Professional Documents
Culture Documents
POLINOMIOS
Uploaded by
m_edurnegmz6608Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
POLINOMIOS
Uploaded by
m_edurnegmz6608Copyright:
Available Formats
EXPRESIONES ALGEBRAICAS - POLINOMIOS
1.- Escribe:
a) Tres monomios semejantes al monomio 3x2y.
b) Un polinomio de segundo grado completo y ordenado.
c) Un polinomio de tercer grado sin término independiente.
2.- Completa la siguiente tabla:
Coeficiente
Término de Término del término de
Polinomio Grado ¿Ordenado? 1º grado independiente 2º grado
2x2 – 2 + 4x - 3x4
x2 - 2x
3 Si 2x -4 5
3.- Completa la siguiente tabla:
Coeficiente
Término de Término del término de
Polinomio Grado ¿Ordenado? 1º grado independiente 2º grado
3x2 + 2x3 – 4+x
6x5 -4x3 + 7x+2
4 No - 3x 2 -8
4.- Calcula el valor numérico de los siguientes polinomios para los valores que se indican:
a) P(x) = 4x3-2x+6 para x = 0, 1,.-1
b) Q(x) = 2x2+7x+2 para x = 0, 2, -2
c) R(x) = x3-5x2+3x+7 para x = 0, 1, -1, 2, -2
5.- Dados los polinomios P(x) = -3x2-4x+8 ; Q(x) = 5x2+6x-9 ; R(x) = x3-5x2+x-8 y
S(x) = x3-6x2-9x+13 ; calcula:
a) P + Q b) P - Q c) R + S d) Q-S
e) P + Q + R f) P - (Q + R) g) R – S + P
3 2
6.- Dados los polinomios P(x) = 2x3 + x2- 3x + 5 y Q(x) = 3x2 - x + ; calcula:
4 3
a) P(x) + Q(x) b) P(x) - Q(x)
7.- Dados los monomios: A = 5x2 ; B = 3x ; C = 7x3 ; D = 2x2 ; calcula:
a) A + D b) A - D c) A + B d) A · C e) A · D f) B · D
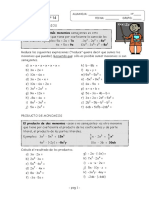
8.- Efectuar las siguientes multiplicaciones de monomios:
2 2 1
a) (6x2y) · (4y) b) (4xy) · (-3x2) c) (-3x2y) · (4xy3) d) (- x ) · (- x3)
5 2
9.- Efectuar las siguientes multiplicaciones de monomios por polinomios:
a) 3x2 (6x3-2x+1) b) -4xy (x3-3x2y+y3) c) -2x2y2 (-4x3y2+5x2y3-6y3)
d) x (2x – y + 5) e) ab (a + b) f) x2y (x + y - 1)
g) 6xy2 (x - y2 + 2) h) 3a2b3 (a – b + 1) i) 2a2 (3a2 + 5a3)
j) -2xy2 (3x2y – 5x + 8) k)
1
2
x 6x 2 4 x 2 l)
3 2
4
x 2x 3 3 x 1
10.- Dado P(x) = 5x2-3x+1, calcula los siguientes productos e indica su grado:
a) x·P(x) b) 3·P(x) c) -4x2 · P(x) d) -x2 ·P(x) e) 5x ·P(x) f) –x · P(x)
11.- Dados los polinomios : P(x) = 5x2-3x+2 ; Q(x) = 2x3-1 ; R(x) = x+1 ; calcula:
a) P + Q b) P - Q c) P · Q d) P - R e) R - Q f) P · R
4 3 1 2
12.-a) Dados los polinomios P(x) = 4x3-x+4+5x2 y Q(x) = x + x -7 ; calcula: P + Q y P - Q
3 2
b)Efectúa la multiplicación: (3x4-2x2+x-7) · (3x2+2x)
13.- Dados los polinomios P(x) = 3x2-2x-1 ; Q(x) = x5-3x3+x y R(x) = x4-2x2+1 ; calcula:
a) 2P - 3Q + 5R b) P·Q - Q·R
14.- Efectúa las siguientes multiplicaciones:
a) (3x2-2x+4) · (5x-2) b) (-2x3+3x+5) · (3x2-5x+2)
c) (2x2-5) · (5x3-3x2+x-4) d) (-3x4+2x+1) · (x2-5x+2)
15.- Simplifica estas expresiones:
a) 2x3 - 5x + 3 – 1 - 2x3 + x2 b) 2x2 - (7 - 5x) - (x2 - 6x + 1)
c) 3x - (2x + 8) - (x2 - 3x) d) 7 – 2 (x2 + 3) + x (x - 3)
