Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestion and Absorption
Uploaded by
Min NimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digestion and Absorption
Uploaded by
Min NimCopyright:
Available Formats
16.
Digestion and Absorption
Digestion
It is the chemical and mechanical breakdown of complex nutrients into simple absorbable
forms.
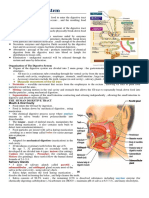
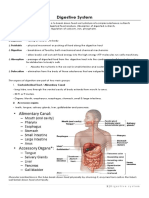
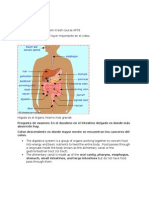
Human digestive system or alimentary canal
Alimentary canal is a long tube that extends from the mouth to the anus.
It consists of mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small
intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
The accessory digestive glands include salivary glands, the liver, gall bladder, and
the pancreas.
Digestion of food begins in mouth. It includes teeth, saliva, and tongue.
Teeth
o Humans have thecodont and diphyodont type of dentition.
o Thecodont: Teeth are embedded in deep sockets of the jaw bone.
o Diphyodont: Two successive sets of teeth, which are deciduous (milk teeth)
and permanent teeth, developed during complete life span Example: as in
human beings
o Dental formula for milk teeth in humans is
2102
2102
. It means that each half of
upper jaw and lower jaw has 2 incisors, 1 canine, and 2 molars. Premolars are
absent in milk teeth. There are 20 teeth in the milk teeth set.
o Dental formula for permanent teeth in human is
2123
2123
. It means that each
half of upper jaw and lower jaw has 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3
molars.
o An adult human has 32 permanent teeth. These are of four types molars,
premolars, incisors, and canines.
Saliva
o It is secreted by salivary glands, which are located under the tongue.
o It contains a digestive enzyme called salivary amylase, which breaks down
starch into sugar.
Tongue
o It helps in chewing and swallowing of food.
Epiglottis closes the windpipe (trachea) when we swallow food to prevent choking.
Cardiac sphincter regulates the movement of food from oesophagus to stomach.
Stomach is divided into 3 parts cardiac, fundic, and pyloric region.
Small intestine is further divided into duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Pyloric sphincter regulates the movement of food from stomach to duodenum.
Large intestine is divided into caecum, colon, and rectum. The opening of rectum is
called anus.
Vermiform appendix arises from the caecum. It is a vestigial organ.
Wall of alimentary canal comprises of four layers:
Serosa Muscularis Sub mucosa Mucosa
outer most inner most
Mucosal layer of the small intestine forms finger-like projections called villi.
Goblet cells are present in the mucosal epithelium of small intestine and secrete mucus
for lubrication.
Rugae are irregular folds present in the innermost lining of stomach.
Rugae and villi increase the surface area for efficient food absorption.
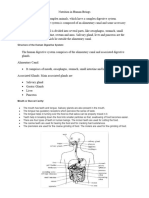
Digestive glands
Three pairs of salivary glands are the parotids, the sub maxillary or sub mandibular, and
the sub lingual.
Liver is the largest gland.
Cystic duct (duct of gall bladder) and hepatic duct (duct of liver) form a common
bile duct.
Bile duct and pancreatic duct opens together into duodenum as hepato-
pancreatic duct.
Sphincter of Oddi is located at the surface of duodenum and controls the secretions
from liver, pancreas, and gall bladder into the duodenum of small intestine.
Crypts of Lieberkuhn are intestinal glands found in epithelial lining of small intestine
and colon. These glands secrete maltase, sucrase, etc.
Pancreas act as both exocrine and endocrine gland.
i. Exocrine part secretes pancreatic juice.
ii. Endocrine part secretes hormones - insulin and glucagon.
Glands present in the mucosa of stomach are called gastric glands. Gastric glands have
three major types of cells.
Mucus cells Secrete mucus
Peptic or chief cells Secrete pepsinogen
Parietal or oxyntic cells Secrete HCl
Digestion of food
Digestion of carbohydrate
It takes place in mouth and in the small intestine region of alimentary canal.
In mouth:
Salivary amylase
pH6.8
Starch Maltose Isomaltose Limit dextrins
Carbohydrate digestion stops in stomach and is then resumed in small intestine.
Mainly, protein digestion takes place in stomach.
In small intestine: Pancreatic juice contains pancreatic amylase.
pancreatic amylase
Starch Disaccharides
Polysacccharides
Intestinal juice contains enzymes such as maltase, lactase, sucrase, etc., which
convert complex sugars into simple sugars.
maltase
lactase
Sucrase
Maltose 2 Glucose
Lactose Glucose Galactose
Sucrose Glucose Fructose
Digestion of protein
It begins in stomach and gets completed in small intestine.
