Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tute 3
Uploaded by
mgayanan0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
392 views4 pagesThis document contains review questions for a computer networks course. It covers topics such as carrier signals, data encoding techniques, error detection, sampling theory, pulse code modulation, and time division multiplexing. There are 25 questions in total asking students to define terms, distinguish between concepts, perform calculations, draw signal diagrams, and solve problems related to encoding digital data for transmission over analog networks.
Original Description:
computer networks
Original Title
tute 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains review questions for a computer networks course. It covers topics such as carrier signals, data encoding techniques, error detection, sampling theory, pulse code modulation, and time division multiplexing. There are 25 questions in total asking students to define terms, distinguish between concepts, perform calculations, draw signal diagrams, and solve problems related to encoding digital data for transmission over analog networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
392 views4 pagesTute 3
Uploaded by
mgayananThis document contains review questions for a computer networks course. It covers topics such as carrier signals, data encoding techniques, error detection, sampling theory, pulse code modulation, and time division multiplexing. There are 25 questions in total asking students to define terms, distinguish between concepts, perform calculations, draw signal diagrams, and solve problems related to encoding digital data for transmission over analog networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ICT2232 Computer Networks Review questions set3
1. Define carrier signal and its role in analog transmission.
2. Distinguish between a signal element and a data element.
3. Distinguish between data rate and signal rate.
4. What is QAM?
5. Calculate the baud rate for the given bit rate and type of modulation.
a. 2000 bps, BFSK
b. 4000 bps, BASK
c. 6000 bps, BPSK
6. Calculate the bit rate for the given baud rate and type of modulation.
a. 1000 baud, BFSK
b. 1000 baud, BASK
c. 1000 baud, BPSK
7. Given the bit pattern 011011111000011, encode this data using BASK, BFSK, and BPSK.
8. Explain the difference between NRZ-L and NRZ-I.
9. Define bi-phase encoding and describe two bi-phase encoding techniques.
10. Encode the following bit streams (assuming that the last signal level has been positive) using
NRZ-L, NRZ-I, RZ, Manchester, differential Manchester and Bipolar AMI scheme.
a. 00000000
b. 11111111
c. 01010101
d. 00110011
e. 01001110
11. Encode the following bits streams using 2B 1Q scheme.
a. 0000000000000000
b. 1111111111111111
c. 0101010101010101
d. 0011001100110011
12. Consider a stream of binary data consisting of a long sequence of 1s followed by a zero
followed by a long string of 1s (assuming the most recent preceding 0 bit (pseudoternary) has
a negative voltage). Draw the waveform for this sequence using
a. NRZ-L
b. Bipolar-AMI
c. Pseudoternary
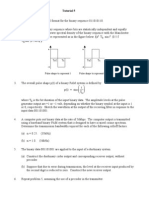
13. Find the 8-bit data stream for each case depicted in Figure below.
14. The waveform of Figure below belongs to a Manchester encoded binary data stream.
Determine the beginning and end of bit periods and give the data sequence.
15. The bipolar-AMI waveform representing the binary sequence 0100101011 is transmitted over
a noisy channel. The received waveform is shown in Figure below; it contains a single error.
Locate the position of this error and explain your answer.
16. One positive side effect of bipolar encoding is that a bipolar violation (two consecutive +
pulses or two consecutive - pulses separated by any number of zeros) indicates to the receiver
that an error has occurred in transmission. Unfortunately, upon the receipt of such a violation,
the receiver does not know which bit is in error (only that an error has occurred). For the
received bipolar sequence
which has one bipolar violation, construct two scenarios (each of which involves a different
transmitted bit stream with one transmitted bit being converted via an error) that will produce
this same received bit pattern.
17. What is the Nyquist sampling rate for each of the following signals?
a. A low-pass signal with bandwidth of 200 KHz?
b. A band-pass signal with bandwidth of 200 KHz if the lowest frequency is 100 KHz?
