Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transitions guide readers through academic writing
Uploaded by
RAINBOW AVALANCHEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transitions guide readers through academic writing
Uploaded by
RAINBOW AVALANCHECopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN OSHKOSH WRITING CENTER. 2012.
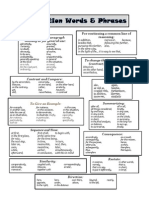
What is a transition?
A transitional sentence is a sentence used to switch from one topic to another. Transitions are most often
used when starting a new paragraph in academic writing. In the table below you will find many transitional words
used to show relationships that you can build an effective transition off of.
What is the purpose of using transitions?
Using transitions guides the reader through your paper and signals relationships between one part of your
paper or argument and another. A reader could completely miss a connection between two points if proper
transitions are not used. Dont assume that your evidence will speak for itself! Instead, use clear transitions.
BREIFLY repeat main idea or word in previous sentence/paragraph + introduce new idea
Example: The following sentence would transition from a paragraph about people left homeless in
New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina to a paragraph about the animals left homeless there after the
hurricane. The underlined fragment shows an example of use of a transitional phrase.
In addition to thousands of people being left homeless after Hurricane Katrina, thousands of
animals were left without owners or homes, as well.
Illustration thus, for example, for instance, namely, to illustrate, in other words, in particular,
specifically, such as
Contrast despite, on the contrary, but, however, nevertheless, in spite of, in contrast, yet,
on one hand, on the other hand, rather, or, nor, conversely, at the same time,
although this may be true, surely, notwithstanding, indeedbut, even so, for all
that, instead, on the contrary, otherwise
Addition in addition to, furthermore, moreover, besides, too, also, both-and, another,
equally important, again, further, last, finally, not only-but also, as well as, in the
second place, next, likewise, similarly, in fact, as a result, consequently, in the
same way, for example, for instance, however, thus, therefore, furthermore, and
Time since, afterward, before, then, once, next, at last, at length, formerly, rarely,
usually, finally, soon, meanwhile, later, ordinarily, generally, in order to,
subsequently, previously, immediately, eventually, concurrently, simultaneously,
first, second, as soon as, at that time
Concession although, at any rate, at least, still, though, even though, granted that, although it
may be true, in spite of, of course, accordingly, to be fair, while its true, in truth
Comparison showing Similarity similarly, likewise, in like fashion, in like manner, analogous to, in the same way
Emphasis above all, indeed, truly, of course, certainly, surely, in fact, really
General commonly, for the most part, in general, on the whole, usually, typically
To Conclude as a result, hence, finally, in short, on the whole, therefore, thus, in conclusion, all
in all, altogether, in other words, in summary, to sum it up
Cause and Effect as a result, because, for this reason, if, so, consequently, thus
Compiled from LB Brief (2011), The Brief Penguin Handbook (2009), UNC APA Quick Reference Guide (2008), and http://www.studygs.net/wrtstr6.htm.
You might also like
- Transition Words and PhrasesDocument1 pageTransition Words and PhrasesjeskentNo ratings yet
- English ConnectorsDocument50 pagesEnglish ConnectorsJuan Carlos Rodriguez100% (1)
- Transitions Book 1Document12 pagesTransitions Book 1api-367521953No ratings yet
- How To Answer Bar Exam Essay Question ImpressivelyDocument18 pagesHow To Answer Bar Exam Essay Question ImpressivelyJernel Janz83% (6)
- UST Golden Notes 2011 - Land Titles and Deeds PDFDocument46 pagesUST Golden Notes 2011 - Land Titles and Deeds PDFiccc100% (1)
- Remedial Law Suggested Answers (1997-2006), WordDocument79 pagesRemedial Law Suggested Answers (1997-2006), Wordyumiganda95% (38)
- Remedial Law Suggested Answers (1997-2006), WordDocument79 pagesRemedial Law Suggested Answers (1997-2006), Wordyumiganda95% (38)
- Customary Law in IndiaDocument29 pagesCustomary Law in IndiaJohir Uddin100% (1)
