Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PETE 411 Well Drilling: Lesson 7 Drilling Bits - Drag Bits
Uploaded by
Oswaldo Chihuala BustamanteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PETE 411 Well Drilling: Lesson 7 Drilling Bits - Drag Bits
Uploaded by
Oswaldo Chihuala BustamanteCopyright:
Available Formats
1
PETE 411
Well Drilling
Lesson 7
Drilling Bits - Drag Bits
2
Contents
The Ideal Bit
Drag Bits
Fishtail Type
Natural Diamond
Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
(PDC)
Relative Costs of Bits
3
Read: ADE, Ch.5 (bits)
HW # 3: due 9 -15 - 04
4
The purpose of Chapter 5 (ADE)
is to introduce the student
to the:
Rotary Drill bits
selection and
operation
of rotary drilling bits.
5
Rotary Drilling Bits
Bit types available
Criteria for selecting the best bit for a
given situation
Standard methods for evaluating dull bits
Factors affecting bit wear and drilling
speed
Optimization of bit weight and rotary
speed
6
Bit Types Available
Drag bits (fixed cutter blades)
Fishtail bit
Natural diamond bits
PDC Bits (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact)
Rolling cutter bits (rock bits - with cones)
Mill tooth bits
Tungsten carbide bits
7
The Ideal Bit *
1. High drilling rate
2. Long life
3. Drill full-gauge, straight hole
4. Moderate cost
* (Low cost per ft drilled)
8
The Ideal Bit
Hardness (soft, medium, hard)
abrasiveness
cuttings stickiness
other considerations e.g. cost
The Ideal Bit will depend on the type
of formation to be drilled
9
Drag Bits
Drag bits drill by physically plowing
or machining cuttings from the
bottom of the hole.
10
Drag Bits
Cutter may be made from:
Steel
Tungsten carbide
Natural diamonds
Polycrystalline diamonds (PDC)
Drag bits have no moving parts, so it is less likely
that junk will be left in the hole.
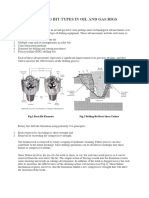
11 Fishtail type drag bit
12
Natural Diamond Bits PDC Bits
13
Natural
Diamond
bit
junk slot
cuttings
radial flow
high p
across face
14
Soft
Formation
Diamond bit
Larger diamonds
Fewer diamonds
Pointed nose
15
Hard
Formation
Diamond bit
Smaller diamonds
More diamonds
Flatter nose
16
Natural Diamonds
The size and spacing of diamonds on a
bit determine its use.
NOTE: One carat = 200 mg precious stones
What is 14 carat gold?
17
Natural Diamonds
2-5 carats - widely spaced diamonds
are used for drilling soft formations such as
soft sand and shale
1/4 - 1 carat - diamonds are used for drilling
sand, shale and limestone formations of
varying (intermediate) hardness.
1/8 - 1/4 carat - diamonds, closely spaced,
are used in hard and abrasive formations.
18
When to Consider Using a Natural
Diamond Bit?
1. Penetration rate of rock bit < 10 ft/hr.
2. Hole diameter < 6 inches.
3. When it is important to keep the bit and
pipe in the hole.
4. When bad weather precludes making trips.
5. When starting a side-tracked hole.
6. When coring.
* 7. When a lower cost/ft would result
19
Top view of diamond bit
20
Side view of
diamond bit
21
PDC
bits
Courtesy
Smith Bits
22
PDC Cutter
23
24
At about $10,000-150,000 apiece, PDC bits cost five to 15 times more
than roller cone bits
PDC Bits
25
The Rise in Diamond Bit Market Share
26
Coring
bit
PDC +
natural
diamond
27
Bi-Center bit
Courtesy Smith Bits
28
Relative Costs of Bits
Diamond WC Insert Milled
Bits Bits Tooth Bits
$/Bit
Diamond bits typically cost several times as much as tri-
cone bits with tungsten carbide inserts (same bit diam.)
A TCI bit may cost several times as much as a
milled tooth bit.
