Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Fields Problems Solutions
Uploaded by
candaguiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Fields Problems Solutions
Uploaded by
candaguiCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics-II Ch-23
1
SOLUTION TO SIMILAR PROBLEMS
Chapter 23: ELECTRIC FIELDS
2 Calculate the number of electrons in a small, electrically neutral silver pin that has a mass
of 10.0 g. Silver has 47 electrons per atom, and its molar mass is 107.87 g/mol. (b) Imagine adding
electrons to the pin until the negative charge has the very large value 1.00 mC. How many
electrons are added for every 10
9
electrons already present?
4 Nobel laureate Richard Feynman (19181988) once said that if two persons stood at arms
length from each other and each person had 1% more electrons than protons, the force of
repulsion between them would be enough to lift a weight equal to that of the entire Earth.
Carry out an order-of-magnitude calculation to substantiate this assertion.
Physics-II Ch-23
2
7 (a) Two protons in a molecule are 3.80 10
10
m apart. Find the magnitude of the electric
force exerted by one proton on the other. (b) State how the magnitude of this force compares
with the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by one proton on the other. (c) What If?
What must be a particles charge-to-mass ratio if the magnitude of the gravitational force
between two of these particles is equal to the magnitude of electric force between them?
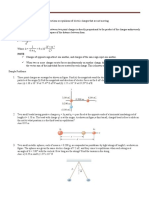
8 Three point charges lie along a straight line as shown in Figure P23.8, where q1=
6.00 C, q2= 1.50 C, and q3= 2.00 C. The separation distances are d1 = 3.00 cm and d2 =
2.00 cm. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the net electric force on (a) q1, (b) q2,
and (c) q3.
Physics-II Ch-23
3
10 Two small metallic spheres, each of mass m = 0.200 g, are suspended as
pendulums by light strings of length L as shown in Figure P23.10. The spheres are
given the same electric charge of 7.2 nC, and they come to equilibrium when
each string is at an angle of = 5.00 with the vertical. How long are the strings?
13 Three charged particles are located at the corners of an
equilateral triangle as shown in Figure P23.13. Calculate the total
electric force on the 7.00-C charge.
Physics-II Ch-23
4
15 Review. In the Bohr theory of the hydrogen atom, an electron moves in a circular orbit
about a proton, where the radius of the orbit is 5.29 10
11
m. (a) Find the magnitude of the
electric force exerted on each particle. (b) If this force causes the centripetal acceleration of the
electron, what is the speed of the electron?
20 A small object of mass 3.80 g and charge 18.0 C is suspended motionless above the
ground when immersed in a uniform electric field perpendicular to the ground. What are the
magnitude and direction of the electric field?
43 An electron and a proton are each placed at rest in a uniform electric field of magnitude
520 N/C. Calculate the speed of each particle 48.0 ns after being released.
Physics-II Ch-23
5
62 Four identical charged particles (q = +10.0 C) are located on the
corners of a rectangle as shown in Figure P23.62. The dimensions of the
rectangle are L = 60.0 cm and W = 15.0 cm. Calculate (a) the magnitude and
(b) the direction of the total electric force exerted on the charge at the lower
left corner by the other three charges.