e) 3 (x2 + 5) - (x2 + 40) f) 3x2 ·5x + 2x · (-3x2)
3 2 2 3 x 3 7x
g) x · x h) - ·x2
5 3 3 3
i) (2x)3 – (3x)2 · x – 5x2 · (-3x+1) j) (2x2 –x + 3) · (x – 3)
16.- Sacar factor común en cada una de las siguientes expresiones:
a) x2-3x b) x2(x-1)+x(x-1) c) –x4+2x2
d) –12x3-28x2 e) 5x2-10x f) 12x4-6x3+3x2
g) 5x-25x2 h) –24x3+8x2+88x i) 8x3y2-2xy6
j) x4-x3+x2-x k) 6x2y-3y3 l) 9x7+45x6+18x2
m) 2x2(x+1)+3x(x+1) n) –2xy2-4x2y-12xy o) 9x3+18x2-3x
3 5 4 x x
p) (x+1)a + (x+1)b –(x+1)c q) 6x2y4 – 3x2y3 + xy r) ( x 5)
2 2 2
xy
s) xy2(x+1) - (x+1) t) x2(x-1) + x2(x-2) + x2 (x-3) u) 2x(y-1) + 3x(y-1) – 9x(y-1)
2
17.- Completa el siguiente cuadro:
IDENTIDADES NOTABLES
2
(a + b) = (a - b)2 = (a + b)(a - b) =
(x + y)2 = (x - y)2 = (x + y)(x - y) =
(x + 1)2 (x - 1)2 (x + 1)(x - 1)
(x + 2)2
(x - 3)2
(x + 4)(x - 4)
(x + 5)2
(x - 6)2
(x + 7)(x - 7)
18.- Desarrolla las siguientes expresiones:
a) (x2+1)2 b) (3x-2)2 c) (x2+y3) (x2-y3)
d) 2x(x+4)2 e) –3x2(x-1)2 f) (4+9x) (9x-4)
g) x2(x+2y)2 h) 2xy(x-5)2 i) x(x3+2) (x3-2)
j) (2x5+3)2 k) (3x2-5y)2 l) (5x3+2y) (-5x3+2y)
19.- Expresa como cuadrado de una suma ó de una diferencia ó bien como producto de una suma
por una diferencia:
a) x2+10x+25 b) 9x2 - 25 c) x2+1-2x
d) x4 - 81 e) 4+4x+x2 f) x2-12x+36
g) x2+6x+9 h) x4-6x2+9 i) –x2+25
j) 4x2-12x+9 k) x2+8x+16 l) x2- 4
m) 9x2-12x+4 n) 25x4 - y2 ñ) 9x6+6x3+1
o) x4-10x2+25 p) y2 - 4x6 q) x6+4x3y+4y2
20.- Sacar factor común y utilizar las identidades notables:
a) 3x2+6x+3 b) 2x3 -18x c) x2y-4xy+4y
d) 2x4- 8x2 e) 4x3- 8x2+4x f) x5+10x4+25x3
g) x4y - y5 h) x3y+12x2y+36xy i) ax2-2ax+a
j) x4-10x3+25x2 k) 2x5- 8x3 l) x3+2x2+x
21.- Reduce las siguientes expresiones:
a) x 6 x 4 x 2 b) x 3x 5 x 1
2 1 2 1 2
2 2
c) (x2 - 3x) ·x – 5 ·(x2 + x3) d) 3x2 (2x + 3) – x (x2 – 1)
e) (5x – 4) (2x + 3) – 5 f) 2 (x2 + 3) –2x (x – 3) + 6 (x2 – x – 1)
5 x 5 x 1 x 3x 3 3 x 2 x 3
g) h)
4 5 4 4 3 12
i)
2
3 2 3
x 3 1 x 1 1 x 2 1 j) (x + 1) (x - 1) –3 (x + 2) – x(x + 2)
k) 3x2 – 2(x + 5) – (x + 3)2 + 19
l) (x + 3)2 - x 2 x 3 2
1
m) x x
3
1
3 3
1 2
x 1 n) (2x + 3)2 – (2x - 3)2 - x (x + 3)
o) – 4x (x – 4)2 + 3 (x2 - 2x + 3) – 2x (- x2 + 5) p) (3x – 4)2 - (3x + 4)2
q) (2x - 5)(2x + 5) – (2x + 5)2 r) (x - 4)2 + (x - 2)(x + 2)
s) (2x - 1)2 – 2(x + 1)2 t) (3x - 1)2 – (2x - 1)(1 + 2x)
22.- Calcula el cociente y el resto de las siguientes divisiones:
a) (x4+2x3+3x2+x+1) : (x2+3x) b) (4x5+x3+19x2+5x+17) : (2x2-x+3)
c) (6x4+11x3-9x2-2x+24) : (3x2-5x+4) d) (x5-6x3-25x) : (x2+3x)
e) (6x5-4x4+6x2-2) : (2x3-6x2+1) f) (2x5-3x4+3x2-x+1) : (x2-3x+2)
g) ( x5 – 7x4 + x3 – 8) : (x2 – 3x + 1) h) (6x4 + 3x3 – 2x) : (3x2 + 2)
23.- Utilizando la regla de Ruffini, halla el cociente y el resto de cada división:
a) (x3 + 4x2 – 5) : (x + 3) b) (3x3 + 2x2 – x) : (x + 2)
c) (x4 – 81) : (x – 3) d) (-x4 + 2x3 – 3x + 1) : (x + 1)
e) (2x4 + x2 – 3x) : (x – 1) f) (x4 – 3x3 + x + 7) : (x – 2)
2
g) (x4 – x2) : (x + 1) h) (3x4 – 7x3 – 3x2 – x) : x
3
You might also like
- Ejercicios de FactorizacionDocument2 pagesEjercicios de FactorizacionandreinadfrNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Apoyo - PolinomiosDocument22 pagesEjercicios Resueltos de Apoyo - PolinomiosjesusNo ratings yet
- Guia de Trabajo PolinomiosDocument2 pagesGuia de Trabajo PolinomiosSita Yani'sNo ratings yet
- Binomio Al CuadradoDocument5 pagesBinomio Al CuadradoAxelMaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Binomio Al CuadradoDocument6 pagesBinomio Al CuadradoStephany Solis GuerraNo ratings yet
- Tarea I Hidrocarburos IngDocument8 pagesTarea I Hidrocarburos IngManuel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Eval Final 7Document5 pagesEval Final 7Carlos Fernando Martinez ClavijoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de InecuacionesDocument13 pagesEjercicios de Inecuacionestayson1212No ratings yet
- Tarae 5 de Matematica BasicaDocument2 pagesTarae 5 de Matematica BasicaAnonymous ApoOsI0klf100% (1)
- MAT111Document5 pagesMAT111Rigoberto ArosemenaNo ratings yet
- Actividad Evaluable de La Semana 8Document10 pagesActividad Evaluable de La Semana 8Diego MirandaNo ratings yet
- Actividad Evaluable de La Semana 6Document17 pagesActividad Evaluable de La Semana 6Diego MirandaNo ratings yet
- Ficha Pedagogica de Matematicas Semana Del 07 Al 11 de SEPTIEMBREDocument5 pagesFicha Pedagogica de Matematicas Semana Del 07 Al 11 de SEPTIEMBRELuis Aladino PanimbozaNo ratings yet
- Números RealesDocument4 pagesNúmeros RealesmaestritasinrecursosNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de álgebraDocument16 pagesEjercicios de álgebrafelipeNo ratings yet
- I. Encierre en Un Círculo La Letra de La Respuesta Que Complete Correctamente Cada EnunciadoDocument1 pageI. Encierre en Un Círculo La Letra de La Respuesta Que Complete Correctamente Cada EnunciadoAneudis Javier Brito100% (1)
- UAPA Algebra Lineal Tarea 2Document13 pagesUAPA Algebra Lineal Tarea 2Henrry SenaNo ratings yet
- Evaluación de Números ComplejosDocument6 pagesEvaluación de Números ComplejosManuel Alejandro MartínezNo ratings yet
- E4 M Numeros-Reales-E-Intervalos 01Document2 pagesE4 M Numeros-Reales-E-Intervalos 01Susana Bonilla Badenas100% (1)
- Guía lectura nivel literalDocument2 pagesGuía lectura nivel literalJuan P. Huguett100% (1)
- 5 Polinomios Repaso PDFDocument4 pages5 Polinomios Repaso PDFEvanescencioNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Factorizacion de Diferencia de CuadradosDocument2 pagesEjercicios de Factorizacion de Diferencia de CuadradosJuan Manuel Rodriguez Mejia67% (3)
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument101 pagesIlovepdf MergedRenso Vnn H. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 02 Sol DeterminantesDocument40 pages02 Sol DeterminantesJUAN AGUSTÍN FRAILE SAN TEODORONo ratings yet
