Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Microsoft Word Document
Uploaded by
Jithesh ParambathOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Microsoft Word Document
Uploaded by
Jithesh ParambathCopyright:
Available Formats
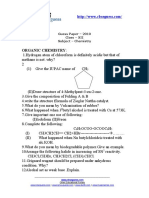
1. 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, lactic acid, is a chiral molecule which is found in muscles and in sour milk.
The 2-
hydroxypropanoic acid formed in muscles is optically active but that in sour milk is not.
(a) (i) Explain the term chiral, stating the feature of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid that makes it chiral. Label this
feature on the formula above. (ii) What is the difference between the 2-hydroxypropanoic acid formed in
muscles and that found in sour milk which gives rise to the difference in optical activity?
(b) 2-hydroxypropanoic acid may be prepared in the laboratory from propanoic acid in a two-stage sequence in
which 2-bromopropanoic acid is formed as an intermediate
:
(i) Stage 2 of this sequence was carried out in two steps. Identify the reagent required for each step in Stage 2.
(ii) When an optically active isomer of 2-bromopropanoic acid is used in Stage 2, the resulting 2-
hydroxypropanoic acid is also optically active. State and explain what this indicates about the mechanism of
the first reaction in Stage 2.
(c) 2-hydroxypropanoic acid may also be prepared from ethanal in the following sequence:
(i) Name the mechanism and type of reaction occurring in Reaction 1.
(ii) Identify the attacking species in Reaction 1.
(iii) Give the first step of the mechanism of Reaction 1, showing the formation of the intermediate.
*(iv) Explain, by referring to the mechanism in (c)(iii), why the 2-hydroxypropanoic acid formed from ethanal
shows no optical activity.
2. This question is about the reactions of butanoic acid, CH3CH2CH2COOH. It has a foulsmell and behaves like a
typical carboxylic acid.
(a) (i) The addition of sodium carbonate solution is often used as a chemical test to distinguish carboxylic acids,
like butanoic acid, from other compounds, such as aldehydes.
Explain why old stocks of aldehydes often react with sodium carbonate solution.
(ii) How would the result of this test distinguish between a carboxylic acid and an old stock of an aldehyde?
(iii) Write the balanced chemical equation, including state symbols, for the reaction of sodium carbonate
solution with butanoic acid.
(b) (i) What would you see when phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5, reacts with butanoic acid?
(ii) Give the structural formula and name of the organic product of this reaction.
(c) (i) Give the name or formula of the organic product of the reaction between butanoic acid and lithium
tetrahydridoaluminate (lithium aluminium hydride).
(ii) Water cannot be used as the solvent in this reaction because it reacts with lithium tetrahydridoaluminate.
Suggest a suitable solvent.
(iii) State the type of reaction that takes place between butanoic acid and lithium tetrahydridoaluminate. Justify
your classification.
(d) (i) Butanoic acid can be reacted with methanol to make methyl butanoate. State two conditions that help to
speed up this reaction.
(ii) Draw the displayed formula of methyl butanoate.
(iii) Identify another chemical, by name or formula, which could be added to methanol to make methyl
butanoate.
*(iv) Give two advantages and one disadvantage of using the reaction occurring in
(d)(iii), compared to the reaction in (d)(i), when making methyl butanoate.
