Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis Introduction Worksheet
Uploaded by
ali7167Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis Introduction Worksheet
Uploaded by
ali7167Copyright:
Available Formats
PHOTOSYNTHESIS THE CHEMICAL REACTION
This is learning by enquiry - research your answers. You may work as a group, but everyone needs to
compile a full set of answers.
Firstly a reminder about the basics of photosynthesis:
Q.1 a) What are the raw materials taken in by a photosynthesising green plant, in order to make its
own organic food?
The raw materials needed are water and carbon dioxide.
b) What else does the plant need from the environment in order to react the raw materials
together?
Sunlight
c) There must be a sort of biological catalyst present in order to enable the combining of the
raw materials. What is his substance?
Chlorophyll
d) The raw materials are reacted together to form which organic compound)
Glucose
e) Photosynthesis produces an important waste product what?
Oxygen
f) Now you should be able to write the word formula for the photosynthesis reaction the raw
materials (reactants or substrates) react together to form products.
Water + Carbon Dioxide Glucose + Oxygen
g) Finally, write the balanced chemical or molecular formula for photosynthesis.
6H2O + 6CO2 C6H12O6+ 602
Now lets look at the raw materials and resources and where they come from. Assume all the time that
we are taking about a rooted, leafy, green plant your answers might be a little different if we were
talking about algae in the oceans.
Q.2 CHLOROPHYLL
a) Green plants actually make their own chlorophyll. Chlorophyll contains one important
mineral ion, which must be absorbed from the soil. What is it?
Magnesium
b) Chlorophyll does not simply hang around inside plant cells, waiting for a bit of sun! The
chlorophyll is found inside tiny organelles in photosynthesising cells. It is inside these
organelles where most of the photosynthesis reaction occurs. What are these organelles
called? Make a simple drawing of one.
Chloroplasts:
c) Very briefly, what do you understand by: i) the light dependent reaction; The first
major set of processes in photosynthesis in which the light is converted into chemical energy.
ii) the light independent reaction? They are
chemical reactions which convert carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose.
Q.3 CARBON DIOXIDE
a) About what percentage of the earths atmosphere is carbon dioxide?
0.04%
b) Is this percentage rising or falling? Why? What might the effect of the change be on the
rate of photosynthesis? (Be very brief with your answers here.)
The percentage is rising because of the increasing amount of cars and factories in the world.
c) Where in plant leaves does the carbon dioxide enter?
The carbon dioxide enters through the stomata (pores) underneath the leaves.
d) A green plant will not be absorbing carbon dioxide a full 24 hours a day. It will therefore
not be photosynthesising a full 24 hours. When will the plants not be absorbing carbon
dioxide?
At night time
Q.4 WATER
a) From where do green plants obtain their water?
The soil
b) So, which parts of the plants must the water travel through in order to reach the leaves,
where most of the photosynthesis takes places? Draw a simple diagram of a plant (root, stem,
leaves) to illustrate the water flow through it.
Root, stem and leaves:
c) As you saw in Q.3 d), photosynthesis does not take place a full 24 hours a day. Yet water
does come up through the plant a full 24 hours a day. What happens to the excess water? How
might you know this by looking at a plant in the early morning? Very briefly explain the
physics behind this process.
The excess water comes out of the leaves as a waste; we know this because in the morning
there are water droplets on the leaves. In the day, the water evaporates too quickly, so we
dont see it, however at night, it condenses, meaning that the next morning we can see the
water droplets.
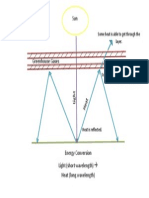
Q.5 ENERGY/SUNLIGHT
a) Roughly which wavelengths of light are used for photosynthesis? How do you know this
from a simple observation about green plants?
The wavelengths used for photosynthesis are the red and the blue. We know this because
when you look at a plant, you see that it is green, this means that the green light is being
reflected (not used) while the red and blue lights are being absorbed by the leaf.
b) A green plant must be able to maximise photosynthesis and absorb as much light as
possible. It therefore has packed chloroplasts in the leaves. But how are the leaves and whole
stems and branches arranged in order to maximise sunlight absorption? Draw some simple
diagrams. Remember that plants in the tropics and in the north and/or south latitudes may
have different characteristics.
c) See if you can find some figures for the amount of sunlight absorbed by green plants on the
Earths surface.
