Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro
Uploaded by
qilaqrsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro
Uploaded by
qilaqrsCopyright:
Available Formats
During the production of metallurgical coke a by-product gas stream is produced
which contains a complex mix of hydrocarbons, including alkylaromatics. You are
currently working for a company involved in assisting a Chinese coke manufacturer
with assessing the potential for converting the gas into high value chemicals. Your
team is tasked with assessing the potential for producing high purity benzene (>97
wt%) from the alkylaromatics. As a starting point your manager has asked you to
examine only the hydrodealkylation of toluene to benzene according to the following
reaction:
C
6
H
5
CH
3
+ H
2
C
6
H
6
+ CH
4
Your manager wants you to establish a process flowsheet for the production of
benzene from toluene, build a working model in ASPEN to solve the mass and energy
balances for the process, and then carry out an in-depth analysis of the process to
determine a range of performance related issues.
Given the size of the coke plant and production rate of by-product gas a basis of
55,000 tonnes of benzene product per annum has been established as a basis for the
assessment. The coke plant also generates a hydrogen rich gas stream containing 10
% (by volume) methane, which could be used as the source of hydrogen needed. If
the results from your team indicate that the potential for benzene production is good,
the results from your project will be extended to include the full range of
alkylaromatics in the gas.
1.1 Objectives and Aims
Recovery of valuable material is important in ensuring maximum utilization of
resources. This report aims to assess the recovery of benzene from by-product gas.
Table XX lists the scope of the report.
In Scope Out of Scope
Production of benzene from toluene Catalyst regeneration (2 reactors, single
standby
Comparison of available production
technologies
Cost to replace catalyst (very long
lifespan
Modeling of selected process in aspen Source of steam
Optimization of selected process *
Economic analysis Separation of other hydrocarbons from
by-product gas stream
1.1 Raw Materials and Products pg
a Raw materials, end uses
1.2 Alternative Technologies 2 pg
b BFD, Alternative Tech
1.3 Process Flow Diagram 1 pg
c PFD
1.4 System Structure 2 pg
d Identify the system structures, the major units in the process, their function and why
they are connected as they are for the chosen process. Identify where heat is being
generated and consumed within the process (which units) and where heat integration
takes place
Structure of the HDA system consists of several major unit operations, discussed
below.
1.4.1 System Structure
The process essentially manipulates the reaction between toluene and hydrogen to
produce benzene, given by the following equation;
The process is constructed revolving this reaction, its kinetics and thermodynamics.
The first phase of the process prepares reactant streams for the reaction, which
includes raising the streams to the required temperature and pressure. The second
phase is the reaction, and the last phase is separation of product from the reactor
output stream. A more detailed process description is discussed below.
functions
arrangement justification
input info
design steps calc needed, dot points
key output
1.4.2 Stream Preparation
Fresh input streams are mixed with recycle streams fresh toluene feed (S03) with
recycle toluene feed (S27), fresh hydrogen feed (S05) with recycle hydrogen feed
(S07) in mixing tanks M001 and M009 respectively. These streams are then mixed in
the mixing tank M002 before passed through heat exchanger H001 to raise its
temperature to 600C, and pressure to 24.81 bar.
1.4.2 Reactor
90% conversion
exothermic
600C
20 to 60 bar
catalyst - ?
side reaction
1.4.3 Flash Drum Separator
1.4.4 Distillation Column
1.4.5 Heat Exchanger
1.4.6 Process Units Connection pg
1.4.7 Heat Integration pg
Reactor and recycle T P to maximize benzene and minimize biphenyl formation.
Both hydrogen and toluene needs to be pressurized before entering reactor.
Will need furnace.
