Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VLSI Lab Man
Uploaded by
Varsha Degaonkar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views7 pagesADC 0808 is an 8 bit successive approximation ADC. This chip has 8channel along with multiplexer. Address lines A, B, C are connected to PB0, PB1 & PB2 for selecting channel 0. Signal conditioner processes the transducer output signal and makes compatible for control, record or display with the help of analog to digital converter. When conversion process is complete then ADC send EOC signal which is connected to the PC1 pin which indicates the end of conversion
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentADC 0808 is an 8 bit successive approximation ADC. This chip has 8channel along with multiplexer. Address lines A, B, C are connected to PB0, PB1 & PB2 for selecting channel 0. Signal conditioner processes the transducer output signal and makes compatible for control, record or display with the help of analog to digital converter. When conversion process is complete then ADC send EOC signal which is connected to the PC1 pin which indicates the end of conversion
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views7 pagesVLSI Lab Man
Uploaded by
Varsha DegaonkarADC 0808 is an 8 bit successive approximation ADC. This chip has 8channel along with multiplexer. Address lines A, B, C are connected to PB0, PB1 & PB2 for selecting channel 0. Signal conditioner processes the transducer output signal and makes compatible for control, record or display with the help of analog to digital converter. When conversion process is complete then ADC send EOC signal which is connected to the PC1 pin which indicates the end of conversion
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
PROBLEM STATEMENT: Write VHDL code and test bench, synthesis, simulate
and down load in to PLD to sense physical parameter such as
temperature/pressure/flow etc., convert in to digital using ADC, and interface
to PLD and display.
OBJECTIVE:
1. To understand the concept of ADC interfacing
2. To understand the concept of converting physical parameters into digital
and display it.
THEORY:
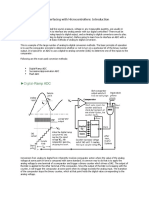
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig: 1.1 Block diagram of temperature/pressure/flow converter into digital
This block diagram is used to convert any physical quantity like temperature,
pressure or flow into digital. The input to the system is physical quantity such as
temperature, pressure or flow such quantity is called as input measurand. With
the help of transducer converts the mesurand into a electrical signal such as
voltage or current. Signal conditioner processes the transducer output signal and
makes compatible for control, record or display with the help of analog to digital
converter.
ADC INTERFACING:
ADC 0808 is an 8 bit successive approximation ADC. This chip has 8channel
along with multiplexer. The channel select has address lines A, B, C. We can use
channel 0 as input thus. Address lines A, B, C are connected to PB0, PB1 &PB2
for selecting channel 0. The ALE pin is connected to thePC6. At the time of power
on the valid channel address is latched at the rising edge of the ALE signal. ADC
0809 has an START on Conversion pin. A positive going pulse of short duration,
is applied to this pin this pin starts the A/D conversion process. When
conversion process is complete then ADC send EOC signal which is connected to
the PC1 pin which indicates the end of conversion. The OE should always be
high, when data is to be read. The port C upper and port B are defined in the
output mode, where as port C lower of 8255 is configured in input mode. The
ASSIGNMENT NO.1
TITLE: Synthesis, simulate and down temperature/pressure/flow
etc., convert in to digital using ADC, interface to PLD and display.
Sensor Signal
conditioner
ADC Linearizer Digital
Display
Page 2
data is read through port B of 8255. Below fig. shows the interfacing diagram of
ADC 0808 with 8086. & timing diagram of ADC
Fig:1.2 ADC interfacing Diagram
ALGORITHM:
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM:
I/O PORTS DETAILS:
SYNTHESIS REPORT:
TEST BENCH WAVEFORMS:
FAQs:
1. Explain dual slope and successive approximation method of ADC in details
2. Define VHDL syntax for
Page 3
A) Entity
B) Architecture
C) Component
D) Process
CONCLUSION:
Page 4
PROBLEM STATEMENT: Write VHDL code and test bench, synthesis, simulate
and down load in to PLD to generate ramp/square waveform using DAC
OBJECTIVE:
1. To understand the concept of square wave using DAC 0808/0809 and
observe wave on CRO.
2. To understand the concept of Ramp wave using DAC 0808/0809 and
observe wave on CRO.
THEORY:
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Clock
Reset
Fig.2.1: Block diagram of DAC converter
This system generates square wave and Ramp wave using Digital to Analog
Converter (DAC).This DAC accepts 8 bits of input data and generates the square
wave and Ramp wave. The logic of the wave generator is written in VHDL that
produces the 8 bit digital outputs which is then applied to the input to DAC
module by interfacing ADC-DAC add on card. The DAC output is then applied
to the CRO to check square wave and Ramp wave.
