Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Anne JillianOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Anne JillianCopyright:
Available Formats
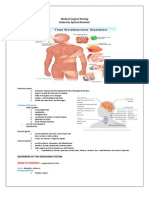
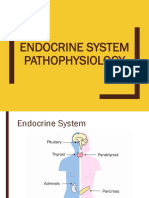
Endocrine system
q a
Hypothalmus
links our endocrine and nervous systems together. It drives the
endocrine system.
Pituitary gland
It receives signals from the hypothalamus. This gland has two lobes,
the posterior and anterior lobes. The posterior lobe secretes
hormones that are made by the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe
produces its own hormones,
Thyroid gland
The gland is critical to the healthy development and maturation of
vertebrates and regulates metabolism.
Adrenal gland
The gland is made up of two glands: the cortex and medulla. These
glands produce hormones in response to stress and regulate blood
pressure, glucose metabolism, and the body's salt and water balance.
Pancreas
Is responsible for producing glucagon and insulin. Both hormones
help regulate the concentration of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
Gonads
The reproductive gonads testes(male),ovaries(female), produce
steroids that affect growth and development and also regulate
reproductive cycles and behaviors. The major categories of gonadal
steroids are androgens, estrogens and progestins.
Hypothalmus produce
what hormone
Oxytoxin and ADH
Oxytoxin hormon fctn
Contract uterine muscle during labor. Releasing milk from
mammary gland ( breast feeding)
ADH fctn
stimulate water reabsorption by the kidney;also constrict blood
vesse
Posterior pituitary? Produceces ADH and oxytocin
Anterior Pituitary
Produces 5 galand hormones such gh, Proclain, tsh, acth, fsh and
gonadotropic hormone.
TSH stimulate the the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone
ACTH Stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete steroids. especially cortisol
GH
Stimulate the growth of bone and soft tissue ; stymulates the
synthesis of glucose during periode of fastingalso called
samatotropin.
FSH Stimulate the ova and sperm.
LH
Causing ovulation in women and stimulates the secretion
ofprogesterone in women and testerone in men.
Prolactin stimulates the breast to develop and produce milk.
Ovary Produces estrogen and progresterone in woman
Testis Produces testosterone
Parathyroid gland Produces Parathyroid hormone
Thyroid hormone (T3,T4)
TrIIodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine. tetralodothyronlne (T4) are
secreted by the thyroid gland: control metabolic rate and regulate
growth and development
Produces Parathyroid
hormone
Secreted by the parathyroid glands: Increases plasma calcium by
stimulating osteoclastic activity. Increasing reabsorption of calcium
by the kidneys. and by Increasing the absorption of dietary calcium
Adrenal medulla
Secretes catecholamines (epinephrine) and small amounts of
norepinephrine Stimulates the "flght-or-flight" response; Increases
blood glucose Epinephrine Is also called adrenalin
Adrenal cortex cortisol
A glucocorticoid that helps regulate glucose. fat. and protein
metabolism;
Aldosterone
A mineralocorticoid that causes the kidneys to reabsorb sodium and
water and to excrete potassium: helps regulate fluid and electrolyte
balance
Sex hormones
Especially the androgens (testosterone): helps develop the
secondary sex
Insulin
Secreted by the beta cells of the Islets of Langerhans: helps regulate
the metabolism of carbohydrates. proteins. and fats: lowers blood
glucose
Glucagon
Secreted by the alpha cells of the Islets of Langerhans: raises blood
glucose
Estrogens and
progesterone
Secreted by the ovaries
Testosterone
Secreted primarily by the testesThe chief male androgen: stimulates
the development of sperm and the secondary sex characteristics In
the male
Thymoslns Stimulates the maturation of the T-Iymphocytes
Melatonin Secreted by the pineal gland and helps set the biorhythms
Acromegally s/s The enlargement bone of the hand, jaws, cheecks, forehead or nose.
Treatment for acromegally Cryosurgery or transphenoidal or removal of the tumor
Drugs for acromegally Parlodel and sandostin
Diet for acromegally Soft food
Oversecretion of GH
before closure of
ephiphyses
Gigantism
Level of gigantism in the
blood .
Dx test for gigantism
Surgical removal or
Irradiation of anterior
pituitary
Treatment for gigantism
Understanding and
emotional support
Nursing responsibility for Gigantism pt.
Too much ADH SIADH
s/s of SIADH
Hypo Na <130 mEq/l/l, Water retention, eight gainConcentrated
urine (n urine osmolality >1200 msom/l, specific gravity >1020,
Muscle cramp, and weakness
Why no pheriperal edema
on SIADH
Because excess fluid accumulating in vascular system
What is Dx test for
SIADH
High Na, specific gravity > 1.032
What is medication for
SIADH
Declomicyn, Lythium Carb.
What treatment for
SIADH
Fluid rest and give Hypertonic SOL
Dibetes indsipidus Def. in ADH
s/s of Diabetes insipidus
Extreemely large urination +/- 25-30 l per24 hr, polydipsia,
dehydration and serious electrolite imbalance.
Dx test for diabetes
insipidus
specific gravity < 1.005
What is the diet for
diabetes insipidus
No caffein and no teeism
Treatment for diabetes
insipidus
Replacement of ADH by injecting or absorption of the hormone
what is cushing syndrome Too much cortisol in the blood (adrenal Hyperfunction)
s/s of cushing syndrome
Buffalo hump, moon face, distention of abdominal, ecchy mosis,
impotensy, osteo H B/P.
Treatment for cushing
syndrome
Radiation c cobalt, surgical
Causing effect for cushing
syndrome
Prolong used of glucocorticoid or corticotropin medication for
chronic inflammatory disorder such as chronic obstruction
pulmonary disease, chron,s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. also
called iatrogenic.
Grave's disease
a syndrome in which thyrotoxicosis is associated w/ diffuse goiter
or autoimmune disease.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
is an autoimmune disease that destroy the essential enzym that is
necessary for prod. of T3 & T4. X. Down syndrome and turner's
syndrom
Cushing syndrome too much cortisol
Thyroid syndrome (blank)
diffuse toxic goiter (blank)
simple nontoxic goiter (blank)
Nodular goiter (blank)
chvostek sign (blank)
Trousseau's sign (blank)
Addison disease (blank)
Pheocromositoma (blank)
Hyperparathyroidism (blank)
Hypoparathyroidism (blank)
Hyperthyroidism (blank)
Hypothyroidism (blank)
Cretinism (blank)
s/s of myexedema
hoarse and raspy voice, slow speech,lethargy, expressionless
face,protruding toungue, coarse and sparse hair, weight gain and dry
skin.
You might also like
- Endocrine ChartDocument7 pagesEndocrine Chartwjg2882No ratings yet
- Eevee: @shea - CrochetDocument13 pagesEevee: @shea - CrochetKarina Magaña100% (4)
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemSheena Pasion100% (2)
- Endocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesEndocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDani Anyika100% (1)
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument17 pagesFluid and Electrolytesdlneisha61100% (9)
- Endocrine ReviewDocument9 pagesEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument96 pagesEndocrine SystemSandhya Kakkar100% (2)
- Anatomy and physiology of bloodDocument4 pagesAnatomy and physiology of bloodDylle Lorenzo ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ChartDocument2 pagesElectrolyte ChartJenny Varghese100% (4)
- Spanish Academy Soccer Coaching Passing DrillDocument2 pagesSpanish Academy Soccer Coaching Passing DrillLucian Nicolau50% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine SystemPeej Reyes100% (1)
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Medical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyDocument30 pagesMedical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyJam Knows Right100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemKimberly Anne SP Padilla100% (2)
- Endocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninDocument4 pagesEndocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninHazel Mae Tapia100% (1)
- The Endocrine System: Hormones and DiseasesDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System: Hormones and DiseasesMd Nasir Uddin Mahmood100% (2)
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Control Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Control Endocrine Systemwipi112No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesEndocrine Systemtheglobalnursing80% (5)
- EndocrineDocument12 pagesEndocrineAna FelNo ratings yet
- 09 Endocrine System PhysiologyDocument43 pages09 Endocrine System PhysiologyKaye Alyssa Enriquez100% (1)
- HematologyDocument15 pagesHematologyGilberto GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument7 pagesEndocrine System Notesmorganical100% (3)
