Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PCL PCL CL Rate K PCL NH No N Horate Knhno No No O Rate Kno
Uploaded by
Jitendra KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PCL PCL CL Rate K PCL NH No N Horate Knhno No No O Rate Kno
Uploaded by
Jitendra KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
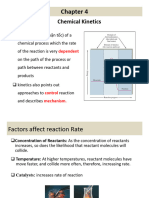
It is to be noted that the order of a reaction is purely an experimental quantity and can not be
known just by seeing the equation. The stoichiometric coefficients present in the balanced
chemical equation have nothing to do with the order of the reaction.
The order of a reaction is usually a whole number. However, it can be zero or fractional also.
8. Reactions of different orders and the units of their rate constants:
i) First order reactions: a reaction of a type A products is said to be of first order, if its
rate law
is given by
Rate = k [A]
1
Obviously, in a first order reaction, the rate is directly proportional to the
concentration of the reactant. If the concentration of reactant A is doubled, the rate of
reaction also gets double, some examples of first order reactions are as follows:
5 3 2 5
4 2 2 2 4 2
2 5 2 2 2 5
2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
; [ ]
2 ; [ ]
1
2 ; [ ]
2
1
; [ ]
2
; [ ]
PCl PCl Cl rate k PCl
NH NO N H O rate k NH NO
N O NO O rate k N O
H O H O O rate k H O
SO Cl SO Cl rate k SO Cl
The units of rate constant for a first order reaction are time
-1
i.e. s
-1
, or min
-1
, or hour
-1
.
ii) Second order reactions: a reaction of the type A products is said to be of second
order , if its rate law is given by
Rate = k [A]
2
Obviously, in a second order reaction, the rate depends upon the square of the concentration
of reactants. When the concentration of reactants is doubled, the rate increases by four times.
Some examples of second order reactions are as follows.
2
2 2 2
2 2 ; [ ] N O NO O rate k NO
2 2 2 2
2 ; [ ][ ] H I HI rate k H I
3 2 2 3
; [ ][ ] NO O NO O rate k NO O
3 2 5 3 2 5 3 2 5
; [ ][ ] CH COOC H NaOH CH COONa C H OH rate k CH COOC H NaOH
The units of rate constant for a second order reaction are conc
.-1
. i.e. mol
-1
ls
-1
. For a gaseous
reaction the units of k will be atm
-1
s
-1
.
iii) Third order reactions: when the rate of a reaction depends upon the cube of the
concentration of reactants, the reaction is said to be of third order. In such a case, when the
concentration is doubled, the rate of reaction increases by eight times.
The most common third order reactions are of the following type;
2A + B Products : rate k [A]
2
[B]
In this case, the reaction is of order 2 with respect to A
Order 1 with respect to B.
The overall order is 2+1 = 3.
Some examples of third order reactions are as follows;
2
2 2 2
2 2 ; [ ] [ ] NO O N O rate k NO O
2
2 2
2 2 ; [ ] [ ] NO Cl NOCl rate k NO Cl
2
2 2
2 2 ; [ ] [ ] NO Br NOBr rate k NO Br
You might also like
- H CL HCL Rate KH CL K NH N H Rate KNH KDocument2 pagesH CL HCL Rate KH CL K NH N H Rate KNH KJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Document10 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Gaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practice Rate Law ProblemsDocument12 pagesPractice Rate Law ProblemsCatrina RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Reaction KineticsDocument142 pages1.0 Reaction KineticsKhairul Aswari Ab RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Key: Units of Reaction Rate Are Unit of Concentration Divided by The Unit of Time (Mol LDocument31 pagesThe Key: Units of Reaction Rate Are Unit of Concentration Divided by The Unit of Time (Mol LSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument134 pagesChemical Kineticstapas kundu100% (1)
- 2023CML101 Tutorial ChemKin-1Document3 pages2023CML101 Tutorial ChemKin-1Bhoomika Singh SirohiNo ratings yet
- Chem Chapt13 PractiseDocument5 pagesChem Chapt13 PractiseqwerNo ratings yet
- DP Chemical KineticsDocument32 pagesDP Chemical KineticsAniket RayNo ratings yet
