Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FM Exercises
Uploaded by
anililhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FM Exercises
Uploaded by
anililhanCopyright:
Available Formats
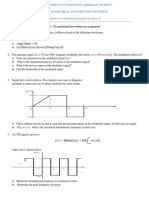
1) An FM signal is given as: ( ) ( ) 100cos 2 100
t
c
s t f t m d
= +
where m(t) is a
rectangular periodic pulse:
a) Sketch the instantaneous frequency of this signal as a function of time.
b) Determine the peak frequency deviation.
2) An angle modulated waveform is given as ( ) ( )
6
20cos 10 10cos 500 s t t t = +
.
a) What is the instantaneous frequency of ( ) s t ?
b) What is the approximate bandwidth of ( ) s t ?
c) If ( ) s t is FM, what is ( ) m t ?
d) If ( ) s t is PM, what is ( ) m t ?
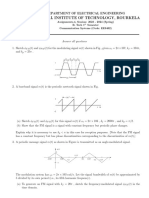
3) A signal ( ) m t is as shown below:
In an experiment, we use FM and PM using this signal and the same carrier
frequency.
a) Find a relation between
p
k and
f
k such that the maximum phase of the
modulated signals in both cases are equal.
b) If 1
p f
k k = = , then what is the maximum instantaneous frequency in each
case?
m(t)
T
p
t
( ) m t
1
-1
1 2
3
t
4) A signal ( )
1
m t is as shown below:
and another signal ( )
2
m t is given as ( ) ( )
4
2
sinc 2 10 m t t = . The value of signals
are in terms of Volts, and t is in terms of sec.s.
a) If ( )
1
m t is frequency modulated on a carrier with frequency 10
6
Hz and a
frequency deviation constant (k
f
) equal to 5 Hz/V, what is the maximum
instantaneous frequency of the modulated signal?
b) If ( )
1
m t is phase modulated on a carrier with frequency 10
6
Hz and a phase
deviation constant (k
p
) equal to 3 rad/V, what is the maximum instantaneous
frequency of the modulated signal? What is the minimum instantaneous
frequency of the modulated signal?
c) If ( )
2
m t is frequency modulated on a carrier with frequency 10
6
Hz and a
frequency deviation constant (k
f
) equal to 10
3
Hz/V, what is the maximum
instantaneous frequency of the modulated signal? What is the bandwidth of
the modulated signal?
(Note that ( )
2
m t is not narrowband, therefore the bandwidth must be
approximated as 2 2W + , where
( ) { }
max
f
k m t
W
= is the frequency deviation,
and W is the bandwidth of the message signal.)
5) An angle modulated signal is formed as ( ) ( ) cos
c c
s t A t t = +
. The signal is
distorted through the channel, so the observation becomes
( ) ( ) ( ) cos
d c d
r t s t A t = + +
.
a) Express the envelope of ( ) r t using phasor vector diagrams and corresponding
magnitudes.
b) On the same vector diagram, obtain phase of ( ) r t .
c) What is the approximate instantaneous frequency of ( ) r t if
c d
A A ?
d) What is the approximate instantaneous frequency of ( ) r t if
d c
A A ?
10
5
1 3 4
t
( )
1
m t
1. We have periodic rectangular message signal ( )
0
0
1, 0 2
1, 2 0
t T
x t
T t
< <
=
< <
where
0
T is
the period.The signal is FM modulated ( ) ( )
cos 2
c c
A f t t + , where
( ) ( )
t
p
t k x d
=
a. Take ( ) 0 0 = and plot ( ) t between
0 0
2 2 T t T < < .
b. If the input is periodic, so is the FM wave, and the F.S. coefficients of the FM
wave can be obtained by the equation:
( )
0
0
0
1
j t n t
n
T
c e dt
T
=
, with the
F.S. representation:
( )
( )
0
Re
c
j n t
c c n
n
x t A c e
+
=
=
. Use this relation to
show that the F.S. coefficients of the FM wave for the given signal is
2 2
1
sinc sinc
2 2 2
j j n j n
n
n n
c e e e
+
= +
, where
0
fT = .
c. Roughly sketch the magnitude of the FM spectrum when is a very large
integer.
2) A frequency-sweep generator is a device that produces a sinusoidal output whose
instantaneous frequency linearly increases from
1
f at 0 t = to
2
f at t T = . Write
the FM wave angle expression if this signal is fed to a modulator with 1
f
k = .
