Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Itopride
Uploaded by
LesValenzuela0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
379 views2 pagesItopride
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentItopride
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
379 views2 pagesItopride
Uploaded by
LesValenzuelaItopride
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Itopride
Itopride (INN, trade name Ganaton) is a prokinetic benzamide derivative
unlike metoclopramide or domperidone. These drugs inhibit dopamine and have
a gastrokinetic effect.
[1]
Itopride is indicated for the treatment of
functional dyspepsia and other gastrointestinal conditions.
Itopride is not currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
for use in the United States, nor is it yet approved in the United Kingdom. This may
explain the apparent lack of patient information available in English compared to
other similar classes of medication.
Clinical use
A blister package of Ganaton (Itopride) 50 mg tablets intended for distribution in the Slovak Republic.
Typically, itopride is indicated in the treatment of GI symptoms caused by reduced GI
motility:
dyspepsia of a non-ulcer/dysmotility type (gastric "fullness", discomfort, and
possible pain)
Delayed gastric emptying
anorexia
heartburn
regurgitation
bloating
nausea and vomiting
other possible gastric, prolactin, or dopamine related conditions
Itopride is typically taken three times a day. The dose is usually taken on an empty
stomach about an hour before meals. However, the dosage and details of
administration may vary depending on the patients age, symptoms, and other factors.
Itopride was shown to significantly improve symptoms in patients with functional
dyspepsia and motility disorders in placebo-controlled trials.
These studies concluded that the reduction in the severity of symptoms of functional
dyspepsia after 8 weeks of treatment with itopride indicated that itopride was
significantly superior to placebo and that itopride yielded a greater rate of response
than placebo in significantly reducing pain and fullness.
Contraindications and precautions
Itopride is a relatively new drug and it is not currently approved for normal prescribed
use nor OTC use in either the US nor the UK. However, this does not necessarily
indicate that itopride is not effective or safe.
Patients taking itopride should report any side-effects to their treating physician.
Itopride is contraindicated in hypersensitivity to itopride or benzamides; lactation,
GI hemorrhage, obstruction or perforation. Itopride may not be indicated for those
suffering from Parkinson's disease or other conditions involving dopamine regulation
issues. Itopride should be used with special caution in the young and the elderly. Little
information is available at this time regarding the safe use of itopride during
pregnancy.
Adverse drug reactions
The most common side-effects of itopride include mild to moderate abdominal pain
and diarrhoea. Some other side effects that may occur include: rash, giddiness,
exhaustion, back or chest pain, increased salivation, constipation, headache, sleeping
disorders, dizziness, galactorrhea, and gynecomastia.
Other side effects may also be present.
Leukopenia, a reduction in the normal level of white blood cells, can be a potentially
life-threatening reaction to itopride.
Central nervous system adverse effects do not tend to occur due to poor penetration
across the blood brain barrier, although a slight raising of prolactin levels may
occur. Raising of prolactin levels is more common with high dose regimes of itopride.
Mechanism of action
Itopride increases acetylcholine concentrations by inhibiting dopamine D2
receptors and acetylcholinesterase. Higher acetylcholine increases GI peristalsis,
increases the lower esophageal sphincter pressure, stimulates gastric motility,
accelerates gastric emptying, and improves gastro-duodenal coordination.
You might also like
- Itopride HCL Pynetic 50mg TabDocument2 pagesItopride HCL Pynetic 50mg TabAusaf AhmadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- DibencozideDocument1 pageDibencozideParsley Non100% (2)
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyShaira Suzane SabidoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedswitchlers anneNo ratings yet
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidDocument1 pageDRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is IndicatedDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is Indicatedianecunar100% (1)
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument8 pagesDrug AnalysisJonie Vince SañosaNo ratings yet
- IrbesartanDocument3 pagesIrbesartanapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Duavent Drug Study - CunadoDocument3 pagesDuavent Drug Study - CunadoLexa Moreene Cu�adoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1 (Done)Document3 pagesDrug Study 1 (Done)Otaku MiyoNo ratings yet
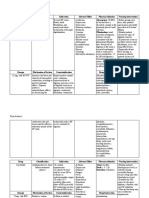
- Drug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N Contraindicatio N Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilit YDocument1 pageDrug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N Contraindicatio N Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilit YNica RodriguezNo ratings yet
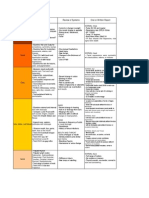
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)Document3 pagesDrug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)amitNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Document3 pagesOmeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Athea MelosantosNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- Act Rapid 2Document2 pagesAct Rapid 2Leah Torcelino-InfanteNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- Filgastrim (GCSF)Document3 pagesFilgastrim (GCSF)Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Carved I LolDocument2 pagesCarved I LolmariaclaramutyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyBridgette ArañesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- Drug Study IsoniazidDocument1 pageDrug Study IsoniazidEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Duty Drug Study'sDocument7 pagesDuty Drug Study'sGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study2Document2 pagesDrug Study2Haifi HunNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MethergineDocument2 pagesDrug Study MethergineJahmil DulatreNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Drug StudySHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- CombiventDocument1 pageCombiventDherick Rosas0% (1)