About 48% of the total incoming solar energy is absorbed by the Earths surface; however,
this doesnt only include green plants,
Q.6 OXYGEN
a) Plants, like all living organisms, use oxygen all the time. For what reaction?
Respiration
b) But they give off more oxygen while they are photosynthesising. This oxygen accumulates
in the atmosphere. What percentage of the atmosphere is oxygen?
20%
c) There will probably be two times during 24 hours when the amount of oxygen absorbed
into the plant equals the amount of oxygen generated in photosynthesis. What is the word
used to describe these moments in the day?
d) Why can we say that this point of balance between oxygen consumption and generation
occurs twice during 24 hours?
Q.7 CARBOHYDRATES
Glucose is first formed by all green plants, but this is rapidly converted into other
carbohydrates and organic compounds, which the plant can store or use.
a) What is the principle chemical storage which plants accumulate in their leaves or roots or
even stems?
Glucose
b) Some plants might use the glucose which they make, right away. For which reaction?
Respiration
c) What two other types of chemical compound might the glucose be converted into?
Cellulose and Proteins
d) What does a green plant use these chemical compounds for?
They are used for cell walls and for growth and repair.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Solution Manual For Oceanography An Invitation To Marine Science 9th Edition by GarrisonDocument12 pagesSolution Manual For Oceanography An Invitation To Marine Science 9th Edition by Garrisona641705730No ratings yet
- Biology 02 TissuesDocument10 pagesBiology 02 TissuesMonika Mehan67% (3)
- MrSnorch Spreadsheet - Sunflower Land (Recuperado Automáticamente)Document201 pagesMrSnorch Spreadsheet - Sunflower Land (Recuperado Automáticamente)Jose GomezNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Concept MapDocument1 pageBiodiversity Concept Mapali7167No ratings yet
- Hotspot WorksheetDocument3 pagesHotspot Worksheetali7167No ratings yet
- Interview 1 RecordDocument1 pageInterview 1 Recordali7167No ratings yet
- Database Vocabulary Sheet: Term What Does It Mean?Document2 pagesDatabase Vocabulary Sheet: Term What Does It Mean?ali7167No ratings yet
- Some Heat Is Able To Get Through The LayerDocument1 pageSome Heat Is Able To Get Through The Layerali7167No ratings yet
- The Definition of SpeciesDocument3 pagesThe Definition of Speciesali7167No ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect Planetary LevelDocument1 pageGreenhouse Effect Planetary Levelali7167No ratings yet
- Lysozyme QuestionDocument2 pagesLysozyme Questionali716750% (2)
- How Does and Electric Motor Work?: Diagram 1 Diagram 2Document1 pageHow Does and Electric Motor Work?: Diagram 1 Diagram 2ali7167No ratings yet
- Hormones and EnzymesDocument1 pageHormones and Enzymesali7167No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymesali7167No ratings yet
- Sex Hormones: Sex Hormone Uses / FunctionsDocument2 pagesSex Hormones: Sex Hormone Uses / Functionsali7167No ratings yet
- Experimental Write-Up "Light Wavelength"Document1 pageExperimental Write-Up "Light Wavelength"ali7167No ratings yet
- HormonesDocument1 pageHormonesali7167No ratings yet
- Article - Ecuador .Vs. ChileDocument3 pagesArticle - Ecuador .Vs. Chileali7167No ratings yet
- SeismographDocument1 pageSeismographali7167No ratings yet
- Seismograph: Alicia Sánchez Year 10Document1 pageSeismograph: Alicia Sánchez Year 10ali7167No ratings yet
- At What Temperature Do Membrane Proteins Denature?: HypothesisDocument3 pagesAt What Temperature Do Membrane Proteins Denature?: Hypothesisali7167No ratings yet
- Peer Assessment SheetDocument1 pagePeer Assessment Sheetali7167No ratings yet
