Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leb12 06 PDF
Uploaded by
yamilmamani1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesEnzymatic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, a cell respiratory poison, in the liver. To investigate the influence of temperature and pH on the metabolic activity.
Original Description:
Original Title
LEB12_06.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnzymatic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, a cell respiratory poison, in the liver. To investigate the influence of temperature and pH on the metabolic activity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesLeb12 06 PDF
Uploaded by
yamilmamani123Enzymatic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, a cell respiratory poison, in the liver. To investigate the influence of temperature and pH on the metabolic activity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
77 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co.
KG D-37070 Gttingen Laboratory Experiments, Biology
LEB 12 Biochemistry
The enzymatic activity of catalase 12.06
Principle and tasks:
To examine the enzymatic decompo-
sition of hydrogen peroxide, a cell
respiratory poison, in the liver. To in-
vestigate the influence of tempera-
ture and pH on the metabolic activi-
ty.
Normal result
Equipment (for the experimental procedure using the Basic-Unit)
Cobra3 Basic Unit 12150.00 1
Power supply, 12 V 12151.99 1
Software Cobra3 - Pressure 14510.61 1
Measuring module, pressure 12103.00 1
Support clamp for small case 02043.10 1
RS232 data cable 14602.00 1
Support base, variable 02001.00 1
Support rod, l = 500 mm, stainless steel 02032.00 1
Bosshead 02043.00 1
Universal clamp 37715.00 1
Magnetic stirrer, mini 47334.93 1
Magnetic stirrer bar, l = 50 mm 46299.03 1
Erlenmeyer flask, narrow neck, PN 29 36424.00 1
Rubber stopper, d = 32/26 mm, 1 hole 39258.01 1
Glass tubes, straight, 80 mm, d = 7 mm, 10 pcs 36701.65 1
Rubber tubing, d = 6 mm, 1 m 39282.00 1
Graduated cylinder, 100 ml 36629.00 1
Mortar with pestle, 150 ml, porcelain 32604.00 1
Strainer, fine mesh, d = 60 mm 40968.00 1
Graduated pipette, 1 ml 36595.00 1
Graduated pipette, 10 ml 36600.00 2
Glass beaker, 250 ml, tall form, DURAN 36004.00 2
Tripod, ring d = 100 mm, h = 180 mm 33299.00 1
Wire gauze 33287.03 1
Bunsen burner, natural gas 32165.05 1
Safety gas tubing, 1 m 39281.10 1
Tubing clip, d = 8...12 mm 40996.01 2
Test tube, 100 mm, d = 12 mm, 1 only 36307.10 1
Glycerol, 99%, 100 ml 30084.10 1
Dropping bottle, plastic, 50 ml 33920.00 1
Hydrogen peroxide, 38%, 250 ml 31710.25 1
Hydrochloric acid, 1 molar, 500 ml 48454.50 1
Sodium hydroxide, 1 molar, 500 ml 48329.50 1
Ice cubes, Chicken liver or pig liver
Distilled water
PC, Windows 95 or higher
What you need:
The enzymatic activity of catalase P4120611
What you can learn about
Enzyme catalase
Decomposition of H
2
O
2
Poisonous by-product of cell
respiration
Influence of temperature and
pH
Result when acidic
Related topics
Enzyme catalase, decomposition of H
2
O
2
, poisonous by-
product of cell respiration, influence of temperature and
pH
Principle and task
To examine the enzymatic decomposition of hydrogen
peroxide, a cell respiratory poison, in the liver. To investi-
gate the influence of temperature and pH on the metabol-
ic activity.
Equipment (for the experimental procedure using the
Basic-Unit)
Cobra3 Basic Unit 12150.00* 1
Power supply, 12 V 12151.99* 1
Software Cobra3 - Pressure 14510.61* 1
Measuring module, pressure 12103.00* 1
Support clamp for small case 02043.10* 1
RS232 data cable 14602.00* 1
Support base, variable 02001.00 1
Support rod, l = 500 mm, stainless steel 02032.00 1
Bosshead 02043.00 1
Universal clamp 37715.00 1
Magnetic stirrer, mini 47334.93 1
Magnetic stirrer bar, l = 50 mm 46299.03 1
Erlenmeyer flask, narrow neck, PN 29 36424.00 1
Rubber stopper, d = 32/26 mm, 1 hole 39258.01 1
Glass tubes, straight, 80 mm,
d = 7 mm, 10 pcs 36701.65 1
Rubber tubing, d = 6 mm, 1 m 39282.00 1
Graduated cylinder, 100 ml 36629.00 1
Mortar with pestle, 150 ml, porcelain 32604.00 1
Strainer, fine mesh, d = 60 mm 40968.00 1
Graduated pipette, 1 ml 36595.00 1
Graduated pipette, 10 ml 36600.00 2
Glass beaker, 250 ml, tall form, DURAN 36004.00 2
Tripod, ring d = 100 mm, h = 180 mm 33299.00 1
Wire gauze 33287.03 1
Bunsen burner, natural gas 32165.05 1
Safety gas tubing, 1 m 39281.10 1
Tubing clip, d = 8...12 mm 40996.01 2
Test tube, 100 mm, d = 12 mm, 1 only 36307.10 1
Glycerol in a dropping bottle, 25 ml 48159.04 1
Hydrogen peroxide, 38%, 250 ml 31710.25 1
Hydrochloric acid, 1 molar, 500 ml 48454.50 1
Sodium hydroxide, 1 molar, 500 ml 48329.50 1
Ice cubes
Chicken liver or pig liver
Distilled water
PC, Windows
Set-up (using the Basic-Unit)
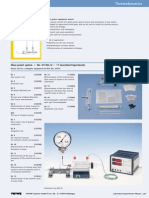
Set up the equipment as shown in Fig. 1.