3) The general instantaneous angle expression for an angle modulation scheme can
be described as ( ) ( ) 2
c c
t f t t = + , and the instantaneous frequency is
( ) ( )
c
d
f t t
dt
= . In this expression, we know phase and frequency modulation
counterparts. However, we can define two more modulation techniques:
Phase integral modulation: ( ) ( )
d
t K x t
dt
= , and
Phase acceleration modulation: ( ) ( )
t
c
f t f K x d
= +
.
Describe the modulated signal with these definitions. Construct a table which
shows ( ) t , ( ) f t , max value of ( ) t , and max value of ( ) f t for PM, FM,
phase integral, and phase acceleration modulation.
4) An angle modulated (PM or FM) wave with 10
m
f kHz = , 2.0 = , 100
c
A = , and
30
c
f kHz = . Write an expression for the instantaneous frequency: ( ) f t .
5) When an FM signal ( ( )
c
x t ) passes through a system ( ( ) H f ), applying phase
linearity approxiation similar to the phase and group delay analysis, the system
output can be approximated as:
( ) ( )
( )
( ) ( )
( )
{ }
cos
c c c
f f t f f t
y t A H f t t H f
= =
+ + which means that
[ ] ( ) cos ( ) with ( ) ( ) ( )
c c c y y
y t A t t t t H f t = + = +
. Define the output
instantaneous frequency as
1
( ) ( )
2
y c y
f t f t
= +
to obtain the output signal and
its instantaneous frequency when the system is given as: ( ) 1 H f = and
( ) ( ) ( )
3
1 3 c c
H f f f f f = + over the positive frequency band.
6) Consider a bandpass signal:
( ) cos 0.2cos sin
c m c
v t t t t = +
a) Show that this is a combination of an AM and an FM signal.
b) Sketch the phasor diagram, and indicate FM AM portions.
7) A sinusoidal signal at 2kHz is FM modulated using a carrier, and the resulting
frequency deviation is observed to be 5 kHz. What is the bandwidth occupied by
the FM wave? If the amplitude of the message sinusoid is multiplied by a factor
of 3 and its frequency is lowered to 1kHz, what is the new bandwidth of the FM
wave?
8) Consider a narrowband FM signal approximately defined by:
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) cos 2 sin 2 sin 2
c c c c m
s t A f t A f t f t
a. Determine the envelope of this modulated signal. What is the ratio of the
maximum to minimum value of this envelope? Plot this ratio versus
between 0 and 0.3 (the narrowband range).
b. Determine the average power of the narrowband FM signal, expressed as a
percentage of the average power of the carrier wave. Plot this result versus
between 0 and 0.3 (the narrowband range).
c. By expanding the instantaneous angle ( )
i
t of the narrowband FM signal
( ) s t in the form of power series, and restricting the modulation index to be
less than 0.3 for narrowband, show that
( ) ( ) ( )
3
3
2 sin 2 sin 2
3
i c m m
t f t f t f t
+
Accordingly, obtain the power ratio of the third harmonic to fundamental
harmonic component for 0.3 = in ( ) s t .
9) The sinusoidal message ( ) ( ) cos 2
m m
m t A f t = is applied to a phase modulator
with phase sensitivity=
p
k . The carrier wave has amplitude
c
A , and frequency
c
f .
a. Determine the spectrum of the resulting PM signal assuming that
0.3
m p
A k = < (narrowband assumption).
b. Construct a phasor diagram for this modulated signal, and compare it to that
of a single tone FM signal.