- How False News Can Spread SVDocument2 pagesHow False News Can Spread SVEffie VlachouNo ratings yet
- The Art of Effortless PowerDocument5 pagesThe Art of Effortless PowerWangshosanNo ratings yet
- The Fathers of The Church A New Translation Volume 003Document250 pagesThe Fathers of The Church A New Translation Volume 003Remon100% (2)
- Whither Oliver O'Donovan?Document10 pagesWhither Oliver O'Donovan?James K.A. Smith100% (1)
- Transitional WordsDocument13 pagesTransitional WordsReza HassanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 TransitionsDocument2 pages1.1 TransitionsSimon LauNo ratings yet
- Examples of Transitions:: IllustrationDocument2 pagesExamples of Transitions:: IllustrationSergio FontanaNo ratings yet
- TRANSITIONSDocument2 pagesTRANSITIONSDianne CantiverosNo ratings yet
- Connector Transition SignalsDocument3 pagesConnector Transition SignalsAnonymous VhW9ifNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation of Group 4 in CSS BLOCK CDocument73 pagesPowerpoint Presentation of Group 4 in CSS BLOCK CRosanna NavarroNo ratings yet
- Transitional DevicesDocument3 pagesTransitional DevicesISABELLE MAXINE MANTONo ratings yet
- Examples of TransitionsDocument15 pagesExamples of TransitionsShengxi ZhangNo ratings yet
- Connecting Your Ideas Linking WordsDocument3 pagesConnecting Your Ideas Linking WordsJefry ortizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cohesion in DiscourseDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Cohesion in Discoursevy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Agreement / Addition / Similarity: The Transition Words Like, ,, and With Preceding MaterialDocument21 pagesAgreement / Addition / Similarity: The Transition Words Like, ,, and With Preceding MaterialIzzuddin GhaniNo ratings yet
- Transitional Words and PhrasesDocument3 pagesTransitional Words and PhrasesEricDenby89% (9)
- Agreement, opposition, cause and effect transitionsDocument12 pagesAgreement, opposition, cause and effect transitionsBetim MetkamberiNo ratings yet
- Opposition / Limitation / ContradictionDocument9 pagesOpposition / Limitation / ContradictionBetim MetkamberiNo ratings yet
- Transitional Writing TechniquesDocument11 pagesTransitional Writing Techniquesalyssa_uy_2No ratings yet
- List of Transition Words for EssaysDocument6 pagesList of Transition Words for Essayspeiling87100% (1)
- Transitionsconnectors 101101194834 Phpapp02 PDFDocument1 pageTransitionsconnectors 101101194834 Phpapp02 PDFJoão JimenezNo ratings yet
- Transitions: Transitions and How They Are UsedDocument2 pagesTransitions: Transitions and How They Are UsedMjimenaNo ratings yet
- TransitionsDocument5 pagesTransitionsdrrnrrNo ratings yet
- Transition WordsDocument14 pagesTransition WordsTherese Canapi100% (2)
- Topic Sentences and TransitionsDocument4 pagesTopic Sentences and TransitionsCheriol Leung100% (1)
- Transitional WordsDocument2 pagesTransitional Wordssn.shoulderNo ratings yet
- Assignment DraftDocument8 pagesAssignment DraftErk ŞAHİNNo ratings yet
- Transitional DevicesDocument3 pagesTransitional DevicesArmel AbarracosoNo ratings yet
- Using Transitions: Similarity Contrast Sequence/Order Time ExampleDocument1 pageUsing Transitions: Similarity Contrast Sequence/Order Time ExampleRamshanUrdog123No ratings yet
- Transition WordsDocument9 pagesTransition Wordsephraim_lermaNo ratings yet
- Five-Paragraph Essay: Body ConclusionDocument21 pagesFive-Paragraph Essay: Body ConclusionAinul AinaNo ratings yet
- L4 Coherence Transition Between IdeasDocument13 pagesL4 Coherence Transition Between IdeasAnthony ArejolaNo ratings yet
- Coherence: Repetition of A Key Term or PhraseDocument10 pagesCoherence: Repetition of A Key Term or PhraseHoanglinh TranNo ratings yet
- Connectives MOREDocument5 pagesConnectives MORENadja STOJANOVICNo ratings yet
- Transition Words 3Document3 pagesTransition Words 3Sasa MilosevicNo ratings yet
- Linking DevicesDocument1 pageLinking DevicestonisohuNo ratings yet
- Transitional Words and Phrases 2021Document2 pagesTransitional Words and Phrases 2021gull skNo ratings yet
- TransitionsDocument1 pageTransitionsKasey WilemanNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions ExplanationDocument2 pagesConjunctions ExplanationLida JonesNo ratings yet
- Transitional WordsDocument2 pagesTransitional Wordsabdu-2009No ratings yet