29
PDC Bits
Ref: Oil & Gas Journal, Aug. 14, 1995, p.12
Increase penetration rates in oil and gas
wells
Reduce drilling time and costs
Cost 5-15 times more than roller cone bits
1.5 times faster than those 2 years earlier
Work better in oil based muds; however,
these areas are strictly regulated
30
PDC Bits
Parameters for effective use
include
weight on bit
mud pressure
flow rate
rotational speed
31
PDC Bits
Economics
Cost per foot drilled measures Bit
performance economics
Bit Cost varies from 2% - 3% of total cost,
but bit affects up to 75% of total cost
Advantage comes when
- the No. of trips is reduced, and when
- the penetration rate increases
32
PDC Bits
Bit Demand
U.S Companies sell > 4,000 diamond drill
bits/year
Diamond bit Market is about $200
million/year
Market is large and difficult to reform
When bit design improves, bit drills longer
33
PDC Bits
Improvements in bit stability, hydraulics,
and cutter design => increased footage per bit
Now, bits can drill both harder and softer
formations
Formations in US are not as conducive to PDC
bits as formations in some other areas
Bit Demand, contd
34
PDC Bits
By year 2000:
PDC bits had control of about 1/3 of
the worldwide drilling market
The total PDC bit market had risen
to $400 million per year
U.S. bit manufacturers had a 2/3
share of this market
35
PDC Bits
Improvements are a result of the following:
Research
Good Engineering Practices
Competition with other PDC bit
manufacturers/rock bit industries
Bit Design
General Electric introduced PDC in 1973
Product Life = 2 years
36
PDC Bits
Bit Design, contd
Now, a speciality tool
PDC bit diameter varies from 3.5 in to 17.5 in
Goals of hydraulics:
clean bit without eroding it
clean cuttings from bottom of hole
37
PDC Bits
Factors that limit operating range
and economics:
Lower life from cutter fractures
Slower ROP from bad cleaning
Bit design, contd
38
PDC Bits
Cutters
Consist of thin layer of bonded diamond
particles + a thicker layer of tungsten carbide
Diamond
10x harder than steel
2x harder than tungsten carbide
Most wear resistant material
but is brittle and susceptible to damage
39
PDC Bits
Diamond/Tungsten Interface
Bond between two layers on cutter is
critical
Consider difference in thermal
expansion coefficients and avoid
overheating
Made with various geometric shapes to
reduce stress on diamond
Cutters, contd
40
PDC Bits
Various Sizes
Experimental dome shape
Round with a buttress edge for high
impact loads
Polished with lower coefficient of friction
Cutters, contd
41
PDC Bits
Bit Whirl (bit instability)
Bit whirl = any deviation of bit rotation
from the bits geometric center
Caused by cutter/rock interaction forces
PDC bit technology sometimes
reinforces whirl
Can cause PDC cutters to chip and break
42
PDC Bits
Preventing Bit Whirl
Cutter force balancing
Bit asymmetry
Gauge design
Bit profile
Cutter configuration
Cutter layout
43
PDC Bits
Applications
PDC bits are used primarily in
Deep and/or expensive wells
Soft - medium hard formations
44
PDC Bits
Advances in metallurgy, hydraulics
and cutter geometry
Have not cut cost of individual bits
Have allowed PDC bits to drill longer
and more effectively
Allowed bits to withstand harder
formations
Application, contd
45
PDC Bits
Application, contd
PDC bits advantageous for high rotational
speed drilling and in deviated hole section
drillings
Most effective: very weak, brittle formations
(sands, silty claystone, siliceous shales)
Least effective: cemented abrasive sandstone,
granites
46
Grading of Worn PDC Bits
CT - Chipped Cutter
Less than 1/3 of cutting
element is gone
BT - Broken Cutter
More than 1/3 of cutting
element is broken to
the substrate
47
Grading of Worn PDC Bits contd
LT - Lost Cutter
Bit is missing one or
more cutters
LN - Lost Nozzle
Bit is missing one or
more nozzles
48
Table 7.7 - Commonly Used Bit Sizes
For Running API Casing
Casing Size Coupling Size Common Bit
(OD in.) (OD in.) Sizes Used (in.)
4 1/2 5.0 6, 6
1/8
, 6
1/4
5 5.563 6
1/2
, 6
3/4
5 1/2 6.050 7
7/8
, 8
3/8
6 6.625 7
7/8
, 8
3/8
, 8
1/2
6 5/8 7.390 8
1/2
, 8
5/8
, 8
3/4
7 7.656 8
5/8
, 8
3/4
, 9
1/2
7 5/8 8.500 9
7/8
, 10
5/8
, 11
8 5/8 9.625 11, 12
1/4
9 5/8 10.625 12
1/4
, 14
3/4
10 3/4 11.750 15
13 3/8 14.375 17
1/2
16 17 20
20 21 24, 26
49
END
of
Lesson 7
- Drag Bits -
You might also like
- Phys 1Document5 pagesPhys 1Sandra Phan50% (2)
- Boiler Efficiency Calculations SheetDocument5 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculations Sheetkalyanm20351578% (9)
- Bits NozzlesDocument197 pagesBits Nozzlesiman100% (2)
- Pete321 Chapter4Document20 pagesPete321 Chapter4Jessica Cecilia Silva AnguloNo ratings yet
- Drill CompleteDocument35 pagesDrill Completesiva kumarNo ratings yet
- Marine PurifierDocument30 pagesMarine PurifierJayDelosSantos100% (1)
- The Ideal Bit Drag Bits: Fishtail Type Natural Diamond Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC)Document45 pagesThe Ideal Bit Drag Bits: Fishtail Type Natural Diamond Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC)ShourovjossNo ratings yet
- Drilling Bits Selection GuideDocument35 pagesDrilling Bits Selection GuideMuhammad Shahid RahimNo ratings yet
- PDC BitsDocument40 pagesPDC BitsRizwan Farid100% (1)
- TRICONE VS PDC BITS: WHICH IS BETTERDocument6 pagesTRICONE VS PDC BITS: WHICH IS BETTERUlianov GilNo ratings yet
- Overview of Drilling OperationsDocument18 pagesOverview of Drilling Operationsali nahiNo ratings yet
- Notes 4Document18 pagesNotes 4Ruben ChirinosNo ratings yet
- BitsDocument94 pagesBitsBurt Powell100% (3)
- Fixed Cutter Bits: Early Diamond Bit HistoryDocument24 pagesFixed Cutter Bits: Early Diamond Bit HistoryTim Clarke100% (1)
- Drill BitsDocument38 pagesDrill Bitsrizky8474No ratings yet
- Ideal One Does The Job With Least Overall Cost - Many Manufacturers With Various Designs Suited For Different Formations and ConditionsDocument15 pagesIdeal One Does The Job With Least Overall Cost - Many Manufacturers With Various Designs Suited For Different Formations and ConditionsShiela ONo ratings yet
- 7 - Drill BitDocument17 pages7 - Drill Bitlovely petsNo ratings yet
- AsdDocument3 pagesAsdMuStafaAbbasNo ratings yet
- Part 6 Drilling BitsDocument27 pagesPart 6 Drilling BitsJood SultanNo ratings yet
- Bit TheoryDocument116 pagesBit Theoryjoonak konwar100% (8)
- Rotary Drilling Bits GuideDocument153 pagesRotary Drilling Bits GuideHeris SitompulNo ratings yet
- Drilling Bits SalamDocument93 pagesDrilling Bits Salamkmelloistaken100% (3)
- Rock BitsDocument17 pagesRock Bitssuresh_501No ratings yet
- Week 6 CasingsDocument21 pagesWeek 6 CasingsSidra IqbalNo ratings yet
- Drilling Bits: Islamic Azad University Science and Research Branch Drilling DepartmentDocument28 pagesDrilling Bits: Islamic Azad University Science and Research Branch Drilling Departmentali nahiNo ratings yet
- Drilling BitsDocument9 pagesDrilling BitsAli AbdelrahemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bits For Oil Well Drilling Introduction To Diamond BitsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Bits For Oil Well Drilling Introduction To Diamond BitsRebar KakaNo ratings yet
- WEPS PDC Reamer Presentation Final5!18!12 AK Time 0425p 2Document37 pagesWEPS PDC Reamer Presentation Final5!18!12 AK Time 0425p 2eleceron7919No ratings yet
- PDC Bits CourseDocument76 pagesPDC Bits CourseRobert Koch100% (1)
- PDC BitsDocument75 pagesPDC Bitsamin peyvand100% (1)
- Drilling BitDocument21 pagesDrilling BitIzzatee Zainuddin100% (1)
- Drilling Bits RehanDocument11 pagesDrilling Bits Rehanrehanromeo010No ratings yet
