wall - outside edge of a cell, usually
permeable
3. mitochondria - long oval shaped units that act like the digestive
system of the cell - provide the cell with nutrients
4. cytoplasm - the liquid that is contained by the cell membrane
5. vacuole - small roundish shaped organelles that store food
6. chloroplasts - found only in plant cells, convert sunlight to energy
III. Multicellular organisms - organisms made up of more than one cell
A. examples - hydra, algae, animals, fungi, plants
IV. Unicellular organisms - organisms made up of one cell
A. examples - paramecium, amoeba, euglena, bacteria, plasmodium,
trypanosoma
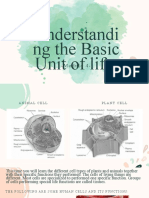
V. Animal and Plant Cell comparison:
A. Animal Cell - notice the difference in shape, typically animal cells are
round and have a thin outer membrane. Notice that Animal cells DO
NOT HAVE CHLOROPLASTS!!!
B. Plant Cell - notice the rectangular shape. They HAVE
CHLOROPLASTS and usually a thicker outer membrane. The
vacuoles in plant cells are generally larger and take up more space
(the big white area inside the cell). These make up things like ower
petals, blades of grass, trees, weeds, and other plants
I. Traits - there are two types of traits, inherited and learned. You must be
able to determine the difference between the two and provide
examples.
A. Inherited traits - traits that are passed on from one generation to
another (grandparents to parents to children)
1. examples -
a) physical - eye color, hair color, size/shape of nose, size/shape
of eyes, size/shape of head, height, body type, dimples, size/
shape of lips, shape of feet. generally any physical trait is going
to be an inherited trait.
b) Behavioral - In addition there are behaviors that are also
inherited, things such as temper, ability to cook, athletic ability,
intelligence in humans. In animals bears hibernating, dogs
burying a bone, birds migrating
B. Acquired or LearnedTraits - traits that help organisms survive or are
learned by the organism
1. examples - hunting for food, a dog learning to roll over, lifting
weights to get stronger. reading to increase knowledge,
Any thing that is learned is considered an acquired trait, if you can not learn
it, then it is inherited usually.
You might also like
- Ten Pussy Eating CommandmentsDocument13 pagesTen Pussy Eating CommandmentsSophie Jenkin100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Human BodyDocument110 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Human BodyMike JohnsonNo ratings yet
- HydrocephalusDocument40 pagesHydrocephalusAstrid Sabirin100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyDianne Comon86% (7)
- Anatomy and Physiology DefinedDocument78 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DefinedFhen Farrel100% (5)
- Bones PDFDocument227 pagesBones PDFAtthapu ThirupathaiahNo ratings yet
- Human Biology Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesHuman Biology Lecture NotesGrace Melissa ChoiNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q2 - Week 3-Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument48 pagesG7 Science Q2 - Week 3-Levels of Biological OrganizationJessa-Bhel AlmueteNo ratings yet
- Human Body Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesHuman Body Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- EcosystemsDocument30 pagesEcosystemsapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Introduction to Animal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument41 pagesIntroduction to Animal Anatomy and Physiologydreih Madrig100% (1)
- Tooth Organs ChartDocument1 pageTooth Organs Chartmildecoy100% (4)
- Human Body Structure and Anatomical Terms OverviewDocument14 pagesHuman Body Structure and Anatomical Terms OverviewScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalDocument14 pagesPATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Plot Structure DiagramDocument2 pagesPlot Structure Diagramapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Study GuideNic Alcala100% (1)
- Introduction to Human Body Systems & StructuresDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Human Body Systems & StructuresChristina Markwart100% (1)
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsDocument18 pagesPlant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human Movement and Performance Lesson 1Document22 pagesAnatomy of Human Movement and Performance Lesson 1Alfredo Arvin Nieva100% (1)
- Students Hand Out Notes in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesStudents Hand Out Notes in Anatomy and PhysiologyCza Mae Arsenal100% (1)
- Basic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Document228 pagesBasic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Hilary Christopher100% (1)
- P.E Anatomical TermsDocument26 pagesP.E Anatomical TermsGerald Mapalo FactorNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure QuestionsDocument16 pagesCell Structure QuestionsDila OzdolNo ratings yet
- Science6 Q2 Mod1 TheHumanBodySystems V4Document30 pagesScience6 Q2 Mod1 TheHumanBodySystems V4ThievesPHNo ratings yet
- Refresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Document21 pagesRefresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Kirby AnaretaNo ratings yet
- Bio 235 Midterm 1 NotesDocument53 pagesBio 235 Midterm 1 NotesNita JosephNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory SystemDocument34 pagesAssessment of Respiratory SystemKristal Jade Yanto Esquillo100% (1)
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- Bikram Yoga Poses - Posture Pictures and BenefitsDocument31 pagesBikram Yoga Poses - Posture Pictures and Benefitsparadigma_12100% (3)
- Adjusting (Chiropractic Manipulative Therapy)Document458 pagesAdjusting (Chiropractic Manipulative Therapy)CasluclNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study Guide - TeacherDocument15 pagesUnit 3 Study Guide - Teacherapi-1986034770% (1)
- Organ Systems Work TogetherDocument15 pagesOrgan Systems Work TogetherShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TraumaDocument8 pagesAbdominal Traumahatem alsrour100% (2)
- Genbio Reviewer 1Document8 pagesGenbio Reviewer 1Franchezkka Mae Belaro100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/RationaleDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/Rationaleyachiru121No ratings yet
- 6.4 Multicellular OrganismsDocument4 pages6.4 Multicellular Organismspriya sundaramNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesBasic Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Shreshta Reddy KNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument7 pagesAnatomyM.AhsanNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1629098154770 6832932906945476564Document8 pagesOrca Share Media1629098154770 6832932906945476564Scar ShadowNo ratings yet
- MAPE 3 Anatomical, Mechanical and Physiological Bases of MovementDocument19 pagesMAPE 3 Anatomical, Mechanical and Physiological Bases of MovementPatricia Jean San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Organization of Body NotesDocument2 pagesOrganization of Body NotesAtikah EikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation: Chapter Outline of AnatomyDocument11 pagesChapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation: Chapter Outline of AnatomySijia HuangNo ratings yet
- GB2Q2-LAS-3-4Document10 pagesGB2Q2-LAS-3-4elyzaventura8No ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryDocument42 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryBrythym Mojeca De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Science Human Body SystemDocument9 pagesScience Human Body SystemJOSE RENE CASILINo ratings yet
- Anatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Document10 pagesAnatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Jay Carlo BagayasNo ratings yet
- W1 - 1 ModuleDocument7 pagesW1 - 1 ModuleGloryvi LatapNo ratings yet
- W1 - 1 ModuleDocument7 pagesW1 - 1 ModuleGloryvi LatapNo ratings yet
- Animal Organ SystemsDocument3 pagesAnimal Organ SystemsmaygracedigolNo ratings yet
- 2e Partie BIO 2054 HoméostasieDocument53 pages2e Partie BIO 2054 HoméostasieMassaou Blama RapataNo ratings yet
- MoreDocument6 pagesMoreLenovoNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System and Its TissuesDocument14 pagesThe Integumentary System and Its Tissuesxuxi dul100% (1)
- Organ Systems Quiz for AnimalsDocument21 pagesOrgan Systems Quiz for AnimalsJerico CastilloNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Module 4Document26 pagesGen Bio 1 Module 4AQUINO JAYSON KIERNo ratings yet
- Cell Types and Cell Modification: LessonDocument6 pagesCell Types and Cell Modification: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lectue August 10 2020Document5 pagesAnaphy Lectue August 10 2020Julianne Marie LacsentoNo ratings yet
- Comparing plant and animal cells, tissues, organs, and organ systemsDocument4 pagesComparing plant and animal cells, tissues, organs, and organ systemsDrin ZekaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologySam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Anatomy Lab MaterialDocument34 pagesVeterinary Anatomy Lab MaterialFira'ol BogalaNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document8 pagesUnit 2CLAUDIU---ALIN BOARTANo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument9 pagesHuman AnatomyJohaimaNo ratings yet
- Final Term - ZoologyDocument21 pagesFinal Term - ZoologyJustin LeeNo ratings yet
- MaxDocument4 pagesMaxagujetasmaxNo ratings yet
- EpithelialDocument8 pagesEpithelialRushyl Angela FaeldanNo ratings yet
- Answer To Module 6 - Q2 (Els)Document4 pagesAnswer To Module 6 - Q2 (Els)Angel MarieNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 ReviewDocument5 pagesCh. 1 ReviewDivine GelasiusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy basics for pg.Document2 pagesAnatomy basics for pg.ag8211729No ratings yet
- 2304 Intro AnatomyDocument6 pages2304 Intro AnatomyLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Level of OrganizationDocument14 pages2.3 Level of OrganizationLenovoNo ratings yet
- Sri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Document22 pagesSri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Sriarliza FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Document33 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Yego EdwinNo ratings yet