- Writing Trasition Words For EssayDocument6 pagesWriting Trasition Words For EssayManjunathBVenkateshNo ratings yet
- Effective Essay Writing Tips.: BazlulDocument8 pagesEffective Essay Writing Tips.: BazlulBazlul KarimNo ratings yet
- Learn Essay With Fatima: Lecture 4: Transitions/Transitional Words/ Linking WordsDocument1 pageLearn Essay With Fatima: Lecture 4: Transitions/Transitional Words/ Linking WordsAbdullah khalidNo ratings yet
- Use Conjunctive Adverbs to Connect IdeasDocument3 pagesUse Conjunctive Adverbs to Connect IdeasCesar CardosoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary For Argumentative WritingDocument2 pagesVocabulary For Argumentative WritingFahim KazmiNo ratings yet
- Plan Your Discursive EssayDocument3 pagesPlan Your Discursive EssayCuteMittinsGNo ratings yet
- Transitional WordsDocument1 pageTransitional WordsFayaz JumaniNo ratings yet
- Also, in Addition, And, Likewise: The Transitional Devices Like, ,, and With Preceding MaterialDocument5 pagesAlso, in Addition, And, Likewise: The Transitional Devices Like, ,, and With Preceding MaterialJovana KojicNo ratings yet
- Transitional DevicesDocument5 pagesTransitional DevicesYell UmahagNo ratings yet
- List of Transition Words For EssaysDocument9 pagesList of Transition Words For EssaysrabeetNo ratings yet
- Transitional Words and Phrases: IllustrationDocument7 pagesTransitional Words and Phrases: IllustrationBilly BlondeNo ratings yet
- Transitional Words and PhrasesDocument5 pagesTransitional Words and Phraseskatak kembungNo ratings yet
- Cohesive DevicesDocument6 pagesCohesive DevicesBayissa BekeleNo ratings yet
- Logical Connectors: Unexpected Result), ConditionDocument12 pagesLogical Connectors: Unexpected Result), ConditionRocelene Veraann RukiminNo ratings yet
- Cohesion & CoherenceDocument20 pagesCohesion & CoherenceMuhammad Ali KausarNo ratings yet
- TransitionDocument2 pagesTransitionapi-250454644No ratings yet
- Transitional Devices PDFDocument2 pagesTransitional Devices PDFSittie Aliah MacatanongNo ratings yet
- Transition WordsDocument15 pagesTransition WordsOkin NawaNo ratings yet
- Prototext-metatext translation shifts: A model with examples based on Bible translationFrom EverandPrototext-metatext translation shifts: A model with examples based on Bible translationNo ratings yet
- Election Digested CasesDocument25 pagesElection Digested CasesHomework PingNo ratings yet
- Ateneo 2007 Provrem-1Document13 pagesAteneo 2007 Provrem-1Ljg BarondaNo ratings yet
- Sales Cases-InterestDocument11 pagesSales Cases-InterestRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Sales Cases-Interest PDFDocument9 pagesSales Cases-Interest PDFRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Elections: Lex Talionis Fraternitas IncDocument11 pagesElections: Lex Talionis Fraternitas IncRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Nature and Character of CIAC: Group 9 Chapter 12 Construction Dispute ArbitrationDocument2 pagesNature and Character of CIAC: Group 9 Chapter 12 Construction Dispute ArbitrationRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Land Titles: A C B O 2007 Civil LawDocument28 pagesLand Titles: A C B O 2007 Civil LawMiGay Tan-Pelaez86% (14)
- En Banc (G.R. NO. 179830: December 3, 2009) LINTANG BEDOL, Petitioner, v. COMMISSION ON ELECTIONS, Respondent. Decision Leonardo-De Castro, J.Document2 pagesEn Banc (G.R. NO. 179830: December 3, 2009) LINTANG BEDOL, Petitioner, v. COMMISSION ON ELECTIONS, Respondent. Decision Leonardo-De Castro, J.RAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Delimitation of the Anglo-French Continental Shelf BoundaryDocument14 pagesDelimitation of the Anglo-French Continental Shelf BoundaryRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Leonido C. Delante For Petitioner. Eduardo C. de Vera For Atty. S.B. AlteradoDocument4 pagesLeonido C. Delante For Petitioner. Eduardo C. de Vera For Atty. S.B. AlteradoRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- COMELEC Independence Upheld, President Cannot Designate Acting ChairDocument3 pagesCOMELEC Independence Upheld, President Cannot Designate Acting ChairRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Cayetano v. Mosod (Digest)Document2 pagesCayetano v. Mosod (Digest)RAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Atienza Vs COMELEC DIGESTDocument3 pagesAtienza Vs COMELEC DIGESTRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Columbres v. COMELECDocument6 pagesColumbres v. COMELECmisterdodiNo ratings yet