1. Square Wave Variable Duty Cycle and Frequency:
To generate square wave we will output FFH and then 00H on port A of 8255.
The output of 8255 (port A) is compulsory connected to the DAC 0808. To vary
the duty cycle it is necessary to vary Ton and Toff time. Variation in Duty cycle
will automatically change the frequency as,
Duty cycle = Ton/(Ton+Toff) = Ton/T frequency
ASSIGNMENT NO.2
TITLE: Synthesis, simulate and down load in to PLD to generate
ramp/square waveform using DAC
Frequency
generator
ADC-DAC
Add- On card
CRO
Page 5
To change time period the Delay between the two outputs (FFH for high output
and 00H for low output) should be change. Below fig shows the interfacing
diagram of DAC 0808 with 8086 & pin configuration of IC 0808
Fig. 2.2: 8bit DAC0808 D/A converter
3. Ramp Wave:
To generate ramp wave output 00H to FFH with some delay after every step
and then immediately output 00H. To obtain ramp wave with reverse direction
then, output above sequence in reverse manner. To obtain ramp wave in
forward direction, initialize, AL = 00H, otherwise AL = FFH for reverse
direction.
ALGORITHM:
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM:
I/O PORTS DETAILS:
SYNTHESIS REPORT:
TEST BENCH WAVEFORMS:
FAQ:
1. What is digital to analog converter explain with different methods and IC
number.
2. Write a short notes on layout rules.
CONCLUSION:
Page 6
PROBLEM STATEMENT: Write VHDL code and test bench, synthesis,
simulate and down load in to PLD to design lift/traffic light controller.
OBJECTIVE:
1. To understand the concept of finite state machine for 2 lane or 4 lane
traffic light controller.
2. To understand the implementation of state model with the help of
FPGA module.
THEORY:
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION AND BLOCK DIAGRAM:
The traffic light controller is for an intersection between a main street and a side
street for four ways of signal. And for all side contains red, yellow and green
signal light. The operating sequence of this intersection begins with the main
street having a green light turn on to run traffic, next light turns yellow for ready
to stop and then turned red for stop the traffic while simultaneously turning on
the side street green light. The side street is green for running the traffic under
normal circumstances. This cycle repeats continuously.
clock
Reset
R1 G1Y1 R2G2Y2 R3G3 Y3 R4 G4 Y4
Fig. 3.1: Block diagram of traffic light controller
ALGORITHM:
FINITE STATE MACHINE:
STATE DIAGRAM:
ASSIGNMENT NO.3
TITLE: Synthesis, simulate and down load in to PLD to design
lift/traffic light controller.
Traffic light controller
Page 7
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM:
I/O PORTS DETAILS:
SYNTHESIS REPORT:
TEST BENCH WAVEFORMS:
FAQ:
1. What is function and procedure? Describe it with VHDL example.
2. Explain VLSI design flow.
CONCLUSION:
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- PDFDocument688 pagesPDFaymanaymanNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterRavi Patel100% (1)
- ADC TutorialDocument17 pagesADC TutorialNagabhushanam KoduriNo ratings yet
- 8 A-D ConverterDocument30 pages8 A-D Converterneoloader145No ratings yet
- Robotic Arm 8051Document9 pagesRobotic Arm 8051Abhishek Shah0% (1)
- Mini Project Report-2Document26 pagesMini Project Report-2Remya Ramakrishnan0% (2)
- Applications of Handshake ModeDocument3 pagesApplications of Handshake Modevyshnu3006No ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterPratyay DharNo ratings yet
- Micro ProcessDocument51 pagesMicro ProcessHoney BhatiaNo ratings yet
- ADC0808Document15 pagesADC0808Ketan SalviNo ratings yet
- 8085 Memory InterfacingDocument17 pages8085 Memory InterfacingMadhavan SamNo ratings yet
- 7-Segment Display & ADC Controls With 8051: LABORATORY - Experiment 5Document12 pages7-Segment Display & ADC Controls With 8051: LABORATORY - Experiment 5Vikas Ravi TPNo ratings yet
- L4 EaDocument7 pagesL4 EaIoanaNicoletaNo ratings yet
- Digital To Analog Converters NotesDocument12 pagesDigital To Analog Converters Noteszoluska xyzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Adc PWMDocument36 pagesLesson Adc PWMDavidRubeomNo ratings yet
- Adc Dac InterfacingDocument25 pagesAdc Dac InterfacingSuchetha SriNo ratings yet
