Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vaginal Discharge Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
Hervis Francisco Fantini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesvery useful
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentvery useful
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesVaginal Discharge Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
Hervis Francisco Fantinivery useful
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
U.S.
Department of Health & Human Services
200 Independence Avenue, S.W.
Washington, D.C.
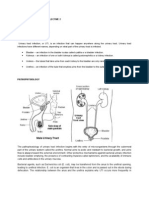
Vaginal Discharge
Fact Sheet
SOURCES:
National Institutes of Health
Vaginal discharge
Cleveland Clinic
Vaginitis
Vaginal discharge
Mayo Clinic
Vaginal discharge
American College of Obstetricians and
Gynecologists
Vaginitis
[No author listed] Information from your family
doctor. Vaginal discharge. Am Fam Physician.
2004 May 1;69(9):2191-2.
WHATS INSIDE:
What is vaginal discharge?
What causes normal vaginal
discharge?
Is vaginal discharge always normal?
Are there tests for vaginal discharge?
How is vaginal discharge treated?
When should a woman see a health
care provider about vaginal
discharge?
Office of Population Affairs Vaginal Discharge Fact Sheet
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
200 Independence Avenue, S.W.
Washington, D.C.
If a woman has more vaginal discharge, it could be due to menopause or cancer
(rare).
If you have discharge plus itching or burning near the vagina, then you may have
vaginitis (va-gin-EYE-tis).
Vaginitis happens when the vagina gets irritated (inflamed)
Signs of vaginitis:
o Increased discharge.
o A strong odor.
o Green, yellow, or gray color.
o Itching.
o Pain.
o Redness around the opening of the vagina.
Vaginitis can be caused by chemicals that could be in creams, liquids, sprays, or
clothing that touch the area around the vagina.
Vaginitis can also be due to an infection. In some cases, the infection is caused by
germs that are passed during sex. Gonorrhea and chlamydia are sexually
transmitted infections (STIs) that can cause discharge.
Other infections are not spread during sex. Infections happen when there are too
many of the yeast and bacteria (germs) that normally live in the vagina.
o Bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections are infections not spread during sex.
If you have a change in vaginal discharge, tests may help figure out the problem.
Possible tests include:
o Pelvic examthe health care provider looks at the vagina and cervix (the part
of the uterus at the top of the vagina).
o pH testthe health care provider checks the acid level of the discharge.
What is vaginal discharge?
Vaginal discharge is fluid that comes out of the vagina. It is
usually clear or white.
Most women have discharge sometimes. Some women have
discharge every day. Other women only have discharge once in a
while.
If the discharge changes color, smells different, or gets heavier,
then you may have a problem like an infection.
Is vaginal discharge always normal?
Are there tests for vaginal discharge?
Office of Population Affairs Vaginal Discharge Fact Sheet
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
200 Independence Avenue, S.W.
Washington, D.C.
o Pap smearduring the pelvic exam, the health care provider takes a sample
to check for cell changes and cancer.
o Wet mount sample of discharge is examined under the microscope to check
for infection
o Culture of the dischargea sample is taken from the vagina to check for
infection.
Normal vaginal discharge doesnt need treatment. Some women douche to remove
vaginal discharge that is actually healthy. This is not a good idea. Using a douche
washes away the healthy bacteria in the vagina and can cause other health
problems. The healthy bacteria prevent other infections.
Treatment of abnormal discharge depends on the problem.
Infections are treated with medicines to kill bacteria (called antibiotics) or to kill
yeast. If you have an STI, your sexual partners need to be treated too. If medication
is given to treat an infection, it is important to finish all medication, even if
symptoms get better before you finish the medication.
Vaginitis due to menopause can be treated with vaginal cream that contains
estrogen.
Vaginitis caused by chemicals is treated by avoiding certain products. Products that
can irritate the vagina include:
o Feminine hygiene sprays.
o Colored or perfumed toilet paper.
o Sanitary pads or tampons that contain a deodorant.
o Bubble bath.
o Laundry detergent.
o Fabric softener.
You should see a health care provider if you have:
o More discharge than usual.
o Thick, white discharge.
o Green or yellow discharge.
o Strong odor.
o Itching or pain around the vagina.
o Pain in the pelvic (lower belly) area.
o Pain with intercourse (sex).
How is vaginal discharge treated?
When should a woman see a health care provider about vaginal
discharge?
You might also like
- Vaginal Discharge Fact Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesVaginal Discharge Fact Sheet PDFPanji HrNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Discharge - Causes, Colors, What's Normal & TreatmentDocument9 pagesVaginal Discharge - Causes, Colors, What's Normal & TreatmentEsti YuniarNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Vaginosis, Trichomoniasis and Yeast Infection: Who Is at Risk For BV?Document4 pagesBacterial Vaginosis, Trichomoniasis and Yeast Infection: Who Is at Risk For BV?Drashua AshuaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner's 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesFrom EverandUrinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner's 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner’s 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesFrom EverandUrinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner’s 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesNo ratings yet
- A Complete Vaginal Discharge Color GuideDocument3 pagesA Complete Vaginal Discharge Color GuideAmna SerafNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenBily ManNo ratings yet
- Vulvovaginitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVulvovaginitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Vaginal Atrophy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVaginal Atrophy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Servisitis (English Ver.)Document3 pagesServisitis (English Ver.)Lidya WidhiariNo ratings yet
- Don't Delay Your Care at Mayo Clinic: Schedule Your Appointment Now For Safe In-Person Care. Learn MoreDocument11 pagesDon't Delay Your Care at Mayo Clinic: Schedule Your Appointment Now For Safe In-Person Care. Learn Moreronaldo palpialy1No ratings yet
- Vaginal Discharge CausesDocument2 pagesVaginal Discharge CausesTherunaNo ratings yet
- Cystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesFrom EverandCystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument2 pagesVaginitisMardatillah WiranataNo ratings yet
- Vagina What's Typical, What's Not - Mayo ClinicDocument1 pageVagina What's Typical, What's Not - Mayo ClinicLeomer Calderon jr.No ratings yet
- Elective 2 ReportDocument7 pagesElective 2 ReportJem TellainNo ratings yet
- Complications of MiscarriageDocument21 pagesComplications of MiscarriagebkbkjNo ratings yet
- Types of Vaginal DischargeDocument2 pagesTypes of Vaginal DischargeTeslim RajiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in Teens and Adults: Topic OverviewDocument1 pageUrinary Tract Infections in Teens and Adults: Topic OverviewRaRa PRawitaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal ItchingDocument2 pagesVaginal ItchingHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Facts, Symptoms & TreatmentsDocument34 pagesReproductive System: Facts, Symptoms & TreatmentsJobelyn MalisaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- STD Symptoms, Tests, and Treatments ExplainedDocument19 pagesSTD Symptoms, Tests, and Treatments ExplainedJayvah EstrellaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Rectal Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Rectal Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Pregnancy Vaginal Discharge Changes to Watch ForDocument2 pagesPregnancy Vaginal Discharge Changes to Watch ForAlmera SangulinganNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Vaginosis Treatment: Home Treatment ReportFrom EverandBacterial Vaginosis Treatment: Home Treatment ReportRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- What Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument6 pagesWhat Causes A Urinary Tract InfectionStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Urethritis in Men - EmedicinehealthDocument3 pagesUrethritis in Men - EmedicinehealthaudreydesireeNo ratings yet
- Vaginismus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVaginismus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Your kitchen is your clinic: no need going to the hospital when you have a kitchenFrom EverandYour kitchen is your clinic: no need going to the hospital when you have a kitchenNo ratings yet
- Mayo Clinic on Managing Incontinence: Practical Strategies for Improving Bladder and Bowel ControlFrom EverandMayo Clinic on Managing Incontinence: Practical Strategies for Improving Bladder and Bowel ControlNo ratings yet
- Skip To Main ContentDocument12 pagesSkip To Main Contentronaldo palpialy1No ratings yet
- Endometriosis and Fibroids ExplainedDocument5 pagesEndometriosis and Fibroids ExplainedJonabel MacayNo ratings yet
- Ureaplasma Infection, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandUreaplasma Infection, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- STIs: Learn About Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HPV, Hepatitis B, Herpes, HIV and Syphilis (35 charactersDocument25 pagesSTIs: Learn About Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HPV, Hepatitis B, Herpes, HIV and Syphilis (35 charactersMohamoud MohamedNo ratings yet
- Uti PathoDocument15 pagesUti PathoEden Astred ObilloNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument3 pagesOverviewAlhaisa BejemilNo ratings yet
- Urinary TractDocument4 pagesUrinary TractRoland APARECENo ratings yet
- Ectopic-Pregnancy - Assign - Khan AliDocument8 pagesEctopic-Pregnancy - Assign - Khan AliMohammad KhanNo ratings yet
- UTI in AdultsDocument4 pagesUTI in Adultsjoan_padilla2000No ratings yet
- Postpartum Complications: Endometritis, Perineal CareDocument5 pagesPostpartum Complications: Endometritis, Perineal CareSherina AllenNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Fetal DemiseDocument7 pagesIntrauterine Fetal DemiseElaisa Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Recurrent UTI Patient Education: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument4 pagesRecurrent UTI Patient Education: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentZaveri Hemant GirishkumarNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- 224 Vaginal DischargeDocument2 pages224 Vaginal DischargeIan Mizzel A. DulfinaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsRalph Patrick SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems and Sexual HealthDocument6 pagesReproductive Systems and Sexual HealthAira Shane MargesNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument3 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseRania S. HamdanNo ratings yet
- AmysaDocument14 pagesAmysaawanisfauzi90No ratings yet
- STD Presentation LATESTDocument90 pagesSTD Presentation LATESTNor AmalinaNo ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDiverticular Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- ProjDocument12 pagesProjرافعہ میر بٹNo ratings yet
- Cervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & TypesDocument1 pageCervicitis Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & Typesramit singlaNo ratings yet
- Am I at Risk For Gonorrhea?: PregnantDocument5 pagesAm I at Risk For Gonorrhea?: PregnantSunny OZNo ratings yet
- Urinary System by Carmelita ChavezDocument16 pagesUrinary System by Carmelita ChaveztankmpNo ratings yet
- JB DigestDocument100 pagesJB DigestHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Waive TBLDocument52 pagesWaive TBLHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- IDG LactaseDocument9 pagesIDG LactaseHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Bed Sharing and Co Sleeping ArticleDocument6 pagesBed Sharing and Co Sleeping ArticleAdalene SalesNo ratings yet
- Wcms 117313Document105 pagesWcms 117313Hervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- !PORTAL - Wwpob PageDocument24 pages!PORTAL - Wwpob PageHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Cad 29Document10 pagesCad 29Hervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Helmreich An Anthropologist UnderwaterDocument21 pagesHelmreich An Anthropologist UnderwaterHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Journal Article 42Document6 pagesJournal Article 42Aura MateiuNo ratings yet
- Antifungal DrugsDocument36 pagesAntifungal Drugssandersonravin1No ratings yet
- Aspergillus and Vaginal Colonization-2329-8731.1000e115Document2 pagesAspergillus and Vaginal Colonization-2329-8731.1000e115Hervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Krin17 Chapter008Document2 pagesKrin17 Chapter008Hervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- 1 - Sept - 2014 v3Document1 page1 - Sept - 2014 v3Hervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Vaginal ItchingDocument2 pagesVaginal ItchingHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- CandidiasisDocument5 pagesCandidiasisHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- CervixDocument8 pagesCervixHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Vaginal or Cesarean BirthDocument52 pagesVaginal or Cesarean BirthHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Preinvasive Disease of Vagina and VulvaDocument67 pagesPreinvasive Disease of Vagina and VulvaHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Icd9 LongDocument4 pagesIcd9 LongHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- RX Guidelines & Essential Drug List Adults 2012Document424 pagesRX Guidelines & Essential Drug List Adults 2012spermmanNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary and Female Pelvic Organ DiseasesDocument7 pagesGenitourinary and Female Pelvic Organ DiseasesHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- 003104-pdf DFDocument46 pages003104-pdf DFDesy ErinaNo ratings yet
- UHG PrescriptionListDocument23 pagesUHG PrescriptionListHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- Sneezes Diseases: A Resource Book For Caregivers & ParentsDocument62 pagesSneezes Diseases: A Resource Book For Caregivers & ParentsHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- STD BrochureDocument2 pagesSTD BrochureHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- WHO List of Essential Drugs 18th - EML - Final - Web - 8jul13Document45 pagesWHO List of Essential Drugs 18th - EML - Final - Web - 8jul13DandaliNo ratings yet
- Tanzania Stgs EmlDocument220 pagesTanzania Stgs EmlHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- WHO List of Essential Drugs 18th - EML - Final - Web - 8jul13Document45 pagesWHO List of Essential Drugs 18th - EML - Final - Web - 8jul13DandaliNo ratings yet
- List of Rare Diseases in Alphabetical OrderDocument133 pagesList of Rare Diseases in Alphabetical OrderHervis Francisco FantiniNo ratings yet
- ICD-9-CM Tabular List of Infectious Diseases (FY03Document748 pagesICD-9-CM Tabular List of Infectious Diseases (FY03Neha UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- DDoS Attack Detection: IoT RequiredDocument18 pagesDDoS Attack Detection: IoT RequirednishitaNo ratings yet
- Familia Lingüística PanoDocument50 pagesFamilia Lingüística PanoValeria TorresNo ratings yet
- Resolving Construction DisputesDocument47 pagesResolving Construction DisputesJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- History Midterm NotesDocument2 pagesHistory Midterm Notesjerick DeligeroNo ratings yet
- Stephenie Meyer - Hell On EarthDocument17 pagesStephenie Meyer - Hell On EarthCarol Adams-WyrdNo ratings yet
- Module4 Search For Filipino OriginsDocument16 pagesModule4 Search For Filipino OriginsJohn Carlo QuianeNo ratings yet
- Republic V BagtasDocument3 pagesRepublic V BagtasLoren SeñeresNo ratings yet
- J Butler - Revisiting Bodies and PleasuresDocument10 pagesJ Butler - Revisiting Bodies and PleasuresDiego Madias100% (1)
- The Liberation War of Bangladesh Was A History of Genocide by Pakistan ArmyDocument3 pagesThe Liberation War of Bangladesh Was A History of Genocide by Pakistan ArmySuva RastafarianNo ratings yet
- Banes V BanesDocument11 pagesBanes V BanesRhinnell RiveraNo ratings yet
- Challenges of History Writing in South A PDFDocument501 pagesChallenges of History Writing in South A PDFFahad100% (1)
- Indonesia New PortsDocument5 pagesIndonesia New PortsyingmeitanNo ratings yet
- Inba - Info - List of Pcab Licensed Contractors For Cfy 2012 2013as of 6 March 2013part2 PDFDocument160 pagesInba - Info - List of Pcab Licensed Contractors For Cfy 2012 2013as of 6 March 2013part2 PDFSwarup ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Holy See Wins Sovereign Immunity CaseDocument2 pagesHoly See Wins Sovereign Immunity CaseRochelle Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Francisco de Liano, Alberto Villa-Abrille JR and San Miguel Corporation Vs CA and Benjamin Tango GR No. 142316, 22 November 2001 FactsDocument2 pagesFrancisco de Liano, Alberto Villa-Abrille JR and San Miguel Corporation Vs CA and Benjamin Tango GR No. 142316, 22 November 2001 FactscrisNo ratings yet
- Religious Extremism in Pakistan. ReasonsDocument45 pagesReligious Extremism in Pakistan. ReasonsAdeel Minhas100% (1)
- Counter ClaimDocument2 pagesCounter ClaimEngelus BeltranNo ratings yet
- A. Practice Writing Accurate Case Names:: Citation Exercise #1Document2 pagesA. Practice Writing Accurate Case Names:: Citation Exercise #1James BondNo ratings yet
- Case Brief FormatDocument2 pagesCase Brief FormatJohnathan KingNo ratings yet
- Legal Issues in Psychiatric NursingDocument24 pagesLegal Issues in Psychiatric NursingRic TinNo ratings yet
- Dube V PSMAS and Another (5 of 2022) (2022) ZWSC 5 (24 January 2022)Document22 pagesDube V PSMAS and Another (5 of 2022) (2022) ZWSC 5 (24 January 2022)toga22No ratings yet
- The PillowmanDocument2 pagesThe Pillowmanexcreto100% (2)
- Development of ADR - Mediation in IndiaDocument8 pagesDevelopment of ADR - Mediation in Indiashiva karnatiNo ratings yet
- HIS3MHI - Research ProjectDocument10 pagesHIS3MHI - Research ProjectAdam Daniel MoravskiNo ratings yet
- Zakat On Pension and AnnuityDocument2 pagesZakat On Pension and AnnuityjamalaasrNo ratings yet
- Ventures Onsite Market Awards 22062023 64935868d0485Document146 pagesVentures Onsite Market Awards 22062023 64935868d0485hamzarababa21No ratings yet
- Are Beauty Pageants Sexist or EmpoweringDocument10 pagesAre Beauty Pageants Sexist or EmpoweringJENNIFER GUANNo ratings yet
- Asia Pacific Chartering Inc. vs. Farolan G.R. No.151370Document2 pagesAsia Pacific Chartering Inc. vs. Farolan G.R. No.151370rebellefleurmeNo ratings yet
- No Delinquent Financial Obligations AffidavitDocument1 pageNo Delinquent Financial Obligations AffidavitLenzy Arnn AgetronNo ratings yet
- Admin Law 1 - US v. Dorr GR No. 1051 19 May 1903 SC Full TextDocument17 pagesAdmin Law 1 - US v. Dorr GR No. 1051 19 May 1903 SC Full TextXIANo ratings yet