Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills
Uploaded by
Venkatesh Gangadhar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
216 views20 pagescritical
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcritical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
216 views20 pagesCritical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills
Uploaded by
Venkatesh Gangadharcritical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Finishing School Course Plan ACD
2511: Critical Thinking & Problem
Solving Skills
BizMentors Pvt. Ltd.
TM
7/4/2013 1 BizMentors Pvt. Ltd.
The Objectives of This Session
To provide insights to the participants, about the role of critical
thinking for success in any problem situation.
To expose participants to likely challenges of critical thinking and
problem solving, and help them develop their problem solving skills.
To thereby help participants develop convictions about the
importance of developing into good problem solvers for success.
TM
7/4/2013 2 BizMentors Pvt. Ltd.
3
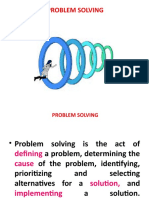
Significance of Problem solving - I
Children On A Railway Track
You are walking along a path running parallel to a railway track,
when you come across some children playing on the tracks.
You notice that its is a live track, with a disused track branching
off from it at a point. The disused track is separated from the
live one by a lever-operated track-change switch. You see that
while most of the children are playing on the disused track,
there is a small, blind boy of around six, who is playing all by
himself on the live track. Suddenly you hear the loud horn and
the thundering sound of an approaching train.
What will you do ?
TM
Significance of Problem solving - II
Problem solving involves :
Holistic understanding of the problem situation.
Gathering input data about the problem.
Analysis.
Solution generation.
Solution selection.
The need to manage conflicting pulls of :
Individual Vs. Team efforts.
Conventional Vs. Creative thinking.
Rational analysis Vs. Judgment ( Gut-feel ).
Quantitative Vs. Qualitative data / analysis.
4
TM
Definitions - I
What is a problem?
A problem occurs, when there is a difference between
the desired result and the actual result of a
process.
What is problem identification?
Realizing such a difference is identification of a
problem. Therefore, problem identification process is
limited by the knowledge available for the process.
5
TM
Definitions - II
What is problem selection?
When we have identified a multitude of problems,
all of which cannot be addressed with the resources
available, we need to prioritize the problems to be
addressed.
What is problem solving?
The process of analyzing the selected problem to
establish the root cause and then finding the best
way of eliminating the same.
6
TM
Dos and Donts of problem solving - I
Attitude towards problem solving:
Every problem is a challenge giving rise to an
opportunity.
One should enjoy the thrill of the challenge rather
than become stressed and look for relief / escape
from it.
Be positive, every challenge will eventually be
overcome if you persevere.
Recognize our jobs / roles exist for solving problems
or overcoming challenges.
7
TM
Dos and Donts of problem solving - II
People Focus :
Should be used to find and leverage useful strengths /
aptitudes that match required processes.
Should aim to improve understanding and execution of
processes.
Should not be aimed at finding who did it wrong, but
rather, who can do it right.
Objective interactions to keep minimize emotional
conflicts.
Create emotional bonds that removes boundaries of
functional structures.
8
TM
Dos and Donts of problem solving - III
9
Process Focus :
Establish methods that ensure control on results.
Minimize dependence human memory / skills /
concentration / etc. for correct execution of processes..
Eliminate errors that occur due to human fallibility.
Establish objectivity in analysis by directing it at the
process rather than people involved.
Seamlessly link processes across boundaries between
functions / departments.
Improvements must be process oriented, with people
orientation being only to train them to support process
improvements.
TM
Challenges Of Problem Selection
What are the issues at hand ?
Which ones are the most crucial for the long term ?
Which ones are necessary for the medium term ?
Which ones are urgent in the immediate term ?
In which cases do we have a choice ?
Which are the forced choices ?
How do we prioritize resource deployment ?
How do we ensure consensus and buy-in by all
concerned while making these choices ?
10
TM
Challenges Of Problem solving
How do we ensure consideration of all inputs for the
solving process ?
How do we ensure that the root cause is correctly
determined ?
How do we ensure consideration of all possible solutions?
How do we evaluate probabilities of success or failure of
each component of the solution ?
How do we ensure that no opportunity is lost in forming
the solution ?
11
TM
Individual vs. Group Problem Solving
In establishing objectives, groups are probably superior
to individuals because of the greater amount of knowledge
available to groups.
In identifying alternatives, the individual efforts of group
members encourage broader searches in various
functional areas of the organization.