- Overview of Drill BitsDocument153 pagesOverview of Drill BitsJohnSmithNo ratings yet
- 5.21 Drill BitsDocument52 pages5.21 Drill BitsSamuel OkezieNo ratings yet
- Drill BitsDocument52 pagesDrill BitsBoyNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit - WikipediaDocument55 pagesDrill Bit - Wikipediaaddisugebre2125No ratings yet
- Rotary Drilling BitsDocument17 pagesRotary Drilling BitsMin Thant MaungNo ratings yet
- Drilling Engineering Pe 311 An Introduction To Drilling Drill BitsDocument14 pagesDrilling Engineering Pe 311 An Introduction To Drilling Drill BitsHamaamNo ratings yet
- Drilling Bit SelectionDocument8 pagesDrilling Bit SelectionanateghpourNo ratings yet
- TSP Bits: by Jack Leave A CommentDocument8 pagesTSP Bits: by Jack Leave A CommentMuhammad Saqib JanNo ratings yet
- DI Geoset Stratapax EngDocument8 pagesDI Geoset Stratapax Engmyounis82No ratings yet
- Cutting Tool FundamentalsDocument25 pagesCutting Tool FundamentalssatenawuNo ratings yet
- Drilling bitsDocument23 pagesDrilling bitsFaniyi Hussein KehindeNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Drill BitsDocument23 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Drill BitsIndah CharismasariNo ratings yet
- Trident PDC CuttersDocument2 pagesTrident PDC CuttersjobsNo ratings yet
- Steeringwheel BitDocument22 pagesSteeringwheel BitAaron MartinNo ratings yet
- Drill BitDocument22 pagesDrill BitPinto JovitaNo ratings yet
- Different Drill Bits Used in Drilling OperationsDocument31 pagesDifferent Drill Bits Used in Drilling OperationsPeterMarkNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON Drill Bits: Submitted To: Er. Akash Rana (HOD) Petroleum DepttDocument26 pagesA Presentation ON Drill Bits: Submitted To: Er. Akash Rana (HOD) Petroleum DepttJohar marwatNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Grinding ProcessesDocument11 pagesMechanics of Grinding ProcessesIndranil BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Bits Reamers & Stabilizer Types in Drilling Oil and Gas IndustryDocument15 pagesBits Reamers & Stabilizer Types in Drilling Oil and Gas IndustryrahulNo ratings yet
- Bit TechnologyDocument86 pagesBit TechnologyGlen RoelNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tools TechnologyDocument47 pagesCutting Tools TechnologyJeff HardyNo ratings yet
- Drilling & Geology 2012 ResourcePres Festningen LongDocument65 pagesDrilling & Geology 2012 ResourcePres Festningen Longruzzo2003No ratings yet
- Presentation1 PP Sem 3 Selection of Grinding WheelDocument41 pagesPresentation1 PP Sem 3 Selection of Grinding Wheeltanvi tamhaneNo ratings yet
- Selecting Bits Based on Formation DataDocument7 pagesSelecting Bits Based on Formation DataSamad Ali SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Proposal of Stinger BitsDocument22 pagesProposal of Stinger BitsAbhinav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Turning Wood with Carbide Tools: Techniques and Projects for Every Skill LevelFrom EverandTurning Wood with Carbide Tools: Techniques and Projects for Every Skill LevelRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Classic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersFrom EverandClassic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 2da PracticaDocument13 pages2da PracticaOswaldo Chihuala BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Solution 15Document15 pagesSolution 15Oswaldo Chihuala Bustamante100% (2)
- TA ED RegularDocument9 pagesTA ED RegularOswaldo Chihuala BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Exam 07Document10 pagesExam 07Oswaldo Chihuala BustamanteNo ratings yet