- Atienza v. ComelecDocument8 pagesAtienza v. ComelecRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Brillantes v. Yorac, 18 December 1990Document2 pagesBrillantes v. Yorac, 18 December 1990Donvidachiye Liwag CenaNo ratings yet
- Cayetano vs. MonsodDocument14 pagesCayetano vs. MonsodCristine TendenillaNo ratings yet
- In The Treatment of Polish Nationals and Other Persons of Polish Origin or Speech at DanzigDocument1 pageIn The Treatment of Polish Nationals and Other Persons of Polish Origin or Speech at DanzigRAINBOW AVALANCHE100% (1)
- ABS-CBN Exit Poll RulingDocument10 pagesABS-CBN Exit Poll RulingSerje BualNo ratings yet
- Delimitation of the Anglo-French Continental Shelf BoundaryDocument14 pagesDelimitation of the Anglo-French Continental Shelf BoundaryRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Rules ExplainedDocument17 pagesCivil Procedure Rules ExplainedRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- North Sea Continental Shelf CasesDocument6 pagesNorth Sea Continental Shelf CasesRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- REMEDIAL LAW Q&ADocument59 pagesREMEDIAL LAW Q&AHazel-mae Labrada0% (1)
- ADRDocument25 pagesADRRAINBOW AVALANCHENo ratings yet
- Land Titles: A C B O 2007 Civil LawDocument28 pagesLand Titles: A C B O 2007 Civil LawMiGay Tan-Pelaez86% (14)
- Borges As Antiphilosopher. Bruno BosteelsDocument11 pagesBorges As Antiphilosopher. Bruno Bosteelsmorgan385100% (1)
- Teubner-Kings Many BodiesDocument27 pagesTeubner-Kings Many BodiesTyss MorganNo ratings yet
- Virtue Ethics in NursingDocument6 pagesVirtue Ethics in NursingMagsNo ratings yet
- Merab Mamardashvili: 1 BibliographyDocument3 pagesMerab Mamardashvili: 1 BibliographyMarios Darviras100% (1)
- Bengalinsixteent 00 DasguoftDocument204 pagesBengalinsixteent 00 DasguoftNirmalya Dasgupta100% (1)
- Predicates P (X) : - A Predicate P (X) Is A Function That Gives A Unique Output (Truth Values) Against Every InputDocument15 pagesPredicates P (X) : - A Predicate P (X) Is A Function That Gives A Unique Output (Truth Values) Against Every InputaqeelNo ratings yet
- 2Document4 pages2ellaine villafaniaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed LP SH 1st Sem-Intro To Philo Demo For CotDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed LP SH 1st Sem-Intro To Philo Demo For CotJecky Josette Asentista100% (1)
- Philosophical Perspectives Through the AgesDocument13 pagesPhilosophical Perspectives Through the Agesshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Jurisprudence ProjectDocument15 pagesJurisprudence ProjectPawas SinghNo ratings yet
- Ethics PhilosophyDocument6 pagesEthics PhilosophysubcribedNo ratings yet
- Chomsky's Cognitive TheoryDocument7 pagesChomsky's Cognitive TheoryCamCatimpo100% (1)
- Logical FallaciesDocument38 pagesLogical FallaciesSeidelle Leigh QuiñonezNo ratings yet
- From ABC News - Famous Atheist Now Believes in GodDocument2 pagesFrom ABC News - Famous Atheist Now Believes in GodLeandro Sjp100% (1)
- English Language An Literature: Contemporary PerspectivesDocument214 pagesEnglish Language An Literature: Contemporary PerspectivesValerijaNo ratings yet
- Expert Judgment and Risk Perception: January 2001Document9 pagesExpert Judgment and Risk Perception: January 2001Achmad IrfaniNo ratings yet
- Super MindDocument12 pagesSuper Mindauro'No ratings yet
- JurisprudenceDocument22 pagesJurisprudenceDeepashikha0% (1)
- PHD Proposal Writing GuidelinesDocument4 pagesPHD Proposal Writing GuidelinesKhawar Abbas BalochNo ratings yet
- Lawyers Pick Up LinesDocument9 pagesLawyers Pick Up LinesDon So HiongNo ratings yet
- Information Processing ModelDocument17 pagesInformation Processing ModelRohayanti Binti YaakopNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Michael of Nebadon, Teachings of Spirit of TruthDocument20 pagesWelcome To Michael of Nebadon, Teachings of Spirit of TruthMichael Of Nebadon100% (2)
- Lecture Notes in Philo of ManDocument22 pagesLecture Notes in Philo of ManJulioRamilloAureadaMercurio100% (4)
- Misconceptions of Spirituality and Delusions of Being Awakened - Version2Document4 pagesMisconceptions of Spirituality and Delusions of Being Awakened - Version2Bhaerava KaalaNo ratings yet
- Truthfulness QuotesDocument2 pagesTruthfulness QuotesTeguh KiyatnoNo ratings yet