Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics Exp 6
Uploaded by
Ck Wong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views6 pagesThe Mendelian Principles, Gene Interaction and Polygenic Inheritance
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Mendelian Principles, Gene Interaction and Polygenic Inheritance
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views6 pagesGenetics Exp 6
Uploaded by
Ck WongThe Mendelian Principles, Gene Interaction and Polygenic Inheritance
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Experiment 4
Title: The Mendelian Principles, Gene Interaction and Polygenic Inheritance
Part A: Gene Interaction
Objective:
To study the way to recognize and interpret maize F2 data which vary from the Mendels law of
segregation and law of independent assortment as a result of gene interaction.
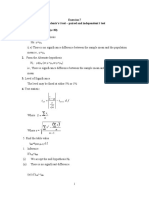
Result
Table 1: The results of the maizes kernels number were counted for each trait.
Maize code
Number of kernels
Purple Yellow White
6660 512 121 40
6680 111 295 98
6690 242 197 -
6700 121 610 -
For maize epistasis code 6660
H
0
: The ratio number of kernels were counted for purple : yellow : white is 12 : 3 : 1.
Phenotypes
Observed,
O
Expected, E O E (O E)
2
(O E)
2
/E
Purple 512 504.75 7.25 52.56 0.104
Yellow 121 126.19 -5.19 26.94 0.213
White 40 42.06 -2.06 4.24 0.1
Total 673 673 0 X
2
= 0.417
P value: 0.05 Degree of freedom: 3-1 = 2 Critical value: 5.991
Since, the calculated
2
value is smaller than the critical value, the H
0
is accepted. The ratio
number of kernels counted for purple : yellow : white is 12 : 3 : 1.
For maize epistasis code 6680
H
0
: The ratio number of kernels were counted for purple : yellow : white is 9 : 3 : 4.
Phenotypes
Observed,
O
Expected, E O E (O E)
2
(O E)
2
/E
Purple 111 126 -15 225 1.79
Yellow 295 283.5 11.5 132.25 0.47
White 98 94.5 3.5 12.25 0.13
Total 504 504 0 X
2
= 2.39
P value: 0.05 Degree of freedom: 3-1 = 2 Critical value: 5.991
Since, the calculated
2
value is smaller than the critical value, the H
0
is accepted. The ratio
number of kernels counted for purple : yellow : white is 9 : 3 : 4.
For maize epistasis code 6690
H
0
: The ratio number of kernels were counted for purple : yellow is 9 : 7.
Phenotypes
Observed,
O
Expected, E O E (O E)
2
(O E)
2
/E
Purple 242 246.94 -4.94 24.4 0.10
Yellow 197 192.06 4.94 24.4 0.13
Total 439 429 0 X
2
= 0.23
P value: 0.05 Degree of freedom: 2-1 = 1 Critical value: 3.841
Since, the calculated 2value is smaller than the critical value, therefore, the H
0
is accepted. The
ratio number of kernels were counted for purple: yellow : white is 9 : 7.
For maize epistasis code 6700
H
0
: The ratio number of kernels were counted for purple : yellow is 13 : 3.
Phenotypes
Observed,
O
Expected, E O E (O E)
2
(O E)
2
/E
Purple 121 137.06 -16.06 257.92 1.88
Yellow 610 593.94 16.06 257.92 0.43
Total 731 731 0 X
2
= 2.31
P value: 0.05 Degree of freedom: 2-1 = 1 Critical value: 3.841
Since, the calculated
2
value is smaller than the critical value , therefore, the H
0
is accepted. The
ratio number of kernels counted for purple : yellow : white is 13 : 3.
Part B: Polygenic Inheritance
Objective:
i. To investigate the way to construct a histogram by using the class data of total ridge counts
(TRC).
ii. To determine the characteristic of polygenic model of inheritance.