18. Consider an audio signal with spectral components in the range 300 to 3000 Hz. Assume that
a sampling rate of 7000 samples per second will be used to generate a PCM signal.
a. For what is the number of uniform quantization levels needed?
b. What data rate is required?
19. What does the sampling theorem tell us concerning the rate of sampling required for an
analog signal?
20. Consider an analog data is shown in the figure below.
The sampled amplitude value of this anolog data with discrete time intervals shown in table
below (assume sample amplitudes are between -1.5 and +2.5 V).
Time Analog signal value [V]
0 2.12
1 1.84
2 -0.08
3 -1.07
4 -0.02
5 0.42
6 1.80
7 1.30
8 1.00
9 -0.50
10 -1.12
With 16 quantization levels encode the analog data to digital data using PCM.
21. Describe the goals of multiplexing.
22. We need to use TDM and combine 20 digital sources, each of 100 Kbps. Each output slot
carries 1 bit from each digital source, but one extra bit is added to each frame for
synchronization. Answer the following questions:
a. What is the size of an output frame in bits?
b. What is the output frame rate?
c. What is the duration of an output frame?
d. What is the output data rate?
e. What is the efficiency of the system (ratio of useful bits to the total bits)
23. Repeat above Exercise if each output slot carries 2 bits from each source.
24. Figure below shows a multiplexer in a TDM system. Each output slot is only 10 bits long (3
bits taken from each input plus 1 framing bit). What is the output stream? The bits arrive at
the multiplexer as shown by the arrows.
25. Figure below shows a de-multiplexer in a TDM. If the input slot is 16 bits long (no framing
bits), what is the bit stream in each output? The bits arrive at the de-multiplexer as shown by
the arrows.
You might also like
- Assignment 2 DatacomDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 DatacomFarman Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- DC Assignment 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesDC Assignment 2019 PDFRashmi VermaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question For FInal ExamDocument6 pagesSample Question For FInal ExamAmir MuzzammilNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4-SolutionDocument11 pagesTutorial 4-SolutionZaidi Mat ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Super SpecialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Digital Transmission - Exercise Question With SolutionDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - Digital Transmission - Exercise Question With SolutionMd Saidur Rahman Kohinoor94% (108)
- Dcs Assignment I - A1 Digital AssinmentDocument2 pagesDcs Assignment I - A1 Digital AssinmentYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3-Assignment I - A1 DIGITAL ASSINMENTDocument2 pages3-Assignment I - A1 DIGITAL ASSINMENTRaj GaneshNo ratings yet
- DC aDCghskjskksks FjsDocument4 pagesDC aDCghskjskksks FjsSaiteja GundapuNo ratings yet
- Baseband Questions StudentsDocument3 pagesBaseband Questions StudentsRishi JhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4+ SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 4+ SolutionsMujaahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Data Communication: By:Eng - Alaa I.HaniyDocument8 pagesData Communication: By:Eng - Alaa I.Haniypömo cNo ratings yet
- Using Complete Sentences Written in Your Own Words, Explain The Meaning of The FollowingDocument6 pagesUsing Complete Sentences Written in Your Own Words, Explain The Meaning of The FollowingVIKRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Assignment FinaleDocument1 pageAssignment FinaleSilas Osei-PokuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document3 pagesAssignment No. 2Faizan ButtNo ratings yet
- Advanced Digital Communication1 December 2011Document2 pagesAdvanced Digital Communication1 December 2011Sneha UpadhyayulaNo ratings yet
- Final Tutorial PDFDocument5 pagesFinal Tutorial PDFAnuj JainNo ratings yet
- Central College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiDocument8 pagesCentral College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiqweweNo ratings yet
