Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TM 601 Homework Assignment One
Uploaded by
Sarab JeetCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TM 601 Homework Assignment One
Uploaded by
Sarab JeetCopyright:
Available Formats
TM 601
HOMEWORK ONE
Due next class
Answer the following questions. You should be able to complete all of the following
problems with your textbook and notes closed.
I pledge on my honor that I have not given or received any unauthorized assistance on this
assignment/examination. I further pledge that I have not copied any material from a book,
article, the Internet or any other source except where I have expressly cited the source.
Name (Print) Sarabjeet Singh Signature ________________ Date: 09/04/2014
Please note that assignments in this class may be submitted to www.turnitin.com, a
web-based anti-plagiarism system, for an evaluation of their originality.
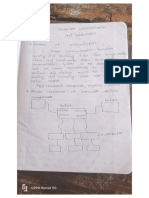
1. Identify the five elements of our simple communications model and discuss the role
of each.
The five elements of simple communication model are as follows:-
1) Source It is the host from where the signal we want to transmit are generated.
These signals are generally digital bit stream generated by personal computer.
2) Transmitter It takes the generated signal from the source & transmit it after
embedding the important information of destination address. In case of personal
computer as a source, a modem could work as transmitter as it modulate at
transmitting end converting digital bit to analog.
3) Transmission System It is the channel through which we can propagate the
generated signal from source to destination. Fiber optic cables, Ethernet wires &
radio channels etc. may be used as transmission channel.
4) Receiver Reception of signal is done here. A modem is used as demodulator at
this end which converts the analog signal again to the digital bit stream & make
error correction if required.
5) Destination Transmitted signal from the source is taken by the destination.
2. In class we discussed that communications is more than connectivity. Identify and
define three tasks in addition to connectivity required for communications.
A communication is said to be established only when the core of the information or
message sent by source may reached the destination. There must be connectivity to
initiate & complete the communication process. The three task in addition to
connectivity are as follows-
1) Interfacing It is the mode of connection by which a source get connected to a
destination. There may be various entities to be connected in between the source
& destination e.g. ISPs, Internet etc. In case of data communication Interfacing
medium can be decided according to the rate of propagation of electromagnetic
signal (Optical Fiber, 4G etc.)
2) Error Detection & Correction Factors like heat dissipation or bad weather at
interfacing channels may lead to undesired alteration in the transmitted data.
These alterations are errors, so in order to rectify the signal we need to perform
error detection & correction. The Automatic Repeat Request scheme is used to
correct the data errors of files & Forward Error Correction scheme is used to
rectify the real time data like voice signals.
3) Flow Control While communicating, the reception can be done by only processing
the data at receiver end so if the incoming data rate is faster than the processing
time at receptor then the system may got hanged up. So, a synchronized flow
control is required in between transmitter & receiver.
3. Identify and discuss three important differences between a WAN and a LAN.
WAN
1) It is used for bigger geographical area & requires public right of ways.
2) Implemented by circuit switching & packet switching by connecting with the
number of switching nodes. It couldnt be wireless due to large covering area.
3) WAN is not owned by primary user or organization it is generally taken on a
lease.
LAN
1) It is used for smaller area mostly for a building & subordinate structures.
2) Implemented by switched LAN (ETHERNET), ATM LANs. It may also
implemented as wireless LAN.
3) It is mostly owned by business users, so while buying care must be taken as
maintenance & network management is sole responsibility of user.
4. Consider the four WAN switching technologies we highlighted in class. Name all
four. Briefly discuss each mentioning any important similarities and differences.
Give an example application for each technology.
Circuit Switching- The connection between source and destination can be made by
nodes of the network. The path is created by the physical links like optical fiber. Now
there are the logical links at the notes such as Router, which directly passes the data to
destination or assigned next note which provides shortest path to destination.
Telecommunication Network
Packet Switching- It can be done by sending the data in chunks by one node to
another. These data chunks are called Packets. The entire packet stored first at node,
then transmitted further. It is used for terminal to computer or computer to computer
communication.
There are Frame Relay & ATM technologies, but we may use MPLS in-stead of
those.
Multi-Protocol Label Switching-While distributing data packets, router takes time to
look up routing tables. In this protocol the header set by PDU at the frame (Data link
Layer) may get the information about the destinations direct path information before
going to PDU segment (Transport Layer). These paths are called Label Switched Path
which gives an opportunity to direct routing. It improves the Quality of Services by
providing services like VPN.
