Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deep Sea and Air Physiology
Uploaded by
avian_roseCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deep Sea and Air Physiology
Uploaded by
avian_roseCopyright:
Available Formats
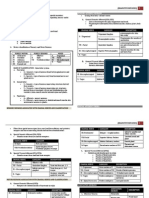
DEEP SEA and AIR PHYSIOLOGY
Hyperbarism
- Exposure of the bood n the ungs to
extremey hgh aveoar gas pressure.
Ideal Gas Law
- descrbes how changes n barometrc
pressure and absoute temperature
ahect gas voume and the human
body.
BOYLES LAW
- states that pressure and voume for an
dea gas vary nversey
- the voume to whch a gven quantty
of gas s compressed s nversey
proportona to the pressure
attude
(as sea depth ncreases)
Decrease voume
Increase Barometrc Pressure
CHARLES LAW
- states that ncreasng temperature
ncreases veocty of gas moecues
ncreasng the pressure forcng the
compant contaner to ncrease n
sze.
DALTOS LAW
- states that barometrc pressure s the
sum of the parta pressure of the
ndvdua gases n the ar mxture.
- Can be expressed by the h:
Parta pressure = tota pressure x fractona
gas conc.
!IC"S LAW
- States that the ow of the gas across
the membrane s proportona to the
pressure gradent of the dhusng gas.
GRAHA#S LAW
- States that dhuson s nversey
proportona to the square root of
moecuar weght.
HERYS LAW
- States that the concentraton gas
dssoved n water s proportona to
the parta pressure of the gas n the
gas phase.
**Gases that can cause sgncant
physoogc ehects at hgh pressures.
NITROGEN
CARBON DIOXIDE - routney removed
OXYGEN - reduced to about 20% or ess
RELATIOSHIP O! THE SEA DEPTH TO
BARO#ETRIC PRESS$RE
Depth (ft) Pressure
(atm)
Depth
(m)
Pressure
(atm)
Sea Leve 1 Sea eve 1
33 2 10 (10.4) 2
66 3 20 3
100 4 30 4
133 5 40 5
166 6 50 6
200 7 60 7
300 10 90 10
400 13 120 13
500 16 150 16
Devces used underwater
- Dvng be
- Cassons
- SCUBA
SCUBA
(Sef Contaned Underwater Breathng
Apparatus)
Fve ma|or eements:
1. Tank of gas
2. Reducng vave
3. Demand breathng vave
4. Exhaust vave
5. Face mask of mouthpece
Potenta probems assocated wth exposure
to ncreased barometrc pressure
a. Ntrogen narcoss
b. Hgh- Pressure nervous Syndrome
c. Oxygen Toxcty
d. Carbon Doxde Posonng
e. Decompresson Sckness
f. Pumonary Embosm
ITROGE ARCOSIS
- Caused by breathng ncreased PN2
when exposed at a pressure of about
4-5 atmospheres for an hour or more.
- 30-40m or 100-133 f depth
Manfestatons:
- Euphora (80%) N2
- Symptoms of acoho ntoxcaton
(greater pressure)
- Impared performance
o Inteectua functon - mpared
o Manua dexterty - norma
- 120ft - rst symptoms of md narcoss
appear (exhbt |ovaty and oss of
psychosoca nhbtons)
- 150-200ft - drowsness
- 200- 250ft weakness (too cumsy)
- Above 250ft - dver becomes amost
useess
Pathophysoogy:
- Reduces neurona exctabty
Management:
- Breathng mxtures of O2, heum,
xenon
HIGH%PRESS$RE ER&O$S SYDRO#E
- Deveops durng deep dves wth
mxtures of gases
Manfestatons:
- Tremors
- Drowsness
- Depresson of apha waves (EEG) -
somnoence
- Inteectua functon - norma
- Manua Dexterty - norma
Pathophysoogy:
- Anesthetc ehect of nert gases at hgh
pressure whch reduces neurona
exctabty (N2, xenon, krypton, argo,
neon and heum.)