- 12 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 19 2012 - Practice ProblemsDocument3 pages12 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 19 2012 - Practice ProblemsEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015Document3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015shreyas_stinsonNo ratings yet
- DC Question BankDocument6 pagesDC Question BankBha RathNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument8 pagesProblem SetADSRNo ratings yet
- NWS 124 Tutorial Sheet 2 (Solutions)Document6 pagesNWS 124 Tutorial Sheet 2 (Solutions)AnnNo ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesPractice Questionspratik shuklaNo ratings yet
- 09 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Practice Problems - March 14 2012Document3 pages09 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Practice Problems - March 14 2012creepymaggotsNo ratings yet
- DCDocument8 pagesDCharshit420No ratings yet
- Comp 3271Document6 pagesComp 3271Ambrose S.No ratings yet
- DCS SolnDocument6 pagesDCS SolnSandeep Kumar100% (1)
- ASSIG5Document1 pageASSIG5meowmeow88No ratings yet
- Digi Comm Model QP P1Document3 pagesDigi Comm Model QP P1bku14677No ratings yet
- Ec2311 - Communication Engineering PDFDocument9 pagesEc2311 - Communication Engineering PDFThasleema BanuNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit IDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank Unit ISnehal RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Dcom QuestionDocument3 pagesDcom Questionsushant sahooNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationDocument16 pagesDigital CommunicationAli Najim Al-AskariNo ratings yet
- FP Data CommDocument5 pagesFP Data CommExperza HillbertNo ratings yet
- QPDocument3 pagesQPAnonymous 9WJ7YeGNo ratings yet
- List of Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesList of Important Questions4025 deeptika pNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chap 2Document3 pagesExercise Chap 2chantinh_hd190No ratings yet
- HDB3Document3 pagesHDB3Ari Machmuddi Kanosri100% (1)
- Ee150hw04 2012Document2 pagesEe150hw04 2012thinkberry22No ratings yet
- Fall 2014 Computer Communication Networks HW#4 (Due Date: 2014/10/20 Hand in On E3 System)Document2 pagesFall 2014 Computer Communication Networks HW#4 (Due Date: 2014/10/20 Hand in On E3 System)Tài LâmNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2: Chapters 2-10: BS Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pagesAssignment No.2: Chapters 2-10: BS Electronics EngineeringBianca QuizonNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentpaper.2014No ratings yet
- Question Bank - DC 6501Document10 pagesQuestion Bank - DC 6501karthikamageshNo ratings yet
- Kasraian ECET375 Week2Document42 pagesKasraian ECET375 Week2Raul PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Gate BitsDocument4 pagesDigital Communication Gate BitsVn LakshmiNo ratings yet
- DC Question BankDocument2 pagesDC Question BankAnanda HembramNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document4 pagesQuiz 1Irish MalibanNo ratings yet
- S (3) : S E T: College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument3 pagesS (3) : S E T: College of Engineering & TechnologyMMhammed AlrowailyNo ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR07 Set No. 2Anonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- CEG3185 Past Final - Docx - 1438983146678Document6 pagesCEG3185 Past Final - Docx - 1438983146678TurabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26Document52 pagesLecture 26Cu BomNo ratings yet
- Ec2311 - Communication EngineeringDocument9 pagesEc2311 - Communication EngineeringBharath RamanNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDFrom EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNo ratings yet
- Modified Liu Estimator With Incomplete Prior Information in Misspecified Regression ModelDocument2 pagesModified Liu Estimator With Incomplete Prior Information in Misspecified Regression ModelmgayananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - MulticollinearityDocument26 pagesChapter 05 - Multicollinearitymgayanan100% (1)
- Transmission of Digital SignalsDocument8 pagesTransmission of Digital SignalsmgayananNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital DataDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital DatamgayananNo ratings yet
- Analog TransmissionDocument8 pagesAnalog TransmissionmgayananNo ratings yet
- CC3502 Computer Networks: Multiplexing and IP Address Tutorial SolutionsDocument4 pagesCC3502 Computer Networks: Multiplexing and IP Address Tutorial Solutionsmgayanan100% (1)
- Stat QuizDocument5 pagesStat Quizmgayanan0% (1)
- MVR - Analog LinksDocument62 pagesMVR - Analog LinksSonalSinghNo ratings yet
- EC SyllabusDocument79 pagesEC SyllabusgorgonbotNo ratings yet
- LC5C5PRO BUM 5268596-100 Rev A.bookDocument891 pagesLC5C5PRO BUM 5268596-100 Rev A.bookErwynsonsaut Simanjuntak100% (1)
- BEE4413 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument3 pagesBEE4413 Digital Signal Processingdinie90No ratings yet
- Elec4505 Exp0Document7 pagesElec4505 Exp0muafhanNo ratings yet
- How To Work On SMT & PSTDocument16 pagesHow To Work On SMT & PSTShamim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dr. Patrick Flanagan's NEUROPHONE - Bypassing DeafnessDocument7 pagesDr. Patrick Flanagan's NEUROPHONE - Bypassing DeafnessJason Verbelli100% (6)
- Ade7752 7752aDocument24 pagesAde7752 7752aKram Nhoj TabatabNo ratings yet
- Canon MF6600 / D1100 Series Service ManualDocument227 pagesCanon MF6600 / D1100 Series Service ManualJoeCihlarNo ratings yet
- Using MATLAB For Signal Analysis PDFDocument56 pagesUsing MATLAB For Signal Analysis PDFAhmad PohanNo ratings yet
- SAS Lab ManualDocument51 pagesSAS Lab Manualjayant5253No ratings yet
- TS-870 Service Manual (OCR)Document157 pagesTS-870 Service Manual (OCR)yu7aw100% (1)
- Magnetic BearingDocument19 pagesMagnetic BearingMamesh MathankarNo ratings yet
- Terminals GALILEOSKY Glonass/Gps V5.1 User's Manual: Quality Reliability SimplicityDocument93 pagesTerminals GALILEOSKY Glonass/Gps V5.1 User's Manual: Quality Reliability SimplicityNikos PapadakisNo ratings yet
- FM ModulationDocument8 pagesFM ModulationDelinger TominNo ratings yet
- ETSI ES 201 235-3: Specification of Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) Transmitters and Receivers Part 3: ReceiversDocument12 pagesETSI ES 201 235-3: Specification of Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) Transmitters and Receivers Part 3: Receivershadiranji4No ratings yet
- Instalacion VR5000Document60 pagesInstalacion VR5000Carlos Andres Silva MaureiraNo ratings yet
- S100 IO HardwareDocument268 pagesS100 IO HardwareFilomenaFerreira100% (1)
- Kalorimetar Data Sheet UH50 - UH106 101kDocument15 pagesKalorimetar Data Sheet UH50 - UH106 101kbobesponjakockaloneNo ratings yet
- Iec 60255-127 2010Document54 pagesIec 60255-127 2010karimi-15No ratings yet
- Syllabus Aryabhatta Knowledge UnivDocument239 pagesSyllabus Aryabhatta Knowledge Univjamesdd10100% (1)
- Copy of Final Report PROJ-FINALDocument34 pagesCopy of Final Report PROJ-FINALMona SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wavelets and Wavelet Transforms - A Primer, Brrus C. S., 1998.Document281 pagesIntroduction To Wavelets and Wavelet Transforms - A Primer, Brrus C. S., 1998.Nitesh GuindeNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Commnication Unit 4 VTUDocument41 pagesMultimedia Commnication Unit 4 VTUraghudathesh100% (1)
- Statistical Analysis System For Use With Public Communication Facility (US Patent 4792968)Document38 pagesStatistical Analysis System For Use With Public Communication Facility (US Patent 4792968)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Protection Relays Guide PDFDocument56 pagesProtection Relays Guide PDFrameez_zafar6138No ratings yet
- 1769 td006 - en PDocument132 pages1769 td006 - en PpaplusNo ratings yet
- Emco Eaom 210 ATS Gen. Set Module FLDocument154 pagesEmco Eaom 210 ATS Gen. Set Module FLAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Itb-05c Linearisation of ThermocoupleDocument20 pagesItb-05c Linearisation of Thermocouplekaushikei22No ratings yet
- Ffe Dfe ExcerptDocument14 pagesFfe Dfe ExcerptSaujal VaishnavNo ratings yet