- TergecefDocument2 pagesTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- AldazideDocument2 pagesAldazideianecunarNo ratings yet
- Actos Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActos Drug StudyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Discharge Plan For AppendectomyDocument1 pageDischarge Plan For AppendectomyMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- HYOSCINEDocument1 pageHYOSCINEzyr2189No ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument5 pagesCeftriaxoneCastillo MikaellaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyHerwincayeNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- AntacidsDocument2 pagesAntacidsMa Corazon MelecioNo ratings yet
- Ganaton SPCDocument8 pagesGanaton SPCNguyen Manh TuanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Pituitary GlandDocument58 pagesThe Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Pituitary GlandMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRai D. MacapantonNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Risk For FallDocument3 pagesRisk For FallLesValenzuela100% (1)
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
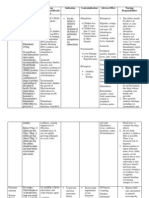
- Generic Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Indications/ Contraindicatio NS Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageName of Drug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Indications/ Contraindicatio NS Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- LoperamideDocument1 pageLoperamideLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument3 pagesLevofloxacinLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- GavisconDocument1 pageGavisconLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Normal Characteristics of EcgDocument96 pagesNormal Characteristics of EcgLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilties Patient TeachingDocument1 pageDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilties Patient TeachingLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document5 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2LesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- DolcetDocument2 pagesDolcetLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Making Ecg'S Easy: Application For The ECG Evaluating The EcgDocument45 pagesMaking Ecg'S Easy: Application For The ECG Evaluating The EcgLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- The Physical Exam, Review of Systems, and ReportsDocument2 pagesThe Physical Exam, Review of Systems, and ReportsJuan DeSantosNo ratings yet
- 2016 Annual Meeting Preliminary ProgramDocument62 pages2016 Annual Meeting Preliminary ProgramDrVijaya VasanthakumarNo ratings yet
- Update Therapeutic CommunicationDocument11 pagesUpdate Therapeutic CommunicationSupriyatin AjjaNo ratings yet
- Retail Chains Aim To Open Up India's Dental Care Market - Wharton UniversityDocument8 pagesRetail Chains Aim To Open Up India's Dental Care Market - Wharton UniversitySivaNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument35 pagesOsteomyelitischinnnababu100% (1)
- No Urut 59 Dan 119Document3 pagesNo Urut 59 Dan 119Risky UntariNo ratings yet
- Cardiology II WorkbookDocument70 pagesCardiology II WorkbookPharmacist Dina100% (1)
- Application (30 Points) :: and Monitoring Schedule For The Next Year Based On The Results From The Outside ReviewDocument7 pagesApplication (30 Points) :: and Monitoring Schedule For The Next Year Based On The Results From The Outside Reviewijaz afzalNo ratings yet
- How to look 「皮疹」Document50 pagesHow to look 「皮疹」Satoshi KobayashiNo ratings yet
- 12 Steps of Aseptic TechniqueDocument7 pages12 Steps of Aseptic TechniqueRobbie MejiaNo ratings yet
- Alana Chan Resume 2015Document2 pagesAlana Chan Resume 2015api-276063860No ratings yet
- MS Wrep IIDocument51 pagesMS Wrep IIiana-almocera-6970No ratings yet
- Free Sample Business English Course PDFDocument9 pagesFree Sample Business English Course PDFakonNo ratings yet
- Tetras ScaleDocument1 pageTetras Scalemerivl2No ratings yet
- HaadDocument13 pagesHaadMac FelicianoNo ratings yet
- (2018) Renal Trauma - The Current Best PracticeDocument9 pages(2018) Renal Trauma - The Current Best PracticePatriana Puspaningrat Anak AgungNo ratings yet
- Typhoid 21Document9 pagesTyphoid 21Nanda Hikma LestariNo ratings yet
- Health Cloud DatasheetDocument2 pagesHealth Cloud DatasheetMadhuri MalayathiNo ratings yet
- ADCHEM Percentage StohsDocument18 pagesADCHEM Percentage StohsMelvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Slides 6 - ObturationDocument22 pagesSlides 6 - Obturationبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- P QuizletDocument2 pagesP QuizletFgg FggNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Best RDocument23 pagesGastroenterology Best RfrabziNo ratings yet
- Miliue Therapy Skill PDFDocument1 pageMiliue Therapy Skill PDFRosalinda SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Pnle CHNDocument25 pagesPnle CHNLrak Eed0% (1)
- American Academy of Pediatrics: ABBREVIATION. PICU, Pediatric Intensive Care UnitDocument3 pagesAmerican Academy of Pediatrics: ABBREVIATION. PICU, Pediatric Intensive Care UnitdoctorsamitNo ratings yet
- Operating LightDocument8 pagesOperating LightrelinNo ratings yet
- Theory of Florence NightingaleDocument1 pageTheory of Florence NightingaleTrisha Fae Loyola BalagotNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Drugs PowerpointDocument17 pagesCardiac Drugs PowerpointNoci M. FrenkNo ratings yet
- Hudson RCI Product CatalogDocument89 pagesHudson RCI Product Catalogmartyf777100% (1)
- UntitledDocument33 pagesUntitledapi-257817850No ratings yet