5. Define the important concept of a protocol architecture. Name two existing protocol
architectures.
Protocol are the rules required to perform the communication. The communication
task is subdivide in to sub-tasks known as different layers. Layers are in hierarchical
vertical stack form. Each layer is distinct & perform the task in a way by which it
serves the next upper layer. The Protocol Architecture requires three things to be
done in communication process.
---To make data format translate function.
---To make transmission control for coordination & error handling.
---To make flow of data sync for sequencing.
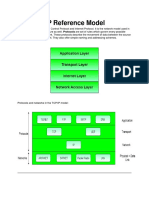
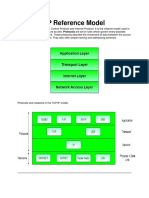
So our architecture layer should comply with these requirements may give TCP/IP as-
Network Access Layer- It exchange data between a computer and network. According
to the information provided by source Network Routes the data to the appropriate
destination. The source may provide additional information like data priority to the
network.
Transport Layer- To provide reliability for exchanging data transport layer is used. It
ascertains that the data arriving in destination is in the same order in which they are
sent from source.
Application Layer- The logic required for each application we want to perform is
different. As an example to perform a file transfer task a separate module is needed.
So, this layer deals with the applications to establish the communication.
The two existing protocols are-
Open System Interconnection Architecture (OSI) & Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
6. Define and give an example of entity.
An entity is a unit active element in which various subsystem may perform the task. It
gives a unified way to manage the distributed devices. The examples of entity are;
Workstation; Telephone Exchange & Computer Cluster.
7. Consider TCP/IP.
Using the OSI model as a reference, what layer protocol is IP? TCP?
In OSI model Layer-3(Network) is IP layer & Layer-4 (Transportation) is TCP
Layer.
What is the function of IP? TCP?
The function of IP is to route end to end devices in different networks. The TCP is
used to give reliability of data transfer to end to end device.
8. Define a PDU and give an example. (Refer to the reading assignment for the answer).
Protocol Data Unit- In the protocol layers the data control information is added as a
header to the data, this combination of data & control information called the Protocol
Data Unit. According to the layers PDU has distinctive job to do at the Physical layer
PDU are called Frame , at Network Access Layer it is called Packet, at Transport
Layer it is Segments. Examples of PDU are An ETHERNET frame, An Internet
Protocol Packet, TCP/UDP Segments etc.
9. The author mentions that two levels (or types) of addressing are required in data
networking. Identify and define each. (Refer to the reading assignment for the
answer).
1) The address line in a network is for specify different computers in a whole
network. This address is unique for each participant computer.(MAC Address)
2) There can be different application in a addressed computer of a network. So, for
communication in multiple application for a computer is performed by address
which is unique for that application. These address are known as Service Access
Point (SAP) or Port.
10. Briefly define the OSI model. What is/are its principal weakness(es) compared to
TCP/IP?
The OSI model is also a standardized model which uses seven layers. These layers are
Physical, Data Link, Network access, Transport, Session, Presentation & Application.
These layers performs as horizontal stack. It provide more data integrity to the network.
Weaknesses-
1) Connection mode transfer in OSI model requires three parties so communication
is relatively slow.
2) It is a complex model. The session & presentation layers are hardly use, even the
Fast LANs show decreased error rate, so data integrity requirement with a
complex model is of no use.