Fasten the support clamp for a small case to the back
of the Cobra3 Basic Unit
Connect the Cobra3 Basic Unit to the PC with the
data cable
Fix the Cobra3 Basic Unit with plugged-on pressure
module to the support rod so that it is directly above
the Erlenmeyer flask
Ease the glass tube, wetted with a drop of glycerol,
into the rubber stopper and connect it to the pressure
module with a short piece of rubber tubing
Place the Erlenmeyer flask on the magnetic stirrer and
hold it with a universal clamp
Procedure (using the Basic-Unit)
Call up the COBRA3 MEASURE programme in Windows
Enter PRESSURE as measuring instrument
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41206 153
LEB
12.06
The enzymatic activity of catalase
Fig. 1: Experimental set-up using the Basic-Unit
Fig. 2: Measurement parameters (using the Basic-Unit)
Set the measurement parameters (see Fig. 2) and go
to measurement with CONTINUE
Put the chicken liver in the mortar, add a little distilled
water, then use the pestle to crush it and decant the
juice off through the strainer and into a beaker
Experiment 1:
Pour 15 ml of 3% hydrogen peroxide solution (10 ml
of 30% H
2
O
2
solution to 90 ml of distilled water) into
a 100 ml graduated cylinder and make it up to 100 ml
with distilled water
Pour this solution into an Erlenmeyer flask, insert the
magnetic stirrer bar and place the flask on the mag-
netic stirrer
Add 1 ml of liver juice and immediately close the flask
with the rubber stopper
Start the measurement (running time 150 s)
Experiment 2:
Procedure as in Experiment 1, but with the addition of
10 ml of 1 molar sodium hydroxide or 10 ml of 1 molar
hydrochloric acid
Experiment 3:
Procedure as in Experiment 1, but previously pour the
liver juice into a test tube and either heat it for 5 min-
utes in a beaker of boiling water or cool it for 5 min-
utes in a beaker of ice cold water containing ice cubes
Results and evaluation
Experiment 1: The pressure curve increases sharply,
but drops down vertically at 1330 hPa, because the
rubber stopper was blown off of the flask (Fig. 3)
Experiment 2: When sodium hydroxide is added, the
pressure curve increases far less sharply than under
normal conditions (Fig. 4). With hydrochloric acid,
there is no increase in pressure (Fig. 5).
Experiment 3: After a 5 minute heat treatment, the
pressure in the flask remains constant (Fig. 6). After a
5 minute iced water treatment, the pressure increases
as under normal conditions. Here again, there is a ver-
tical pressure drop at 1330 hPa (blown-off stopper)
(Fig. 7).
Catalase is an enzyme, which occurs in humans pre-
dominately in the liver and in erythrocytes. It decom-
poses hydrogen peroxide H
2
O
2
, a poisonous by-
product of cell respiration, to water and oxygen. When
one mixes blood, for example, with H
2
O
2
, the forma-
tion of small bubbles of oxygen can be seen.
Enzymes are pH dependent. Experiment 2 shows that
catalase prefers alkaline conditions. It is not active
under acidic conditions.
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41206 154
LEB
12.06
The enzymatic activity of catalase
Fig. 4: Result when alkaline
Fig. 3: Normal result
Fig. 5: Result when acidic
Fig. 6: Result after heating
Enzymes are composed of proteins. Proteins are
denatured at high temperatures. This is the reason
why there is no pressure increase after the 5 minute
heat treatment in Experiment 3. The enzyme proteins
are destroyed. On the other hand, a cold shock only
temporarily inactivates catalase. When the tempera-
ture increases, the enzyme again acts optimally.
Note
This experiment can also be carried out using the hand-
held measuring instrument pressure 07136.00, pressure
sensor 07136.01, software pressure 14416.61, data cable
07157.01 and boss head 02043.00. In this case, the
entries in the equipment list (Fig. 8) which are marked with
an asterisk are not required.