Result
Table 2: The data sheet for fingerprints of student
Left hand
Thumb Second Third Fourth Fifth
Pattern Loop Arch Arch Arch Loop
Ridge
Count
2 0 0 0 11
Fingerprints
Total Ridge Count (TRC) =13
Right hand
Thumb Second Third Fourth Fifth
Pattern Loop Arch Arch Arch Loop
Ridge
Count
8 0 0 0 4
Fingerprints
Total Ridge Count (TRC) = 12
Student Number of Fingers with TRC Sex
Loop Whorl Arch
YK 2 8 0 104 M
EW 9 0 1 85 M
SW 9 1 0 129 M
CH 5 4 1 133 M
Ben 9 0 1 68 M
WM 5 5 0 158 M
Henry 8 2 0 147 M
Sow Chan 7 3 0 195 F
Anna 10 0 0 179 F
Weni 7 3 0 102 F
Suzie 10 0 0 111 F
Elaine 0 10 0 155 F
Jess 3 7 0 143 F
Caryn 5 3 2 88 F
Joanne 4 6 0 162 F
Bryan 10 0 0 102 M
Krish 7 3 0 144 F
Chin Keong 4 0 6 25 M
Shu Jian 6 4 0 189 M
Chai Ching 7 2 1 95 F
Thong Wah 10 0 0 160 M
Shi Jing 5 0 5 56 F
Yong Syuan 3 7 0 167 F
Kok Sim 5 5 0 163 M
Yee Teng 6 0 4 83 F
Totals 156 73 21 3143
% of Totals 62.4% 29.2% 8.4%
Mean TRC 125.72
Mean Female TRC 129.23
Mean Male TRC 121.92
Table 4: The number of students in each category of TRC
TRC range
Number of students
Male Female
0 50 1 0
51 100 2 4
101 150 5 4
151 200 4 5
201 250 0 0
1
2
5
4
0 0
4 4
5
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0 50 51 100 101 150 151 200 201 250
Histogram of TRC amount of male and
female students
Number of students Number of students
Questions :
1. Is there a difference between male and female average TRCs?
From data collected, male has an average of 121.92 while female has an average of
129.23.
Yes, there is a difference between male and female average TRCs.
2. If so, what might account for this difference?
According to Acrees 1999 theory, men have coarse ridge detail that result in fewer
ridges while women tend to have finer ridge detail and therefore having more ridges.
(Bell, n.d.)
Reference:
Bell, A., n.d. Loop ridge count differences between genders. [Online]
Available at:
http://www.neiai.org/neiai/uploads/Kent%20Smotherman/files/Ridge%20counts%20between%20males
%20and%20females.pdf
[Accessed 10 July 2013].
You might also like
- BARRAQUIAS Probability and Chi SquareDocument3 pagesBARRAQUIAS Probability and Chi SquareFatima Shiera BarraquiasNo ratings yet
- Bio3TC17 Chi Square Test NotesDocument9 pagesBio3TC17 Chi Square Test NotesFounder ChaNo ratings yet
- 10 Inferential Statistics X - June 2 2014Document32 pages10 Inferential Statistics X - June 2 2014Bijay ThapaNo ratings yet
- Basic Genetics Lab Report 3 TmmorowDocument8 pagesBasic Genetics Lab Report 3 Tmmorowsharmeen17031995No ratings yet
- Chi Square Practice Problems KEYDocument4 pagesChi Square Practice Problems KEYKashim AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Set 5Document32 pagesLecture Set 5Dirt KickNo ratings yet
- Acquired CuppingDocument8 pagesAcquired CuppingjhuevosNo ratings yet
- Chi Squared TestDocument12 pagesChi Squared Testapi-188431847No ratings yet
- Chi Square TutorialDocument4 pagesChi Square TutorialCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Chi SquareDocument10 pagesChi Squareaaditya01No ratings yet
- Practice T-Test (12 Sample)Document14 pagesPractice T-Test (12 Sample)Samar KhanzadaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: H0: p1 p2 p3 Ha: Not All Population Proportions Are EqualDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: H0: p1 p2 p3 Ha: Not All Population Proportions Are Equalmartino chongasisNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing ExamplesDocument5 pagesHypothesis Testing ExamplesSenthilNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Test Lecture Note Final 2018Document19 pagesChi Square Test Lecture Note Final 2018Tumabang DivineNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet.280185356Document4 pagesChi Square Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet.280185356jaysonNo ratings yet
- Drosophila Lab ReportDocument7 pagesDrosophila Lab ReportTim HepburnNo ratings yet
- DIHIBRIDDocument8 pagesDIHIBRIDFata HalaniNo ratings yet
- 04 Activity Chi SquareDocument2 pages04 Activity Chi SquareRalph JustineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13-14-15 Chi - Square TestDocument22 pagesLecture 13-14-15 Chi - Square TestShahadat HossainNo ratings yet
- Gene311 LaguraDocument2 pagesGene311 LaguraJESSEL LEA LAGURANo ratings yet
- Section 9.5:: Versus: With 4 and 6Document23 pagesSection 9.5:: Versus: With 4 and 6hellomiketest_365886No ratings yet
- Emtinuiy T: (Eurvvcl)Document3 pagesEmtinuiy T: (Eurvvcl)sujay giriNo ratings yet
- K-S TestDocument34 pagesK-S TestKirithiga SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- The Test Use This Test WhenDocument23 pagesThe Test Use This Test WhenHellen Jeans TutorNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4-Genetic of Corn The Dhi-Square Analysis (Monohybrid Cross)Document5 pagesExperiment 4-Genetic of Corn The Dhi-Square Analysis (Monohybrid Cross)NUR SABRINA MOHD SHAHNo ratings yet
- Chi Square 2 - 2Document13 pagesChi Square 2 - 2Fruelan SaritaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument60 pagesUntitledJatin ParajiyaNo ratings yet
- Drosophilia Lab ReportDocument5 pagesDrosophilia Lab ReportMaddie BleaseNo ratings yet
- 485 HWDocument22 pages485 HWjiuj78No ratings yet
- Case Analysis FinalDocument7 pagesCase Analysis FinalPatricia ArominNo ratings yet
- ChiDocument26 pagesChiAbhinav RamariaNo ratings yet
- Chi Squared TestDocument20 pagesChi Squared Testaby251188No ratings yet
- Activity No.7 - Chi Square and Binomial Probability-LEPASANADocument4 pagesActivity No.7 - Chi Square and Binomial Probability-LEPASANAMichael Clyde lepasana100% (2)
- Chi Square AnalysisDocument15 pagesChi Square AnalysisPotatoNo ratings yet
- 0 and H 0. Place 1 P-Value: ST NDDocument2 pages0 and H 0. Place 1 P-Value: ST NDSherina CapolaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Statistical GeneticsDocument61 pagesIntroduction of Statistical GeneticsJubair Al-rashid100% (2)
- MathsDocument13 pagesMathsfaroukgamer797No ratings yet
- Commuting Time High Moderate Low Total 32 53 31 Total 44 19 53 116 StressDocument13 pagesCommuting Time High Moderate Low Total 32 53 31 Total 44 19 53 116 StressShobhit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chi - Square Test: PG Students: DR Amit Gujarathi DR Naresh GillDocument32 pagesChi - Square Test: PG Students: DR Amit Gujarathi DR Naresh GillNaresh GillNo ratings yet
- Chi SquaredDocument13 pagesChi SquaredTheophilus FrimpongNo ratings yet
- MSN Uji U Mann WhitneyDocument29 pagesMSN Uji U Mann Whitney3rlangNo ratings yet
- Aieee Papercode 2011Document17 pagesAieee Papercode 2011Anonymous eCmTYonQ84No ratings yet
- Bordallo Sample Problems 3rd ExamDocument4 pagesBordallo Sample Problems 3rd ExamAngela SANo ratings yet
- Statistics Assignement Final 11Document72 pagesStatistics Assignement Final 11Samuel LemaNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Autosaved)Document75 pagesStatistics (Autosaved)sabel sardillaNo ratings yet
- HMMDocument13 pagesHMMJudd Maverick Rufin TanNo ratings yet
- One Sample Sign TestDocument24 pagesOne Sample Sign TestRohaila RohaniNo ratings yet
- Levelt Geer Plomp (1966) TRIADIC COMPARISONS OF MUSICAL INTERVALSDocument18 pagesLevelt Geer Plomp (1966) TRIADIC COMPARISONS OF MUSICAL INTERVALSnajiNo ratings yet
- Confidence Interval For Median Based On Sign TestDocument32 pagesConfidence Interval For Median Based On Sign TestRohaila Rohani100% (1)
- Corn Genetics - Kelompok 4Document7 pagesCorn Genetics - Kelompok 4Delia NurusyifaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24-Population GeneticsDocument72 pagesChapter 24-Population GeneticsJean Pierre RullierNo ratings yet
- Chi SquareDocument37 pagesChi SquareGhazie HadiffNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Distributions: Prof G.R.C.NairDocument20 pagesChi Square Distributions: Prof G.R.C.Nairanindya_kunduNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet.280185356Document4 pagesChi Square Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet.280185356Gaurang Dave100% (3)
- Lab 7 (Fruit FliesDocument3 pagesLab 7 (Fruit FliesStevwhitkneeNo ratings yet
- Sample ProblemsDocument21 pagesSample ProblemsReshma ShivanandNo ratings yet
- 68th AACC Annual Scientific Meeting Abstract eBookFrom Everand68th AACC Annual Scientific Meeting Abstract eBookNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionFrom EverandQuantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Analysis of Tomato FungiDocument3 pagesEnzymatic Analysis of Tomato FungiCk WongNo ratings yet
- Enzymology Experiement 3Document11 pagesEnzymology Experiement 3Ck Wong100% (1)
- Determining The Water Content of A Given Hydrated SaltDocument5 pagesDetermining The Water Content of A Given Hydrated SaltCk WongNo ratings yet
- Determining The Concentration of NaOH Solution.Document6 pagesDetermining The Concentration of NaOH Solution.Ck WongNo ratings yet
- Epistasis (Lect 16 & 17)Document15 pagesEpistasis (Lect 16 & 17)Erum JanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative GeneticsDocument27 pagesQuantitative GeneticsCapitán NemoNo ratings yet
- Activity2 Cancer Patients Teacher PDFDocument8 pagesActivity2 Cancer Patients Teacher PDFIsmael FernandezNo ratings yet
- II Year IV Semester 2017 SyllabusDocument32 pagesII Year IV Semester 2017 SyllabusRamanan RNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab SyllabusDocument5 pagesGenetics Lab SyllabusKumael JafriNo ratings yet
- The Evolutionary Paradox and The Missing Heritability of SchizophreniaDocument15 pagesThe Evolutionary Paradox and The Missing Heritability of SchizophreniadrnecromanceNo ratings yet
- Gene TikaDocument5 pagesGene Tikaluluk.farichaNo ratings yet
- 7 EpistasisDocument33 pages7 EpistasisDasari SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Specialty CornsDocument469 pagesSpecialty CornsKarina Renostro DucattiNo ratings yet
- Inheritance of Kernel Color in Corn: Explanations & InvestigationsDocument8 pagesInheritance of Kernel Color in Corn: Explanations & InvestigationsEricNo ratings yet
- Cyto311 Lec - Week 11 - Modification of Mendelian Ratios (Part 1)Document3 pagesCyto311 Lec - Week 11 - Modification of Mendelian Ratios (Part 1)Jayvhie Gulane LayanNo ratings yet
- Quantative Genetics and EvolutionDocument8 pagesQuantative Genetics and EvolutionKarlo MarksićNo ratings yet
- CDSI - GB2 12 PPT5 - Gene InteractiongDocument104 pagesCDSI - GB2 12 PPT5 - Gene Interactiongjzjz14324No ratings yet
- ALE 2019 - CROP SCIENCE - Mockboard Exam Set A-B With Answer SheetDocument15 pagesALE 2019 - CROP SCIENCE - Mockboard Exam Set A-B With Answer SheetEda Mirafuentes100% (1)
- BBCCT 121Document12 pagesBBCCT 121Sahil TyagiNo ratings yet
- Agricultural ScienceDocument266 pagesAgricultural ScienceAnonymous XXENB3eONo ratings yet
- Bangalore University: B.SC., Genetics SyllabusDocument34 pagesBangalore University: B.SC., Genetics Syllabussuna ljNo ratings yet
- Gene Interaction NS W12Document38 pagesGene Interaction NS W12Jasmin Hernandez CataranNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology: InheritanceDocument35 pagesA Level Biology: InheritanceMaisarah HalimNo ratings yet
- L5 - Gene InteractionDocument23 pagesL5 - Gene Interactioncora o brien100% (1)
- Polygenic Inheritance PBGDocument7 pagesPolygenic Inheritance PBGPrasanna GopikaNo ratings yet
- Adaptation To High Rates of Chromosomal Instability and Aneuploidy Through Multiple Pathways in Budding YeastDocument19 pagesAdaptation To High Rates of Chromosomal Instability and Aneuploidy Through Multiple Pathways in Budding YeastFernandoNo ratings yet
- LifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionDocument174 pagesLifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionSatyam SoniNo ratings yet
- 2 GeneovrhDocument28 pages2 GeneovrhAndres ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Suppressor MutationsDocument46 pagesSuppressor MutationsBobbyWhiteNo ratings yet
- Heredity Inheritance and VariationDocument87 pagesHeredity Inheritance and Variationmj Canilang100% (1)
- Syllabus For 5-Years Integrated M. Sc. Degree: UM-DAE Centre For Excellence in Basic SciencesDocument92 pagesSyllabus For 5-Years Integrated M. Sc. Degree: UM-DAE Centre For Excellence in Basic SciencesAubal ShaubalNo ratings yet
- Interaction of GenesDocument15 pagesInteraction of GenesAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- GENETIC ANALYSIS OF RESISTANCE TO POD SHATTERING IN SOYBEAN (Glycine Max, L Merrill) - by Haruna Mohammed.Document88 pagesGENETIC ANALYSIS OF RESISTANCE TO POD SHATTERING IN SOYBEAN (Glycine Max, L Merrill) - by Haruna Mohammed.Barkat2012100% (2)
- AS 318-Plant Genetics and Breeding (3 CHRS)Document7 pagesAS 318-Plant Genetics and Breeding (3 CHRS)Warner OkianNo ratings yet