Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stages of Behavior Escalation
Uploaded by
Jan IwaseOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stages of Behavior Escalation
Uploaded by
Jan IwaseCopyright:
Available Formats
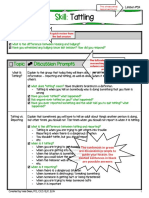
Stages of Behavior Escalation (Colvin & Sugai, 1989)
Behavior Stage Description of Stage Area(s) of Focus for Staff Intervention Tips
Calm
Student is relatively calm and
cooperative
Focus on maintaining a
clear, consistent
environment and building
rapport with the student
Establish 3-5 behavioral expectations
Give student feedback using the 4 to 1 ratio (4
positives for every 1 corrective/negative)
Teach replacements for interfering behaviors
Precorrect problem situations
Trigger
Student experiences
unresolved conflicts that trigger
behavior to escalate
May displace anger on safe
target (aide, teacher, parent)
Focus on prevention and
redirecting the students
behavior
Remove/adjust the trigger (if appropriate)
Use behavioral momentum to shape behavior
and reinforce small efforts
Remind student of rewards (if used)
Remind student to use replacement skills
Agitation
Student is increasingly
unfocused/upset
May exhibit avoidance
May challenge adult authority
Focus on reducing student
anxiety and increasing
predictability in the
students environment
Use non-confrontational non-verbal behavior
Break down directions into smaller steps
Use start, instead of stop directions
Provide reasonable options/choices
Use Speak and Retreat prompting
Set clear, reasonable, and enforceable limits
Acceleration
With conflict unresolved, this
becomes students sole focus
May become noncompliant
May be beginning to lose
rational thought
Focus on maintaining a
safe environment for
yourself, the student in
crisis and any observers
Use short phrases and allow processing time
Maintain calmness and detachment
Use active listening, reflection and
restatement to clarify students concerns and
show you understand his/her feelings
Remember this is not a teachable moment
Peak
Student is out of control and
may have temporarily lost
ability to think rationally
Exhibits severe behavior
(screaming, SIBs, aggression)
Focus on crisis
intervention procedures to
maintain a safe
environment for student in
crisis, self and observers
Isolate student by removing the audience
Call for help/ staff witness if needed
Dont threaten consequences now; discuss
when the student is more rational
De-Escalation
Having vented, the severity of
students behavior subsides
Drop in energy level of student
after a crisis
Focus on removing excess
attention, helping student
regain composure and
demonstrating cooperation
with neutral requests
Allow Cool-Down time
Make sure the student has regained control
before proceeding; look for less tense
appearance, normal breathing, and
willingness to comply with small requests
Recovery
Students may feel shame,
sorrow, fear, or regret
May not be able to verbalize
feelings/ details of outburst
Focus on debriefing/
problem solving then
transitioning student back
to academics
Debrief before following through with
consequences set earlier
Problem solve and develop a plan with the
student for better future behavior
Remember to document the incident/event
You might also like
- 6 Enhance Social and Friendship Skills PDFDocument5 pages6 Enhance Social and Friendship Skills PDFximomixNo ratings yet
- Selecting Prosocial Replacement BehaviorDocument1 pageSelecting Prosocial Replacement BehaviorAmna AliNo ratings yet
- Sensory Circuit Info and Ideas For School and HomeDocument11 pagesSensory Circuit Info and Ideas For School and HomeJulie SharpNo ratings yet
- Boys TownDocument23 pagesBoys Townapi-259445277No ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 3 (Eced 6) (Tamayo, Julia)Document20 pagesACTIVITY 3 (Eced 6) (Tamayo, Julia)Julia TamayoNo ratings yet
- Sample Estr ReportDocument8 pagesSample Estr Reportapi-271853611No ratings yet
- Workbook: Emotional ResilienceDocument30 pagesWorkbook: Emotional ResilienceAzmyNo ratings yet
- Demopreviewpdf PDFDocument8 pagesDemopreviewpdf PDFAlexandra Dragomir100% (1)