- Medical and Surgical Nursing Notes For NLEDocument63 pagesMedical and Surgical Nursing Notes For NLEBel Zeta DonaireNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Endocrine DrugsDocument123 pagesPharmacology - Endocrine DrugsBenjamin Joel BreboneriaNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts of Endocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesKey Concepts of Endocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyMarcus, RN100% (1)
- Endocrine Disorders: Adrenal Gland and Thyroid DiseaseDocument27 pagesEndocrine Disorders: Adrenal Gland and Thyroid Diseaseasdfgrttt100% (4)
- Endocrine SystemDocument36 pagesEndocrine SystemMohamadMahdiKesserwan100% (4)
- NursingBulletin Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesNursingBulletin Respiratory Systemseigelystic100% (3)
- List of Important Hormones and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesList of Important Hormones and Their FunctionsLilyraj777 GilberNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: An OverviewDocument7 pagesThe Endocrine System: An OverviewAshy LeeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Pathophysiology)Document18 pagesEndocrine System (Pathophysiology)roselle legson100% (1)
- Cell Injury and Cell DeathDocument35 pagesCell Injury and Cell DeathMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument14 pagesCardiovascular SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Histology Lec-11 EndocrineDocument10 pagesHistology Lec-11 EndocrineKevin C. AguilarNo ratings yet
- SGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismDocument7 pagesSGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismTinesh RajahNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes (PDF File) : A. Body FluidsDocument5 pagesFluid and Electrolytes (PDF File) : A. Body FluidsLegendX100% (3)
- Disorders of Acid Base BalanceDocument1 pageDisorders of Acid Base BalanceLyn Domingo EllaquezNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Endocrine GlandDocument73 pagesUnit 13 Endocrine GlandChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionNgoc TranNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument3 pagesEndocrine DisordersIrish OrleansNo ratings yet
- 1 Body FluidsDocument9 pages1 Body FluidsSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of CA+ MetabolismDocument41 pagesDisorders of CA+ MetabolismSuliman GarallehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing PharmacologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Nursing PharmacologyJon Adam Bermudez SamatraNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Endo F 2017Document152 pagesCH 18 Endo F 2017JuliaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics Flash CardsDocument17 pagesPharmacology Pharmacokinetics Flash Cardsbobiome100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemMikaella Viador100% (2)
- Hormones of Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandDocument16 pagesHormones of Thyroid and Parathyroid Glandapi-25908492100% (1)
- Lab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesLab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemJohn Louis AguilaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Review NotesDocument9 pagesEndocrine Review Noteslisette_sakura100% (5)
- Cardiac SystemDocument7 pagesCardiac Systemsccctutor100% (3)
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDocument33 pagesReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- Embryo Trans Unofficial TransDocument14 pagesEmbryo Trans Unofficial TransMark LopezNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AcidosisDocument16 pagesRespiratory AcidosisIssa GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 The Male Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 21 The Male Reproductive SystemEllä Pabustan100% (1)
- Q. List Different Functions of The Kidney: (A) Homeostatic FunctionDocument42 pagesQ. List Different Functions of The Kidney: (A) Homeostatic Functionramadan100% (4)
- Endocrine DiseasesDocument170 pagesEndocrine DiseasesJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniDocument21 pagesHormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniPadma VishwanathNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarismDocument2 pagesHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistDocument5 pagesEndocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistSakshi BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Kuliah PituitariDocument48 pagesKuliah PituitariLona Veronika HutajuluNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Lt. Antonio Carvajal: The Arrival of The SpaniardsDocument5 pagesLt. Antonio Carvajal: The Arrival of The SpaniardsAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Types of Bone Fractures ExplainedDocument9 pagesTypes of Bone Fractures ExplainedAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Census For WardDocument1 pageCensus For WardAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Art Movements of the Early 20th CenturyDocument2 pagesArt Movements of the Early 20th CenturyAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Mental Health MedsDocument5 pagesMental Health MedsAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Surgical Dressing TechniqueDocument2 pagesSurgical Dressing TechniqueAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Jacques' Monologue on the Seven Stages of Man in As You Like ItDocument1 pageJacques' Monologue on the Seven Stages of Man in As You Like ItAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Art Movements of the Early 20th CenturyDocument2 pagesArt Movements of the Early 20th CenturyAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Values Formation Through Literary PiecesDocument17 pagesValues Formation Through Literary PiecesAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Santiago To LaucpaoDocument1 pageSantiago To LaucpaoAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Swot Ana and SchedulingDocument2 pagesSwot Ana and SchedulingAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument2 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisdesaatibagosNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives - Goals, Needs and LimitationsDocument3 pagesManagement by Objectives - Goals, Needs and LimitationsAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Eight Is Enough 041107Document50 pagesEight Is Enough 041107api-3748828No ratings yet
- Star Wars RPG - d20 - The Smugglers of NabooDocument25 pagesStar Wars RPG - d20 - The Smugglers of NabooJackson Eich92% (12)
- SM6-UT-U4 UnitTest With AnswersDocument3 pagesSM6-UT-U4 UnitTest With AnswersRaquel Prous TrigoNo ratings yet
- Libro Ingles U3Document168 pagesLibro Ingles U3Andrés ArenasNo ratings yet
- Correcciones ClientesDocument687 pagesCorrecciones ClientesJorge PrietoNo ratings yet
- Afl Fact SheetDocument1 pageAfl Fact Sheetapi-257609033No ratings yet
- Grade 6 ReviewDocument3 pagesGrade 6 ReviewVivien Lee DetallaNo ratings yet
- Review: Name: - ClassDocument2 pagesReview: Name: - Classmatthew deividNo ratings yet
- Jason Behrendorff: Personal Information Full Name BornDocument2 pagesJason Behrendorff: Personal Information Full Name BornRashid AnwerNo ratings yet
- Ficha Editavel PDFDocument2 pagesFicha Editavel PDFLpsf PertyNo ratings yet
- Verbs 2Document2 pagesVerbs 2bruceNo ratings yet
- GP General Announcement 2023-24 - FinalDocument16 pagesGP General Announcement 2023-24 - FinalKrayzelle KimNo ratings yet
- Cricket Infrastructure BangladeshDocument23 pagesCricket Infrastructure BangladeshShakil AlamNo ratings yet
- Big Weekend Ahead: ... More Than Just A GAMEDocument5 pagesBig Weekend Ahead: ... More Than Just A GAMEfelix kagotaNo ratings yet
- Lifeboat CheatsheetDocument2 pagesLifeboat Cheatsheetx213451seNo ratings yet
- AlyssaDocument1 pageAlyssaicetrolaNo ratings yet
- 5a8fbc22d0ce57481 PDFDocument80 pages5a8fbc22d0ce57481 PDFMahendra SofyanNo ratings yet
- Manual Book VibroDocument157 pagesManual Book Vibrodirma wansyahNo ratings yet
- GOTTLIEB Buck - RogersDocument23 pagesGOTTLIEB Buck - Rogersvince benNo ratings yet
- Legend of Zelda ManualDocument12 pagesLegend of Zelda ManualAaron Ekman100% (2)
- Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions and ThreeDocument25 pagesChapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions and Threefitri dwi hartatiNo ratings yet
- The Sales of A TOTO Site Sports Betting SystemDocument3 pagesThe Sales of A TOTO Site Sports Betting Systemleafmark5No ratings yet
- Sheiko Advanced Large Load SpreadsheetDocument35 pagesSheiko Advanced Large Load SpreadsheetMán EdeNo ratings yet
- Engargoladora de LatasDocument21 pagesEngargoladora de LatasAngel PerezNo ratings yet
- NBA 2K12 Manual PC FinalDocument14 pagesNBA 2K12 Manual PC FinalJohn BrennanNo ratings yet
- E CatalogDocument29 pagesE CatalogdajglimosneroNo ratings yet
- Percy Jackson - All Grown Up - Bruce T. ForbesDocument53 pagesPercy Jackson - All Grown Up - Bruce T. ForbesNick LuaneNo ratings yet