- A270134180 - 23715 - 17 - 2019 - Chemical Kinetics - 1Document50 pagesA270134180 - 23715 - 17 - 2019 - Chemical Kinetics - 1omer faruqeNo ratings yet
- Cbse Chem Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsDocument14 pagesCbse Chem Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsUjwal baijuNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 Chemical Kinetics (E)Document10 pagesCHP 10 Chemical Kinetics (E)Khe ManshuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Unit IDocument43 pagesChemical Kinetics: Unit IEanna Jullienne UyvicoNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument20 pagesDefinitionsudipta chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 105768Document32 pages105768Anyumiza InnocentNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument28 pagesEnzyme Kineticsghislain22.kevinNo ratings yet
- Kinetics IntroductionDocument55 pagesKinetics IntroductionAgano juma mwakasendoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-12Document18 pagesChemical Kinetics-12Manas ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry: Course No.: CH 101Document14 pagesDepartment of Chemistry: Course No.: CH 101liz_hobbs79No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactor Technology Lecture Notes: Module - 5Document6 pagesChemical Reactor Technology Lecture Notes: Module - 5Anonymous 6oIKmXPivNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Chem Kinetics - Modified GutoDocument40 pagesLecture 4 - Chem Kinetics - Modified GutoSamwel MwetichNo ratings yet
- 4 Che - KinDocument16 pages4 Che - KinRoxanneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document32 pagesChapter 4Nguyen NhatNo ratings yet
- CHM096 1 Chem Kinetics RMDocument100 pagesCHM096 1 Chem Kinetics RMAinul AqilaNo ratings yet
- STK 1102 Chemical Kinetics: LU1 Basic Terms and ConceptsDocument65 pagesSTK 1102 Chemical Kinetics: LU1 Basic Terms and ConceptsNurain Jinal AhbidinNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument41 pagesChemical Kineticskishangopi1230% (1)
- Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics: ConceptDocument23 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Kinetics: ConceptRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetic Module 3Document13 pagesChemical Kinetic Module 3Prabhnoor SinghNo ratings yet
- CHM101 Chemical KineticsDocument45 pagesCHM101 Chemical Kineticsvictoradedoyin.pcNo ratings yet
- C1 Reaction KineticsDocument12 pagesC1 Reaction KineticsChloeNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document116 pagesLec 3Cheng Chao HanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument29 pagesChemistry ProjectMuhannad RabeeNo ratings yet
- Mahic Tricks PrankDocument18 pagesMahic Tricks PrankPavan Kulkarni100% (3)
- Chemical KineticsDocument90 pagesChemical KineticsDayasagar VS100% (1)
- KineticsDocument51 pagesKineticsSaumil Sachdeva100% (1)
- Topic 4.1 Kinetics Rate Equations Determining Orders of Reaction Explaining Orders of Reaction Effect of Changing Conditions On The Rate ConstantDocument10 pagesTopic 4.1 Kinetics Rate Equations Determining Orders of Reaction Explaining Orders of Reaction Effect of Changing Conditions On The Rate ConstantNur Kintan ApriliaNo ratings yet
- 13lectureppt 101122094708 Phpapp01Document41 pages13lectureppt 101122094708 Phpapp01Salim Ahmad Salim AlirajaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics 2Document98 pagesKinetics 2Hem Chandra ShahNo ratings yet
- L-16 Chemical KineticsDocument16 pagesL-16 Chemical KineticsAkhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 and 2-ChemicalKineticsDocument86 pagesTopic 1 and 2-ChemicalKineticsNOR AZAM BIN ENDOT / FSNo ratings yet
- 11 Reaction KineticsDocument95 pages11 Reaction KineticsSyamil Adzman100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Students VersionDocument124 pagesChapter 2 Students VersionMuhd BazliNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument22 pagesChemical Kineticspragun0507No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Chemical KineticsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 - Chemical KineticsMADHAVNo ratings yet