You might also like
- c (t) =100 cos2 π f t .The modulation index is 6Document9 pagesc (t) =100 cos2 π f t .The modulation index is 6Nafeesa SalehNo ratings yet
- Quiz 0429to0505 SolutionDocument4 pagesQuiz 0429to0505 SolutionDr-Eng Imad A. ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Tut 3Document3 pagesTut 3rohankataria26100% (1)
- Communication SystemsDocument35 pagesCommunication SystemsSudhamsh Maddala100% (1)
- Questoes AMDocument7 pagesQuestoes AMDaniel Costa AraújoNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Waveguides: TE ModesDocument20 pagesRectangular Waveguides: TE ModesGrant Heileman100% (1)
- Angle Modulation NotesDocument88 pagesAngle Modulation Notesareebarajpoot0453879100% (1)
- ANALOG & DIGITAL COMMUNICATION: ANGLE MODULATION AND BANDWIDTH CALCULATIONSDocument5 pagesANALOG & DIGITAL COMMUNICATION: ANGLE MODULATION AND BANDWIDTH CALCULATIONSTanzeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument4 pagesAnalog CommunicationsJagadeesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ECEN 4652 Lab 9: ASK, PSK, and FSKDocument37 pagesECEN 4652 Lab 9: ASK, PSK, and FSKAldawi SatNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Antenna 2005Document18 pagesFinal Exam Antenna 2005abdulwahab1250% (2)
- Analog and Digital Communication Question BankDocument4 pagesAnalog and Digital Communication Question BankPrabhakara RaoNo ratings yet
- Exercises - Antenna & Propagation, Assig. 1 FundamentalsDocument1 pageExercises - Antenna & Propagation, Assig. 1 Fundamentalstelecom_amateurNo ratings yet
- Sample AM NumericalsDocument4 pagesSample AM NumericalsDisha GoelNo ratings yet
- Patch Antenna Design MAnualDocument36 pagesPatch Antenna Design MAnualkarthikvel_852246No ratings yet
- Antenna TheoryDocument5 pagesAntenna Theorysekhar90No ratings yet
- Ap2011 Solutions 04Document9 pagesAp2011 Solutions 04Zobeda MariumNo ratings yet
- Assigment 3 AntennaDocument2 pagesAssigment 3 Antennaabdulwahab12100% (1)
- Antenna QuizDocument12 pagesAntenna Quizvs_prabhu88No ratings yet
- Ch4 Amplitude ModulationDocument55 pagesCh4 Amplitude ModulationsrijanNo ratings yet
- Solution 2 AntennaDocument7 pagesSolution 2 Antennaabdulwahab12100% (1)
- 1 BasicDocument39 pages1 BasicanililhanNo ratings yet
- Antenna and Wave Propagation ConceptsDocument5 pagesAntenna and Wave Propagation ConceptsMayur BundelNo ratings yet
- Analog Signal Transmission and ReceptionDocument109 pagesAnalog Signal Transmission and ReceptionMicheal MathanNo ratings yet
- Frequency ModulationDocument47 pagesFrequency ModulationAko si Gian100% (1)
- Ofdm Simulation in MatlabDocument59 pagesOfdm Simulation in MatlabBinh ThanhNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Antenna Theory by Balanis Edition2 Chapter12bDocument33 pagesSolution Manual Antenna Theory by Balanis Edition2 Chapter12bpouty567100% (2)
- Antenna Assignment1Document14 pagesAntenna Assignment1karthikrao191919No ratings yet
- Poc FormulaDocument5 pagesPoc FormulaShivika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reflector Antennas PDFDocument78 pagesReflector Antennas PDFsankararao gullipalliNo ratings yet
- AM, FM, and Digital Modulated SystemsDocument26 pagesAM, FM, and Digital Modulated Systemskooleffie82No ratings yet
- DFT and FFT - 2021Document134 pagesDFT and FFT - 2021Sourya DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation All 0Document64 pagesAngle Modulation All 0Yanyan100% (1)
- Antennas and Radiation Course NotesDocument136 pagesAntennas and Radiation Course NotesNitsan Ofer100% (1)
- Antenna and Wave Propagation Assignment 1Document2 pagesAntenna and Wave Propagation Assignment 1Samridhi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - ParametersDocument32 pagesLecture 2 - ParametersSagar PrateekNo ratings yet
- Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) - Wireless PiDocument13 pagesQuadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) - Wireless PiDuong Phi ThucNo ratings yet
- Waveguides AssignmentDocument5 pagesWaveguides AssignmentYvesExequielPascua100% (1)
- PAM and Flat Top PAMDocument13 pagesPAM and Flat Top PAMGoitom HaileNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Frequency ModulationDocument88 pagesChapter 4 Frequency ModulationtestNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Wave GuidesDocument44 pagesRectangular Wave GuidesArshadahcNo ratings yet
- Bartlett Window Using MatlabDocument5 pagesBartlett Window Using MatlabAnushree ShahdeoNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument2 pagesMidtermAbdullah HabibNo ratings yet
- 5 - Optimum Receivers For The AWGN Channel - Test - MODIFIED PDFDocument45 pages5 - Optimum Receivers For The AWGN Channel - Test - MODIFIED PDFajayroy12No ratings yet
- Assigment 2 AntennaDocument2 pagesAssigment 2 Antennaabdulwahab12100% (1)
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3Zero ChengNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document3 pagesHW 2Zero ChengNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4Document5 pagesAssignment-4Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercise Solutions Chapter 5Document9 pagesExtra Exercise Solutions Chapter 5Vikri JanuarismaNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation Tutorial 1Document23 pagesAngle Modulation Tutorial 1Haider Al RikabiNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument12 pagesAngle ModulationMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument52 pagesAngle ModulationkshitijNo ratings yet
- Comm AssntIIDocument6 pagesComm AssntIIkalNo ratings yet
- ) 2 Sin ) 2 Sin (Sin (1) ) 2 Sin (Cos (: T F T F T FDocument37 pages) 2 Sin ) 2 Sin (Sin (1) ) 2 Sin (Cos (: T F T F T FV DhinakaranNo ratings yet
- FMDocument76 pagesFMNicole Guzman100% (1)
- Calculating Bandwidth of a Composite Channel Using Frequency Division MultiplexingDocument25 pagesCalculating Bandwidth of a Composite Channel Using Frequency Division MultiplexingHunain AKNo ratings yet
- Lab 9: M - Ary Amplitude and Frequency Shift Keying, Signal SpaceDocument19 pagesLab 9: M - Ary Amplitude and Frequency Shift Keying, Signal SpaceAyman YounisNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Systems IDocument64 pagesAnalog Communication Systems Itadepeace23No ratings yet
- Analog Communication (ECE - 3103) PDFDocument2 pagesAnalog Communication (ECE - 3103) PDFDevender DuaNo ratings yet
- Analog ModulationDocument27 pagesAnalog ModulationmarypugazhNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Indoor Positioning Systems PDFDocument11 pagesBayesian Indoor Positioning Systems PDFanililhanNo ratings yet
- A Robust RFID Based Method For Precise Indoor PositioningDocument11 pagesA Robust RFID Based Method For Precise Indoor PositioninganililhanNo ratings yet
- Wright 1229465514Document84 pagesWright 1229465514anililhanNo ratings yet
- ALR-9900 Hardware Setup Guide: Alien TechnologyDocument23 pagesALR-9900 Hardware Setup Guide: Alien TechnologyanililhanNo ratings yet
- Group:A: MAT194 Calculus II 2008-2009 Summer School Final ExamDocument9 pagesGroup:A: MAT194 Calculus II 2008-2009 Summer School Final ExamanililhanNo ratings yet
- Ise 9 TutDocument168 pagesIse 9 TutanililhanNo ratings yet
- CPP 2 PythonDocument4 pagesCPP 2 PythonNishfaan NaseerNo ratings yet
- Power Spectral Density of Random Processes (PSDDocument5 pagesPower Spectral Density of Random Processes (PSDanililhanNo ratings yet
- Group: MAT194 Calculus II Final Exam: Name: Number: Exam RulesDocument10 pagesGroup: MAT194 Calculus II Final Exam: Name: Number: Exam RulesanililhanNo ratings yet
- MAT194 Final A 0708sumDocument8 pagesMAT194 Final A 0708sumanililhanNo ratings yet
- Student ID & Name: Experiment Name & Number: Group: ConclusionDocument1 pageStudent ID & Name: Experiment Name & Number: Group: ConclusionanililhanNo ratings yet
- LBCDocument14 pagesLBCanililhanNo ratings yet
- Group: MAT194 Calculus II Final Exam: Name: Number: Exam RulesDocument10 pagesGroup: MAT194 Calculus II Final Exam: Name: Number: Exam RulesanililhanNo ratings yet
- Alien On-Reader Programming Overview, ARCADocument23 pagesAlien On-Reader Programming Overview, ARCAanililhanNo ratings yet