You might also like
- Aliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesFrom EverandAliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNo ratings yet
- From Biosynthesis to Total Synthesis: Strategies and Tactics for Natural ProductsFrom EverandFrom Biosynthesis to Total Synthesis: Strategies and Tactics for Natural ProductsNo ratings yet
- Class: XII Marks: 60 Time: One Period: Bangladesh International Tutorial Class Test (I) Session: 2021 - 22Document13 pagesClass: XII Marks: 60 Time: One Period: Bangladesh International Tutorial Class Test (I) Session: 2021 - 22JerryNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids & Their Derivatives Exercise Section ADocument3 pagesCarboxylic Acids & Their Derivatives Exercise Section AMelody OngNo ratings yet
- Por Jorge L: Uis Breña OréDocument32 pagesPor Jorge L: Uis Breña OréAlexa TorresNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes QuestionsDocument1 pageHaloalkanes QuestionsHanaa KhaldiNo ratings yet
- Topic 20 Practice TestDocument10 pagesTopic 20 Practice TestminjiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument11 pagesWorksheet of Carbonyl CompoundsAyush ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1Document27 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document8 pagesTutorial 3Ahmad WahideeNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes Q BankDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes Q BankVishnuNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone &carboDocument18 pagesAldehyde Ketone &carboFaraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 2 QPDocument6 pagesAlcohols 2 QPHailey WongNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbyyb W54zpzfswkn8k3vq0clq6et8mk Ne Px62hvrlk5chrlql9xx83xtq2sr0dqcuhrswcoglr Ueky068cras4ph7jxkmy 143kq0wnhekbynbh 4 Eq1p0kvslajoriecir6ikqqswDocument8 pagesAcfrogbyyb W54zpzfswkn8k3vq0clq6et8mk Ne Px62hvrlk5chrlql9xx83xtq2sr0dqcuhrswcoglr Ueky068cras4ph7jxkmy 143kq0wnhekbynbh 4 Eq1p0kvslajoriecir6ikqqswThanh Hằng NgôNo ratings yet
- Chem c2 Exer1Document3 pagesChem c2 Exer1jalrizal7No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document5 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2ibdpNo ratings yet
- AkcDocument4 pagesAkcGirishmaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesCarboxylic AcidssuryaisonemailNo ratings yet
- S2 Q4: Organic Chemistry Carboxylic AcidDocument21 pagesS2 Q4: Organic Chemistry Carboxylic AcidMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Latihan HydrocarbonDocument9 pagesLatihan HydrocarbonThilagaNo ratings yet
- (A) Define The Term Structural Isomerism. (2 Marks)Document2 pages(A) Define The Term Structural Isomerism. (2 Marks)Tudio GamingNo ratings yet
- A2 Chemistry ExamzoneDocument4 pagesA2 Chemistry ExamzoneSan SiddzNo ratings yet
- Acid and AlkaliDocument9 pagesAcid and Alkali云吸仓鼠吉尼斯保持者No ratings yet
- Cem 3005 Tutorial August 2013 Natural Products and Organoanalytical ChemistryDocument4 pagesCem 3005 Tutorial August 2013 Natural Products and Organoanalytical ChemistryZama MakhathiniNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Containing Organic Compound-III - WorkbookDocument41 pagesOxygen Containing Organic Compound-III - Workbookagrimsinghal28No ratings yet
- B2 6.2.5 Organic Synthesis 2020-21Document27 pagesB2 6.2.5 Organic Synthesis 2020-21noornhhhNo ratings yet
- Alcoholes, Phenols and Ethers. WORKSHEETDocument8 pagesAlcoholes, Phenols and Ethers. WORKSHEETmanasvNo ratings yet
- CH4 Hots QuestionsDocument1 pageCH4 Hots Questionsprabhat7969tiagoNo ratings yet
- 4.2.1 Alcohols QPDocument22 pages4.2.1 Alcohols QPsohaibshauket16No ratings yet
- Biochemistry QuestionsDocument7 pagesBiochemistry QuestionsCatherine JennensNo ratings yet
- CQ Petroleum ProductsDocument15 pagesCQ Petroleum Productsapi-3826629No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesDocument12 pagesCarboxylic Acids and DerivativessupniggasNo ratings yet
- Revision Organic Tutorial 2Document3 pagesRevision Organic Tutorial 2Danish HamizanNo ratings yet
- L Energy and Respiration I PDFDocument12 pagesL Energy and Respiration I PDFMichelle Yeap67% (3)
- Practice Questions AlkenesDocument9 pagesPractice Questions Alkenesibrahim ahmedNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 11 Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsDocument47 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 11 Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsFelix YueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class: O-Level Time: 50 Min Marks: 45Document7 pagesChemistry Class: O-Level Time: 50 Min Marks: 45Zainab ShigriNo ratings yet
- DPP803Document7 pagesDPP803anikephantomNo ratings yet
- Test Paper - Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument1 pageTest Paper - Carbon and Its CompoundsJagpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Topic, Students Should Be Able To:: Tutorial 19: Amino AcidsDocument5 pagesAt The End of The Topic, Students Should Be Able To:: Tutorial 19: Amino AcidsizabelNo ratings yet
- Chimie GB 2013 FinalDocument11 pagesChimie GB 2013 FinalChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Gerak Gempur 3 Term 3 With AnswersDocument11 pagesGerak Gempur 3 Term 3 With AnswersShima SenseiiNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid - Xii Group-2-2023Document14 pagesAldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid - Xii Group-2-2023Shashwat R TripathyNo ratings yet
- Practice Reactions of Alocohols WorksheetDocument3 pagesPractice Reactions of Alocohols WorksheetJoshua GeddesNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chemistry QB CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic PrinciplesDocument7 pagesHsslive Xi Chemistry QB CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic PrinciplesAshly Santhosh KNo ratings yet
- 10.0 Carboxylic Acid 2022 (Lecturer)Document15 pages10.0 Carboxylic Acid 2022 (Lecturer)naderaqistina23No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Imp. QuestionDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Imp. QuestionMahesh Daxini ThakkerNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 25Document5 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 25Anthony AndyNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 12 Level 1 Test 1Document1 page12 Chemistry ChapterTests Chapter 12 Level 1 Test 1usethis840No ratings yet
- Pharmachemistry-I: Short Question Carrying 4 MarksDocument17 pagesPharmachemistry-I: Short Question Carrying 4 MarksRajiv DarogaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem (With Solution) 2Document75 pagesOrganic Chem (With Solution) 2vlNo ratings yet
- OC QP OBE 21 DUDocument3 pagesOC QP OBE 21 DUGauri ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper Set 3Document1 pageChemistry Paper Set 3katravathanjamma1978No ratings yet
- QUIMICASL Paper3Document43 pagesQUIMICASL Paper3Fiona DonovanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Sk027 OverviewDocument12 pagesChapter Sk027 OverviewNor AfidahNo ratings yet
- CQ BleachDocument7 pagesCQ Bleachapi-3826629No ratings yet
- WS 1 - 18.08.22Document6 pagesWS 1 - 18.08.22Micheelle JeannethNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab 1-4 Module DK024 (Question)Document12 pagesPre Lab 1-4 Module DK024 (Question)Irdina WnNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Questions - 2019-20 - SET1Document8 pagesCHEMISTRY Questions - 2019-20 - SET1-Uddipan BagchiNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesFrom EverandAliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNo ratings yet
- Atomic STR & Periodictable Week Assignment 01Document2 pagesAtomic STR & Periodictable Week Assignment 01Mary MannuNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test 2 - August 2014 Section ADocument4 pagesMonthly Test 2 - August 2014 Section AJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Monthly Test FinalDocument10 pagesGrade 11 Monthly Test FinalJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- A Sample of Iron From A Meteorite Was Found To Contain The Isotopes 54fe, 56fe and 57feDocument5 pagesA Sample of Iron From A Meteorite Was Found To Contain The Isotopes 54fe, 56fe and 57feJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document11 pagesChemistry 1Jithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Atomic STR & Periodictable Week Assignment 01Document2 pagesAtomic STR & Periodictable Week Assignment 01Mary MannuNo ratings yet
- AHSDocument7 pagesAHSJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Strategic Goals & Objectives: School MissionDocument4 pagesStrategic Goals & Objectives: School MissionJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Strategic Goals & Objectives: School MissionDocument4 pagesStrategic Goals & Objectives: School MissionJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- PTS 12DDocument24 pagesPTS 12DJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 4 March 2012Document17 pagesChemistry Unit 4 March 2012Jithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Alence Hell Lectron Air Epulsion Theory: V S E P RDocument13 pagesAlence Hell Lectron Air Epulsion Theory: V S E P RJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 5 March 2012Document18 pagesChemistry Unit 5 March 2012Jithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument40 pagesElectrochemistryJithesh Parambath0% (1)
- Grade 11 Monthly TestDocument6 pagesGrade 11 Monthly TestJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic TrendsDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic TrendsJithesh ParambathNo ratings yet
- HSE-Acoustic & Fire DoorsDocument6 pagesHSE-Acoustic & Fire DoorsInterior ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Pre Requisites For Project ImplementationDocument3 pagesPre Requisites For Project ImplementationTage NobinNo ratings yet
- MTK 1023-Material and ConsumableDocument13 pagesMTK 1023-Material and ConsumableGraceLamNo ratings yet
- Basics of CT and PTDocument15 pagesBasics of CT and PTanamika1690% (1)
- Argus Dual System Pi enDocument2 pagesArgus Dual System Pi enfahmi1987No ratings yet
- Servomotor WedgeDocument24 pagesServomotor WedgeAlanNo ratings yet
- Recondition BatteryDocument46 pagesRecondition Batteryafic219473100% (1)
- Pmled 6 5K 10a 66Document6 pagesPmled 6 5K 10a 66Eduardo SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Building A Model Steam Engine From Scratch Chapter 1, 150 121Document19 pagesBuilding A Model Steam Engine From Scratch Chapter 1, 150 121Liam Clink100% (2)
- Diagrama Electrico VespaDocument1 pageDiagrama Electrico Vespavetgesto3No ratings yet
- CostingDocument5 pagesCosting83pankajNo ratings yet
- Grinding Polishing: Kiesow Dr. BrinkmannDocument36 pagesGrinding Polishing: Kiesow Dr. BrinkmannChoice OrganoNo ratings yet
- Electrical ContactorDocument14 pagesElectrical ContactorRaphael212219No ratings yet
- Vsi 52 Dec 2010Document4 pagesVsi 52 Dec 20103LifelinesNo ratings yet
- E-TON Vector ST 250 Vxl-250 St-Part ManualDocument53 pagesE-TON Vector ST 250 Vxl-250 St-Part ManualmariusgrosyNo ratings yet
- Superior Tuffy Valves: 290 Series LPD Globe Line ValvesDocument1 pageSuperior Tuffy Valves: 290 Series LPD Globe Line ValvesR M Abdullah WakeelNo ratings yet
- NPT Thread Dimensions PDFDocument1 pageNPT Thread Dimensions PDFRamnandan MahtoNo ratings yet
- ITC Guide For Thesis PreparationDocument26 pagesITC Guide For Thesis PreparationPanha MenhNo ratings yet
- Re-Measurement Sheet FOR UNIT 148 Interconnecting Piperack M44-Pr3Document6 pagesRe-Measurement Sheet FOR UNIT 148 Interconnecting Piperack M44-Pr3Vasilica BarbarasaNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Calculation As Per ASCE 7 10Document8 pagesWind Load Calculation As Per ASCE 7 10ani145yadav100% (1)
- Viscoelastic Modeling of Flexible Pavement With Abaqus PDFDocument143 pagesViscoelastic Modeling of Flexible Pavement With Abaqus PDFcabrel TokamNo ratings yet
- GPU Programming in MATLABDocument6 pagesGPU Programming in MATLABkhaardNo ratings yet
- Free Gear Calculator - KHK GearsDocument5 pagesFree Gear Calculator - KHK GearslawlawNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering EconomicsDocument4 pagesSoftware Engineering Economicsazam_rasheed50% (2)
- Copeland Cr28k6 PFV Recip Compressor Technical Specifications2Document1 pageCopeland Cr28k6 PFV Recip Compressor Technical Specifications2PerezNo ratings yet
- MB Biostar P4SDP 3 PDFDocument12 pagesMB Biostar P4SDP 3 PDFEustahije BrzicNo ratings yet
- Finals DSP WithMinimalErrors PDFDocument64 pagesFinals DSP WithMinimalErrors PDFanembam putobungbongNo ratings yet
- Torre Sauter 0 - 5 - 320 - 025 - 4 PDFDocument27 pagesTorre Sauter 0 - 5 - 320 - 025 - 4 PDFGuiNo ratings yet
- AR15.40-P-5032TA Remove/install Alternator 4.2.09 Engine 648.961 in MODEL 211.023 /223 /026 /226Document2 pagesAR15.40-P-5032TA Remove/install Alternator 4.2.09 Engine 648.961 in MODEL 211.023 /223 /026 /226Stefan AdrianNo ratings yet
- Rftmdc6a PDFDocument17 pagesRftmdc6a PDFShakeebNo ratings yet