In evaluating alternatives, the collective judgment of the
group, with its wider range of viewpoints, often turn out to
be superior to that of individual decision makers.
TM
13
TM
Brainstorming
Pareto chart
Cause& Effect
Run
Histogram & Normal Distribution
Scatter
Control
Problem
Identification
Problem Solving
Problem Solving tools
Flow Chart
Problem
Selection
5 Whys
QFD
DOE
Check Sheet
TM
17
TM
Brainstorming With The Mind-Map Tool
18
TM
19
Exercise on Brainstorming
Brainstorm to find the possible solutions for the problem
of children playing on the railway track.
TM
TM
7/4/2013 20 BizMentors Pvt. Ltd.
You might also like
- Principles of Microeconomics Bbek1103Document18 pagesPrinciples of Microeconomics Bbek1103Angel Deborah John0% (2)
- Competency MatrixDocument16 pagesCompetency Matrixcimsanthosh100% (1)
- Leadership in Work ForceDocument82 pagesLeadership in Work Forcejitendra jaushik100% (2)
- Problem Solving StrategiesDocument3 pagesProblem Solving StrategiesJA M ESNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking & Problem SolvingDocument7 pagesCritical Thinking & Problem SolvingMahmoud GaberNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Power in BusinessesDocument4 pages5 Types of Power in Businessesravi dosad0% (1)
- AnnuityDocument3 pagesAnnuityizzatkadisNo ratings yet
- Mutually Exclusive and Inclusive Events PDFDocument5 pagesMutually Exclusive and Inclusive Events PDFMarieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 11 Law309 (DP)Document2 pagesTutorial Week 11 Law309 (DP)AlNo ratings yet
- Business EthicsDocument3 pagesBusiness EthicsUyen LeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Business Law.2Document12 pagesAssignment Business Law.2Abe ManNo ratings yet
- Ogn 117 2021 Problem SolvingDocument8 pagesOgn 117 2021 Problem SolvingjoequshNo ratings yet
- Week - 1 Introduction of CpiDocument14 pagesWeek - 1 Introduction of CpiDhairyaaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making (DM) : - Every Manager Strives To Do Making Good DecisionsDocument30 pagesDecision Making (DM) : - Every Manager Strives To Do Making Good DecisionsTommba TommyNo ratings yet
- 7-Problem SolvingDocument13 pages7-Problem SolvingcathyNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument29 pagesProblem Solvingscas deptpsy100% (2)
- Problem-Solving Skills NTC PDFDocument60 pagesProblem-Solving Skills NTC PDFMunther MurjanNo ratings yet
- KASE Decesion MakingDocument51 pagesKASE Decesion MakingvishuNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving, Critical Thinking and Decision MakingDocument49 pagesProblem Solving, Critical Thinking and Decision MakingIncia100% (1)
- 1 Problem Solving & Dicision MakingDocument55 pages1 Problem Solving & Dicision MakingteklayNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument55 pagesProblem SolvingMark Antony LevineNo ratings yet
- Ask These Strategic Management Questions To Cultivate Decentralized CommandDocument3 pagesAsk These Strategic Management Questions To Cultivate Decentralized Commandturningpoint innospaceNo ratings yet
- Module (2) Lecture 3 - Problem SolvingDocument7 pagesModule (2) Lecture 3 - Problem SolvingPoLaRoiDNo ratings yet
- Decision Making - MEDocument14 pagesDecision Making - MERashi GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Math ResearchDocument4 pagesMath ResearchMary Christine Formiloza MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- Project Management InterviewDocument16 pagesProject Management InterviewSubba Rao GantiNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument7 pagesDecision Making Processspencer2003No ratings yet
- Problem Solving TechniquesDocument10 pagesProblem Solving Techniquesaiman zahidNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument35 pagesProblem SolvingFizza AwanNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Grade 10Document30 pagesBusiness Studies Grade 10nombuleloNo ratings yet
- 29al UsDocument6 pages29al UshdfcblgoaNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making: Mahesh K PrasadDocument36 pagesDecision-Making: Mahesh K PrasadSwathi GovindarajanNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Skills - Management ProjectDocument26 pagesDecision Making Skills - Management ProjectPrathap Vimarsha100% (2)
- Seven Steps For Effective Problem Solving in The WorkplaceDocument10 pagesSeven Steps For Effective Problem Solving in The WorkplaceLynyrd SkynyrdNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lecture 4 Problem SolvingDocument7 pagesModule 2 Lecture 4 Problem SolvingPoLaRoiD100% (1)