- Bil200 hw2Document1 pageBil200 hw2anililhanNo ratings yet
- 1 BasicDocument39 pages1 BasicanililhanNo ratings yet
- Soru NumaralarDocument1 pageSoru NumaralaranililhanNo ratings yet
- LCR MeterDocument1 pageLCR MeterLinux lnxNo ratings yet
- Pipe Material Specs (MCP)Document106 pagesPipe Material Specs (MCP)BoulHich BoulHichNo ratings yet
- VA CarparkManagementSysDocument22 pagesVA CarparkManagementSysmerkermanNo ratings yet
- Parabolic Leaf Spring OptimizationDocument8 pagesParabolic Leaf Spring OptimizationRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Implement state machine diagram and develop activity diagram for pharmaceutical order management systemDocument1 pageImplement state machine diagram and develop activity diagram for pharmaceutical order management systemDaigree NadiaNo ratings yet
- SAP EDUCATION - C_THR12_66 SAMPLE QUESTIONSDocument5 pagesSAP EDUCATION - C_THR12_66 SAMPLE QUESTIONSaijlalNo ratings yet
- Hands On PythonDocument240 pagesHands On PythonAmol MunaseNo ratings yet
- SS CatalogueDocument6 pagesSS Catalogueahmadgce04No ratings yet
- The 4 - 95 Stirling Engine For Underwater ApplicationDocument4 pagesThe 4 - 95 Stirling Engine For Underwater ApplicationVladimirDvortsovNo ratings yet
- 013 - Engine - Throttle - Pedal Position Sensor - Switch A Circuit MalfunctionDocument4 pages013 - Engine - Throttle - Pedal Position Sensor - Switch A Circuit MalfunctionMortada AlsonniNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in General Mathematics: Grade 11-Archdiocese of Nuevasegovia (Inocenciog., Romualdo, Medina, Sagutin)Document18 pagesPerformance Task in General Mathematics: Grade 11-Archdiocese of Nuevasegovia (Inocenciog., Romualdo, Medina, Sagutin)Sheila Formentera-AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Application for Accounting MajorDocument1 pageSummer Internship Application for Accounting MajorMohammad Jibran ChangiNo ratings yet
- Tenor Ax Voip Multipath/Gateway Switch: Product GuideDocument131 pagesTenor Ax Voip Multipath/Gateway Switch: Product GuideEdgar A CanizalezNo ratings yet
- Shandong Lingong Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. Null Product Parts CatalogDocument353 pagesShandong Lingong Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. Null Product Parts Catalogadelmomoura100% (1)
- Stony Brook Parking Map 2016Document2 pagesStony Brook Parking Map 2016Chris VarugheseNo ratings yet
- LOW POWER SOLUTIONSDocument48 pagesLOW POWER SOLUTIONSDavidNo ratings yet
- Clean BotDocument26 pagesClean BotCrystal FrostNo ratings yet
- Richard Bandler's Guide to Harnessing HypnosisDocument3 pagesRichard Bandler's Guide to Harnessing HypnosisChristy Mayo0% (1)
- Unit Outline - EnS5257 Microprocessor SystemsDocument3 pagesUnit Outline - EnS5257 Microprocessor SystemsAnup VanarseNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security and Reliability in A Digital CloudDocument95 pagesCyber Security and Reliability in A Digital CloudBob GourleyNo ratings yet
- Doosan Retrofit ServiceDocument99 pagesDoosan Retrofit Servicestopless_dalian685No ratings yet
- Sieving For Perfect Quality Control: MillingDocument12 pagesSieving For Perfect Quality Control: Millingtuhintahmid1093No ratings yet
- Noxerior Brochure Special Plants 2014Document7 pagesNoxerior Brochure Special Plants 2014Arjav DesaiNo ratings yet
- AC CIRCUIT Power AnalysisDocument48 pagesAC CIRCUIT Power AnalysisFerrer Francia Nel SabasNo ratings yet
- Glory gfs220 Manual (01 90) (31 40)Document10 pagesGlory gfs220 Manual (01 90) (31 40)alexander quintero romeroNo ratings yet
- BDocument136 pagesBJuan Manuel Ugalde FrancoNo ratings yet
- Latihan HitunganDocument9 pagesLatihan HitunganMuhamad FadilahNo ratings yet
- Theory Basics - 12 Chromatic Tones PDFDocument2 pagesTheory Basics - 12 Chromatic Tones PDFPramod Govind SalunkheNo ratings yet
- ADJUST FUEL TIMINGDocument3 pagesADJUST FUEL TIMINGSanjay MadakaNo ratings yet
- B6 Industrial+Elbe2013-7lrDocument160 pagesB6 Industrial+Elbe2013-7lrhernan dueñasNo ratings yet