You might also like
- Network Engineer Interview QuestionsDocument34 pagesNetwork Engineer Interview QuestionsMir Farhan Ali Abedi100% (5)
- Typically Payroll Interface Requirements: - Requirements Are Often Expressed Like ThisDocument56 pagesTypically Payroll Interface Requirements: - Requirements Are Often Expressed Like Thissyedmehar100% (1)
- COBOL V6.3 Whats NewDocument74 pagesCOBOL V6.3 Whats NewMUSICA MUSICA100% (1)
- NirCmd - Freeware Command-Line Tool For WindowsDocument59 pagesNirCmd - Freeware Command-Line Tool For Windowsmario_iv1No ratings yet
- Logical Backup PDFDocument107 pagesLogical Backup PDFG.R.THIYAGU ; Oracle DBA100% (7)
- Easy Way To Hack The Admin Joomla SQL Injection Hack How To Hack PHP Mysql WebsiteDocument23 pagesEasy Way To Hack The Admin Joomla SQL Injection Hack How To Hack PHP Mysql Websiteropoloko100% (4)
- Communications Layers SummaryDocument7 pagesCommunications Layers SummaryKarthickmanikandan GNo ratings yet
- IPv4 - Quick GuideDocument12 pagesIPv4 - Quick Guidekarthik chithariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument21 pagesUnit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inprince keshriNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: CRT Technical by Naresh I TechnologiesDocument7 pagesData Structures: CRT Technical by Naresh I Technologieskark437No ratings yet
- Network Programming: MT-24C Assignment-1Document17 pagesNetwork Programming: MT-24C Assignment-1Inder2002No ratings yet
- CN 1Document7 pagesCN 1T024KOUSTAV CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- IPv 4Document20 pagesIPv 42224 Momynul IslamNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222Document13 pagesComputer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222RAY COOLNo ratings yet
- IPv4 - Quick GuideDocument21 pagesIPv4 - Quick GuidemispanshieNo ratings yet
- 201980090184+computer Network Final AssignmentDocument10 pages201980090184+computer Network Final AssignmentMd. Ziaul Haque ShiponNo ratings yet
- Logical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer NetworksDocument19 pagesLogical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer Networksblessing pakachenaNo ratings yet
- Logical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer NetworksDocument19 pagesLogical Addressing: IPV4 Addressing - Computer Networksblessing pakachenaNo ratings yet
- First Assignment in CnsDocument7 pagesFirst Assignment in CnsAlcala, John Paul P.No ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument3 pagesNetworkingKshitij PanditNo ratings yet
- Osi Model LanDocument8 pagesOsi Model LanRenegade DiverNo ratings yet
- IPv4 and Addressing CompleteDocument24 pagesIPv4 and Addressing CompleteusamaNo ratings yet
- Network Protocols - TutorialspointDocument5 pagesNetwork Protocols - TutorialspointThusharika ThilakaratneNo ratings yet
- Name - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Document4 pagesName - Prajwal Ghale Roll On - NP000477 Section - B: Question No.1Prajwal GhalezNo ratings yet
- Computernetwork For InterviewDocument9 pagesComputernetwork For InterviewSangeetha ShankaranNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Week 3 & 4 Manalo, Ryan Jay A. FEBRUARY 10, 2022 Iii-Bscpe Engr. Arnold F. ReanoDocument6 pagesActivity 2 Week 3 & 4 Manalo, Ryan Jay A. FEBRUARY 10, 2022 Iii-Bscpe Engr. Arnold F. ReanoRyan Jay ManaloNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document5 pagesWeek 3hiren_keepsmilingNo ratings yet
- 17BCS2998 Assignment1Document7 pages17BCS2998 Assignment1samswag2898No ratings yet
- Network ProtocolDocument5 pagesNetwork ProtocolNayana SurendranNo ratings yet
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocument5 pagesDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNo ratings yet
- # TCP/IP Protocol Layers:-1.application Layer: Protocols UsedDocument8 pages# TCP/IP Protocol Layers:-1.application Layer: Protocols UsedPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocument4 pagesDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNo ratings yet
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocument4 pagesDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNo ratings yet
- Q1. Draw The Block Diagram of A General Communication Model andDocument42 pagesQ1. Draw The Block Diagram of A General Communication Model andAditi VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CCN Note First Module - CompressedDocument21 pagesCCN Note First Module - CompressedsbaleemaNo ratings yet
- Cat 1 Exam Notes - CN Unit 1Document50 pagesCat 1 Exam Notes - CN Unit 1Deepan surya RajNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument67 pagesNetworkBiplov SapkotaNo ratings yet
- TCP-IP Part-1Document38 pagesTCP-IP Part-1Aadya SharmaNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument8 pagesOSI ModelMuhammad RehanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Computer Networks NotesDocument18 pagesUNIT 1 Computer Networks NotesdoctoraseenNo ratings yet
- Network Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument22 pagesNetwork Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringBlue BloodNo ratings yet
