Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diuretic Drugs For Nursing Pharmacology
Uploaded by
lhayes1234Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diuretic Drugs For Nursing Pharmacology
Uploaded by
lhayes1234Copyright:
Available Formats
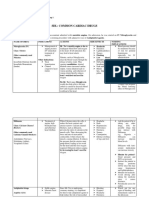
DIURETIC AGENTS
INDICATIONS ACTIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS DRUG - DRUG
CLASSIFICATION / DRUG
treatment of edema caused Block the chloride pump interference with the normal Gout Cholestyramine or
by congestive heart failure Keep the chloride and regulatory mechanisms of Systemic lupus colestipol (take 2
(CHF), liver disease, or renal sodium in the tubule to be Nephron Diabetes hrs. apart)
THIAZIDE DIURETICS disease, and for adjunctive excreted in the urine, thus Hypokalemia Hyperparathyroidism
hydrochlorothiazide treatment of hypertension preventing the reabsorption Decreased calcium excretion Bipolar disorders Digoxin
(HydroDIURIL) of both in the vascular d blood glucose levels Pregnancy and lactation Antidiabetic agents
system Slightly alkalinized urine Lithium
Acute CHF Block the chloride pump in Related to the imbalance in Electrolyte depletion Aminoglycosides
Acute pulmonary edema the ascending loop of Henle, electrolytes and fluid Anuria and cisplatin
Edema associated with CHF causing reabsorption of Hypokalemia Severe renal failure (ototoxicity)
LOOP DIURETICS Edema associated with renal sodium and chloride Alkalosis Hepatic coma ↑Anticoagulation
furosemide or liver disease Hypocalcemia – causes Pregnancy and lactation Indomethacin,
(Lasix) Hypertension tetany Cautions ibuprofen,
Pharmacokinetics SLE, gout, and diabetes salicylates, and
mellitus NSAID
--Block the effects of Related to disturbances in Angle closure glaucoma Salicylates and
Adjunct to other diuretics carbonic anhydrase, slowing acid and base balance and Cautions:Lactation lithium
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE Glaucoma down the movement of electrolyte balance F/E imbalances
INHIBITORS hydrogen ions Metabolic acidosis Renal or hepatic disease
(enzyme) --More sodium and Hypokalemia Adrenocortical insufficiency
**Not used for HTN or bicarbonate are lost in the Paresthesias of extremities, Respiratory acidosis
diuretic urine confusion, drowsiness COPD
--Adjuncts with thiazide or Cause a loss of sodium while Hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia, renal disease, Salicylates
POTASSIUM-SPARING loop diuretics retaining potassium and anuria
DIURETICS --Patients who are at risk for Block the actions of Patients taking amiloride and
spironolactone hypokalemia aldosterone in the distal triamterene
(Aldactone) tubule
Increased cranial pressure or Pull water into the renal Related to sudden drop in Renal disease and anuria
acute renal failure due to tubule without sodium loss fluid levels Pulmonary congestion
OSMOTIC DIURETICS shock, drug overdose, or N/V Intracranial bleeding and
mannitol trauma hypotension dehydration
(Osmitrol) light-headedness, confusion CHF
headache
You might also like
- Lab ValuesDocument3 pagesLab Valuessurviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Values PDFDocument1 pageHemodynamic Values PDFAudrey DelfinNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1Document9 pagesCommonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1annatw100% (10)
- Common Cardiac MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Cardiac MedicationsPaige HardekopfNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Med ChartsDocument6 pagesCardiac Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (15)
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDocument15 pagesAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Urinary Tract and Bladder DrugsDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract and Bladder Drugslhayes1234100% (2)
- Urinary Tract and Bladder DrugsDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract and Bladder Drugslhayes1234100% (2)
- Nursing Study SitesDocument16 pagesNursing Study Sitesspartacuslives100% (3)
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaPascal St Peter NwaorguNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Drugslhayes123488% (16)
- Spotlight On Cardiac DrugsDocument2 pagesSpotlight On Cardiac Drugspauerish100% (2)
- Nursing Cheat LabValuesDocument4 pagesNursing Cheat LabValuessasukenoneko100% (5)
- Nursing School Drug ChartDocument13 pagesNursing School Drug ChartEve Lester100% (3)
- Pulmonary Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pagePulmonary Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes123475% (4)
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Endocrine NursingDocument2 pagesEndocrine Nursingsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Drug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut HereDocument60 pagesDrug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut Heredlneisha61100% (13)
- Chart of Neuro DisordersDocument1 pageChart of Neuro DisordersNursingSchoolNotes100% (2)
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Patho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept MapsDocument139 pagesPatho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept Mapslauramphs79100% (5)
- HNN215 Drug Diary GuideDocument10 pagesHNN215 Drug Diary GuideMaddison MitchellNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NursingDocument2 pagesEndocrine NursingUnclePorkchop94% (34)
- Common Cardiac Drugs for Angina and StentingDocument13 pagesCommon Cardiac Drugs for Angina and StentingDonna Deala100% (2)
- Endocrine Drug ChartDocument1 pageEndocrine Drug ChartJessicaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants Drug TableDocument1 pageAnticoagulants Drug Tablecdp158767% (3)
- Mnemonics and Acronyms For Nursing School - IStudentNurse SiteDocument27 pagesMnemonics and Acronyms For Nursing School - IStudentNurse SiteCharity T.100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Cardiovascular DisordersDocument38 pagesNursing Care of Cardiovascular Disordersprototypeallhell100% (1)
- Pharmacology ATI Study Guide: Thyroid and Insulin MedicationsDocument3 pagesPharmacology ATI Study Guide: Thyroid and Insulin MedicationsTanya Viars88% (34)
- Electrolyte ChartDocument2 pagesElectrolyte ChartJenny Varghese100% (4)
- Med BundleDocument36 pagesMed Bundlejamie sealNo ratings yet
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocument5 pagesAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDocument33 pagesReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- Med Surge 2 Mod 3 Study Guide2Document21 pagesMed Surge 2 Mod 3 Study Guide2Dirk Buckner100% (3)
- Drug: Milrinone Presentation: Action & Indication:: 30 WeeksDocument1 pageDrug: Milrinone Presentation: Action & Indication:: 30 WeeksSIDHARTH GOYALNo ratings yet
- Renal System PPT (Pharmacology)Document100 pagesRenal System PPT (Pharmacology)Cheska DillupacNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal PharmacologyDocument18 pagesMusculoskeletal PharmacologyBLEEMAGE100% (2)
- Anti Infective Drug ChartDocument1 pageAnti Infective Drug ChartJessica100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyCheyee MaeNo ratings yet
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- EKG Flash CardsDocument5 pagesEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasNo ratings yet
- Food and Drug InteractionsDocument16 pagesFood and Drug InteractionsSirijoti KanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Pregnancy, Labour and Puerperium: Presented By:-Ms Lisa Chadha F.Y. MSC Nursing Bvcon, PuneDocument87 pagesDrugs Used in Pregnancy, Labour and Puerperium: Presented By:-Ms Lisa Chadha F.Y. MSC Nursing Bvcon, PuneSanjay Kumar SanjuNo ratings yet
- ER DRUGS AT A GLANCEDocument3 pagesER DRUGS AT A GLANCEmyleneacar100% (3)
- Anatomy 102 Practice Exam #3Document13 pagesAnatomy 102 Practice Exam #3lhayes123467% (6)
- 1430 Drug CardsfinalDocument7 pages1430 Drug CardsfinalLizSherman100% (1)
- NCM 106 Learning Activities (Semis)Document12 pagesNCM 106 Learning Activities (Semis)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableDocument7 pagesCritical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableVictoria Romero100% (2)
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDocument3 pagesLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- Study Guide Med Surg #1Document22 pagesStudy Guide Med Surg #1cfunk929No ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing 75 Items TestDocument13 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing 75 Items Testwiffato25% (4)
- Emergency TrolleyDocument9 pagesEmergency TrolleyAaron Wallace100% (1)
- PHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsDocument17 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsLeilani Sablan100% (2)
- Fluid Volume BalanceDocument73 pagesFluid Volume BalanceSalman HabeebNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument4 pagesDiureticsBill John100% (1)
- Hot Tub Mystery Case Study ResponseDocument6 pagesHot Tub Mystery Case Study ResponseAdie9475% (8)
- Pharmacology Mid ExamDocument7 pagesPharmacology Mid ExamHSC UNITEDNo ratings yet
- Nle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsDocument30 pagesNle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsSpoonNo ratings yet
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Med Charts Part 2Document2 pagesPulmonary Med Charts Part 2NursingSchoolNotes100% (3)
- Heart Rhythms S SDocument3 pagesHeart Rhythms S SGloryJane100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Document2 pagesRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- Top Nursing Actions for Chest Pain, Transfusions, Evisceration and MoreDocument4 pagesTop Nursing Actions for Chest Pain, Transfusions, Evisceration and MoreAnn ChenNo ratings yet
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Drug MnemonicsDocument1 pageCholinergic Drug Mnemonicssunshine151100% (1)
- Test InformationDocument5 pagesTest InformationCatalina BorquezNo ratings yet
- Med-surg Restrictive and Obstructive Lung Disease: Key Presentations and TreatmentsDocument11 pagesMed-surg Restrictive and Obstructive Lung Disease: Key Presentations and Treatmentsorganictallgirl50% (2)
- Study Guide For Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument5 pagesStudy Guide For Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMandi Goetz HarmonNo ratings yet
- Drug CardsDocument4 pagesDrug CardsBrittany Lynn MyersNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Cardiovascular Disease in PregnancyDocument3 pagesObstetrics - Cardiovascular Disease in PregnancyJonathanNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Linda Hayes Weekly Patient Assignment 1-26-11Document5 pagesLinda Hayes Weekly Patient Assignment 1-26-11lhayes1234No ratings yet
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) Overview: Functions, Sources and MoreDocument4 pagesVitamin B1 (Thiamine) Overview: Functions, Sources and MoreJetindar PuriNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions 2Document6 pagesSample Questions 2Filipino Nurses CentralNo ratings yet
- Ralph's ProposalDocument15 pagesRalph's ProposalHeilene Ethel AngcayaNo ratings yet
- Vol 06, Issue 01, Supplement I, March 2015 PDFDocument484 pagesVol 06, Issue 01, Supplement I, March 2015 PDFAisya Amalia MuslimaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CSDocument7 pagesDrug Study CSFrancis MendozaNo ratings yet
- Trade Name Generic Name Group: TetracyclinesDocument11 pagesTrade Name Generic Name Group: Tetracyclinesmisfer72No ratings yet
- Combined QDocument46 pagesCombined QRoh JitenNo ratings yet
- Improve Cardiac Output Through Nursing InterventionsDocument8 pagesImprove Cardiac Output Through Nursing InterventionsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Case StudyDocument3 pagesCardiac Case StudyJessi ParsonsNo ratings yet
- CKD Patient at Risk for Respiratory, Fluid and Skin IssuesDocument3 pagesCKD Patient at Risk for Respiratory, Fluid and Skin IssuesMichael Baylon Dueñas100% (2)
- Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesNursing Responsibilityايام اول الشحيNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study - FurosemideryanNo ratings yet
- Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: ReviewDocument11 pagesAcute Decompensated Heart Failure: ReviewFercee PrimulaNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide preclinical toxicity profileDocument15 pagesBumetanide preclinical toxicity profileKrishna MahidaNo ratings yet
- CKD SCT DNDocument55 pagesCKD SCT DNKim Jun-myeonNo ratings yet
- Drug TabulationDocument6 pagesDrug TabulationRosemarie Canete Delarita100% (1)