- Parallel and Serial AdcDocument45 pagesParallel and Serial AdcAman Deep100% (1)
- Adc Lab Pic18Document23 pagesAdc Lab Pic18Bolarinwa Joseph100% (1)
- Interfacing ADC To 8051Document3 pagesInterfacing ADC To 8051Aditya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Interfacing With Data Converters and Steeper MotorDocument28 pagesInterfacing With Data Converters and Steeper Motorsatyanarayana12No ratings yet
- Statement: Write A Assembly Program To Transmit A Message FromDocument12 pagesStatement: Write A Assembly Program To Transmit A Message Froms,reegan_siet5749100% (1)
- National Institute of Technology, Rourkela: Embedded Systems LaboratoryDocument13 pagesNational Institute of Technology, Rourkela: Embedded Systems Laboratoryprateekkumardash2002No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: 8-Bit A/D and D/A ConverterDocument28 pagesData Sheet: 8-Bit A/D and D/A ConverterSainathan AiyarNo ratings yet
- Adc0808 CodeDocument3 pagesAdc0808 CodebalabooksNo ratings yet
- (Model No:VBMB - 002) : 8-Bit Digital To Analog Converter Interface BoardDocument56 pages(Model No:VBMB - 002) : 8-Bit Digital To Analog Converter Interface BoardSanthanu Surendran100% (1)
- 5.AD and DA ConvertersDocument7 pages5.AD and DA ConvertersAkram TahaNo ratings yet
- Applications of 8085 Microprocessor Dac InterfaceDocument4 pagesApplications of 8085 Microprocessor Dac InterfaceSai PrakashNo ratings yet
- Interfacing Adc 0808 To 8051 Micro ControllerDocument4 pagesInterfacing Adc 0808 To 8051 Micro Controllermatrixworld20No ratings yet
- PIC PPT 13104022 (4th Year)Document41 pagesPIC PPT 13104022 (4th Year)Daman Deep Singh100% (1)
- 8051 InterfacingDocument32 pages8051 InterfacingSrikar NamburuNo ratings yet
- ADC and DACDocument16 pagesADC and DACThota Indra MohanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 6 - Analog To DigitalDocument4 pagesLaboratory Experiment 6 - Analog To DigitalyellowsubmirNo ratings yet
- Interfacing To The Analog WorldDocument47 pagesInterfacing To The Analog WorldRM ZhaloNo ratings yet
- ADC Interfacing With MicrocontrollersDocument9 pagesADC Interfacing With MicrocontrollersLuis MezaNo ratings yet
- Adc 0808Document14 pagesAdc 0808Vikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Interface Part IV MicroprocessorDocument30 pagesDigital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Interface Part IV MicroprocessorVineeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Interfacing Adc 0808 To 8051 Micro Controller - A Knol by Amol ShahDocument9 pagesInterfacing Adc 0808 To 8051 Micro Controller - A Knol by Amol ShahSamantha TanNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed Control Using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)Document30 pagesDC Motor Speed Control Using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)अमरेश झाNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument12 pagesAdc DacSonu SauravNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConversionDocument4 pagesAnalog To Digital ConversionAnkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Quadrature Encoder Receiver Module: An Implementation On FPGADocument12 pagesQuadrature Encoder Receiver Module: An Implementation On FPGAสหายดิว ลูกพระอาทิตย์No ratings yet
- Adc 0808Document6 pagesAdc 0808GokulThalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Analog-to-Digital Converter: The PIC18 MicrocontrollerDocument74 pagesChapter 12: Analog-to-Digital Converter: The PIC18 MicrocontrollerHamzah NaserNo ratings yet
- μP Compatible A/D Converters with 8-Channel: ADC0808/ADC0809 8-Bit MultiplexerDocument16 pagesμP Compatible A/D Converters with 8-Channel: ADC0808/ADC0809 8-Bit MultiplexerKasi ChinnaNo ratings yet
- Tty To Rs232Document8 pagesTty To Rs232sandeepverma8257100% (2)
- Berkes - Interfacing Exp ArrangementDocument20 pagesBerkes - Interfacing Exp ArrangementAditya K NNo ratings yet
- MP Lab ManualDocument11 pagesMP Lab ManualRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Project Objective:: Simple AdcDocument10 pagesProject Objective:: Simple AdcaravindnehaNo ratings yet
- Dac Interface To 8051 PDFDocument4 pagesDac Interface To 8051 PDFRAVI100% (1)
- AdcDocument3 pagesAdcGopi ChannagiriNo ratings yet
