Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5 Cell Division
Uploaded by
Vjayan DharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5 Cell Division
Uploaded by
Vjayan DharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
26/7/2014
1
CELL DIVISION
Concept map
Consist of
Occur in
Lead to
CELL DIVISION
Mitosis Meiosis
Controlled mitosis Uncontrolled mitosis
meiosis I meiosis II
Testis, ovary and anther
Cloning
(asexual reproduction,
regeneration, healing)
Advantages and
disadvantages of cloning
Comprises of
Lead to
Lead to
considering
Subdivides into
Cause by
1
Mitosis
Mitosis is a division of the nucleus to produce
two new daughter cells containing
chromosomes identical to the parent cell.
Significance of mitosis
Growth- allows a zygote to produce more cell
in order to grow
Repair and replacement- allow the multicellular
organism maintain its tissues, example skin
cells and blood
Asexual reproduction- clone
2
Phases in the cell cycle
The cell cycle divided into two major phases
a. Interphase
b. Mitosis
Interphase is the period between division,
divided into 3 sub phases (G1, S and G2)
a. G1- cells grow rapidly and new organelle are
synthesis
b. S- synthesis of DNA and chromosomes are
replicated
c. G2- cells prepares for mitosis, synthesis
protein and mitotic spindle begin to form
3
Mitosis
Mitosis is a continuous process and divided
into 4 main phases based on the appearance
and behavior of the chromosomes.
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
4
26/7/2014
2
5
Prophase
Early prophase
Chomatids condense and become visible in a
light microscope
Nucleolus disappears
Paired centrioles move to opposite ends of the
cell
Late prophase
Nuclear membrane disappears
Spindle form
6
Metaphase
Spindle fibres are fully form
Sister cromatids line up at the spindle
equator
At the end of metaphase, the centromers
divide
Anaphase
Anaphase begin with the separation of the
centromers
The sister cromatids are drawn to opposite
poles of the cell by contraction of spindle
fibres
7
Telophase
Telophase begin when the two sets of daughter
chromosomes have reached the two poles of
the cell.
The spindle fibres disintegrate, the nuclear
membrane forms around each set of daughter
chromosomes and the nucleoli reappear
The chromosomes uncoil and become less
visible under the light microscope
8
26/7/2014
3
In plant cells, the stages of mitosis are same.
Only cytokinesis in plant cells is markedly
different.
A cleavage furrow does not form. Instead,
membrane-enclosed vesicle gather at a plant
cells equator between the two nuclei.
Vesicle fuse to form a cell plate
9
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process of cytoplasmic division
to form two daughter cells.
Cytokinesis usually begins before nuclear
division is completed.
Cytokinesis in animal cells and plant cells are
different.
Animal cells, the cytoplasm contracts to pull the
plasma membrane inwards, forming groove
called a cleavage furrow
10
11 12
26/7/2014
4
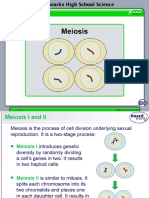
Meiosis
In a diploid cell, chromosomes occur as pairs
(homologous chromosomes).
Meiosis is a process to convert a diploid cell to
a haploid gamete and cause a change in the
genetic information to increase diversity in the
offspring
Meiosis involves two successive nuclear
division that produce four haploid cells. The
first division (meiosis I) is the reduction
division; the second division (meiosis II)
separates the chromatids.
13 14
15 16
26/7/2014
5
17 18
19 20
26/7/2014
6
21
The effects of uncontrolled mitosis in
living things
Mutation is the change in the DNA
structure of the cell.
This change in the DNA corrupts the
coded genetic instructions for mitosis
control.
This leads to uncontrolled mitosis, which
is the non-stop division of cells, producing
a mass of new daughter cells, called
tumour.
22
Causes of cancer
1. Genetic- some forms of cancer like prostate, colon,
breast, skin, ovary are suspected to be inherited
from the parents
2. Carcinogens- these are chemicals which affect
genetic activity and cause cancer, e.g. of carcinogen
a diesel exhaust, cigarette smoke, hair dyes, soot,
arsenic, benzene and formaldehyde.
3. Radiation- excess exposure to x-ray, gamma-rays
and ultra violet rays lead to increase cancer risk.
4. Age- some cancers are found primarily in young
people (e.g. leukemia), while some cancers (e.g.
colon cancers) are found mostly in older adults.
5. Viruses- some viruses (such as the EB and HIV-1)
cause cancer.
23
Cloning
1. Cloning is the process of the making Clones
are genetically identical cells produced from a
single parent cell by mitotic division, or
through asexual reproduction.
2. genetically identical copies of an original plant
or animal.
3. We shall study the application of knowledge
on mitosis the cloning of
a) Microbes
b) Plants
c) animals 24
26/7/2014
7
Cloning of microbes
Clone microbes using cells culture and fermenters,
Cell culture
a) You can easily clone microbes (bacteria and some
fungi) in you science laboratory through natural asexual
reproduction.
b) First, grow a sample of microbial cells on a solid nutrient
medium in an agar plate.
c) Then identify, isolate and select strain from the agar
plate and grow it in liquid medium in a culture flask.
Fermenters
a) Fermenters are vessels use in biotechnology to grow
microbes on a large scale.
b) Microbes, like yeast are mixed with a culture medium
and left in a fermenters to grow by mitosis.
c) The fermenters is constantly stirred, and aerated.
d) The environmental conditions ( such as pH, oxygen,
pressured and temperature) are constantly monitored
using proves ti ensure the maximum growth of the
microbes.
25
Cloning in plants-tissue culture
1. Plants can be cloned using tissue culture.
2. Tissue culture is the process of growing cells artificially
in the laboratory, it is a modern and efficient way of
cloning plants.
3. Tissue culture produces genetically identical clones.
26
The main principals of tissue culture:
a) A pieces of tissue, called explants, its taken from a parents plant (e.g.
carrot root or stem tissue,)
b) The pieces of tissues are sterilised with dilute sodium hypochlorite
solution to prevent the growth of pathogens (such as bacteria and
fungus).
c) Each sterile tissue piece is placed on to a growth medium (gel
containing nutrients and growth regulators).
d) The tissues cells divided by mitosis to produce a mass of loosely
arranged undifferentiated cells called callus.
e) Callus is stimulated with shoot-stimulating hormone to form multiple
shoots.
f) The shoots are separated and each is placed in nutrient medium with
root-stimulating hormone to encourage rooting
g) Once the roots grow, the plantlets (little plants) are planted in sterile
compost to grow.
27
Cloning of animals
There are two types of animal cloning according
to purpose:
1. Reproductive cloning
Producing an entire animal that is genetically
identical to the parent animal
The entire animal is produced from a single cell
by asexual reproduction through mitosis.
2. Therapeutic cloning
Is a branch of medicine concerned with the
treatment of diseases.
Parts of a person skin, heart, liver or even just a
few cells are duplicated to produce a clone.
The clone tissue is used to replace a damaged
or diseases tissue without the risk of tissue
rejection. 28
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Chapter 10 Group 2Document8 pagesChapter 10 Group 2Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Latent HeatDocument6 pagesLatent HeatVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Chapter 15 HydrocarbonsDocument16 pagesChapter 15 HydrocarbonsVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- ElectromagnetismDocument42 pagesElectromagnetismVjayan Dharma100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- FOrm 5 SPM PhysicsElectronicsDocument19 pagesFOrm 5 SPM PhysicsElectronicsVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is Symmetry?: Chapter 7: Symmetry 7.1 - Lines of SymmetryDocument4 pagesWhat Is Symmetry?: Chapter 7: Symmetry 7.1 - Lines of SymmetryVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Fractions and Decimals Form 2Document16 pagesChapter 4 Fractions and Decimals Form 2Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Cardiac CycleDocument1 pageCardiac CycleVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
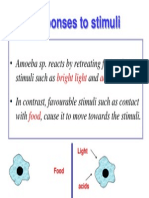
- Responses To Stimuli of AmoebaDocument1 pageResponses To Stimuli of AmoebaVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
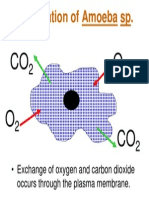
- Respiration of Amoeba SPDocument1 pageRespiration of Amoeba SPVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- SPM Transport Form 5Document107 pagesSPM Transport Form 5Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Government's Role On GM Food RegulationDocument7 pagesGovernment's Role On GM Food RegulationVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Cell Cycles: Mitosis, Cytokinesis and MeiosisDocument22 pagesCell Cycles: Mitosis, Cytokinesis and MeiosisRestiyana VitaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Licensure Exam Reviewer Crop Science Exam (Set 1)Document43 pagesAgriculture Licensure Exam Reviewer Crop Science Exam (Set 1)maria lou chiva67% (3)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- GCE AS/A Level 311/01 Biology - Bi1: A.M. TUESDAY, 3 June 2008 1 HoursDocument15 pagesGCE AS/A Level 311/01 Biology - Bi1: A.M. TUESDAY, 3 June 2008 1 Hoursramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Inheritance: (Syllabus Points 3.13 - 3.33)Document58 pagesInheritance: (Syllabus Points 3.13 - 3.33)Azween SabtuNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Biology - ANSWERS - Peeters, Talbot and Mayrhofer - Third Edition - IBID 2008Document27 pagesBiology - ANSWERS - Peeters, Talbot and Mayrhofer - Third Edition - IBID 2008rosafuenfloNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Cell DivisionDocument44 pagesCell DivisionOyananasha RonNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Dawes Hoang, Rachel - Heston, Katherine - Meneely, Philip Mark - Okeke, Iruka N - Genetics - Genes, Genomes, and Evolution-Oxford University Press (2017)Document775 pagesDawes Hoang, Rachel - Heston, Katherine - Meneely, Philip Mark - Okeke, Iruka N - Genetics - Genes, Genomes, and Evolution-Oxford University Press (2017)Wahyu W'cas Pamungkas100% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Bio 1Document3 pagesBio 1James TolentinoNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Life Sciences P2 Survival KitDocument35 pagesLife Sciences P2 Survival KitMashamba CoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 8-Q4Document5 pagesReviewer in Science 8-Q4katherine bacallaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Document14 pagesMeiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Selenia BonoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument1 pageMitosis WorksheetFrician Bernadette Muyco100% (1)
- Mcqs Chapte 21 Cell CycleDocument3 pagesMcqs Chapte 21 Cell Cyclehasnain100% (3)
- Malfunction of Cell CycleDocument12 pagesMalfunction of Cell CycleveberlyNo ratings yet
- Karyotype Activity GoodDocument12 pagesKaryotype Activity GoodSATZU MALAKASNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Reproductive System of Humans 15.1.1 Characterise The Anatomy Of: (I) Male Reproductive System. Ii) Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages15.1 Reproductive System of Humans 15.1.1 Characterise The Anatomy Of: (I) Male Reproductive System. Ii) Female Reproductive SystemHi YelloNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Life Sciences Book Please Share To Others - 041647Document113 pagesGrade 12 Life Sciences Book Please Share To Others - 041647mathebulawitness3No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Cell DivisionDocument60 pagesCell DivisionCharmaineNo ratings yet
- 2020 F4 Science Notes KSSM Chapter 4 6Document15 pages2020 F4 Science Notes KSSM Chapter 4 6紫菱No ratings yet
- Fungal Genetics PDFDocument10 pagesFungal Genetics PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (4)
- Biology ReviewerDocument14 pagesBiology ReviewerMarianne Tiffany RegalaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle - Meiosis NotesDocument63 pagesCell Cycle - Meiosis NotesKathleen Claire MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- scsc7211's Version of Alan's DAT Biology NotesDocument47 pagesscsc7211's Version of Alan's DAT Biology NotesMusawir YasinNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Test - v1Document5 pagesCell Cycle Test - v1api-316239296No ratings yet
- m2 l2. Check in ActivityDocument2 pagesm2 l2. Check in ActivityTiffany SelirioNo ratings yet
- Structure of Chromosomes, Cell Cycle, Cell DivisionDocument35 pagesStructure of Chromosomes, Cell Cycle, Cell DivisionXyzNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Diagnostic TestDocument6 pagesScience 8 Diagnostic TestMerlyn Mendoza100% (2)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Jr. Botany IPE 2024 Imp QuestionsDocument14 pagesJr. Botany IPE 2024 Imp Questionsnelapatlaravipaul677No ratings yet
- BiopracticalDocument51 pagesBiopracticalSourav joshiNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4Document22 pagesSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4Kah WeiiNo ratings yet