1.5 Process Goals 1 pg
Identify the goals (technical, economic, operational, health and safety, environmental)
of the process and where goals are competing Your team is tasked with assessing the
potential for producing high purity benzene (>97wt%) from the alkylaromatics
basis of 55,000 tonnes of benzene product per annum
1.6 Operating Conditions pg
1.6.1
1.6.2
1.6.3
1.6.4
Provide key operating conditions for the units within the process, explaining the
significance of those operating conditions
1.7 Hazards and Risks 1 pg
g Hazards Risk
1.8 World Trends 1 pg
h World Trends
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Maths Master FileDocument2 pagesMaths Master FileqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Household Kitchen & Laundry: Bath & BeautyDocument1 pageHousehold Kitchen & Laundry: Bath & Beautyqilaqrs100% (1)
- Children's Classics Daddy-Long-Legs His Dark Materials The Diary of A Young GirlDocument6 pagesChildren's Classics Daddy-Long-Legs His Dark Materials The Diary of A Young GirlqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CIPSDocument1 pageCIPSqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Meal PrepDocument6 pagesMeal PrepqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Test of DocumentDocument1 pageTest of DocumentqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Chapter 3 Forces & Pressure StudentDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Forces & Pressure StudentAhmad ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- No Topic Maths Sheet Source Given To Student: 01 Initial Audit - Unit F2 - Algebraic Concepts PDFDocument2 pagesNo Topic Maths Sheet Source Given To Student: 01 Initial Audit - Unit F2 - Algebraic Concepts PDFqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Meal PrepDocument6 pagesMeal PrepqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Intro To OSHDocument52 pagesIntro To OSHqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Backpacking Gear List Template & ChecklistDocument30 pagesBackpacking Gear List Template & ChecklistqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Meal PrepDocument6 pagesMeal PrepqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 06 Overview of Ra1Document71 pages06 Overview of Ra1Dana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Maths Straight LinesDocument1 pageMaths Straight LinesqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Travel Plan v02Document15 pagesTravel Plan v02qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Appendix Yield EvaluationDocument1 pageAppendix Yield EvaluationqilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Indices and Logs: 1.0 Integer Indices (The Round Power )Document4 pagesChapter 5 - Indices and Logs: 1.0 Integer Indices (The Round Power )qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Maths Form 4Document10 pagesMaths Form 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Maths Form4 StraightLine Student v01Document9 pagesMaths Form4 StraightLine Student v01qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Configuration 4Document9 pagesConfiguration 4qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Configuration 1Document2 pagesConfiguration 1qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Configuration 1Document2 pagesConfiguration 1qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Configuration 1Document2 pagesConfiguration 1qilaqrsNo ratings yet
- Ductless Fume Hood Brochure - FEB19Document2 pagesDuctless Fume Hood Brochure - FEB19Musz MusaNo ratings yet
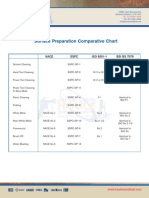
- Surface Preparation Comparative ChartDocument1 pageSurface Preparation Comparative Chartcmms88No ratings yet
- 3 Oxidation and ReductionDocument25 pages3 Oxidation and ReductiondonutNo ratings yet
- HRF 669ffa SP (04 09 27)Document5 pagesHRF 669ffa SP (04 09 27)yayayalNo ratings yet
- DRM Wha B PDFDocument31 pagesDRM Wha B PDFBryan JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Taka Gas Spring CatalogueDocument14 pagesTaka Gas Spring CatalogueAdem YıldızhanNo ratings yet
- tp6140 PDFDocument72 pagestp6140 PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- Ce 326 Principles of Environmental Engineering: SPRING 2010Document2 pagesCe 326 Principles of Environmental Engineering: SPRING 2010Jorge Gomez RamirezNo ratings yet
- MesTer 01 EL Lighting Fixture SchedulesDocument4 pagesMesTer 01 EL Lighting Fixture SchedulesFatih ÖzmerdivanlıNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- An Overview of Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementDocument7 pagesAn Overview of Cathodic Protection Potential MeasurementKhanh DTNo ratings yet
- IR231 ManualDocument27 pagesIR231 Manualharleystroker2No ratings yet
- Brochure D-R 290 enDocument1 pageBrochure D-R 290 enDandy Harris FirdiandaNo ratings yet
- 002 MillingDocument29 pages002 MillingCindelle Mariae GomiegaNo ratings yet
- MITx2 854 1x-V000900 - DTH-enDocument3 pagesMITx2 854 1x-V000900 - DTH-enLeonardo RamosNo ratings yet
- Miniature Lamp GuideDocument3 pagesMiniature Lamp GuideKAZIMALI25No ratings yet
- Cleasby Conveyors MaintenanceDocument2 pagesCleasby Conveyors MaintenanceRino AdityaNo ratings yet
- Strategic MGMT Ch-3Document30 pagesStrategic MGMT Ch-3Desu MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Danfoss DML Filter DriersDocument16 pagesDanfoss DML Filter DrierswidhiantoNo ratings yet
- MaterialogyDocument181 pagesMaterialogyrajraj3550No ratings yet
- A 250Document1 pageA 250AnuranjanNo ratings yet
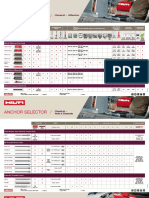
- HiltiDocument3 pagesHiltiLiam WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Brochure SteelDocument8 pagesBrochure SteelNur Arhami LailaNo ratings yet
- Nanoscale Thermoelectric Materials and DevicesDocument24 pagesNanoscale Thermoelectric Materials and DevicesArsad ThaibNo ratings yet
- Hoja Técnica Lanco 1890 CDocument2 pagesHoja Técnica Lanco 1890 CBryan GavilanezNo ratings yet
- Aluminum PipeDocument5 pagesAluminum PipeKhian PinedaNo ratings yet
- 10 Stainless Steel PDFDocument86 pages10 Stainless Steel PDFPopovici PaulNo ratings yet
- PT South East Asia Pipe Industries - Downloaded From Steelads ComDocument10 pagesPT South East Asia Pipe Industries - Downloaded From Steelads ComRizki TrisnasariNo ratings yet
- Creality CR-6 SE User Manual English - Chinese PDFDocument24 pagesCreality CR-6 SE User Manual English - Chinese PDFstryzackNo ratings yet
- Gambar Sistem Proses 03Document5 pagesGambar Sistem Proses 03Novianti NoviNo ratings yet
- Global Talent 2021Document48 pagesGlobal Talent 2021Mentari Clara dewantiNo ratings yet
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarFrom EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaFrom EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (242)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)