Professional Documents
Culture Documents
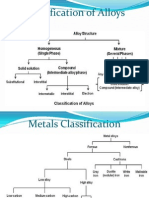
Hardness Brittleness Ductility Castability Formability Weldability Machinability
Uploaded by
Anup DalalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hardness Brittleness Ductility Castability Formability Weldability Machinability
Uploaded by
Anup DalalCopyright:
Available Formats
CAST IRON /STEEL (ALLOY OF Fe & C)
If C%
Hardness
Brittleness
Ductility
Castability
Formability
Weldability
Machinability
Increases
Decreases
PROPERTIES OF CAST IRON
High Compressive strength .
High Damping capacity . ( generally
with Gray C.I from which lathe bed
are made .)
High Casting capability.
High Machinability .( even it is hard
and brittle ) , so its exception .
Poor Weldability because of high %
of carbon .
Poor Formability .
IRON
STEEL
.008% to 2%
Carbon
ALLOY STEEL
HIGH Speed
Steel
TUNGSTEN
BASED
W : Cr : V
18 : 4 : 1
Cutting tool
materials
MOLEYBEDNUM
BASED
10 % TO 12%
Moleybednum
Used in industries
nowdays, Cheaper
Stainless Steel
18 : 8
Cr : Ni
Syringes,knifes,
Shaving Blades.
(Diificult to
machine , difficult
to weld ) . More
tougher and
harder.
PLAIN STEEL
Low Carbon
Steel
Upto .35% C
Parts ,
Components
Medium Carbon
Steel
.35% to .83% C
Screw drivers,
Knife, Shafts,
Chiesels
High Carbon
Steel
.83% to 2% C
Cutting tools,Single
point , Chiesel, Dril
bits, Hacksaw Blade
CAST IRON
2% to 6.67% C
TUNGSTEN based
H.S.S
W : Cr : V
(18 : 4 : 1)
TUNGSTEN
( W)
Has Hot hardness Property
( improved hardness even at
high temperatures)
CHROMIUM
(Cr)
Improves Corrosion
Resistance as well as
Strength of material.
VANADIUM
(V)
Improves Impact Strength ,
Fatigue Strength of the
Material
IRON
STEEL
.008% to 2%
Carbon
CAST IRON
2% to 6.67% C
ALLOY C.I
1. By small
addition of
alloying
elements like
Nickel ,
Chromium ,
Moleybednu
m ,
Vanadium.
GRAY C.I
(soft)
1. Self Lubricating
Property.
2. when cut , Gray
colour appears on
cutting portion.
3. Carbon content is in
the form of Graphite
4.In Lathe Stock , where
tailstock move (
sideways) , made up of
Gray C.I
WHITE
C.I(hard)
1.mostly
water
quenching.
(rapid cooling
in water)
2.Railway
Tracks,
Railway
wheels.
MALLEABLE
C.I
1. As
compared to
other C.I ,
Malleable C.I
has more
malleability
DUCTILE
C.I
(spheroidical
C.I)
1.By small addition
of magnesium or
cerium .
2.Has more fluidity
and castibility.
3.In general it is
used for intricated
castings as well as
big sized castings
due to excellent
casting property.
Through Hardening
(Quenching)
Through Annealing
ALLOY C.I
NICKEL
Improves machinability
and corrosion resistance .
CHROMIUM
Improves corrosion
resistance and prevents
formation of graphite .
MOLEYBEDNUM
Improves strength and
wear reasistance property
, but decrease the
machinability.
VANADIUM
Improves carbide
formation and this
improves the impact
strength and hardness .
HEAT TREATMENT
PROCESSES
ANNEALING
(furnace cooling)
1.For softening , improving the
ductility of metals through
very slow cooling in furnace .
2.internal stresses can be
relieved.
3.Remove surface defects.
NORMALIZING
(air cooling)
1.Similar to annealing, but
cooling rate is higher than
annealing.
2.So, softness is less
compared to annealing.
HEATING ABOVE CRITICAL
TEMPERATURES.
HARDENING
(rapid cooling)or
(Quenching)
1.Rapid cooling in the form of
water quenching or oil
quenching .
2. More internal stresses
produced .
3.Surface cracks produced .
TEMPERING
1. Always done after
hardening process to remove
internal stresses and surface
defects
2.Improves toughness
3. But loss in surface hardness
occurs .
ALWAYS DONE BELOW
LOWER CRITICAL
TEMPERATURE. (Heat
around 200 deg - 300 deg
celsius , maintain temp.
for long period of time
and furnace cooling is
done .)
CASE HARDENING
1. Used to generate outer
surface hardening .
Carburizing , Nitriding ,
Cyaniding , Flame
Hardening , Induction
Hardening .
AUSTENITE (727
deg celsius)
Water Quenching
will form
( Martensite Structure )
( More hard and brittle)
Oil Quenching
/cooling
will form
( Very fine Pearlite )
Air cooling
will form
( Fine Pearlite )
Furnace cooling
will form
( Coarse Pearlite )
Temperatures
Critical temp.
Lower critical
temp.
( after this phase
change ,
properties change
occurs)
upper critical
temp.
( after this no
change occurs)
Recrystallization
temp.
It is approxi.
equal to 40% of
melting point of
the metal , but it
depend upon
prior working of
the metal
Working on metal
below rec. temp. is
called Cold Working
and above this temp. is
called hot working
processes.
BCC delta -Iron
FCC Non-magnetic gamma - Iron
BCC magnetic alpha - Iron
IRON
1539
1403
TEMP
908
768
You might also like
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy of Grey Cast IronDocument15 pagesMetallurgy of Grey Cast IronAmit PathakNo ratings yet
- What is cast iron? Key properties and typesDocument27 pagesWhat is cast iron? Key properties and typesSanthoshsharma Devaraju100% (1)
- 5 Ta3004 m2 l5 Metal1Document59 pages5 Ta3004 m2 l5 Metal1Gean GenizaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Carbon Steel & Heat TreatmentDocument32 pages7 - Carbon Steel & Heat TreatmentAbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Cast IronDocument21 pagesCast Irondellibabu509No ratings yet
- 5 Ferrous and Non FerrousDocument63 pages5 Ferrous and Non FerrousKiran ThunuguntlaNo ratings yet
- Plain Carbon Steels GuideDocument7 pagesPlain Carbon Steels GuideaadhithyarajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Cutting Tool Materials and FluidsDocument88 pagesModule 3: Cutting Tool Materials and FluidssushilNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument25 pagesMetallurgyPandu Damay PutraNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Indexing Drill Jig For Inclined Profile ComponentDocument47 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Indexing Drill Jig For Inclined Profile ComponentANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Werkstoffkunde Der Stähle - Kurzzusammenfassung en-US - UnlockedDocument8 pagesWerkstoffkunde Der Stähle - Kurzzusammenfassung en-US - UnlockedLorena juárezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cast IronDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Cast IronHelen AdugnaNo ratings yet
- Processing: Hot Forming Heat Treatments MachiningDocument32 pagesProcessing: Hot Forming Heat Treatments MachiningThân KhaNo ratings yet
- N CGLDocument70 pagesN CGLjoshibecNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Metallurgy-Manufacturing Process, Grades & Role of Alloying ElementsDocument35 pagesStainless Steel Metallurgy-Manufacturing Process, Grades & Role of Alloying ElementsLalit MohanNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical Alloys Part IiDocument6 pagesAeronautical Alloys Part IimaximinogarciaalejandraNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering-Chapter 11Document3 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering-Chapter 11JurgenNo ratings yet
- Theory of Heat TreatmentDocument8 pagesTheory of Heat Treatmentayie740% (1)
- MaTek #9 Metal-AlloyDocument32 pagesMaTek #9 Metal-AlloyJefri SinuratNo ratings yet
- Steel MaterialsDocument10 pagesSteel Materialsmanideep219No ratings yet
- Special CastingDocument71 pagesSpecial CastingPawan RathiNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag OptimisationDocument41 pagesStainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag OptimisationRamiz Shaikh100% (1)
- Casting Processes: DR Ajay BatishDocument46 pagesCasting Processes: DR Ajay BatishAlisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Study Notes For Test 5: Tools SteelsDocument9 pagesStudy Notes For Test 5: Tools SteelsVy ThoaiNo ratings yet
- 211 2aDocument33 pages211 2aMada ChohNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment 8Document15 pagesHeat Treatment 8watersoul.nNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment (CHAPTER 3)Document48 pagesHeat Treatment (CHAPTER 3)Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Tooling Materials&Heat TreatmentDocument13 pagesTooling Materials&Heat TreatmentVinod MadireddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Alloys and Influence of Elements: Alloys and Melting 01 - Alloys - and - Melting - EN - Docx 1/13Document13 pagesIntroduction in Alloys and Influence of Elements: Alloys and Melting 01 - Alloys - and - Melting - EN - Docx 1/13luisA1923No ratings yet
- Cast Iron and Steel Types GuideDocument16 pagesCast Iron and Steel Types GuideBeesam Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Alloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaDocument25 pagesAlloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaChandima K PriyamalNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Guide for MetalsDocument105 pagesHeat Treatment Guide for MetalsAryan RajNo ratings yet
- Carbon SteelDocument5 pagesCarbon SteelKun Hadipati Kusuma NegaraNo ratings yet
- Acero para BarcosDocument39 pagesAcero para BarcosviyfNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Pallav Radia Asst Prof. Aits, RajkotDocument33 pagesPrepared By: Pallav Radia Asst Prof. Aits, Rajkotnaseema shaikNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment: Workshop Technology MME 1103Document12 pagesHeat Treatment: Workshop Technology MME 1103Murad Mahmoud Al-hidmiNo ratings yet
- Plasma Nitriding Process - DataDocument11 pagesPlasma Nitriding Process - Datayadu kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Free Cutting SteelsDocument6 pagesFree Cutting SteelsRidvan GecuNo ratings yet
- Lec 5-Heat Treatment, Alloy Steels, Cast IronDocument26 pagesLec 5-Heat Treatment, Alloy Steels, Cast IronMobashir AliNo ratings yet
- MMEN 120 - Surface HardeningDocument19 pagesMMEN 120 - Surface HardeningnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Tool Life, Tool Material, Cutting Force, Cutting Fluids and Machinable MaterialDocument17 pagesTool Life, Tool Material, Cutting Force, Cutting Fluids and Machinable MaterialShakeel MohmandNo ratings yet
- Iron Carbide Phase Diagram ExplainedDocument20 pagesIron Carbide Phase Diagram ExplainedKushNo ratings yet
- Plain Carbon SteelDocument6 pagesPlain Carbon Steelحسين كاظم ياسينNo ratings yet
- P6 of CE 104 Eng Mat Metal AlloysDocument37 pagesP6 of CE 104 Eng Mat Metal Alloysmubashir ahmedNo ratings yet
- AnnealingDocument9 pagesAnnealingRathne AbeynayakeNo ratings yet
- Aviation Maintenance Technician B1 - Certification Series: Summary MaterialsDocument71 pagesAviation Maintenance Technician B1 - Certification Series: Summary MaterialsSMK Penerbangan SPN Dirgantara BatamNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Mec 208Document20 pagesTerm Paper Mec 208lksingh1987No ratings yet
- FERROUS MATERIAL PROPERTIESDocument20 pagesFERROUS MATERIAL PROPERTIESLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Green Book SolutionDocument44 pagesGreen Book SolutionCaleb RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Metal AlignmentDocument16 pagesMetal AlignmentAli AbidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Heat Treatment of SteelsDocument60 pagesChapter 13 - Heat Treatment of Steelsahmedmagdi2009100% (1)
- Wrought IronDocument32 pagesWrought IronHicham KorichiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Processing of Automotive MaterialsDocument34 pagesLecture 5 - Processing of Automotive MaterialsKamal SurenNo ratings yet
- Piping MaterialDocument45 pagesPiping MaterialLcm TnlNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument34 pagesProjectSTAR PRINTINGNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Watch Repair - Barrels, Fuses, Mainsprings, Balance Springs, Pivots, Depths, Train Wheels and Common Stoppages of WatchesFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Watch Repair - Barrels, Fuses, Mainsprings, Balance Springs, Pivots, Depths, Train Wheels and Common Stoppages of WatchesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AME 3313 Landing Gear PDFDocument130 pagesAME 3313 Landing Gear PDFDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- ImmuneDocument1 pageImmuneDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- ImmuneDocument1 pageImmuneDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- SDF 7Document1 pageSDF 7Deepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- ImmuneDocument1 pageImmuneDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Budget 2017 MCQsDocument11 pagesBudget 2017 MCQsDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Managing CVID with immune globulin therapyDocument1 pageManaging CVID with immune globulin therapyDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) treatment and managementDocument1 pageCommon variable immunodeficiency (CVID) treatment and managementDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- ImmuneDocument1 pageImmuneDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- LD ENR 1 10 enDocument18 pagesLD ENR 1 10 enDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- The Sbi Po Mains Final Power CapsuleDocument80 pagesThe Sbi Po Mains Final Power CapsuleAnonymous ICJcmDstNo ratings yet
- Nehru Institute of Mountaineering Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand (India) - 249193Document2 pagesNehru Institute of Mountaineering Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand (India) - 249193Deepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- SPP ADC Wake Separation PDFDocument5 pagesSPP ADC Wake Separation PDFDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Renewal of CPLDocument5 pagesRenewal of CPLSourav NaikNo ratings yet
- Flight PlanDocument1 pageFlight PlanDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Flight Plan PDFDocument1 pageFlight Plan PDFDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- SPP ADC Wake Separation PDFDocument5 pagesSPP ADC Wake Separation PDFDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Tolerance ChartDocument1 pageDimensional Tolerance Chartpushkar_k123No ratings yet
- Radiotelephony Communications 1 HandbookDocument64 pagesRadiotelephony Communications 1 HandbookNg Wei JiangNo ratings yet
- Market ConsequencesDocument1 pageMarket ConsequencesSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- How It Works - KuhnausenDocument7 pagesHow It Works - KuhnausenDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- RTO Mechanical 08-06-2014 Question PaperDocument84 pagesRTO Mechanical 08-06-2014 Question PaperDeepak Logeson100% (1)
- Places Around BangaloreDocument10 pagesPlaces Around BangaloreDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- CAD/CAM Principles and Applications: CH 4 Geometric ModellingDocument76 pagesCAD/CAM Principles and Applications: CH 4 Geometric Modellingantony1993No ratings yet
- GATE 2015 Mechanical Engineering - GATE 2015 - GATE Study Material For Fluid Mechanics SubjectDocument4 pagesGATE 2015 Mechanical Engineering - GATE 2015 - GATE Study Material For Fluid Mechanics SubjectDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- GraphicsDocument64 pagesGraphicsDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- RadiatorDocument46 pagesRadiatorjd4u100% (1)
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDocument8 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- GDT Applications PDFDocument36 pagesGDT Applications PDFBikash Chandra SahooNo ratings yet
- Link To The Drawing - Dassault - Catia Products - Eng-TipsDocument1 pageLink To The Drawing - Dassault - Catia Products - Eng-TipsDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet