Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Strategic planning guide
Uploaded by
Jorgelindo Ramos Lucas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pageseducation
Original Title
Strategic Planning
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenteducation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesStrategic planning guide
Uploaded by
Jorgelindo Ramos Lucaseducation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Strategic planning
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
Not to be confused with Strategic thinking.
It has been suggested that Long range planning be merged into this article. (Discuss)
Proposed since June 2012.
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making
decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy.
In order to determine the future direction of the organization, it is necessary to understand its
current position and the possible avenues through which it can pursue particular courses of
action. Generally, strategic planning deals with at least one of three key questions:
[1]
1. "What do we do?"
2. "For whom do we do it?"
3. "How do we excel?"
George Friedman in The Next 100 Years summarises "the fundamental principle of strategic
planning: hope for the best, plan for the worst".
[2]
Contents
[hide]
1 Key components
2 Tools and approaches
o 2.1 Situational analysis
3 See also
4 References
5 Further reading
Key components[edit]
Video explaining the strategic plan of the Wikimedia Foundation
The key components of strategic planning include an understanding of an entity's vision,
mission, values and strategies. In the commercial world a vision statement or a mission statement
may encapsulate the vision and mission.
Vision outlines what the organization wants to be, or how it wants the world in which it
operates to be (an "idealised" view of the world).
[citation needed]
Mission defines the fundamental purpose of an organization or an enterprise, succinctly
describing why it exists and what it does to achieve its vision.
[citation needed]
Values are beliefs that are shared among the stakeholders of an organization.
[citation needed]
Strategy, narrowly defined, means "the art of the general".
[citation needed]
Organizations sometimes summarize goals and objectives into a mission statement or a vision
statement. Others begin with a vision and mission and use them to formulate goals and
objectives. A newly emerging approach is to use a visual strategic plan such as is used within
planning approaches based on outcomes theory. When using this approach, the first step is to
build a visual outcomes model of the high-level outcomes being sought and all of the steps which
it is believed are needed to get to them. The vision and mission are then just the top layers of the
visual model.
Tools and approaches[edit]
Tools include:
Balanced Scorecards, which creates a systematic framework for strategic planning;
Scenario planning, which was originally used in the military and recently used by large
corporations to analyze future scenarios.
PEST analysis (Political, Economic, Social, and Technological)
EPISTEL (Environment, Political, Informatic, Social, Technological, Economic and
Legal).
ATM Approach (Antecedent Conditions, Target Strategies, Measure Progress and
Impact).
[3]
Situational analysis[edit]
There are several factors to assess in the external situation analysis:
1. Markets (customers)
2. Competition
3. Technology
4. Supplier markets
5. Labor markets
6. The economy
7. The regulatory environment
It is rare to find all seven of these factors having critical importance. It is also uncommon to find
that the first two - markets and competition - are not of critical importance.
[4]
With regard to market planning specifically, researchers have recommended a series of action
steps or guidelines in accordance to which market planners should plan.
[5]
You might also like
- Strategic Planning - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesStrategic Planning - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning Is An: Organization StrategyDocument14 pagesStrategic Planning Is An: Organization Strategysinghm0077No ratings yet
- An Overview of Strategic ManagementDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Strategic ManagementBedri M Ahmedu100% (1)
- Strategic Planning Is An: Organization Process Strategy Decisions Strategic Management StrategistsDocument4 pagesStrategic Planning Is An: Organization Process Strategy Decisions Strategic Management StrategistsSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- SM Week 2Document54 pagesSM Week 2Kwyneth DeomaniaNo ratings yet
- STM UNIT TEST - I NotesDocument19 pagesSTM UNIT TEST - I NotesHemasri ChinnuNo ratings yet