- Chemical KinaticsDocument22 pagesChemical KinaticsAsif SiamNo ratings yet
- Document From JenDocument51 pagesDocument From JenAksh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6.2hl Rate Expression and Reaction MechanismDocument44 pages6.2hl Rate Expression and Reaction MechanismJESUS EDUARDO CARBONO NIEBLESNo ratings yet
- Che-Unit 2 Chemical KineticsDocument26 pagesChe-Unit 2 Chemical Kineticsmuchakayala umeshNo ratings yet
- Fucking KineticsDocument28 pagesFucking KineticsReginal MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Document13 pagesChemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)shubhamgajraj5566No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Study Material & QuestionsDocument26 pagesChemical Kinetics Study Material & QuestionsKRITHIKA .MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Chemical KineticsDocument70 pagesChapter 12 Chemical KineticsiB13eNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 17 18 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 4Document20 pagesCLS Aipmt 17 18 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 4Shimon LalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Types of ReactionDocument14 pagesChemical Kinetics Types of ReactionM AroNo ratings yet
- Chem Kine SulDocument4 pagesChem Kine SulChutvinder LanduliyaNo ratings yet
- Akd Geology Phys Chem Chapter 7Document29 pagesAkd Geology Phys Chem Chapter 7yonas BerhaneNo ratings yet
- PRT 140 Physical Chemistry Programme Industrial Chemical Process SEM 1 2013/2014Document72 pagesPRT 140 Physical Chemistry Programme Industrial Chemical Process SEM 1 2013/2014Anusia ThevendaranNo ratings yet
- SCCCCDocument1 pageSCCCCJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- SLNNNDocument2 pagesSLNNNJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Cable Preacher CurlsDocument2 pagesCable Preacher CurlsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Unbalanced, Single-Element Gas Lift ValvesDocument1 pageUnbalanced, Single-Element Gas Lift ValvesJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- S 3Document3 pagesS 3Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Primary Drive MechanismsDocument1 pageReservoir Primary Drive MechanismsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Pilot-Operated Gas Lift ValvesDocument1 pagePilot-Operated Gas Lift ValvesJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Waterdrive ReservoirsDocument1 pageWaterdrive ReservoirsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Waterdrive and Aquifer ClassificationDocument1 pageWaterdrive and Aquifer ClassificationJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Reservoir EnergyDocument1 pageTypes of Reservoir EnergyJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Volatile-And Black-Oil Fluid CharacteristicsDocument1 pageVolatile-And Black-Oil Fluid CharacteristicsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Example 2: Solution Isolate The Reservoir Performance To Visualize The Effect of Changing Reservoir Pressure. TheDocument1 pageExample 2: Solution Isolate The Reservoir Performance To Visualize The Effect of Changing Reservoir Pressure. TheJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Hydrogen BondDocument2 pagesIntermolecular Hydrogen BondJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Performance: Fig. 1 Shows The Performance in Terms of Pressure, Producing GOR, and Gas Saturation As A Function ofDocument1 pagePerformance: Fig. 1 Shows The Performance in Terms of Pressure, Producing GOR, and Gas Saturation As A Function ofJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Necessity of Examining Flow Through SystemDocument1 pageNecessity of Examining Flow Through SystemJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis Examples: Example 1Document1 pageSystems Analysis Examples: Example 1Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Theory of Simulation: Assumptions For Ideal SWCT Test ModelingDocument2 pagesTheory of Simulation: Assumptions For Ideal SWCT Test ModelingJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Field Example: Fig. 3 Shows The Reservoir Performance in Terms of Pressure and Producing GOR As A Function ofDocument1 pageField Example: Fig. 3 Shows The Reservoir Performance in Terms of Pressure and Producing GOR As A Function ofJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Stages of ProductionDocument2 pagesStages of ProductionJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- 6 Tips and TrapsDocument16 pages6 Tips and TrapsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Hydrogen Bonding: Covalent Bond Ionic BondDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Hydrogen Bonding: Covalent Bond Ionic BondJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Hydrogen BondingDocument1 pageDefinition:: Hydrogen BondingJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- API Conversion 3Document4 pagesAPI Conversion 3Teuku KhamilNo ratings yet
- Ansi MV Gis 8dadb Flyer enDocument2 pagesAnsi MV Gis 8dadb Flyer enNBWNo ratings yet
- Dialux Output 30OCT2013Document3 pagesDialux Output 30OCT2013Kamran KhanNo ratings yet
- Insulin Chart 072610Document1 pageInsulin Chart 072610cutevives100% (1)
- Water Interruption - Dunrakin DriveDocument2 pagesWater Interruption - Dunrakin DriveCrombieWard5No ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic FieldsDocument2 pagesElectric and Magnetic FieldsShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- Acetylsalicylic AcidDocument13 pagesAcetylsalicylic AcidMuhammad Tariq Khan100% (1)
- Cost of QualityDocument11 pagesCost of QualityraveendramanipalNo ratings yet
- AMP Model Question PaperDocument3 pagesAMP Model Question Paperelson_paulNo ratings yet
- Waiver of Right4Document2 pagesWaiver of Right4Amanda HernandezNo ratings yet
- PowerSuite GeneratorDocument1 pagePowerSuite GeneratorKunik SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research Case 1 & 2Document1 pageMarketing Research Case 1 & 2Jasmine RichmondNo ratings yet
- Comparing HSRP Versus VRRPDocument2 pagesComparing HSRP Versus VRRPirfeeaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Sigma S 10w API CDSFDocument1 pageDiesel Sigma S 10w API CDSFnguyenquoc1988No ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives MultipleDocument1 pageComparatives and Superlatives Multipleslavica_volkanNo ratings yet
- Abundance of Isotopes: Name - Chem Worksheet 4-3Document1 pageAbundance of Isotopes: Name - Chem Worksheet 4-3Hailey KristiansenNo ratings yet
- Vapor Liquid Equilibrium GraphsDocument7 pagesVapor Liquid Equilibrium Graphsmahbub1332No ratings yet
- Frequency Response and Bode Plot: Walter Joseph, Asst. Professor, Dec, RsetDocument19 pagesFrequency Response and Bode Plot: Walter Joseph, Asst. Professor, Dec, RsetwalternampimadomNo ratings yet
- Grounding RingDocument2 pagesGrounding Ringoadipphone7031No ratings yet
- Migrations and Other Stories by Lisa HernandezDocument177 pagesMigrations and Other Stories by Lisa HernandezArte Público PressNo ratings yet
- Assessment 15Document3 pagesAssessment 15ccharp123No ratings yet
- BioCheck GBDocument13 pagesBioCheck GBSionoONo ratings yet
- Ec 201 Lecture 20Document6 pagesEc 201 Lecture 20Abdul Karim KhanNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure (Sop) AND Pacwave2011 Exercise For FijiDocument11 pagesStandard Operating Procedure (Sop) AND Pacwave2011 Exercise For Fijinajill10No ratings yet
- CE765 - Advanced Steel DesignDocument3 pagesCE765 - Advanced Steel DesignatklingerNo ratings yet
- Plate Brake Tester Pro - enDocument2 pagesPlate Brake Tester Pro - enPavle TerzicNo ratings yet
- Cables ConnectorsDocument18 pagesCables ConnectorsRaviram BoppayNo ratings yet
- Hanyoung Control SwitchDocument3 pagesHanyoung Control SwitchBeruang Kodding LagiNo ratings yet
- Software Quotation enDocument1 pageSoftware Quotation enSudtana Rattanadilok Na PhuketNo ratings yet
- GL 313 Live Tank Circuit Breaker For 170 KV Brochure GBDocument2 pagesGL 313 Live Tank Circuit Breaker For 170 KV Brochure GBsaltandmoreNo ratings yet