You might also like
- Numerical Problems SolvedDocument5 pagesNumerical Problems Solvedahmad irtisamNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSS100% (1)
- Numerical Problems-1Document2 pagesNumerical Problems-1Hur ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Work SheetDocument6 pagesUnit - 4 Work SheetNathan GetachewNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Forces, Charges and FieldsDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Forces, Charges and FieldsDeepak PachauriNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Coulomb y Campo ElectricoDocument8 pagesEjercicios Coulomb y Campo ElectricoJuan Pablo Rincón AguiarNo ratings yet
- Serway 6 e Problems 23Document15 pagesSerway 6 e Problems 23_hoper_0% (1)
- Lesson 27 Coulombs LawDocument11 pagesLesson 27 Coulombs Lawi5piritiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 7 ExercisesBao Hoang LeNo ratings yet
- UnitTest D10 Feb 2024Document26 pagesUnitTest D10 Feb 2024dev.shah8038No ratings yet
- Electrostatic Forces and FieldsDocument8 pagesElectrostatic Forces and FieldsAryan DeepNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics PS XIIDocument24 pagesElectrostatics PS XIIDark gaming liveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapter 15 ProblemsekojantiNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Forces and PotentialsDocument5 pagesElectric Field Forces and PotentialsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- CPP ElectrostiaticsDocument6 pagesCPP Electrostiaticsdhvdcqcrv6No ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Electric Charges and FieldsDocument7 pagesChapter 5: Electric Charges and FieldsNATASHA MARCELA DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Numerical On ElectrostaticsDocument2 pagesNumerical On ElectrostaticsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument9 pagesElectric Charge and Electric FieldRehan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Vật Lý Đại Cương 2 - 23dvt_clc_hk2-Nh 2023-2024Document7 pagesBài Tập Vật Lý Đại Cương 2 - 23dvt_clc_hk2-Nh 2023-2024nndung.2k5No ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument2 pagesElectric FieldAndres ZerrathoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 4 PDFAhmed Attalla100% (1)
- Practice Problems 1 - 210 - QuestionsDocument3 pagesPractice Problems 1 - 210 - Questionsh.aideed220No ratings yet
- Class XII PHYSICS Investigatory ProjectDocument7 pagesClass XII PHYSICS Investigatory ProjectGopal Mishra22% (9)
- General Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Document53 pagesGeneral Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Ronnel MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1Pinky RoseNo ratings yet
- Print Question PaperDocument8 pagesPrint Question PaperSaniya MemonNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- KD4010 - EM - Seminar - 5 - ProblemsDocument2 pagesKD4010 - EM - Seminar - 5 - Problemsmohamed redaNo ratings yet
- Electric Field NumericalsDocument2 pagesElectric Field NumericalsFatoom KazemiNo ratings yet
- 1.electrico Statics WorksheetDocument3 pages1.electrico Statics WorksheetAdithyaNo ratings yet
- FisicaDocument6 pagesFisicaJorge Frank UreñaNo ratings yet
- DPPS 1 Coulomb's LawDocument1 pageDPPS 1 Coulomb's LawRakesh Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Fields, Gauss’s Law Module Physics ProblemsDocument2 pagesElectric Forces and Fields, Gauss’s Law Module Physics ProblemsMelvin LiewNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Coulomb's Law WorksheetDocument4 pagesElectrostatics and Coulomb's Law WorksheetBhanu AdaveniNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014Document21 pagesSolved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014believer149No ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class XII Physics Electrostatics Charges Forces Fields Guess Paper 2012 Set IDocument3 pagesCBSE Class XII Physics Electrostatics Charges Forces Fields Guess Paper 2012 Set Ishubhioo7No ratings yet
- Tute I IIDocument4 pagesTute I IIsachini weesingheNo ratings yet
- U1 ExercisesDocument6 pagesU1 ExercisesArturo MarmolejoNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS - University Physics 2 - Homework 1 - Electric FieldDocument3 pagesPROBLEMS - University Physics 2 - Homework 1 - Electric FieldNguyễn Hoàng ĐăngNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument47 pagesElectrostaticsKaran JeetNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TopicwiseDocument19 pagesUnit 1 TopicwiseSimran singhNo ratings yet
- Illustrations: (Int: Cos)Document3 pagesIllustrations: (Int: Cos)LODHKA RAVINo ratings yet
- Slides PHY 112Document221 pagesSlides PHY 112salman104alviNo ratings yet
- 2003 Qualifying Exam Part I Mathematical TablesDocument5 pages2003 Qualifying Exam Part I Mathematical TablesrujintoNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 05mar2024 CBSE QPDocument3 pagesElectrostatics 05mar2024 CBSE QPholaheg352No ratings yet
- Class 12 /eng /HHW /2023-24Document29 pagesClass 12 /eng /HHW /2023-24Yogya AroraNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields & Potential WorksheetDocument4 pagesElectric Fields & Potential WorksheetFandy Ardy50% (2)
- Fall 2008 P 2Document4 pagesFall 2008 P 2eka123No ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1234123Document3 pagesElectrostatics 1234123Last UnknownNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostaticsLast UnknownNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostaticsLast UnknownNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1 (Coulomb's Law)Document2 pagesElectrostatics 1 (Coulomb's Law)vidhi agarwalNo ratings yet
- MidTerm Physics2 RevisedDocument8 pagesMidTerm Physics2 Revisedalecksander2005No ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsFrom EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsNo ratings yet
- Research Method Syllabus-F14Document6 pagesResearch Method Syllabus-F14kanssaryNo ratings yet
- Lexicology Week 3 2020Document6 pagesLexicology Week 3 2020liliNo ratings yet
- 1 - Script Ceu Azul 2023Document21 pages1 - Script Ceu Azul 2023Indigo Graficos50% (2)
- Proceedings Atee 2008 FinalDocument350 pagesProceedings Atee 2008 FinalRuel LlagosoNo ratings yet
- How To Study & Teach The BibleDocument121 pagesHow To Study & Teach The BibleLiem Sien Liong100% (2)
- A Sample Case Analysis For OB-IDocument3 pagesA Sample Case Analysis For OB-IKunal DesaiNo ratings yet
- Gestalt Therapy Fundamentals in Contemporary ContextDocument24 pagesGestalt Therapy Fundamentals in Contemporary ContextVeronicaNo ratings yet
- UDC Statistics MeasuresDocument16 pagesUDC Statistics MeasuresLuccas ZNo ratings yet
- Legal Writing TechniquesDocument5 pagesLegal Writing TechniquesGloria TarucNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in H.O.P.E 3 Dance Traditional Dance I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in H.O.P.E 3 Dance Traditional Dance I. Objectivesrosemarie fortaleza100% (3)
- The 68 Blemishes of The Nafs Aka The Commanding Self (Sufi, Anonymous)Document2 pagesThe 68 Blemishes of The Nafs Aka The Commanding Self (Sufi, Anonymous)stimoceiverNo ratings yet
- Les - Literary DevicesDocument6 pagesLes - Literary Devicesapi-285838342100% (1)
- Systemic Approach in Teaching Irregular VerbsDocument54 pagesSystemic Approach in Teaching Irregular VerbsRahmaeni Syarif100% (2)
- History of Slavery in Islam Part-IIDocument2 pagesHistory of Slavery in Islam Part-IImeccaholycityNo ratings yet
- JFL Volume 3 Issue 11 Pages 79-90Document12 pagesJFL Volume 3 Issue 11 Pages 79-90imaNo ratings yet
- The Break-off Phenomenon: A Feeling of Separation from Earth at High AltitudeDocument6 pagesThe Break-off Phenomenon: A Feeling of Separation from Earth at High AltitudegwernNo ratings yet
- Ufo DictionaryDocument106 pagesUfo Dictionarysohelalam100% (1)
- Orientation of Students to Science TopicsDocument115 pagesOrientation of Students to Science TopicsShaynie Mhe Amar AntonioNo ratings yet
- (Bassiouney,-Reem) - Language-And-Identity-In-Modern Egypt PDFDocument418 pages(Bassiouney,-Reem) - Language-And-Identity-In-Modern Egypt PDFmarija999614350% (2)
- Chapter I The Self From Various PersDocument45 pagesChapter I The Self From Various PersMavyNo ratings yet
- Boling - Literary Analysis of Judges 13Document9 pagesBoling - Literary Analysis of Judges 13Michael Boling100% (1)
- Englisg 10Document4 pagesEnglisg 10Djoana Rose Hiponia JunsayNo ratings yet
- Managing Industrial Relations and Trade UnionsDocument22 pagesManaging Industrial Relations and Trade UnionsSai PrabhasNo ratings yet
- Martha GrahamDocument3 pagesMartha GrahamMark allenNo ratings yet
- Lateral Violence in NursingDocument5 pagesLateral Violence in NursingJea GarciaNo ratings yet
- A Day On The Grand Canal With The Emperor of ChinaDocument2 pagesA Day On The Grand Canal With The Emperor of ChinaÇağrı KoçNo ratings yet
- Consumer Attitudes Toward Ready-To-Eat Packed Food Items (With Special Reference To Jaffna Divisional Secretariat Division)Document12 pagesConsumer Attitudes Toward Ready-To-Eat Packed Food Items (With Special Reference To Jaffna Divisional Secretariat Division)Sundus AshrafNo ratings yet
- Edst Portfolio FinalDocument15 pagesEdst Portfolio Finalapi-250555568No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan YEAR 2 KSSRDocument11 pagesLesson Plan YEAR 2 KSSRWan MaisarahNo ratings yet