- PVTDocument3 pagesPVTOswaldo Chihuala BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Libro 1Document3 pagesLibro 1Oswaldo Chihuala BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Libro 1Document3 pagesLibro 1Oswaldo Chihuala BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Aws Gtaw Study GuideDocument2 pagesAws Gtaw Study GuideTouil HoussemNo ratings yet
- 1 SR Star Jee Main GTM 02 - 03 01 2024 KeyDocument14 pages1 SR Star Jee Main GTM 02 - 03 01 2024 Keyjahnavimogarala9No ratings yet
- Paper 4 Jun 2001 PhysicsDocument2 pagesPaper 4 Jun 2001 Physicssolarixe100% (1)
- PH Scale BrochureDocument1 pagePH Scale BrochureMherwin RetanalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document6 pagesExperiment 6Sobana Kanthi33% (3)
- HPLC ExperimentDocument4 pagesHPLC ExperimentFrances PaulineNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Metal Working Process ClassificationDocument5 pagesManufacturing and Metal Working Process ClassificationPeeka Prabhakara RaoNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument12 pagesResearch PaperKiran Niazi100% (1)
- MKS 112 GEN AZ7 SP 01 A Specification For PaintingDocument31 pagesMKS 112 GEN AZ7 SP 01 A Specification For PaintingĐiệnBiênNhâm100% (2)
- Dental Materials: Metals (Alloys) Non-MetalsDocument32 pagesDental Materials: Metals (Alloys) Non-MetalsShahriar honarmandNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument22 pagesHPLCKafi Mahmood NahinNo ratings yet
- Thermaline 400 Finish PDSDocument3 pagesThermaline 400 Finish PDSQuy RomNo ratings yet
- Msds Icr 122 LSFDocument12 pagesMsds Icr 122 LSFWisnu AbaraiNo ratings yet
- PSA Oxygen Generator: Typical ApplicationsDocument2 pagesPSA Oxygen Generator: Typical ApplicationsRaghu Vir ArjampudiNo ratings yet
- Ipc2022-86856 Influence of Strain Hardening Model On The Corlastm Model ForDocument12 pagesIpc2022-86856 Influence of Strain Hardening Model On The Corlastm Model ForOswaldo MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Macronutrient Project FinalDocument6 pagesMacronutrient Project Finalapi-259363834No ratings yet
- Techstuff 3.09Document117 pagesTechstuff 3.09Hazairin As-Shiddiq RahmanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power: Pros, Cons and FutureDocument4 pagesNuclear Power: Pros, Cons and FutureSamarthNo ratings yet
- Entner Duodroff PathwayDocument2 pagesEntner Duodroff PathwayDr. SHIVA AITHALNo ratings yet
- UTP ABRADISC 6000 Offers Cost-Efficient Wear ProtectionDocument4 pagesUTP ABRADISC 6000 Offers Cost-Efficient Wear ProtectionpakhansNo ratings yet
- Welds CracksDocument8 pagesWelds Cracksaltaf94No ratings yet
- Optical Emission From SemiconductorsDocument36 pagesOptical Emission From SemiconductorsvardhanNo ratings yet
- Prodinfo Antox-75-E Eng FinalDocument2 pagesProdinfo Antox-75-E Eng FinalKumar RamanNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Raw Wastewater From TanneriesDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Raw Wastewater From TanneriesMaliha CheemaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Unit II: Aromatic AminesDocument20 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Unit II: Aromatic AminesSaili SawardekarNo ratings yet
- UOP PX-Plus ™ XPDocument2 pagesUOP PX-Plus ™ XPana_dcz7154No ratings yet
- Ellc Rmnbemae Llce Bmmneera Lecl Mebmaren Lcel Nbmemaer: Cell MembraneDocument9 pagesEllc Rmnbemae Llce Bmmneera Lecl Mebmaren Lcel Nbmemaer: Cell MembraneAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet