Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Esque Matic o
Uploaded by
Sergio Otiniano AlcaldeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Esque Matic o
Uploaded by
Sergio Otiniano AlcaldeCopyright:
Available Formats
MikroElektronika
Serial Ethernet
Manual
All Mikroelektronikas development systems feature a large number of peripheral
modules expanding microcontrollers range of application and making the
process of program testing easier. In addition to these modules, it is also
possible to use numerous additional modules linked to the development system
through the I/O port connectors. Some of these additional modules can operate
as stand-alone devices without being connected to the microcontroller.
A
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
a
l
B
o
a
r
d
Serial Ethernet
MikroElektronika
Serial Ethernet Additional Board
The Serial Ethernet additional board is used to connect a microcontroller to the Ethernet network. It features an on-board Ethernet
controller ENC28J60 that exchanges data with microcontrollers via a standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) at a data rate of up
to 10 Mbit/s. It serves as an Ethernet interface for all microcontrollers supplied with SPI. There are three 10-pin IDC connectors
marked SPI-dsPIC, SPI-AVR-8051 and SPI-PIC provided on the additional board. They enable the board to be connected to one
of Mikroelektronikas development systems intended for work with dsPIC, PIC, AVR and 8051 microcontrollers. In addition to these
connectors, the board also features a single-line 10-pin connector whose pins are connected to the ENC28J60s SPI communication
lines. This connector enables the additional board to be connected to other microcontroller families.
Figure 1: Serial Ethernet additional board Figure 2: Serial Ethernet additional board connected to a development system
Figure 3: Serial Ethernet additional board connection schematic
Serial Ethernet
MikroElektronika
The Serial Ethernet board features three LEDs:
POWER: indicates that the additional board is turned on;
LED A: indicates that the Ethernet cable is connected; and
LED B: indicates Ethernet network activity. It will be illuminated on every data package receive/transmite.
The ENC28J60 requires the 3.3V power supply voltage, but it is designed to be easily used with 5V devices. Its input pins CS, SCK,
SI and RESET are 5V tolerant, which means that it will be able to receive data from the microcontroller. However, if the microcontroller
operates at 5V, it likely will not be able to receive data correctly from the Ethernet controller with 3.3.V outputs. For this reason, voltage
level translators, such as 74LVCC3245 and 74LVC1T45, that are used to adjust voltage levels are provided on the board.
The position of jumper J1 depends on the power supply voltage of the microcontroller connected to the Serial Ethernet additional
board:
- If the power supply voltage is 5V, jumper J1 should be placed in the 5V position.
- If the power supply voltage is 3.3V, jumper J1 should be placed in the 3.3V position.
Figure 4: Block diagram of the 74LV1T45 circuit
Figure 5: Block diagram of the 74LVCC3245 circuit
I
f
y
o
u
w
a
n
t
t
o
l
e
a
r
n
m
o
r
e
a
b
o
u
t
o
u
r
p
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
,
p
l
e
a
s
e
v
i
s
i
t
o
u
r
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
a
t
w
w
w
.
m
i
k
r
o
e
.
c
o
m
I
f
y
o
u
a
r
e
e
x
p
e
r
i
e
n
c
i
n
g
s
o
m
e
p
r
o
b
l
e
m
s
w
i
t
h
a
n
y
o
f
o
u
r
p
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
o
r
j
u
s
t
n
e
e
d
a
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
a
l
i
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
,
p
l
e
a
s
e
p
l
a
c
e
y
o
u
r
t
i
c
k
e
t
a
t
w
w
w
.
m
i
k
r
o
e
.
c
o
m
/
e
n
/
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
I
f
y
o
u
h
a
v
e
a
n
y
q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
,
c
o
m
m
e
n
t
s
o
r
b
u
s
i
n
e
s
s
p
r
o
p
o
s
a
l
s
,
d
o
n
o
t
h
e
s
i
t
a
t
e
t
o
c
o
n
t
a
c
t
u
s
a
t
o
f
f
c
e
@
m
i
k
r
o
e
.
c
o
m
You might also like
- ControlLogix EthernetIPDocument31 pagesControlLogix EthernetIPSergio Otiniano AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- Dmb51cm EngDocument4 pagesDmb51cm EngSergio Otiniano AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- Densimeter PressureDocument14 pagesDensimeter PressureSergio Otiniano AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- Manual Pic 18F2550Document430 pagesManual Pic 18F2550Pancho NuncioNo ratings yet
- 8 - Vigirex - Relés Diferenciales PDFDocument128 pages8 - Vigirex - Relés Diferenciales PDFSergio Otiniano AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- Guia Rapida Ats 01Document4 pagesGuia Rapida Ats 01Sergio Otiniano AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- BI Lab ManualDocument41 pagesBI Lab Manualtanay.bhor3No ratings yet
- 01 SushilChowdhury PDFDocument25 pages01 SushilChowdhury PDFShabnam BarshaNo ratings yet
- Ed 9Document11 pagesEd 9Mark Emmanuelle AsiloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cognos Reportnet 2. Architecture 3. Installation and Configuration 4. Framework Manager 5. Query Studio 6. Report Studio BasicsDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Cognos Reportnet 2. Architecture 3. Installation and Configuration 4. Framework Manager 5. Query Studio 6. Report Studio BasicsakanshachaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Year 1Document6 pagesYear 1Ticer Mon UsopNo ratings yet
- VantageSerialProtocolDocs v230Document52 pagesVantageSerialProtocolDocs v230Ebert Ocares LunaNo ratings yet
- OWASP Application Security Verification Standard 4 0 2-EnDocument40 pagesOWASP Application Security Verification Standard 4 0 2-EnAmanda VanegasNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Lower Primary Community LivingDocument30 pagesSyllabus Lower Primary Community LivingRynette FerdinandezNo ratings yet
- Deuteronomy 33 PDFDocument2 pagesDeuteronomy 33 PDFRoman NovotnýNo ratings yet
- Elements of WritingDocument11 pagesElements of WritingEkemini-AbasiNo ratings yet
- Control Interface For Antenna Line Devices: Antenna Interface Standards Group Standard No. AISG v2.0Document41 pagesControl Interface For Antenna Line Devices: Antenna Interface Standards Group Standard No. AISG v2.0BeeeeeeeelaPNo ratings yet
- Description of Columns A B C - J K - R S - Al Am - An Ao - BL BM - Bo BP - BR Bs - BT Bu - BV BW BX - CGDocument954 pagesDescription of Columns A B C - J K - R S - Al Am - An Ao - BL BM - Bo BP - BR Bs - BT Bu - BV BW BX - CGIce JokerNo ratings yet
- Articles CommonDocument2 pagesArticles CommonAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- SSR Directions s1Document2 pagesSSR Directions s1api-327965506No ratings yet
- The Sahapedia-UNESCO Project Fellowship 2019 Annexure IV: Description of DeliverablesDocument4 pagesThe Sahapedia-UNESCO Project Fellowship 2019 Annexure IV: Description of DeliverablesSurya GayathriNo ratings yet
- Priority Queues With Simple Queue ServiceDocument6 pagesPriority Queues With Simple Queue Servicelokenders801No ratings yet
- Philosophy Module 2 Grade 12-1-7Document35 pagesPhilosophy Module 2 Grade 12-1-7Rheynan LumainoNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten HandbookDocument281 pagesKindergarten Handbookrharaksi100% (10)
- Guide Engineering Optimization L TEX Style Guide For Authors (Style 2 + Chicago Author-Date Reference Style)Document17 pagesGuide Engineering Optimization L TEX Style Guide For Authors (Style 2 + Chicago Author-Date Reference Style)skyline1122No ratings yet
- Parent Guide To Standards-Based Report CardsDocument2 pagesParent Guide To Standards-Based Report Cardsapi-295569699No ratings yet
- Optimization and Improvement of Fake News Detection Using Deep LearningDocument11 pagesOptimization and Improvement of Fake News Detection Using Deep Learningprema vathiNo ratings yet
- DOMINO - First ConditionalDocument3 pagesDOMINO - First Conditionalver.ma.vm15No ratings yet
- ASCP User Guide 11iDocument450 pagesASCP User Guide 11iRajesh RavulapalliNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and Dialectic in Plato's Republic VI-VII: Kozi AsanoDocument35 pagesMathematics and Dialectic in Plato's Republic VI-VII: Kozi AsanoGiannis DimitriouNo ratings yet
- Words and SentencesDocument163 pagesWords and SentencesEduardo CastellanosNo ratings yet
- ETECH Module 5 Weeks 6 7Document20 pagesETECH Module 5 Weeks 6 7Hersley PhynomeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Graphs: IIT KanpurDocument7 pagesLecture 5: Graphs: IIT KanpursevroussnapeNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Reviewer MidtermDocument9 pagesPurposive Communication Reviewer MidtermEidelveise De-ita CelesteNo ratings yet
- How To Write US College Admissions Essay: PerfectDocument9 pagesHow To Write US College Admissions Essay: PerfectNazmoon NaharNo ratings yet
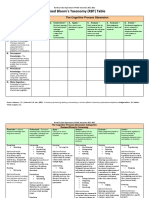
- RBT CognitiveProcesses Knowledge Definitions PDFDocument4 pagesRBT CognitiveProcesses Knowledge Definitions PDFAmadh Pereyra100% (1)