- Network Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument22 pagesNetwork Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringJoyNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument6 pagesTCP Ipkannanperu123No ratings yet
- The TCPDocument4 pagesThe TCPSYAMANTA GARUDNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document10 pagesAssignment 4anil rajputNo ratings yet
- A Brief Summary On TCP/IPDocument30 pagesA Brief Summary On TCP/IPShubham VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- ECE541 Data Network 1: Communicating Over The NetworkDocument37 pagesECE541 Data Network 1: Communicating Over The NetworkAzri AzsrNo ratings yet
- Ccna 1Document3 pagesCcna 1Enrique BecerraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Protocol Architecture - Computer NetworksDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - Protocol Architecture - Computer Networkschandushar1604100% (3)
- Network Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument22 pagesNetwork Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineeringআসিফ রেজাNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument3 pagesTCP IpsangeetadineshNo ratings yet
- 9IP ModelDocument4 pages9IP ModelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- 9IP Model-1Document4 pages9IP Model-1Jawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- The TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument4 pagesThe TCP/IP Reference ModelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Network Support Group (Rajasthan)Document177 pagesNetwork Support Group (Rajasthan)Pankaj Barala100% (1)
- Computer Networks Set 2Document19 pagesComputer Networks Set 2madhavibandari609No ratings yet
- FAQ'sDocument24 pagesFAQ'sduvvuruvitNo ratings yet
- IPv4 NetworkDocument19 pagesIPv4 Networkbackbencher kiddoNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Cn: Syeda Pakiza ImranDocument5 pagesAssignment-Cn: Syeda Pakiza Imrannauman tariqNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Computer Networks LabDocument11 pagesAssignment 1: Computer Networks LabNickNo ratings yet
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument3 pagesOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelReign Earl B. Gup-ayNo ratings yet
- IT Notes Unit 5Document14 pagesIT Notes Unit 5Deepankar Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- TCP IP Explained 17.01.2024Document5 pagesTCP IP Explained 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- TCP IP ApplicationsDocument10 pagesTCP IP ApplicationsJetesh DevgunNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- A Simple QuadTree Implementation in C# - CodeProjectDocument13 pagesA Simple QuadTree Implementation in C# - CodeProjectDhiresh DasNo ratings yet
- PKZIP 2.5 - UsersguideDocument184 pagesPKZIP 2.5 - Usersguideparani_scribdNo ratings yet
- DWM 2Document245 pagesDWM 2HamsaNo ratings yet
- Cao MCQDocument13 pagesCao MCQsaiananyaNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Examinations: Marks Obtained Gradeteacher'S SignatureDocument6 pagesHalf Yearly Examinations: Marks Obtained Gradeteacher'S SignatureRamyaNo ratings yet
- Rights FlagValue of Solidworks PDMDocument1 pageRights FlagValue of Solidworks PDMNataraj MohanNo ratings yet
- Sap ErpDocument17 pagesSap ErpGisella Julissa GarciaNo ratings yet
- The PC Hacking FAQDocument24 pagesThe PC Hacking FAQapi-3712211No ratings yet
- Web Services OverviewDocument58 pagesWeb Services OverviewA Shahrizal MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Guidance Note FEEM European Code Structure Mod.1 April 2013Document24 pagesGuidance Note FEEM European Code Structure Mod.1 April 2013Catarina MendesNo ratings yet
- Hiren's Boot CD 8Document10 pagesHiren's Boot CD 8api-3834725No ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument5 pagesOsi ModelTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- Cost Center Change Request Summary:: Optional Except Where Indicated)Document3 pagesCost Center Change Request Summary:: Optional Except Where Indicated)tanishgupta1234No ratings yet
- SET CommandsDocument22 pagesSET CommandsSreedhar ThatipallyNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Oracle Database ArchitectureDocument4 pagesExploring The Oracle Database ArchitectureNguyễnXuânLươngNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Curriculum IntensiveDocument9 pagesFundamentals Curriculum IntensiveraviembfilesNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 Disaster Recovery Operations GuideDocument240 pagesMicrosoft Exchange Server 2003 Disaster Recovery Operations Guideapi-3731341100% (2)
- V6 Supercharger For Android-Update9 Beta 6.1.ShDocument41 pagesV6 Supercharger For Android-Update9 Beta 6.1.ShMihuţ CINo ratings yet
- ALV With Totals and Sub Totals in SAP ABAPDocument5 pagesALV With Totals and Sub Totals in SAP ABAPwasiuddinNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Replication 61 Admin PDFDocument112 pagesVsphere Replication 61 Admin PDFstric123No ratings yet
- Powerstore - Configuring NFSDocument26 pagesPowerstore - Configuring NFSMikko VirtanenNo ratings yet
- 1Document2,019 pages1Pankaj Kamble0% (1)
- SerialDocument59 pagesSerialnelson_herreraNo ratings yet
- DBDocument92 pagesDBsmataire100% (1)