O'YGE TO'ICITY (A)*+e O,y-en
P.is.nin-/
- Occurs when oxygen s breathed at a
very hgh pressure
Manfestatons:
- Sezures and coma (4 atm w/n 30-60
mns)
- Nausea
- Musce twtchng
- Dzzness
- Dsturbances of vson
- Irrtabty
- Dsorentaton
Pathophysoogy
- Excessve ntraceuar oxdaton whch
eads to the formaton of free radcas
(oxdzng poyunsaturated ftty acd
component of ce membranes)
- Oxygen Free Radcas (actve form of
oxygen)
o Superoxde (O2)
o Hydrogen Peroxde (H2O2)
O'YGE TO'ICITY
- Exposure to ony 1atm pressure of
oxygen after 12hrs or more
Manfestatons:
- Pumonary arway congeston
- Pumonary edema
- Ateectass
- Pumonary brn formaton
- Lung consodaton
Pathophysoogy:
- Exposure of ar spaces of the ungs to
the hgh O2 exposure.
Management:
- Lowerng the fractona O2 n nspred
ar
CARBO DIO'IDE POISOIG
- Depth aone does not ncrease the CO2
parta pressure n the aveo
- Depth does not ncrease rate of CO2
producton n the body
- Caused by the bud up of CO2 n the
dead space ar of the rebreathng
apparatus (dvdng hemet) and be
rebreathed by the dver. (PCO2 of
>80mmHg)
- Depresson f the respratory center
- Respratory Acdoss
Manfestatons:
- Lethargy
- Narcoss
- Anesthesa
De).mpressi.n Si)0ness (Bends1
Caiss.ns Dse1 C.mpressed Airness1
Di2ers Paralysis1 Dysbarism/
- Increased dssoved N2 n the body
- Rapd decreased of eevated PN2 (rapd
ascent)
- Rapd dhuson of N2 from the tssue
and the bood (ncreased parta
pressure gradent)
- Formaton of bubbes
- Occuson of bood vesses
- Tssue schema
Manfestatons:
- Appear 10-30mn
- Severe pans (around the |onts and
musces)
o 85-90%
o Bends
- Dzzness - 5%
- Paresthesa and tchng
- Bran and Spna Cord Damage - 5-
10%
- Parayss - 3%
- Dyspnea - 2%
o Chokes
Management:
- Prompt recompresson foowed by
sow decompresson (usng tank
decompresson)
Decompresson Tabe:
- Ntrogen emnaton from the body
Safe Decompresson
- 2/3 berated wthn 1hr, 90% n 6hrs
60mns at a depth of 190ft
10mns at 50ft depth
17mns at 40ft depth
19mns at 30ft depth
50mns at 20ft depth
84mns at 10ft depth
AIR E#BOLIS#
- Caused by ar that goes to the bood
after rupture of the pumonary vens
- Can cause sudden death
- Fata embosm has occurred durng
rapd ascent from as shaow as depth
as 5m
- Caused by exposve decompresson
(wa of pressurzed cabn of an
arpane or rocket at hgh attude s
breached.)
HYPERBARIC O'YGE THERAPY
- Usuay admnstered at PO2 of 2-3 atm
of pressure through a mask or
ntratrachea tube whe the gas
around the body s norma ar
compressed to the same hgh pressure
eve.
- Uses: treatment of
o gas gangrene
o eprosy
o decompresson sckness
o artera gas embosm
o carbon monoxde posonng
o osteomyets
o myocarda nfarcton
- ncrease attude, decreases
barometrc pressure --- decreases PO2
--- decrease aveoar O2 --- hypoxa
PROBLEMS:
- ow oxygen pressure
- acceeratory forces
- weghtessness
Barometrc Pressure (Sea Leve) - 760mmHg
Parta Pressures of Dh. Gases
Oxygen - 21% - 159mmHg
CO2 - 0.04% - 0.3 mmHg
Ntrogen - 78% - 593 mmHg
Others - 0.92%- 7 mmHg
Norma Aveoar Oxygen = 104 mmHg
Water Vapor Pressure (37
o
C) = 47mmHg
PCO2 = 40mmHg (unaccmatzed)
= 7mmHg (accmatzed)
AC$TE E!!ECTS O! HYPO'IA
12,000 ft
- drowsness
- asstude
- menta and musce fatgue
- headache, nausea and euphora
(occasona)
18,000ft (above)
- twtchng
- sezures
23,000ft (above)
- coma (unaccmatzed)
- other mportant ehects of hypoxa
(decreased menta procency)
- decreased |udgment
- decreased memory
- decreased motor movements
(decrease work capacty)
ACCLIMATIZATION to LOW PO2 (ncrease
attude toerance)
- ncrease n pumonary ventaton
- ncrease n RBC and hemogobn
- ncrease dhusng capacty of the
ungs
- ncrease caparty
- ceuarty accmatzaton
ICREASE I P$L#OARY &ETILATIO
- hypoxc stmuaton of perphera
chemoreceptors
- ncreasng respratory stmuatory
actvty of respratory center
- ncrease n aveoar ventaton (65%)
- reducton of PCO2 and ncreasng pH
Ehects of Decreased Barometrc Pressure
Attude
Barometrc PO2
pressure
hypoxc stmuaton of the chemoreceptor
pumonary ventaton
PCO2 and pH
(-) respratory center (2-5 days)
HCO2 and pH
Pumonary ventaton
Increased RBC and Hemogobn
Concentraton
- average ncrease n Hb concentraton
- 15 to 20 g/d
- Increase n hematocrt 40 to 60
- Increase n bood voume by 20-30% (
Hgb)
Hypoxa
Erythropoetn reease
(+) BM
RBC (Hgb and Hct)
Increase n Dhusng Capacty
- Increase pumonary capary bood
voume and ung voume
- Increase surface area for oxygen
dhuson
- Increase pumonary artera pressure
- NORMAL: 21 m/mmHg/mn
Capary bood vo. ----expands capary ---
surf. Area
3 DI!!$SIO
Lung voume --- surface area of the
aveo
= DIFFUSION
Pumonary pressure --- CHP --- DIFFUSION
Increase n Capary
- Increase n CO by 30% but ths
decreases back to norma as Hct
ncreases
- Increased caparty = ncrease n the
number of systemc crcuatory
capares n the nonpumonary tssue
(R ventrce)
Cell*lar A))lima+i4a+i.n
- Increase n the number of
mtochondra
- Increase n the myogobn that
factates the movement of O2 n
tssues
- Increase n the tssue of cytochrome
oxdase
Other changes:
- Increase n chest sze
- Rght ventrcuar hypertrophy
AC$TE #O$TAI SIC"ESS AD HIGH
ALTIT$DE P$L#OARY EDE#A
- Deveops 8-24 hrs after rapd ascent
to hgh attude and asts 4-8 days.
- Characterzed by:
o Headache
o Nausea and vomtng
o Irrtabty
o Insomna
o Breathessness
Two events
- Acute pumonary edema
o Hypoxa - oca vasodaton -
ncrease CHP
- Acute Cerebra Edema
o Hypoxa - vasoconstrcton
(pumonary arteroes) -
ncrease bood ow to
unconstrcted vesses - ncrease
CHP --- EDEMA
CHROIC #O$TAI SIC"ESS
!ea+*res5
- Red ce mass and hematocrt
becomes exceptonay hgh
o Increases bood vscosty
o Decrease bood ow
- Eevaton of pumonary artera
pressure
o Hypoxc pumonary
vasoconstrcton
- Rght sde of the heart greaty
vasoconstrcton
o Increased pumonary artera
pressure
- Perphera artera pressure begns to
fa
- Congestve heart faure
- Death
EFFECTS OF ACCELERATORY FORCES ON
THE BODY
- Acceeratory forces
- Due to rapd changes n veocty and
drecton of moton n arpane and
spacecraft.
- Types:
o Lnear acceeraton
o Deceeraton
o Centrfuga acceeraton
mv
2
R
- measured n G
o + 1G = weght = -1G
o + 2G = 2x = -2G
o + 3G = 3x = -3G
EFFECTS OF CENTRIFUGAL FORCE ON THE
BODY
Postve G
Crcuatory System
- Transocaton of bood (ower part) -
ncrease HP ((ower part) -
Vasodaton - decrease VR - decrease
CO
- > than 4 to 6G - backout of vson -
unconscous
Vertebrae
- Fracture (> 20 G)
Negatve G
- Ehects are ess dramatc but more
damagng permanenty
Hyperema of the head (-4 to -6 G)
- Transocaton of bood (upper part) -
ncrease HP - transudaton of ud -
edema
- Rupture of bood vesse (rare -> -6G)
- Temporary bndness of the eye red-
out
PROTECTION
- Tghtenng of the abdomna musce
(+G)
- Use ant-G suts (+G)
Ehects of Lnear Acceeratory Forces
- Deeterous ehects are prevented by
sem recnng poston
WEIGHTLESSESS
- Experenced when a person s n
orbtng satete or a non propeed
spacecraft
- Person s not drawn to the bottom
sdes or top of the spacecraft but
smpy oat nsde the chamber
- Cause s not due to faure of gravty to
pu on the body
Probems:
- Moton sckness
- Transocaton of ud n the body
- Decrease physca actvty
- Decrease bood voume
- Decrease cardac output
- Decrease Ca
++
and PO4
-
- Decrease ABP
You might also like
- HB RespirationDocument6 pagesHB RespirationJessicaWiryantoNo ratings yet
- Knes 313 Chapter 6 ReviewDocument3 pagesKnes 313 Chapter 6 Reviewюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Applied Respiratory PhysiologyDocument4 pagesApplied Respiratory PhysiologyMitul JainNo ratings yet
- High Altitude and High Pressure (DIVING) M 20232024Document34 pagesHigh Altitude and High Pressure (DIVING) M 20232024aqiasaftryNo ratings yet
- Altitude PDFDocument47 pagesAltitude PDFMohd AsadNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FailureDocument5 pagesRespiratory FailureLovely Acabado Tampoco100% (1)
- RS 2nd PartDocument14 pagesRS 2nd Parthpcdhp4wkmNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Respiratory PrelabDocument23 pagesLab 6 Respiratory Prelabkkk13whyNo ratings yet
- 10 HighAltitudePhysiologyDocument29 pages10 HighAltitudePhysiologyFaiqa WaniNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Rate and Alveolar VentilationDocument9 pagesMetabolic Rate and Alveolar VentilationSimran SukhijaNo ratings yet
- Kin 14212 Altitude and Performance MWwebDocument13 pagesKin 14212 Altitude and Performance MWwebGursimar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapt 21 Part 1 OxygenationDocument4 pagesChapt 21 Part 1 Oxygenationssharma311No ratings yet
- My Own Critical Care NotesDocument4 pagesMy Own Critical Care NotesSamer GobreialNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure (ACUTE) : Dora M Alvarez MD LH 2004Document72 pagesRespiratory Failure (ACUTE) : Dora M Alvarez MD LH 2004Lovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- EBreathing Support 17Document44 pagesEBreathing Support 17lia ancillaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument192 pagesRespiratory SystemQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Respiratory FailureDocument8 pagesRespiratory FailureAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument3 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesMaahika MitraNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and PerfusionDocument2 pagesVentilation and PerfusionJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy: Dr. Subhankar ChatterjeeDocument49 pagesOxygen Therapy: Dr. Subhankar ChatterjeesubhankarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Regulation During ExerciseDocument20 pagesRespiratory Regulation During ExerciseDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (2)
- Oxygen Therapy: Prof. Dr. Ioana GrigorașDocument109 pagesOxygen Therapy: Prof. Dr. Ioana GrigorașAna-Maria Croitoru100% (1)
- AKLIMATISASIDocument16 pagesAKLIMATISASIsatyasanthiniNo ratings yet
- Ebme 202 NotesDocument2 pagesEbme 202 NotesShriya KannanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure: Dr. Sat Sharma Univ of ManitobaDocument38 pagesRespiratory Failure: Dr. Sat Sharma Univ of ManitobaGonzalo Venegas RojasNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument13 pagesMechanical VentilationNithiya NadesanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument35 pagesPulmonary Function Testsnirilib100% (4)
- Respiratory ModalitiesDocument87 pagesRespiratory ModalitiesLj Ferolino100% (2)
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument51 pagesRespiratory PhysiologyumaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Under StressDocument34 pagesThe Respiratory System Under Stressjaydoc_paed@yahoo.co.inNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument66 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationlenafitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Gas Transfer: Diffusing CapacityDocument7 pagesPulmonary Gas Transfer: Diffusing CapacityKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests ScribdDocument34 pagesPulmonary Function Tests ScribdNamita JadhaoNo ratings yet
- Phisylogy Respiratory2 Ø Ø Ù Ù Ù Ø Ù Ù Ù ÙDocument5 pagesPhisylogy Respiratory2 Ø Ø Ù Ù Ù Ø Ù Ù Ù Ùmaisa.alsalem4No ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Pernapasan Dr. MDocument87 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Pernapasan Dr. MARIF BSNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNo ratings yet
- Ards and RF FileDocument12 pagesArds and RF FileEdwin Delos Reyes Abu100% (1)
- Exercise in Copd: Dr. Anirban MallickDocument40 pagesExercise in Copd: Dr. Anirban MallickHiten GuptaNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of Gases PDFDocument34 pagesBreathing & Exchange of Gases PDFAmythNo ratings yet
- SPIROMETRYDocument5 pagesSPIROMETRYJayarubini JeyapalNo ratings yet
- Resp Physio SAQsDocument25 pagesResp Physio SAQsanaeshkl100% (1)
- Anatomi Fisiologi PernapasanDocument87 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi PernapasanAndre ChundawanNo ratings yet
- Hypoxia and CyanosisDocument33 pagesHypoxia and CyanosisRamlah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Oxygen SupplementationDocument15 pagesOxygen SupplementationEloisa BretañaNo ratings yet
- Altitude Și DivingDocument5 pagesAltitude Și DivingAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Altitude PhysiologyDocument88 pagesAltitude PhysiologyMoussa Kalifa N'GADJAGANo ratings yet
- Respiratory DiseasesDocument14 pagesRespiratory DiseasesKira100% (6)
- Respiratory Physiology ClearDocument80 pagesRespiratory Physiology Clearvelangni100% (1)
- High Altitude PhysiologyDocument33 pagesHigh Altitude Physiologydoctoroid100% (1)
- Adeyomoye Respiratory PhysiologyOER6954487Document25 pagesAdeyomoye Respiratory PhysiologyOER6954487hminuwa3No ratings yet
- Control of RespirationDocument14 pagesControl of RespirationgunawanNo ratings yet
- Mechvent Review (Topnotcher)Document284 pagesMechvent Review (Topnotcher)Gleo Matthew100% (1)
- Respiratory Physiology PostedDocument25 pagesRespiratory Physiology PostedYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument65 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationDaniel AryanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology NOTESDocument3 pagesRespiratory Physiology NOTESJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (1)
- Biochemical Case 1Document2 pagesBiochemical Case 1Affie SaikolNo ratings yet
- H.circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesH.circulatory SystemElleNo ratings yet
- D Physiology of RespirationDocument45 pagesD Physiology of RespirationValluri Mukesh100% (1)
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsFrom EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Determination of Biologically Actie Constituents of The Fruits of Cucumis Sativus Linn Using GC-MS AnalysisDocument5 pagesDetermination of Biologically Actie Constituents of The Fruits of Cucumis Sativus Linn Using GC-MS Analysisavian_roseNo ratings yet
- Brainstem ReflexesDocument2 pagesBrainstem Reflexesavian_rose100% (1)
- Physio - Water BalanceDocument8 pagesPhysio - Water Balanceavian_rose100% (2)
- Epithelial Tissue IIDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissue IIavian_roseNo ratings yet
- Lethal Midline Granuloma-Stewart Nasal Nk/T-Cell Lymphoma-0ur ExperienceDocument9 pagesLethal Midline Granuloma-Stewart Nasal Nk/T-Cell Lymphoma-0ur Experienceopi akbarNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The National Health Policy - 2017: July 2019Document3 pagesSalient Features of The National Health Policy - 2017: July 2019Deepanshu JharkhandeNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Case StudyDocument3 pagesHomeostasis Case Studyapi-332887331No ratings yet
- Water Treatment With Exceptional Virus Inactivation Using Activated Carbon Modified With Silver Ag and Copper Oxide CuO Nanoparticles PDFDocument13 pagesWater Treatment With Exceptional Virus Inactivation Using Activated Carbon Modified With Silver Ag and Copper Oxide CuO Nanoparticles PDFMarcela FernandesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Respiratory SystemDocument38 pagesChapter 10 - Respiratory SystemAsma MuhammadNo ratings yet
- The Sixth House - Psychology of Self-Integration - Robert Glasscock - B00F07KNZ0 - EBOKDocument155 pagesThe Sixth House - Psychology of Self-Integration - Robert Glasscock - B00F07KNZ0 - EBOKAndrew Khabaza100% (6)
- Bivalirudin Anticoagulant1Document6 pagesBivalirudin Anticoagulant1walid hassanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For BipolarDocument3 pagesNursing Care For BipolarAnthonyChapotin100% (2)
- Utsmidterms PDFDocument10 pagesUtsmidterms PDFJazzie SorianoNo ratings yet
- Course Task 19Document1 pageCourse Task 19Laira CañeteNo ratings yet
- Clinico-Microbiological Spectrum of Hemodialysis Catheter-Related Blood Stream Infections: A Concise ReviewDocument7 pagesClinico-Microbiological Spectrum of Hemodialysis Catheter-Related Blood Stream Infections: A Concise ReviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Physiology Study Guide CH 7 Nervous System Neurons KeyDocument4 pagesPhysiology Study Guide CH 7 Nervous System Neurons KeyJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Paper - B Written Test Paper For Selection of Teachers: CSB 2013 English (PGT) : Subject Code: P11Document4 pagesPaper - B Written Test Paper For Selection of Teachers: CSB 2013 English (PGT) : Subject Code: P11Amrit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On NADOPOD Regulations 2004Document28 pagesGuidelines On NADOPOD Regulations 2004LuqmanAlHakimNo ratings yet
- Ra 4688Document6 pagesRa 4688JeaneteCaragNo ratings yet
- Medical Books December 2010Document21 pagesMedical Books December 2010matchealthNo ratings yet
- Nicu ReportDocument66 pagesNicu ReportEr Shah Rukh QadriNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Ashwatha Ksheer Sutra and Udumber Ksheer Sutra in The Management of Bhagandara (Fistula in ANO)Document9 pagesComparative Study of Ashwatha Ksheer Sutra and Udumber Ksheer Sutra in The Management of Bhagandara (Fistula in ANO)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Guía Manejo Del Shock 2023Document67 pagesGuía Manejo Del Shock 2023Alvaro ArriagadaNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorder WebQuestDocument2 pagesEating Disorder WebQuestFiona Wang100% (1)
- Hex A Chloro But A DieneDocument15 pagesHex A Chloro But A DieneAfraNo ratings yet
- 3 Antenatal CareDocument24 pages3 Antenatal CareDrSabah Lotfy100% (1)
- Anemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic MacrocyticDocument1 pageAnemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic Macrocyticمحمد عقيلي100% (1)
- Concept of Community and Environmental HealthDocument17 pagesConcept of Community and Environmental HealthJoy Gunday100% (1)
- 100 Test Aarogya 2.0:: Mrs - Gunjan MisraDocument19 pages100 Test Aarogya 2.0:: Mrs - Gunjan Misramomo misraNo ratings yet
- Ozomed BrochureDocument4 pagesOzomed BrochurechirakiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical CareDocument114 pagesPharmaceutical CareRisdaFitriaNo ratings yet
- NGS and Sequence Analysis With Biopython For Prospective Brain Cancer Therapeutic StudiesDocument14 pagesNGS and Sequence Analysis With Biopython For Prospective Brain Cancer Therapeutic StudiesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics For UTIs in Pregnancy - What You Need To Know - GoodRxDocument22 pagesAntibiotics For UTIs in Pregnancy - What You Need To Know - GoodRxricardoatejassNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Transformation Summit 2022 Day 3Document5 pagesDiabetes Transformation Summit 2022 Day 3Paul Ioan PopescuNo ratings yet