Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
markhabmOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
markhabmCopyright:
Available Formats
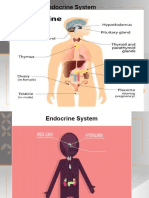
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FACT SHEET
KEY FUNCTION
Endocrine glands (ductless glands) secrete hormones that travel thru the
bloodstream to signal specific target cells
Along with the NS the endocrine system function to achieve and maintain
stability of the internal environment
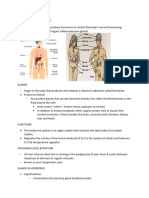
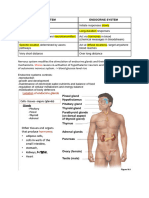
GLANDS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
HYPOTHALAMUS
Part of the diencephalon below the thalamus
Connects to pituitary gland
Regulates the ANS temp, appetite, sweating, thirst, sexual behavior
this occurs thru its connection with the pituitary
PITUITARY
Size of a pea located @ the base of the brain stem
2 separate glands adenohypophysis (anterior) and neurohypophysis
(posterior)
MOST IMPORTANT endocrine gland b/c it releases hormones that
regulate several other endocrine glands
Influenced by seasonal changes and emotions
Secretes endorphins that act on NS and reduce sensitivity to pain
Controls ovulation and works as a catalyst for the testes and ovaries
to create sex hormones
THYROID
Located anterior/laterally to trachea it is responsible for producing
triiodothyronine which controls the rate @ which cells burn the fuel
from food
PARATHYROID
Produce parathyroid hormone which is an antagonist to calcitonin
and is important for the maintenance of normal blood levels of
calcium and phosphate
Increases the reabsorption of calcium and phosphate from bones to
blood
Secretion of parathyroid is stimulated by hypocalcaemia
ADRENAL GLANDS
Outer portion = adrenal cortex, inner portion = adrenal medulla
Produces corticosteroids that regular water/sodium balance, bodys
response to stress, immune system, sexual development and
metabolism
Medulla produces epinephrine that increases HR and BP w/ increase
stress
PANCREAS
Includes both endocrine and exocrine tissues
Islets of Langerhans are hormone producing cells of the pancreas
Alpha cells produce glucagon and beta cells produce insulin
These hormones work together to ensure a consistent level of glucose
and maintain stores of energy
OVARIES
Provide estrogens and progesterone that regular menstrual
cycle/pregnancy
Estrogen is secreted by ovarian follicles: needed for the development
and maintenance of female characteristics
Progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum and maintains the
lining of the uterus @ a level necessary for pregnancy
TESTES
Secrete androgens (most important = testosterone) which support
male sexual characteristics and production of sperm
HORMONE CLASSES
STERIOD HORMONES
Example = prostaglandins
Created by all cells from the phospholipids of the cell membranes
Do not circulate in blood but exert effects only where they are
produced
Effects include inflammation, pain, vasodilation, vasoconstriction,
nutrient metabolism and blood clotting
AMINE HORMONES
Example = catecholamines which are epinephrine, norepinephrine
and dopamine
Synthesized from chromaffin cells w/in adrenal medulla
Stimulated by SNS
Epinephrine has largest effect on the sympathetic nervous system
o Target receptors are in the cardiovascular system and
metabolic system
Other effects = increasing cardiac contraction, vasoconstriction,
activation of glycogen breakdown, blocking insulin secretion, increase
metabolic rate, dilation of airways
PEPTIDE HORMONES
Example = insulin
Secreted by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans w/in pancreas
You might also like
- Vishram Singh AnatomyDocument5 pagesVishram Singh AnatomyShahab Uddin33% (3)
- UNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Document7 pagesUNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesEndocrine System•Svbrinv29•No ratings yet
- Endocrine RegulationDocument18 pagesEndocrine RegulationAdela RomeroNo ratings yet
- Presented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarDocument34 pagesPresented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarSohaib NasirNo ratings yet
- HormonDocument19 pagesHormonhusni fauzi hartiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesLesson 10 Endocrine SystemBai Donna S. AlimanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNo ratings yet
- Secretion From The Pineal GlandDocument8 pagesSecretion From The Pineal GlandVince Laurence BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument6 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationRonaldNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemNovie Jane HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Endorine SystemDocument27 pagesEndorine SystemBenjamin YickNo ratings yet
- Muscular-Endocrine 1Document7 pagesMuscular-Endocrine 1JD BunielNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Report (ANATOMY)Document24 pagesEndocrine System Report (ANATOMY)Pen TuraNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDocument35 pagesThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesShe JocelynNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument15 pagesEndocrineapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Control of Our Bodies HomeostasisDocument20 pagesControl of Our Bodies HomeostasisJohn Philip VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. SevillenoDocument55 pagesAnatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. Sevillenocoral jade cuaNo ratings yet
- Async Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchDocument156 pagesAsync Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- What Are Hormones?Document4 pagesWhat Are Hormones?Uzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesOverview of The Endocrine SystemTAGUIAM, Danica A.No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Different Glands of The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesDifferent Glands of The Endocrine SystemNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument45 pagesEndocrine Glandsabhaytyagi98No ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrineHoney Mie MorenoNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SystemDocument54 pagesENDOCRINE SystemSJO1 G6- Escaro,Shaira JoyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument51 pagesEndocrine SystemJb MoratallaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument13 pagesThe Endocrine SystemhelenafuertestoranNo ratings yet
- Sistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKDocument25 pagesSistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKRichas Interisti SumatraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument3 pagesEndocrine DisordersIrish OrleansNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System-JULYDocument40 pagesThe Endocrine System-JULYKELVINNo ratings yet
- Chemical CoordinationDocument29 pagesChemical Coordinationjackieaj093100% (1)
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Noteshannah pelonia100% (1)
- Role of Hormones Endocrine 1Document37 pagesRole of Hormones Endocrine 1zyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- CLASS:10 Subject:Biology Chapter:Control and CoordinationDocument14 pagesCLASS:10 Subject:Biology Chapter:Control and Coordinationkhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- An Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesAn Endocrine SystemEvbogame Iyare IbhadeNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesVisibleBody Endocrine Systemcascavelette0% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument95 pagesEndocrine SystemUmar Ilyasu JibrilNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesEndocrine Systemkevin maheshNo ratings yet
- Compiled by Howie BaumDocument40 pagesCompiled by Howie BaumMaría José Castellanos GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument1 pageEndocrineDiwata DonatoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninDocument4 pagesEndocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninHazel Mae Tapia100% (1)
- Adrenal Glands: Subject AboutDocument17 pagesAdrenal Glands: Subject AboutHareth mohammad mahmod NawajaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 2Document13 pagesEndocrine 2Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemChechan AmbaNo ratings yet
- What Does The Endocrine System Do?Document10 pagesWhat Does The Endocrine System Do?hadiqa azizNo ratings yet
- HistoEndocrineSystem by DR - NaDocument64 pagesHistoEndocrineSystem by DR - NaAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- BT101 - Introductory Biology (Endocrine/Exocrine) DR - Navin Gupta Dept of BSBE, IIT GuwahatiDocument17 pagesBT101 - Introductory Biology (Endocrine/Exocrine) DR - Navin Gupta Dept of BSBE, IIT GuwahatirechinNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRyan Kim FabrosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System A & P MODDocument14 pagesEndocrine System A & P MODDollyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReportDocument5 pagesNervous System ReportsharkNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System A & PDocument14 pagesEndocrine System A & PDollyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Hormone RegulationDocument20 pagesEndocrine System: Hormone RegulationMark RamosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Document61 pagesEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 PhysiologyDocument49 pagesChapter - 17 PhysiologyAhsanullah PathanNo ratings yet
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument12 pagesHeartRebar photographyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex ActivityDocument53 pagesChapter 13 - The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activityramadan100% (1)
- Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesCell BiologySharad DahalNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Human BodyDocument6 pagesOrganization of The Human BodySharmaine DurangoNo ratings yet
- Workbook3 ExcretionDocument12 pagesWorkbook3 ExcretionDarambazar GantulgaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument55 pagesUrinary SystemChristian UdaundoNo ratings yet
- Biology Presentation Class 7Document11 pagesBiology Presentation Class 7binu biju100% (2)
- Suprarenal GlandDocument13 pagesSuprarenal GlandAaa JjjjNo ratings yet
- 2 AnsDocument29 pages2 AnsSara AljadaniNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument48 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary GlandMohsin AbbasNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Case StudyDocument41 pagesTetanus Case StudyFAt Ty100% (1)
- LEOPOLD MANEUVER RetdemDocument3 pagesLEOPOLD MANEUVER Retdemjohncarlo ramosNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Worksheet 3Document5 pagesLaboratory Worksheet 3Johanna AlexaNo ratings yet
- Massage Therapy Treatment ManualDocument52 pagesMassage Therapy Treatment ManualShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Unicellular and Multicellular OrganisemsDocument54 pagesUnicellular and Multicellular Organisemsmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism Is A Common and Potentially Lethal ConditionDocument13 pagesPulmonary Embolism Is A Common and Potentially Lethal ConditionJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Form 3 BioDocument4 pagesForm 3 BioBen ChelagatNo ratings yet
- Complications of Bed RestDocument51 pagesComplications of Bed Restsuderson100% (1)
- The Cytoskeleton and Cell MotilityDocument38 pagesThe Cytoskeleton and Cell MotilityerikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Seeleys Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition TateDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Seeleys Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Edition TateAdrianLynchnbjf100% (35)
- Gen Bio 2 Summative Test Q4 Week 1 and 2Document3 pagesGen Bio 2 Summative Test Q4 Week 1 and 2Daniel Angelo Esquejo ArangoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test - QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnatomy Test - QuestionsNom NomNo ratings yet
- 12-2 - Fri - vision-hearing-EQDocument13 pages12-2 - Fri - vision-hearing-EQTyler DeanNo ratings yet
- Physio CAT 2 AnsweredDocument34 pagesPhysio CAT 2 AnsweredJohn KennedyNo ratings yet
- MaxilaDocument360 pagesMaxilaCristian Belous0% (1)
- MUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingDocument42 pagesMUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingMerhella Amor Suerte MendozaNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urinary System Crossword Answers GR 4Document1 pageRenal and Urinary System Crossword Answers GR 4Raymond EdgeNo ratings yet
- ObsgynDocument105 pagesObsgynNugroho SigitNo ratings yet
- L3 Hematology Regulation of Iron MetabolismDocument3 pagesL3 Hematology Regulation of Iron MetabolismMurtadha AlrubayeNo ratings yet