- Science Welcome LetterDocument1 pageScience Welcome Letterapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Themes in Fiction 1Document1 pageThemes in Fiction 1api-261172766No ratings yet
- Comparing Ecosystems Study GuideDocument1 pageComparing Ecosystems Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Ecosystems Study GuideDocument2 pagesEcosystems Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Good Evening ParentsDocument1 pageGood Evening Parentsapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Parent News 1Document1 pageParent News 1api-261172766No ratings yet
- Aquatic EcosystemsDocument16 pagesAquatic Ecosystemsapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Themes in Fiction 2Document1 pageThemes in Fiction 2api-261172766No ratings yet
- Terrestrial EcosystemsDocument17 pagesTerrestrial Ecosystemsapi-323449449No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Weather Study GuideDocument2 pagesWeather Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Ecosystems VocabularyDocument2 pagesEcosystems Vocabularyapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument25 pagesHeat Transferapi-261172766No ratings yet
- CloudsDocument3 pagesCloudsapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Convection Conduction Radiation Fact SheetDocument1 pageConvection Conduction Radiation Fact Sheetapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Wind NotesDocument6 pagesWind Notesapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Big Ten ExplorersDocument29 pagesBig Ten Explorersapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Exploration and The Colonial EraDocument38 pagesExploration and The Colonial Eraapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Opinion WritingDocument1 pageOpinion Writingapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Native Americans Who Discovered AmericaDocument5 pagesNative Americans Who Discovered Americaapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Making InferencesDocument1 pageMaking Inferencesapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Vikings European Explorers The VikingsDocument5 pagesVikings European Explorers The Vikingsapi-3234494490% (1)
- Pushing Your ThinkingDocument1 pagePushing Your Thinkingapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Reasons Evidence To Support Points in Informational TextDocument1 pageReasons Evidence To Support Points in Informational Textapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Vikings and European Explorers Christopher ColumbusDocument6 pagesVikings and European Explorers Christopher Columbusapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Show Me The EvidenceDocument1 pageShow Me The Evidenceapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Sentence FramesDocument1 pageSentence Framesapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Key WordsDocument1 pageKey Wordsapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Growth Assessment ParametersDocument97 pagesGrowth Assessment ParametersAurthi ElamparithiNo ratings yet
- Fawzia PhysiologyDocument42 pagesFawzia PhysiologySHARMIN UrmiNo ratings yet
- Week 7-9 SIM Human AnatomyDocument41 pagesWeek 7-9 SIM Human AnatomyVine OrtegaNo ratings yet
- PG 0093Document1 pagePG 0093MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Ob Notes EditedDocument28 pagesOb Notes EditedJake IliganNo ratings yet
- Holiday Package Biology f4 2017Document2 pagesHoliday Package Biology f4 2017putri_latifahNo ratings yet
- 18.19 the-role-of-the-supraglottic-area-in-voice-production-2161-119X.S1-001Document7 pages18.19 the-role-of-the-supraglottic-area-in-voice-production-2161-119X.S1-001Diana Carolina Cerón EstradaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment LandmarksDocument15 pagesRespiratory Assessment LandmarksChilled Moo MooNo ratings yet
- Cytologic Patterns - Eclinpath PDFDocument5 pagesCytologic Patterns - Eclinpath PDFJD46No ratings yet
- Module in Science 9: First Quarter/Week 1/day4Document5 pagesModule in Science 9: First Quarter/Week 1/day4Frederick EspejoNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia VeraDocument33 pagesPolycythemia VeramesseeeNo ratings yet
- How Do Phagocytes Work in The BodyDocument2 pagesHow Do Phagocytes Work in The Bodykei04086100% (1)
- RenalDocument1 pageRenalYezin Shamoon100% (1)
- Inclusion BodiesDocument5 pagesInclusion BodiespavanNo ratings yet
- Cells - Basic Unit of LifeDocument45 pagesCells - Basic Unit of Lifeapi-202349222No ratings yet
- HHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Document88 pagesHHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Lubomira SucheckiNo ratings yet
- 5 Anatomy of The Spleen DiyaDocument25 pages5 Anatomy of The Spleen DiyaBra KojoNo ratings yet
- The Human Circulatory System: Teacher: D.Bleau School: ST Anthony's Secondary SchoolDocument10 pagesThe Human Circulatory System: Teacher: D.Bleau School: ST Anthony's Secondary SchoolCaiden HenryNo ratings yet