- Clase 4 Multiplicación y División de Polinomios-1Document5 pagesClase 4 Multiplicación y División de Polinomios-1Gabyy GaryyNo ratings yet
- Autoevaluación de Ecuaciones de Primer Grado y Segundo Grado de 2º ESODocument3 pagesAutoevaluación de Ecuaciones de Primer Grado y Segundo Grado de 2º ESORafael Merelo GuervósNo ratings yet
- Examen de Factorización de PolinomiosDocument2 pagesExamen de Factorización de PolinomiosFede NegroNo ratings yet
- Examen Factorización 8° OkDocument2 pagesExamen Factorización 8° OkMarcela Palacio MazoNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Uapa 2Document6 pagesTrabajo Uapa 2Enriqueta MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de FactorizaciónDocument8 pagesEjercicios de FactorizaciónALDO PIGUAVENo ratings yet
- Suma de PolinomiosDocument7 pagesSuma de Polinomioslester lopezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios MonomiosDocument6 pagesEjercicios MonomiosSaRySerranoNo ratings yet
- Guía Nº1 Álgebra 8º BásicoDocument4 pagesGuía Nº1 Álgebra 8º BásicoRomina Becerra FuentesNo ratings yet
- Sistemas de ecuaciones con dos incógnitasDocument27 pagesSistemas de ecuaciones con dos incógnitasTwiliNo ratings yet
- Taller Refuerzo Matematicas de 9Document11 pagesTaller Refuerzo Matematicas de 9EMILSEAZANo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Matematica Decimo EgbDocument20 pagesEjercicios Resueltos de Matematica Decimo Egbdorismariel_c0% (1)
- Evaluacion Productos NotablesDocument1 pageEvaluacion Productos NotablesjeaniveNo ratings yet
- Guia de Desigualdades e Inecuaciones TALLER 1Document2 pagesGuia de Desigualdades e Inecuaciones TALLER 1Axel ErazoNo ratings yet
- Solución ejercicios olimpiadas matemáticasDocument14 pagesSolución ejercicios olimpiadas matemáticasJacqueline Ettedgui100% (1)
- Practica Productos y Cocientes NotablesDocument3 pagesPractica Productos y Cocientes NotablesArelis SantosNo ratings yet
- QUIMICA ORGÁNICA JOHN NEPERDocument6 pagesQUIMICA ORGÁNICA JOHN NEPERJohn NeperNo ratings yet
- CC - PPT - División de Polinomios, Teorema RestoDocument35 pagesCC - PPT - División de Polinomios, Teorema RestoJuanito peña100% (1)
- PotenciasDocument8 pagesPotenciasLorena CastilloNo ratings yet
- Guía de Ecuaciones LinealesDocument2 pagesGuía de Ecuaciones LinealeskropitaNo ratings yet
- Actividades de Polinomios - OdtDocument3 pagesActividades de Polinomios - OdtvalentinaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de FactorizaciónDocument2 pagesEjercicios de FactorizaciónTIC INTERACTIVO IE GAITANNo ratings yet
- FactorizaciónDocument6 pagesFactorizaciónapi-250398026No ratings yet