- Chapter One The Nature of Strategic ManagementDocument15 pagesChapter One The Nature of Strategic ManagementmedrekNo ratings yet
- Dev't PPA (Chap-Three)Document22 pagesDev't PPA (Chap-Three)ferewe tesfayeNo ratings yet
- CSME SummaryDocument80 pagesCSME SummaryEdiomo NicholasNo ratings yet
- What Is Strategic PlanningDocument20 pagesWhat Is Strategic PlanningJeffreyReyesNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning Process and Background References PDFDocument11 pagesStrategic Planning Process and Background References PDFMarmie CamayangNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Key Concepts & ProcessDocument4 pagesStrategic Management: Key Concepts & ProcessHarshita SainiNo ratings yet
- SMDocument13 pagesSMabrarNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument9 pagesStrategic ManagementkavirishiNo ratings yet
- Strategy: in The Field of ManagementDocument7 pagesStrategy: in The Field of ManagementrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Quality StandardsDocument24 pagesStrategic Management: Quality StandardsKushal GowdaNo ratings yet
- Strategic MGT U-1Document26 pagesStrategic MGT U-1Mitiku ShewaNo ratings yet
- Strategic management fundamentalsDocument157 pagesStrategic management fundamentalsAstraea KimNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Strategic ManagementDocument17 pagesThe Nature of Strategic ManagementFredrick OmbakoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management m1Document35 pagesStrategic Management m1dibyaranjanbhrNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning - Uc2Document16 pagesStrategic Planning - Uc2Aliyan Aman100% (1)
- University of Colombo Faculty of Graduate Studies: Master of Business Studies Marketing Management Strategic ManagementDocument29 pagesUniversity of Colombo Faculty of Graduate Studies: Master of Business Studies Marketing Management Strategic Managementbandaranayake2323No ratings yet
- G11 ABM Org and MGT Lesson 3 Part 1 HandoutsDocument8 pagesG11 ABM Org and MGT Lesson 3 Part 1 HandoutsLeo SuingNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy and TechnologyDocument13 pagesBusiness Strategy and TechnologyLireni EzungNo ratings yet
- Mm202 - Individual 3 Body - StratplanDocument10 pagesMm202 - Individual 3 Body - StratplanLemon MaphosaNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Strategic and ProcessDocument20 pagesUnit I - Strategic and Processjul123456No ratings yet
- What Is That Strategic Planning Process?Document6 pagesWhat Is That Strategic Planning Process?elmarcomonalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management in A HotelDocument11 pagesStrategic Management in A HotelСофи БреславецNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Processes: Formulation, Implementation, and EvaluationDocument18 pagesStrategic Management Processes: Formulation, Implementation, and EvaluationdikpalakNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument20 pagesStrategic ManagementPrajakta BhabalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning: Scholarship Wikimania 2010 Apply Now!Document10 pagesStrategic Planning: Scholarship Wikimania 2010 Apply Now!sesinghNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Notes-230Document230 pagesStrategic Management Notes-230Eshu Subramani100% (1)
- Strategic Management: School of Business & Management Jaipur National UniversityDocument63 pagesStrategic Management: School of Business & Management Jaipur National Universitysumit januNo ratings yet
- Bba16 PDFDocument229 pagesBba16 PDFTirusew GeresuNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Complete NotesDocument233 pagesStrategic Management Complete NotesArunNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Art Science Formulating Implementing EvaluatingDocument3 pagesStrategic Management Art Science Formulating Implementing EvaluatingKhondaker Fahad JohnyNo ratings yet
- 2020 Corporate Strategy PPT Sample NotesDocument6 pages2020 Corporate Strategy PPT Sample Notesamol0134No ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument37 pagesStrategic Managementsimranarora2007No ratings yet
- Managmnt 2Document25 pagesManagmnt 2Farhan M HussainNo ratings yet
- Strategy- Definition, Components and BenefitsDocument4 pagesStrategy- Definition, Components and BenefitsVir Ved Ratna Jaipuria LucknowNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument227 pagesStrategic ManagementSky509No ratings yet
- BKMG104 Business Strategy 2008Document236 pagesBKMG104 Business Strategy 2008Tu Thanh ThuyNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument16 pagesStrategic Managementkhan moinNo ratings yet
- World Strategic Management Process - Strategic Management InsightDocument9 pagesWorld Strategic Management Process - Strategic Management InsightAbdullah AnsariNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument9 pagesStrategic ManagementRubayet AbedinNo ratings yet
- Resources Organization Mission Balanced Scorecard BusinessDocument4 pagesResources Organization Mission Balanced Scorecard BusinessA KNo ratings yet
- Module 3-Strategic Planning and ImplementationDocument115 pagesModule 3-Strategic Planning and ImplementationPriya BhowanNo ratings yet
- SM 1Document58 pagesSM 1thebestofworld2014No ratings yet
- Strategic management process and levelsDocument4 pagesStrategic management process and levelsvikas123gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: BSP028 Strategic ManagementDocument28 pagesWelcome To: BSP028 Strategic ManagementswarnimpathakNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument7 pagesUnit IILamiyaNo ratings yet
- Planning Sec2Document27 pagesPlanning Sec2Mark EssamNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Strategic Management Course Code: MBA 733 Credit Hours: 3Document41 pagesCourse Title: Strategic Management Course Code: MBA 733 Credit Hours: 3Rachel Haile100% (1)
- Strategic ManagementDocument4 pagesStrategic ManagementNicholas BradleyNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management OverviewDocument30 pagesStrategic Management OverviewRiaz safiNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Quality Form FR-INS-04.Rev00 TOS No.Document2 pagesTable of Specification: Quality Form FR-INS-04.Rev00 TOS No.Jorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Inset Cover PagesDocument10 pagesInset Cover PagesJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- NVSU BA English Faculty ProfileDocument3 pagesNVSU BA English Faculty ProfileJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben2013 PortraitDocument7 pagesAben2013 PortraitJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Area II Faculty ProfileDocument13 pagesArea II Faculty ProfileJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben2013 PortraitDocument7 pagesAben2013 PortraitJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Self-Survey Report (SSR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishDocument14 pagesSelf-Survey Report (SSR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- AREA 7 - LibraryDocument37 pagesAREA 7 - LibraryJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Area II Faculty ProfileDocument13 pagesArea II Faculty ProfileJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben2013 LandscapeDocument60 pagesAben2013 LandscapeJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben2013 PortraitDocument7 pagesAben2013 PortraitJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben2013 LandscapeDocument60 pagesAben2013 LandscapeJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Area II Faculty ProfileDocument13 pagesArea II Faculty ProfileJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- NVSU BA English Faculty ProfileDocument3 pagesNVSU BA English Faculty ProfileJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben2013 LandscapeDocument60 pagesAben2013 LandscapeJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Self-Survey Report (SSR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishDocument17 pagesSelf-Survey Report (SSR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
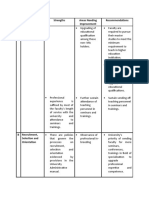
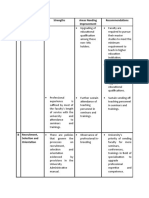
- Parts Strengths Areas Needing Improvement Recommendations A Academic Qualifications and Professional ExperienceDocument3 pagesParts Strengths Areas Needing Improvement Recommendations A Academic Qualifications and Professional ExperienceJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Compliance Report (CR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishDocument23 pagesCompliance Report (CR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Description of The Institution'S System (Procedure) in The Recruitment and Selection of FacultyDocument4 pagesDescription of The Institution'S System (Procedure) in The Recruitment and Selection of FacultyJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben 2016 - 1PPP (Updated)Document52 pagesAben 2016 - 1PPP (Updated)Jorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Compliance Report (CR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishDocument23 pagesCompliance Report (CR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aben 2016 - 1PPP (Updated)Document52 pagesAben 2016 - 1PPP (Updated)Jorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Parts Strengths Areas Needing Improvement Recommendations A Academic Qualifications and Professional ExperienceDocument3 pagesParts Strengths Areas Needing Improvement Recommendations A Academic Qualifications and Professional ExperienceJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Self-Survey Report (SSR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishDocument17 pagesSelf-Survey Report (SSR) : Bachelor of Arts in EnglishJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Aritao Central School Yes-O Club Activities 2015-2016Document1 pageAritao Central School Yes-O Club Activities 2015-2016Jorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Developmental BiologyDocument1 pageDevelopmental BiologyJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Description of The Institution'S System (Procedure) in The Recruitment and Selection of FacultyDocument4 pagesDescription of The Institution'S System (Procedure) in The Recruitment and Selection of FacultyJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Department of Aquatic Biology Bemidji State UniversityDocument4 pagesDepartment of Aquatic Biology Bemidji State UniversityJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- College of Arts and Sciences: Jorgelindo R. Lucas Assoc Prof IIDocument11 pagesCollege of Arts and Sciences: Jorgelindo R. Lucas Assoc Prof IIJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaJorgelindo Ramos LucasNo ratings yet
- Tumbler Test For CokeDocument3 pagesTumbler Test For CokeDavid CazorlaNo ratings yet
- MDI Gurgaon Derivatives Course OutlineDocument5 pagesMDI Gurgaon Derivatives Course OutlinePuneet GargNo ratings yet
- Shona Made Easy: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument25 pagesShona Made Easy: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleInnocent Clifford Marandu100% (1)
- (CPR) Balindong Vs CA, GR No 177600, 19 October 2015 Case DigestDocument4 pages(CPR) Balindong Vs CA, GR No 177600, 19 October 2015 Case Digestarceo.ezekiel0No ratings yet
- Presentation Slides: Contemporary Strategy Analysis: Concepts, Techniques, ApplicationsDocument11 pagesPresentation Slides: Contemporary Strategy Analysis: Concepts, Techniques, ApplicationsMonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- TS 2030Document289 pagesTS 2030dhmartiniNo ratings yet
- Ingredient Trends in The: Personal Care and Cosmetics Industry 2020Document33 pagesIngredient Trends in The: Personal Care and Cosmetics Industry 2020Akash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Atty Paras Reprimanded for Delayed ComplianceDocument10 pagesAtty Paras Reprimanded for Delayed ComplianceMK KMNo ratings yet
- ID Strategi Persaingan Operator Telekomunikasi Seluler The Competition Strategy of PDFDocument14 pagesID Strategi Persaingan Operator Telekomunikasi Seluler The Competition Strategy of PDFnada anggunNo ratings yet
- Homer Help ManualDocument416 pagesHomer Help ManualAnnisa Fadia DelianaNo ratings yet
- Internal Control QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesInternal Control Questionnairepeterpancanfly100% (2)
- StabilityDocument77 pagesStabilitybabissoul100% (2)
- Emergency HospitalDocument11 pagesEmergency Hospitalikyu_san_1No ratings yet
- Chaotic Sword GodDocument1,928 pagesChaotic Sword Godxdmhundz999100% (1)
- Toyota DocumentDocument32 pagesToyota Documentrajat0989No ratings yet
- Economy India (Bain Report)Document103 pagesEconomy India (Bain Report)Yogesh GuttaNo ratings yet
- Kehar Singh CaseDocument8 pagesKehar Singh CaseSunil beniwalNo ratings yet
- OET Letter Writing - Top 8 Tips For Doctors & NursesDocument3 pagesOET Letter Writing - Top 8 Tips For Doctors & NursesClassNo ratings yet
- Dos Vs Linux PDFDocument2 pagesDos Vs Linux PDFJawad Sandhu0% (1)
- Bbg3 AnswersDocument123 pagesBbg3 AnswersAbraham Castro JuarezNo ratings yet
- Neha Datta: ContactDocument4 pagesNeha Datta: ContactasdasdNo ratings yet
- Job Offer Letter Agreement Paris Job Pierre Gattaz PDFDocument3 pagesJob Offer Letter Agreement Paris Job Pierre Gattaz PDFBiki Dutta100% (2)
- MilestoneDocument36 pagesMilestoneRiza ZaharaNo ratings yet
- The Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceDocument4 pagesThe Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceParimala DhanasekaranNo ratings yet
- Double-Letter Conconant Sounds Flash Cards PDFDocument96 pagesDouble-Letter Conconant Sounds Flash Cards PDFAriadna Galdón AlbaNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS PROBLEMSDocument3 pagesENGINEERING MECHANICS PROBLEMSAraiza FloresNo ratings yet
- International Humanitarian Law - Atty. Mercado (July 2016)Document77 pagesInternational Humanitarian Law - Atty. Mercado (July 2016)MiroNo ratings yet
- Plant Inspector CV.Document7 pagesPlant Inspector CV.Khalilahmad KhatriNo ratings yet
- Collocations For StudentsDocument3 pagesCollocations For StudentsOldemary Deschamps100% (1)
- Pre-BASIC VOCABULARY BRILLIANT ENGLISH COURSEDocument7 pagesPre-BASIC VOCABULARY BRILLIANT ENGLISH COURSERisMank Sani QuiCken Heart100% (1)