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41206 155
LEB
12.06
The enzymatic activity of catalase
Fig. 7: Result after cooling
Fig. 8: Experimental set-up using the hand-held measuring instrument pressure
Room for notes
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41206 156
LEB
12.06
The enzymatic activity of catalase
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Wax Depilation ManualDocument17 pagesWax Depilation ManualAmit Sharma100% (1)
- PLAB 2 VISA Guidelines by Omar AlamDocument18 pagesPLAB 2 VISA Guidelines by Omar Alamrafew19No ratings yet
- HIPULSE U 80kVA 500kVA-Manual - V1.1Document157 pagesHIPULSE U 80kVA 500kVA-Manual - V1.1joseph mendezNo ratings yet
- Classical and Operant Conditioning ExamplesDocument6 pagesClassical and Operant Conditioning ExamplesPersephone355100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument47 pagesCardiovascular SystemAtnasiya GadisaNo ratings yet
- Insurance CodeDocument18 pagesInsurance CodeKenneth Holasca100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanjamieboyRN91% (32)
- Glass Jacket System No. 01196.12 17 Described ExperimentsDocument3 pagesGlass Jacket System No. 01196.12 17 Described Experimentsyamilmamani123No ratings yet
- Demonstration Experiments Physics - Magnetic Board HeatDocument3 pagesDemonstration Experiments Physics - Magnetic Board Heatyamilmamani123No ratings yet
- 4.1.01-15 Ohm's Law With FG-Module: What You NeedDocument1 page4.1.01-15 Ohm's Law With FG-Module: What You Needyamilmamani123No ratings yet
- Physics Demonstration Experiments - Magnet Board OpticsDocument3 pagesPhysics Demonstration Experiments - Magnet Board Opticsyamilmamani123No ratings yet
- Phywe Systeme GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Göttingen Federal Republic of GermanyDocument1 pagePhywe Systeme GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Göttingen Federal Republic of Germanyyamilmamani123No ratings yet
- Biology: Laboratory ExperimentsDocument16 pagesBiology: Laboratory Experimentsyamilmamani123No ratings yet
- Cdd161304-Manual Craftsman LT 1500Document40 pagesCdd161304-Manual Craftsman LT 1500franklin antonio RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Coconut MilkDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Coconut Milkea6mkqw2100% (1)
- Raffles Hotel Jakarta Pricelist 2020Document2 pagesRaffles Hotel Jakarta Pricelist 2020kielachela aaNo ratings yet
- Dearcán Ó Donnghaile: ProfileDocument2 pagesDearcán Ó Donnghaile: Profileapi-602752895No ratings yet
- Scenario of Shale Gas Exploration in IndiaDocument24 pagesScenario of Shale Gas Exploration in IndiaManish TiwariNo ratings yet
- O OP PE ER RA Attiin NG G Iin NS STTR RU UC Cttiio ON NS S: UF 755 G UF 455 GDocument14 pagesO OP PE ER RA Attiin NG G Iin NS STTR RU UC Cttiio ON NS S: UF 755 G UF 455 GHomeroPerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Animal CareDocument8 pagesLesson 1 Animal CareLexi PetersonNo ratings yet
- Study On Optimization and Performance of Biological Enhanced Activated Sludge Process For Pharmaceutical Wastewater TreatmentDocument9 pagesStudy On Optimization and Performance of Biological Enhanced Activated Sludge Process For Pharmaceutical Wastewater TreatmentVijaya GosuNo ratings yet
- February 2023 PROGRAM OF THE MPLEDocument8 pagesFebruary 2023 PROGRAM OF THE MPLEDale Iverson LacastreNo ratings yet
- PaperDocument21 pagesPaperAnonymous N2TkzrNo ratings yet
- CA500Document3 pagesCA500Muhammad HussainNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Solutions: ADMET Testing SystemsDocument2 pagesInformation Technology Solutions: ADMET Testing Systemskrishgen biosystemsNo ratings yet
- Strep Throat FactsDocument2 pagesStrep Throat FactsFactPaloozaNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of CloningDocument5 pagesThe Ethics of CloningUpai MbembNo ratings yet
- Kerala Medico Legal Code - Annexure2Document19 pagesKerala Medico Legal Code - Annexure2doctor82No ratings yet
- Thornburg Letter of RecDocument1 pageThornburg Letter of Recapi-511764033No ratings yet
- Ronnel Del RioDocument5 pagesRonnel Del Rioamity balweg100% (2)
- Child-Centered and Progressive EducationDocument2 pagesChild-Centered and Progressive EducationDibyendu ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Huayi: Refrigeration CompressorDocument2 pagesHuayi: Refrigeration CompressorVARDANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document9 pagesChapter 23Trixie Myr AndoyNo ratings yet
- Interactive and Comprehensive Database For Environmental Effect Data For PharmaceuticalsDocument5 pagesInteractive and Comprehensive Database For Environmental Effect Data For PharmaceuticalsRaluca RatiuNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PROPOSAL AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT TOOLS GROUPWORK (Situation No. 3 - BSSW 3A)Document21 pagesPROJECT PROPOSAL AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT TOOLS GROUPWORK (Situation No. 3 - BSSW 3A)Hermida Julia AlexandreaNo ratings yet