Enzymes involved are called proteases.
In stomach:
o Gastric juice contains HCl, pepsinogen, and rennin.
o HCl creates acidic medium that activates pepsinogen into pepsin.
Proteins + pepsin-------- Proteoses + peptones
o Rennin plays a role in coagulation of milk.
In small intestine
o Pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes such as trypsinogen,
chymotrypsinogen, and carboxypeptidases.
o Enterokinase secreted by intestinal mucosa activates trypsinogen into
trypsin.
Enterokinase
Trypsinogen Trypsin Inactive peptide
Trypsin
Chymotrypsinogen Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin
Proteins Peptides
Carboxypeptidase
Peptides Smaller peptide chain Amino acids
o Intestinal juice contains dipeptidases, which digest dipeptides into amino
acids.
Dipeptidase
Dipeptides Amino acids
Digestion of fat
It takes place in small intestine.
Bile juice is secreted by liver and is stored in gall bladder.
Bile juice contains bile salt that helps in breakdown of fat into smaller globules. It
is known as emulsification of fat.
Pancreatic lipase
Fats Triglyceride+Diglycerides
Lipases
Di and Monoglycerides Fatty acids+Glycerol
Chylomicrons are large particles of lipoproteins that transport dietary lipids from
the small intestine to other locations in the body.
Absorption of digested products:
The absorption of food materials is carried out by passive (e.g. chloride ions), active
(e.g. amino acids, glucose), or facilitated diffusion (e.g. fructose).
Digested food is absorbed mainly through intestinal walls.
The inner lining of small intestine has villi. Villi contain lymph vessels called lacteal to
absorb the products of fat digestion.
Large intestine absorbs water and minerals from undigested food.
Rectum stores the undigested matter before they are excreted out from body via anus.
Digestive system disorders
Jaundice Yellowing of eyes due to deposition of bile pigments
Vomiting Ejection of food through mouth
Diarrhoea Frequent bowel movement and liquefied faecal discharge
Constipation Irregular bowel movement
Indigestion Improper digestion of food
* *
You might also like
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument5 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Karthik Bharadwaj'S: PresentationDocument32 pagesKarthik Bharadwaj'S: PresentationMahir AfranNo ratings yet
- Essay # 4. DigeDocument9 pagesEssay # 4. DigeAbdul Karim BurkiNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument18 pagesBiology NotesajairafingerishiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Grade 10-11Document7 pagesDigestive System Grade 10-11Nandana Nayana KumaraNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument82 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionCoc FanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Human BeingsDocument8 pagesNutrition in Human Beingsparashakthi PRNo ratings yet
- Digestive System of Frog PDFDocument20 pagesDigestive System of Frog PDFJake tarsNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NewDocument49 pagesDigestive System NewPHAMAE JOY MEMBREVENo ratings yet
- Rajkumar Biology Unit - 5 by RajatDocument52 pagesRajkumar Biology Unit - 5 by RajatShrikant KumarNo ratings yet
- Core 9Document25 pagesCore 9snehashreemohanty39No ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes Digestion and AbsorptionDocument4 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes Digestion and AbsorptionBħuvi ÀnthaRaNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument26 pagesHuman PhysiologyLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System and NutritionDocument6 pagesDigestive System and NutritionAthena HuynhNo ratings yet
- THE Digesti VE SystemDocument35 pagesTHE Digesti VE SystemgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewDocument2 pagesDigestive System ReviewSherriena LeangNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Digestion and AbsorptionDocument4 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Digestion and AbsorptionHasharaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System MODULEDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System MODULEBen Moldenhaur100% (2)
- Chemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreDocument14 pagesChemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreVarun WadhwaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (Second Term)Document55 pagesBIOLOGY (Second Term)carlaplana2008No ratings yet
- Biology - Zoology Unit 7 Detailed Study of FrogDocument0 pagesBiology - Zoology Unit 7 Detailed Study of Frogwww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Presentation On The Digestive SystemDocument48 pagesPresentation On The Digestive SystemOsman Saidu Sesay0% (1)