- Training Behavior Change Agents and Parents To Implement DTTDocument14 pagesTraining Behavior Change Agents and Parents To Implement DTTJéssica CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Lamp Words For LifeDocument3 pagesLamp Words For Lifeapi-400249453No ratings yet
- Living with Hearing Difficulties: The process of enablementFrom EverandLiving with Hearing Difficulties: The process of enablementNo ratings yet
- Rubricsample For SociDocument1 pageRubricsample For Sociapi-283845327No ratings yet
- Teaching Grooming SkillsDocument17 pagesTeaching Grooming SkillsblossomcygnetNo ratings yet
- Children and Young People With Anxiety: A Guide For Parents and CarersDocument17 pagesChildren and Young People With Anxiety: A Guide For Parents and CarersImtiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Tantrums Don't Fix My ProblemsDocument12 pagesTantrums Don't Fix My ProblemsBox OfficeNo ratings yet
- Feelings Thermometer Wisconsin Office of Children's Mental HealthDocument1 pageFeelings Thermometer Wisconsin Office of Children's Mental HealthKeselle RamosNo ratings yet
- CARSDocument18 pagesCARSzarish.shireenNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 Unit 8 Family LetterDocument5 pagesVol 2 Unit 8 Family LetteramakazeNo ratings yet
- 09 Cpi Int 013Document14 pages09 Cpi Int 013bonedNo ratings yet
- Theory of Mind: An Observational ReportDocument3 pagesTheory of Mind: An Observational ReportMalavika MenonNo ratings yet
- 05fba and BSPDocument6 pages05fba and BSPkatschriberNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - 011 PDFDocument57 pagesSilo - Tips - 011 PDFأحلام كبيرةNo ratings yet
- Other Ways of Speaking Final PDFDocument29 pagesOther Ways of Speaking Final PDFDavy SornNo ratings yet
- Zones Parent LetterDocument1 pageZones Parent Letterapi-251228209No ratings yet
- Rak Uk: in TheDocument289 pagesRak Uk: in TheAgustina AcostaNo ratings yet
- Symbolstix Online From Start To FinishDocument6 pagesSymbolstix Online From Start To Finishapi-208596155No ratings yet
- Fba - Bip 610 #5Document3 pagesFba - Bip 610 #5Emily KlemmeNo ratings yet
- ResponsibleDocument1 pageResponsiblejuteauj626No ratings yet
- Practice Writing The Vocabulary WordsDocument3 pagesPractice Writing The Vocabulary WordsLaura BocsaNo ratings yet
- De-Escalation Techniques: Strategies For Preventing The Escalation of Behavior in The School SettingDocument52 pagesDe-Escalation Techniques: Strategies For Preventing The Escalation of Behavior in The School SettingPablo escorcheNo ratings yet
- 6 Pillars of CharacterDocument1 page6 Pillars of Characterapi-249413578100% (1)
- Free Lesson Plan: Observation or Evaluation?Document4 pagesFree Lesson Plan: Observation or Evaluation?The Psycho-Educational Teacher67% (3)
- Road Advisors: Massachusetts Driver's LicenseDocument35 pagesRoad Advisors: Massachusetts Driver's LicenseDavid Gonzalez100% (1)
- Blackline Design: Student Attention GettersDocument7 pagesBlackline Design: Student Attention Gettersapi-240617339No ratings yet
- Life Skills Young Learners Poster PDFDocument2 pagesLife Skills Young Learners Poster PDFandi9merinoNo ratings yet
- 16PF GuideDocument17 pages16PF GuidesmacujaNo ratings yet
- Behavior ContractsDocument8 pagesBehavior Contractsapi-287718398No ratings yet
- GROW: My Own Thoughts and Feelings on Stopping the Hurt: A Child's Workbook About Exploring Hurt and AbuseFrom EverandGROW: My Own Thoughts and Feelings on Stopping the Hurt: A Child's Workbook About Exploring Hurt and AbuseNo ratings yet
- Beth's Behavior Intervention Plan: GoalDocument2 pagesBeth's Behavior Intervention Plan: GoalJéssica CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Parent Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesParent Brochure PDFUme NaomiNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Verbal Behavior AppliedDocument34 pages4.8 Verbal Behavior AppliedSudhakar PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Helping Kids Perform: Mental Skills Every Parent, Teacher, And Coach Should Master!From EverandHelping Kids Perform: Mental Skills Every Parent, Teacher, And Coach Should Master!No ratings yet
- Parent-Teacher LettersDocument8 pagesParent-Teacher Lettersapi-242270654No ratings yet
- Visual Supports PDFDocument4 pagesVisual Supports PDFAleksandarĐorđević100% (1)
- Visual Aid TemplatesDocument38 pagesVisual Aid TemplatesomayaNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Skills II PMPDocument2 pagesInterpersonal Skills II PMPYogeetaDeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Us Letter Emotional Regulation WorksheetsDocument27 pagesUs Letter Emotional Regulation Worksheetswbfpfwr58nNo ratings yet
- Social Skills GroupsDocument2 pagesSocial Skills Groupsioana sabinaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Friends: Aspergers... What Does It Mean?Document6 pagesUnderstanding Friends: Aspergers... What Does It Mean?Lucia SaizNo ratings yet
- k-5 Weekly Counseling Activities - April 20Document2 pagesk-5 Weekly Counseling Activities - April 20api-168735866No ratings yet
- Grieving ChildrenDocument2 pagesGrieving Childrenapi-371885143No ratings yet
- Resource Guide Organizer LPDocument7 pagesResource Guide Organizer LPapi-358123410No ratings yet
- Expected and Unexpected Behavior Sorts: FreebieDocument7 pagesExpected and Unexpected Behavior Sorts: FreebieSeemaNoorNo ratings yet
- Life Skills A Facilitator Guide For Teenagers PDFDocument79 pagesLife Skills A Facilitator Guide For Teenagers PDFMonia AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Articulation ProblemDocument3 pagesArticulation ProblemErrorry JecksonNo ratings yet
- Fba Functional Behavior Assessment Template 1 - 3Document4 pagesFba Functional Behavior Assessment Template 1 - 3api-338037250No ratings yet
- Positive Behavior Support Plan For GsDocument11 pagesPositive Behavior Support Plan For Gsapi-210400247No ratings yet
- Test 16PF-5 BookletDocument12 pagesTest 16PF-5 BookletScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- School Intervention Plan 1Document4 pagesSchool Intervention Plan 1api-547360536No ratings yet
- Dressing PDFDocument13 pagesDressing PDFEllyn GraceNo ratings yet
- DKIES Calendar 2017-2018Document1 pageDKIES Calendar 2017-2018Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Super STEMSaturdayfor Boys OnlyDocument1 pageSuper STEMSaturdayfor Boys OnlyJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Super STEM Saturday For Girls OnlyDocument2 pagesSuper STEM Saturday For Girls OnlyJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Hale Kula Es - Mih Presentation 160127Document16 pagesHale Kula Es - Mih Presentation 160127Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Space FestDocument1 pageSpace FestJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- After School PEDocument1 pageAfter School PEJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Hale Kula Article - 11 DEC 15Document1 pageHale Kula Article - 11 DEC 15Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- May Breakfast & Lunch MenuDocument2 pagesMay Breakfast & Lunch MenuJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Remind NotificationDocument1 pageRemind NotificationJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Breakfast & Lunch Menu - February 2015Document1 pageBreakfast & Lunch Menu - February 2015Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Breakfast & Lunch Menu - April 2015Document1 pageBreakfast & Lunch Menu - April 2015Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Breakfast & Lunch Menu - March 2015Document1 pageBreakfast & Lunch Menu - March 2015Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- ParentTrainingFlyer-Hale Kula Solomon Wheeler ElDocument1 pageParentTrainingFlyer-Hale Kula Solomon Wheeler ElJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Matisse Collage 14Document9 pagesMatisse Collage 14Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Breakfast & Lunch Menu - November 2014Document1 pageBreakfast & Lunch Menu - November 2014Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- I Need Assistance With - SEP 2014Document1 pageI Need Assistance With - SEP 2014Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Breakfast & Lunch Menu - August 2014Document1 pageBreakfast & Lunch Menu - August 2014Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Breakfast & Lunch Menu - December 2014Document1 pageBreakfast & Lunch Menu - December 2014Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Breakfast & Lunch Menu - October 2014Document1 pageBreakfast & Lunch Menu - October 2014Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- September MenuDocument1 pageSeptember MenuJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- September Parent BulletinDocument6 pagesSeptember Parent BulletinJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- August 2014 Parent BulletinDocument6 pagesAugust 2014 Parent BulletinJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- May Breakfast and Lunch MenuDocument1 pageMay Breakfast and Lunch MenuJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- April MenuDocument1 pageApril MenuJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- 2014 Academic Plan #2Document15 pages2014 Academic Plan #2Jan IwaseNo ratings yet
- Learning CPRDocument7 pagesLearning CPRJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- March Breakfast & Lunch MenuDocument1 pageMarch Breakfast & Lunch MenuJan IwaseNo ratings yet
- 12 Skills SummaryDocument39 pages12 Skills SummarytsegazelalemNo ratings yet
- 4 Tips To Improve Active Listening Skills AEUKDocument7 pages4 Tips To Improve Active Listening Skills AEUKIrina KazakovaNo ratings yet
- CONFFLICT NOTES NewDocument52 pagesCONFFLICT NOTES NewOBVIOUS CHAPASUKANo ratings yet
- As17 Teaching and Assessment of The Macro SkillsDocument9 pagesAs17 Teaching and Assessment of The Macro SkillsJane ButalidNo ratings yet
- BSBPEF502 Assessment Manual V1.0Document19 pagesBSBPEF502 Assessment Manual V1.0Naysha Blas TrujilloNo ratings yet
- BSBCMM401 Task 3Document13 pagesBSBCMM401 Task 3nicky wanjiru100% (1)
- Chapter 008Document20 pagesChapter 008Neverends2011No ratings yet
- Intercultural Communication and Its BarriersDocument40 pagesIntercultural Communication and Its BarriersRox PurdeaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Diploma - EditedDocument255 pagesAdvanced Diploma - EditedWan TechNo ratings yet
- 7 Tips For Setting Boundaries With Your Adult ChiDocument2 pages7 Tips For Setting Boundaries With Your Adult ChipuskasNo ratings yet
- Barriers of CommunicationDocument7 pagesBarriers of CommunicationambrienNo ratings yet
- Work With Clients - Assessment 2 - S1 - 2022Document12 pagesWork With Clients - Assessment 2 - S1 - 2022Rehab AdelNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills PPT FinalDocument20 pagesListening Skills PPT FinalAmrit Kang67% (3)
- Soft Skills 2 Unit 1 - LSRW SkillsDocument3 pagesSoft Skills 2 Unit 1 - LSRW SkillsSatyajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- HWR MBA 2018 IC LeadershipDocument43 pagesHWR MBA 2018 IC LeadershipPhaniNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Barriers ToDocument10 pagesOvercoming Barriers ToHimanshu RajaNo ratings yet
- Module 1.4 Dynamic Listening and Rumour ManagementDocument16 pagesModule 1.4 Dynamic Listening and Rumour ManagementKensley Anne Braulio100% (1)
- Managerial Skill Development Unit-3Document44 pagesManagerial Skill Development Unit-3Arif QuadriNo ratings yet
- Reflective Log TEMPLATE NegotiationDocument2 pagesReflective Log TEMPLATE NegotiationTanasica NegreaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Practice Questions Answer KeyDocument15 pagesMidterm Practice Questions Answer Keybs9y9frwyxNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument7 pagesListening SkillsTumpa GhoshNo ratings yet
- Soft Skills Notes 1Document51 pagesSoft Skills Notes 1Mohan Kalawate100% (2)
- Host and Helper GuidelinesDocument2 pagesHost and Helper GuidelineshoopburnNo ratings yet
- Deliver and Monitor Aservice To CustomersDocument10 pagesDeliver and Monitor Aservice To CustomersJemal SeidNo ratings yet
- Cummication & SkillsDocument8 pagesCummication & SkillsSyed BurhanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document19 pagesModule 2James DellavaNo ratings yet
- Critiquing A Journal Article NotesDocument3 pagesCritiquing A Journal Article NotesChangu Matildah JacobNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence PatternsDocument2 pagesBasic Sentence PatternsSABORDO, MA. KRISTINA COLEENNo ratings yet
- Managerial Communication MBADocument142 pagesManagerial Communication MBAManjurkhanushiya88% (50)
- Effective Communication Skills For Medical PracticDocument8 pagesEffective Communication Skills For Medical Practicfakhrina nur fadhillahNo ratings yet