- Kodu: Peer Assessment Sheet: Student Name: Alicia Sánchez Assessed By: Jhuvon JamesDocument1 pageKodu: Peer Assessment Sheet: Student Name: Alicia Sánchez Assessed By: Jhuvon Jamesali7167No ratings yet
- Kodu: Peer Assessment Sheet: Student Name: Assessed byDocument1 pageKodu: Peer Assessment Sheet: Student Name: Assessed byali7167No ratings yet
- Kodu: Peer Assessment Sheet: Student Name: Alicia Sánhez Assessed By: Jhuvon JamesDocument1 pageKodu: Peer Assessment Sheet: Student Name: Alicia Sánhez Assessed By: Jhuvon Jamesali7167No ratings yet
- Domestication Genetics WheatDocument21 pagesDomestication Genetics Wheatari novitasariNo ratings yet
- Codigo Nacional ElectricoDocument144 pagesCodigo Nacional ElectricoBrianParedes100% (1)
- Syllabus of Class: UKG (2018-19) UT-1: BZ (H) DH Ek K (M (Q) DH Ek K ( (W) DH Ek K, (S) DH Ek KDocument2 pagesSyllabus of Class: UKG (2018-19) UT-1: BZ (H) DH Ek K (M (Q) DH Ek K ( (W) DH Ek K, (S) DH Ek KYOGESH BAGHELNo ratings yet
- Types of EcosystemDocument2 pagesTypes of EcosystemnaweedNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Radial and Bilateral SymmetryDocument1 pageDifference Between Radial and Bilateral Symmetrymanojitchatterjee2007No ratings yet
- Classification of Horticultural CropsDocument14 pagesClassification of Horticultural Cropsmonkey luffy80% (5)
- WBI02 01 Que 20190525Document28 pagesWBI02 01 Que 20190525alialiNo ratings yet
- Vintage Cellars Corporate Catalogue 133Document25 pagesVintage Cellars Corporate Catalogue 133VintageCellarsNo ratings yet
- AthirasaDocument4 pagesAthirasapsshnkrNo ratings yet
- Banana VCA (Full Blown) PDFDocument143 pagesBanana VCA (Full Blown) PDFlyn castonesNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Gardening For Nutritional SecurityDocument4 pagesKitchen Gardening For Nutritional SecuritySrijita SircarNo ratings yet
- Bio-FIT Book EN PDFDocument256 pagesBio-FIT Book EN PDFCesar Augusto Colorado RamirezNo ratings yet
- KintamaniDocument32 pagesKintamaniKevin AdrianNo ratings yet
- Caiet de Lucru Optional Limba Engleza PDFDocument32 pagesCaiet de Lucru Optional Limba Engleza PDFDaniela CorneciNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 7 - 10Document21 pagesDLL Week 7 - 10rotshen casilacNo ratings yet
- Chip BuddingDocument5 pagesChip BuddinggheorghiudNo ratings yet
- Wheat Straw As A Paper Fiber Source: Nist Mep Environmental ProgramDocument55 pagesWheat Straw As A Paper Fiber Source: Nist Mep Environmental ProgramFrank Mtetwa0% (1)
- Brown BookDocument199 pagesBrown BookbajricaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property RightsDocument13 pagesIntellectual Property RightsThisho NanthNo ratings yet
- Rabbits: Species: Cottontail RabbitDocument7 pagesRabbits: Species: Cottontail Rabbitlehigh79No ratings yet
- NIIR List of BooksDocument15 pagesNIIR List of BooksRakeshKumarNo ratings yet
- FastPlants2 LPA 21-22Document16 pagesFastPlants2 LPA 21-22Isabelle VershawNo ratings yet
- Other Economically Important Species of Piper: Indian Institute of Spices Research, Kozhikode-673012, Kerala, IndiaDocument13 pagesOther Economically Important Species of Piper: Indian Institute of Spices Research, Kozhikode-673012, Kerala, IndiaAleksandra MilenkovićNo ratings yet
- The Cell ActivitiesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Activitiestiareximena0308No ratings yet
- Arts q2Document2 pagesArts q2Ruthchel YaboNo ratings yet
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds BiomesDocument4 pagesApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomesapi-235647128No ratings yet
- BIO CDSI - GB2 12 PPT1-Mendelian Genetics (1) - CompressedDocument387 pagesBIO CDSI - GB2 12 PPT1-Mendelian Genetics (1) - Compressedjzjz14324No ratings yet