- Nutrition in Human Beings Class 6Document5 pagesNutrition in Human Beings Class 6Sarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 1Document11 pagesDigestive System 1Louise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM EXPLAINEDDocument44 pagesTHE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM EXPLAINEDJoy NatividadNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverCharise Ligores67% (6)
- Nutrition in Humans: By: Khizar Hayat & Ade Bhai 10-ADocument40 pagesNutrition in Humans: By: Khizar Hayat & Ade Bhai 10-AWaqas TahirNo ratings yet
- Part I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesPart I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemLleana TanNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument11 pagesNUTRITIONRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Guia para Human Body CareDocument48 pagesGuia para Human Body CareVyelkaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-16 Digestion and AbsorptionDocument6 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-16 Digestion and AbsorptionPriya SatheeshNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument10 pagesDigestive System NotesArchanna VyassNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Absorption NotesDocument15 pagesDigestion & Absorption NotesKankana BiswasNo ratings yet
- Digestive System SS2Document19 pagesDigestive System SS2Oluwatoniloba TellaNo ratings yet
- GIT Anatomy and Physiology: Gastrointestinal System OverviewDocument6 pagesGIT Anatomy and Physiology: Gastrointestinal System OverviewAntonette LeiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Overview: Parts and FunctionsDocument62 pagesDigestive System Overview: Parts and FunctionsKeturah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Digestive-SystemDocument93 pagesDigestive-SystemJulia Stefanel PerezNo ratings yet
- m6 Digestive SystemDocument23 pagesm6 Digestive Systemapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Gastrointestinal System (GITDocument10 pagesIntroduction to the Gastrointestinal System (GITjaninesimbol24No ratings yet
- Introduction to the Gastrointestinal System (GITDocument10 pagesIntroduction to the Gastrointestinal System (GITjaninesimbol24No ratings yet
- Digestive GlandDocument22 pagesDigestive GlandMalinus TorquatusNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System: by Ruhan Shukla Class 10 ADocument16 pagesHuman Digestive System: by Ruhan Shukla Class 10 ARuhan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument25 pagesDigestive Systembazaar9No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption by Dr. Sunita Saxena Part - 1Document39 pagesDigestion and Absorption by Dr. Sunita Saxena Part - 1Divya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Digestive System-1Document3 pagesDigestive System-1elinandreaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System A&p BookletDocument11 pagesDigestive System A&p Bookletnurse1990No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesDigestive SystemCurex QANo ratings yet
- Clase 10-16-2015Document9 pagesClase 10-16-2015jv9937No ratings yet
- Shakila Hamed Report PDFDocument9 pagesShakila Hamed Report PDFShakila HamidNo ratings yet
- Digestioninman Copy 200527150922Document17 pagesDigestioninman Copy 200527150922dimpleNo ratings yet
- 10 BiologyDocument3 pages10 BiologyNaveen NNo ratings yet
- The 4 Stages of Food Processing in the Digestive SystemDocument30 pagesThe 4 Stages of Food Processing in the Digestive SystemUniversal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Digestive System-PowerpointDocument21 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Digestive System-Powerpointlynflores272402100% (2)
- xyeuES 6Document34 pagesxyeuES 6Min NimNo ratings yet
- WS 1 (N) ForceDocument1 pageWS 1 (N) ForceMin NimNo ratings yet
- VB Physics Eng 12Document20 pagesVB Physics Eng 12abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- Phy 12 2003Document24 pagesPhy 12 2003Min NimNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument9 pagesWave OpticsDhilipan RamachandranNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYDocument98 pagesELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYShashank Rai0% (1)
- Goitre: Deficiency DiseasesDocument1 pageGoitre: Deficiency DiseasesMin NimNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYDocument98 pagesELECTROSTATICS AND CURRENT ELECTRICITYShashank Rai0% (1)
- Previous Board QuestionsDocument41 pagesPrevious Board QuestionsMin NimNo ratings yet
- Phys102 Old Exams Chapter26Document4 pagesPhys102 Old Exams Chapter26Min NimNo ratings yet
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- Electric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesElectric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsMin NimNo ratings yet
- Sample Papers Class 12 PhysicsDocument53 pagesSample Papers Class 12 Physics0910ashuNo ratings yet
- Multiple factors distinguish me as a strong candidate for CMU's Biological Sciences programDocument5 pagesMultiple factors distinguish me as a strong candidate for CMU's Biological Sciences programMin NimNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometryMin NimNo ratings yet
- Physics XII 2011 12Document226 pagesPhysics XII 2011 12Min NimNo ratings yet
- ShakespeareDocument4 pagesShakespeareMin NimNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesElectric Charge Physics Problems and SolutionsMin NimNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument9 pagesWave OpticsDhilipan RamachandranNo ratings yet
- PhotoDocument5 pagesPhotoMin NimNo ratings yet
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- Phy3 PDFDocument9 pagesPhy3 PDFOshin LambaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic DampingDocument57 pagesMagnetic DampingMin NimNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Current Electricity Concepts ExplainedDocument48 pagesElectrostatics and Current Electricity Concepts ExplainedMin NimNo ratings yet
- 13283cbse Important QuestionsDocument3 pages13283cbse Important QuestionsMin NimNo ratings yet
- Dragonfly - Julia GoldingDocument210 pagesDragonfly - Julia GoldingMin Nim86% (7)
- 2012 CBSE XIIScience 5 2 SET1 SectionbDocument6 pages2012 CBSE XIIScience 5 2 SET1 SectionbMin NimNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsDocument33 pagesLecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- Bilateral Maxillary Canines Agenesis: A Case Report and A Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesBilateral Maxillary Canines Agenesis: A Case Report and A Literature ReviewLiga Odontopediatria Rondoniense100% (1)
- LUCAS How Teeth Work 1st Ed 2004 PDFDocument372 pagesLUCAS How Teeth Work 1st Ed 2004 PDFRobert KruszynskiNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument38 pagesDental AnatomyChristopher H. Clarke100% (1)
- DEvelopment of Normal OcclusionDocument7 pagesDEvelopment of Normal OcclusionMohammed HassanNo ratings yet
- Development of The Curve of SpeeDocument9 pagesDevelopment of The Curve of SpeeMirnaLiz100% (1)
- Development of Normal Occlusion Part 2 Copy 2Document49 pagesDevelopment of Normal Occlusion Part 2 Copy 2MSA universityNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 16 SummaryDocument6 pagesDigestion and Absorption Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 16 SummaryBrijesh BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Lovejoy 1985Document10 pagesLovejoy 1985mikulcicaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 9 Digestive SystemDocument187 pagesUNIT - 9 Digestive SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- 1 AnthropologyDocument330 pages1 Anthropologydr_nilofervevai2360100% (2)
- Diagnosing Early Interceptive Orthodontic Problems - Part 1: 2 CE CreditsDocument11 pagesDiagnosing Early Interceptive Orthodontic Problems - Part 1: 2 CE CreditsVijay Prabu GNo ratings yet
- RS DentGrowthandDev PDFDocument1 pageRS DentGrowthandDev PDFAnita PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Space RegainerDocument28 pagesSpace RegainerSandeep SidralNo ratings yet
- Development of OcclusionDocument17 pagesDevelopment of OcclusionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentofocclusionDocument33 pagesDevelopmentofocclusionDeepak NarayanNo ratings yet
- Tooth Numbering SystemDocument19 pagesTooth Numbering Systemحسين الفلاحNo ratings yet
- Development of OcclusionDocument50 pagesDevelopment of OcclusionSaid Said100% (1)
- Biology Scheme Form 2Document11 pagesBiology Scheme Form 2VictorNo ratings yet
- Development of OcclusionDocument79 pagesDevelopment of Occlusionp0ya100% (2)
- Model Analysis: Essential Diagnostic Tool for Orthodontic Treatment PlanningDocument20 pagesModel Analysis: Essential Diagnostic Tool for Orthodontic Treatment PlanningYmer El Uaeb100% (1)
- Lobodontia Case Report: Unravelling the Wolf TeethDocument3 pagesLobodontia Case Report: Unravelling the Wolf TeethInas ManurungNo ratings yet
- Treatment PlanningDocument12 pagesTreatment PlanningFernaz Behlim100% (1)
- Fabrication of Myofunctional AppliancesDocument116 pagesFabrication of Myofunctional AppliancesPranav Dave100% (2)
- Tooth Formation and Eruption - Lessons Learnt From Cleidocranial DysplasiaDocument9 pagesTooth Formation and Eruption - Lessons Learnt From Cleidocranial DysplasiaSofiaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic AnalysisDocument18 pagesRadiographic AnalysisJessica GallegosNo ratings yet
- FPSC No: 39 Mcqs On Submission Deadline: 5 April 2011: Oral Health in Primary CareDocument4 pagesFPSC No: 39 Mcqs On Submission Deadline: 5 April 2011: Oral Health in Primary Carev_vijayakanth7656100% (2)
- Leeway Space of NanceDocument11 pagesLeeway Space of NanceGauriNo ratings yet
- Management of Ectopic TeethDocument21 pagesManagement of Ectopic TeethHaffie HafiziNo ratings yet
- Sindrome de Dientes Cortos Sthepen ChuDocument11 pagesSindrome de Dientes Cortos Sthepen Chujorefe12No ratings yet
- 3805592299Document212 pages3805592299Abdalmonem AlbazNo ratings yet