- Experiment #5 Interfacing A/D and D/A With The MicrocontrollersDocument3 pagesExperiment #5 Interfacing A/D and D/A With The MicrocontrollersErgin ÖzdikicioğluNo ratings yet
- Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC) Interfacing With MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Converter (ADC) Interfacing With MicrocontrollerSridhar DineshNo ratings yet
- μP Compatible A/D Converters with 8-Channel: ADC0808/ADC0809 8-Bit MultiplexerDocument16 pagesμP Compatible A/D Converters with 8-Channel: ADC0808/ADC0809 8-Bit MultiplexerKudo ShinichiNo ratings yet
- M4 Micro OneNoteDocument6 pagesM4 Micro OneNoteAryan RaiNo ratings yet
- Adc 0808Document6 pagesAdc 0808src e-solutionsNo ratings yet
- TMS320F2812-Analogue To Digital ConverterDocument26 pagesTMS320F2812-Analogue To Digital ConverterPantech ProLabs India Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Flash ADC Design in ElectricDocument22 pagesFlash ADC Design in ElectricNagaraj HegdeNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Conversion: IntroductionDocument8 pagesAnalog To Digital Conversion: IntroductionKeyur ParekhNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- Interfacing Programs For 8085Document37 pagesInterfacing Programs For 8085archankumarturagaNo ratings yet
- MPI Lab ManualDocument103 pagesMPI Lab ManualVeerayya JavvajiNo ratings yet
- Pin Out Mikroprosesor 8088 Pertemuan IIDocument13 pagesPin Out Mikroprosesor 8088 Pertemuan IIFuat muzakiNo ratings yet
- Microproceesor Lab ManualDocument5 pagesMicroproceesor Lab ManualrajanNo ratings yet
- 8255 - SeminarDocument28 pages8255 - SeminarJKNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument72 pagesProjectsellysaidi100% (1)
- Microprocessors: MicrocontrollersDocument5 pagesMicroprocessors: MicrocontrollersSureshNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller 1 J2 and 3 Module NotesDocument38 pagesMicrocontroller 1 J2 and 3 Module NotesArun RajNo ratings yet
- MM Mod3 QBDocument2 pagesMM Mod3 QBAnu CadzieNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor & Interfacing (BELL/BETL-504) Question Bank / TutorialDocument16 pagesMicroprocessor & Interfacing (BELL/BETL-504) Question Bank / TutorialVikas MahorNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 Interfacing PIC Using PPIDocument5 pagesLab 11 Interfacing PIC Using PPIlimanmembersNo ratings yet
- Ece MpiDocument68 pagesEce MpiVamshi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MP Lab ManualDocument51 pagesMP Lab ManualdevirpasadNo ratings yet
- DAQ NI PCI-6509 DatasheetDocument9 pagesDAQ NI PCI-6509 DatasheetSoaib ImranNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicrocontrollerDocument55 pages8085 MicrocontrollerSathieshKumarNo ratings yet
- (AN778) Implementing External Memory Interface On PIC18C601,801 PDFDocument32 pages(AN778) Implementing External Memory Interface On PIC18C601,801 PDFnokchin100% (1)
- M&M KEC502 Unit-3 Assignment-2Document1 pageM&M KEC502 Unit-3 Assignment-2manavh857No ratings yet
- 8255Document84 pages8255spowna0% (1)
- CaoDocument13 pagesCaoragavendharNo ratings yet
- MPMC Lab Manual EEE PDFDocument124 pagesMPMC Lab Manual EEE PDFPreetham Raja100% (3)
- 8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface: Features Pinout Block Diagram BSR Mode I/O Mode Mode 1 Mode 2Document4 pages8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface: Features Pinout Block Diagram BSR Mode I/O Mode Mode 1 Mode 2Kiran James MathewNo ratings yet
- 8085 Programable Peripheral InterfaceDocument16 pages8085 Programable Peripheral InterfaceShiva ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering Fifth Semester: Lab ManualDocument28 pagesBachelor of Engineering Fifth Semester: Lab ManualAkanksha DixitNo ratings yet
- MPI Mid Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesMPI Mid Exam Questionskranthi6330% (1)
- Now and Get: Best VTU Student Companion You Can GetDocument7 pagesNow and Get: Best VTU Student Companion You Can GetJamey WalkerNo ratings yet
- AC23Microprocessor Based System Desig1Document87 pagesAC23Microprocessor Based System Desig1kushalNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument59 pagesMCQ - Microprocessor and Microcontrollerhod itNo ratings yet