- Operaciones Con Monomios.1548075189 PDFDocument4 pagesOperaciones Con Monomios.1548075189 PDFNom BreNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios AlgebraDocument5 pagesEjercicios AlgebraJaime Sarmiento ZegarraNo ratings yet
- Operaciones con polinomiosDocument9 pagesOperaciones con polinomiosEVA MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Taller de Matemáticas de Recuperación SupletoriosDocument14 pagesTaller de Matemáticas de Recuperación SupletoriosLucy Lulucyta LascanoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial de Factorización Rosario RivasDocument34 pagesTutorial de Factorización Rosario RivasMaría del Rosario Rivas Alvarez100% (1)
- Guia 1 Raices 2°Document3 pagesGuia 1 Raices 2°Andres Hernandez100% (1)
- Fundamentos algebraicas básicasDocument13 pagesFundamentos algebraicas básicasRobert100% (1)
- Formato Diseño de Situación de Aprendizaje 02042021 Tf3Document7 pagesFormato Diseño de Situación de Aprendizaje 02042021 Tf3walter_loachamin2545No ratings yet
- Fracciones AlgebraicasDocument3 pagesFracciones Algebraicaslentesqr3912No ratings yet
- 5.5. Anexo 5 - Actividades para Reconocer y Desarrollar Habilidades para La Vida-4261620041136Document17 pages5.5. Anexo 5 - Actividades para Reconocer y Desarrollar Habilidades para La Vida-4261620041136Luis Alfonso Flores DelgadoNo ratings yet
- ACTIVIDADES DE ENSEÑANZA APRENDIZAJE Unidad 5 Expresiones AlgebraicasDocument10 pagesACTIVIDADES DE ENSEÑANZA APRENDIZAJE Unidad 5 Expresiones AlgebraicasSamuel Vera ChamorroNo ratings yet
- T.P. PolinomiosDocument2 pagesT.P. PolinomiosBarbaraNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Práctico 2Document5 pagesTrabajo Práctico 2Thiara VásquezNo ratings yet
- Actividad 15 Evidencia 1Document14 pagesActividad 15 Evidencia 1Luis Meñaca VergaraNo ratings yet
- Evaluacion de Negocio - Manzana Verde 1Document9 pagesEvaluacion de Negocio - Manzana Verde 1JHIMMYNo ratings yet
- Manual Tecnología para La ApiculturaDocument324 pagesManual Tecnología para La ApiculturamiltonNo ratings yet
- Timeline PDFDocument9 pagesTimeline PDFapi-435931410No ratings yet
- La Migración y Desintegración Familiar - Grupo 2Document16 pagesLa Migración y Desintegración Familiar - Grupo 2Santiago MotiñoNo ratings yet
- Tarea Esqueleto AxialDocument6 pagesTarea Esqueleto AxialdieneNo ratings yet
- Plantea, Hipot, Probl Obj Antec Marco Tabla Metodologia 6-7Document27 pagesPlantea, Hipot, Probl Obj Antec Marco Tabla Metodologia 6-7Celeste ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Orar Hoy, Con Los Salmos de Siempre. Tiempo Ordinario.Document287 pagesOrar Hoy, Con Los Salmos de Siempre. Tiempo Ordinario.AngelSainz100% (1)
- Luis Manzo Guaquil Sede Valparaiso Santiago IquiqueDocument25 pagesLuis Manzo Guaquil Sede Valparaiso Santiago IquiqueLuis manzoNo ratings yet
- Procesos Metalurgicos Laboratorio N 2 inDocument18 pagesProcesos Metalurgicos Laboratorio N 2 inHeydi CalloNo ratings yet
- Guia de Conformacion Del Comite de Mejora Continua de La Calidad y Seguridad Del PacienteDocument18 pagesGuia de Conformacion Del Comite de Mejora Continua de La Calidad y Seguridad Del PacienteHospital Municipal Vicente nobleNo ratings yet
- Cle 4Document10 pagesCle 4Soraya Vica Sosa100% (1)
- Informe Turmalina Saldivar GonzaDocument20 pagesInforme Turmalina Saldivar GonzaLi SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Acordes para El Himnario 2010 V 2.1Document79 pagesAcordes para El Himnario 2010 V 2.1Belén AndreaNo ratings yet
- Actividad Estructura de La Industria Semana 8Document6 pagesActividad Estructura de La Industria Semana 8Yobana Romero100% (1)
- Enfoques económicos y relaciones interdisciplinariasDocument3 pagesEnfoques económicos y relaciones interdisciplinariasGherveth Santis SantizoNo ratings yet
- Maquinaria PesadaDocument18 pagesMaquinaria PesadaJorge Luis Medina ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Guía aprendizaje sistemas CNDocument6 pagesGuía aprendizaje sistemas CNMauricio Alejandro Riquelme AguirreNo ratings yet
- Cansi - Símbolos y Técnicas de Dramatización para La CatequesisDocument56 pagesCansi - Símbolos y Técnicas de Dramatización para La CatequesisBarakaja CaraviasNo ratings yet
- Avanzando OROGENIAS Y PRINCIPALES METALOTECTOS EN EL PERÚDocument4 pagesAvanzando OROGENIAS Y PRINCIPALES METALOTECTOS EN EL PERÚIvanm Otazu MaytaNo ratings yet
- Diferencia de Trastornos DSM-VDocument3 pagesDiferencia de Trastornos DSM-VMercedes Limanta RamosNo ratings yet
- PRACTICA EDUCATIVA II Programas UNEFA Licenciatura Educación Integral Octavo Semestre 8vo. SemestreDocument5 pagesPRACTICA EDUCATIVA II Programas UNEFA Licenciatura Educación Integral Octavo Semestre 8vo. SemestreJhony PradoNo ratings yet
- Isaías, figura de espera por la salvaciónDocument2 pagesIsaías, figura de espera por la salvaciónEDMUNDO JIMÉNEZNo ratings yet
- Prueba SextoDocument7 pagesPrueba SextoEusebio MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mediciones de laboratorioDocument18 pagesMediciones de laboratoriojosezxcNo ratings yet
- Modelos de Atención Hacia Las Dificultades de AprendizajeDocument6 pagesModelos de Atención Hacia Las Dificultades de AprendizajeDenys Soto100% (1)
- Caso SturbucksDocument15 pagesCaso SturbucksEliecer Roberto Escobar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Causales de Improcedencia de Habeas CorpusDocument16 pagesCausales de Improcedencia de Habeas CorpusCHARBELIN FAVIOLA BAÑICO GARCIA100% (1)
- Tratamiento Dolor Miembro FantasmaDocument8 pagesTratamiento Dolor Miembro Fantasmamanolo123456No ratings yet
- Auditoría patrimonio Distribuidora AlimentosDocument88 pagesAuditoría patrimonio Distribuidora AlimentosMendoza ElmerNo ratings yet