- Steps To Decison MakingDocument4 pagesSteps To Decison MakingvinodinikNo ratings yet
- A Study On Problem Situations Faced by A Manager and Skills Used To Tackle ThemDocument10 pagesA Study On Problem Situations Faced by A Manager and Skills Used To Tackle Themandy williamNo ratings yet
- The Power of Decisions: M. Akbar BhattiDocument21 pagesThe Power of Decisions: M. Akbar BhattiAkbar BhattiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Application of Critical Thinking Skills in Private Investigation ProfessionsDocument32 pagesChapter 6 - Application of Critical Thinking Skills in Private Investigation ProfessionsLalita A/P AnbarasenNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - PROBLEM SOLVINGDocument8 pagesActivity 6 - PROBLEM SOLVINGSol MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 of B628 - UpdatedDocument24 pagesChapter 03 of B628 - UpdatedAhmed DahiNo ratings yet
- DECISION MAKING - Chapter 2Document28 pagesDECISION MAKING - Chapter 2NamraNo ratings yet
- Presentaion of Mis 2...Document10 pagesPresentaion of Mis 2...Akesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Change and Decision Making: Presentedby AshwinnairpimsrcollegeDocument38 pagesStrategic Change and Decision Making: Presentedby AshwinnairpimsrcollegeAshwin NairNo ratings yet
- L5 Problem-Solving SkillsDocument51 pagesL5 Problem-Solving SkillsLPMbasicPPA A.WilujengNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument27 pagesProblem SolvingParamveer100% (2)
- How Good Is Your Decision Making (Lecture)Document54 pagesHow Good Is Your Decision Making (Lecture)ERNIE CERADONo ratings yet
- Creative Problem Solving and Decision MakingDocument55 pagesCreative Problem Solving and Decision Makingkhairolanuarmasuan100% (4)
- MGT Unit 4Document30 pagesMGT Unit 4Tarekegn DemiseNo ratings yet
- A 3 Thinkingwebinar 2012Document33 pagesA 3 Thinkingwebinar 2012mancheung6429No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document47 pagesUnit 2Manju ABNo ratings yet
- Accounts Term PaperDocument12 pagesAccounts Term PaperHarish UpmanyuNo ratings yet
- Tackling Case AnalysisDocument33 pagesTackling Case AnalysisAditya VidolkarNo ratings yet
- Problem Solved EmployeesDocument16 pagesProblem Solved EmployeesMuntaha SyedNo ratings yet
- Effective Team DecisionDocument3 pagesEffective Team DecisionMia BogdanovicNo ratings yet
- Dr. Noor Session On Problem Solving Aug 2018Document43 pagesDr. Noor Session On Problem Solving Aug 2018shaziafirdoosNo ratings yet
- Decision Making The Process of Choosing Among The Alternative Solutions Available To A Course of Action or A Problem SituationDocument5 pagesDecision Making The Process of Choosing Among The Alternative Solutions Available To A Course of Action or A Problem Situationdanee しNo ratings yet
- The Recognition-Primed Decision ModelDocument13 pagesThe Recognition-Primed Decision ModelJeddahlyn Atienza RamosNo ratings yet
- Notes - Lateral Thinking and Problem Solving - PGDM - 21-23 Trimester IIIDocument8 pagesNotes - Lateral Thinking and Problem Solving - PGDM - 21-23 Trimester IIIsharventhiriNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems.: Checklist 012Document5 pagesSolving Problems.: Checklist 012Sofiya BayraktarovaNo ratings yet
- Week 04 - Problem - Solving - Tools - and - TechniquesDocument26 pagesWeek 04 - Problem - Solving - Tools - and - TechniquesMUSIC & TECHNo ratings yet
- Internship & Placement BrochureDocument9 pagesInternship & Placement BrochureVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Creating PDF Reports With Pandas, Jinja and WeasyPrint - Practical Business PythonDocument20 pagesCreating PDF Reports With Pandas, Jinja and WeasyPrint - Practical Business PythonVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Oppe 2Document16 pagesOppe 2Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)Document2 pagesBachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Butterfly ValvesDocument8 pagesButterfly ValvesVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- TeamcenterDocument481 pagesTeamcenterVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- ButhanDocument1 pageButhanVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing) Term-End Examination) Une, 2009Document4 pagesBachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing) Term-End Examination) Une, 2009Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Jun 2011 Bme-030Document3 pagesJun 2011 Bme-030Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing) Term-End Examination June, 2014Document3 pagesB.Tech. Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing) Term-End Examination June, 2014Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Power ScrewsDocument15 pagesPower ScrewsVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)Document8 pagesBachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Design of ShaftsDocument23 pagesDesign of ShaftsVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Finishing School Course Plan ACD 2511: Marketing & Selling SkillsDocument18 pagesFinishing School Course Plan ACD 2511: Marketing & Selling SkillsVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Bme 023Document4 pagesBme 023Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- EMM2512 AssignmentDocument4 pagesEMM2512 AssignmentVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Tower Are The Supporting Structure For Wind Mill Which Carry Load Generated From TurbineDocument3 pagesTower Are The Supporting Structure For Wind Mill Which Carry Load Generated From TurbineVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- A-A Scale 1:10: 3D CAD MASTER PART NAME: Lifting Arm - 1 - ReinforcementDocument1 pageA-A Scale 1:10: 3D CAD MASTER PART NAME: Lifting Arm - 1 - ReinforcementVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Iiyiegrated Mai/'Ijfacturing)Document4 pagesBachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering (Computer Iiyiegrated Mai/'Ijfacturing)Venkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Statistics For ManagersDocument100 pagesStatistics For ManagersVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering: Session Delivered byDocument75 pagesReverse Engineering: Session Delivered byVenkatesh GangadharNo ratings yet
- Learning Through PlayDocument2 pagesLearning Through PlayThe American Occupational Therapy Association100% (1)
- 14 Amazing Psychology Facts You Should Keep To YourselfDocument12 pages14 Amazing Psychology Facts You Should Keep To YourselfKim ComandaoNo ratings yet
- Poster: Sensory Garden Design For Adolescents With Dual Sensory ImpairmentDocument1 pagePoster: Sensory Garden Design For Adolescents With Dual Sensory ImpairmentNeroulidi854No ratings yet
- Modeling Anxiety in Healthy Humans: A Key Intermediate Bridge Between Basic and Clinical SciencesDocument12 pagesModeling Anxiety in Healthy Humans: A Key Intermediate Bridge Between Basic and Clinical SciencesGabriel Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- A Correlative Study of Mother Parenting Style and Emotional Intelligence of Adolescent LearnerDocument7 pagesA Correlative Study of Mother Parenting Style and Emotional Intelligence of Adolescent LearnerpiousfNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Critique PaperDocument2 pagesActivity 3 Critique PaperKarl Angelo ArceñoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Methods of Teaching by ChaDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Methods of Teaching by Chacha tuscanoNo ratings yet
- COMM414 - CHAPTER 5 Control System CostDocument4 pagesCOMM414 - CHAPTER 5 Control System CostBlaze GlazerNo ratings yet
- Organizational ContextDocument16 pagesOrganizational ContextKavinda KosgodaNo ratings yet
- English 9 PPT DAY 1Document21 pagesEnglish 9 PPT DAY 1Evelyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Calendar Spring 2023Document672 pagesUndergraduate Calendar Spring 2023Alexander BergNo ratings yet
- Definition of Reading and Its LevelDocument8 pagesDefinition of Reading and Its LevelMuhammad Hidayatul Rifqi100% (1)
- Environmental PsychologyDocument24 pagesEnvironmental PsychologySamson GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Time Management GuideDocument99 pagesTime Management GuideRacso ZamboangaNo ratings yet
- Student Teaching Edtpa Indirect Instruction Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesStudent Teaching Edtpa Indirect Instruction Lesson Plan Templateapi-301105637No ratings yet
- Book Review - Surfing UncertaintyDocument6 pagesBook Review - Surfing UncertaintySamuel Bellini LeiteNo ratings yet
- Simple Process - Consumer Decision-MakingDocument58 pagesSimple Process - Consumer Decision-MakingNew_EricNo ratings yet
- Understanding Measurement, Developing Questions, and Designing The QuestionnaireDocument47 pagesUnderstanding Measurement, Developing Questions, and Designing The QuestionnaireSamiha MjahedNo ratings yet
- Code Blue Group-Psychiatry History FormatDocument10 pagesCode Blue Group-Psychiatry History FormatsakariyeNo ratings yet
- Suggested Parent Interview GuideDocument7 pagesSuggested Parent Interview Guideadhiema resureccionNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed Review Material 3 With ANSWERSDocument4 pagesProf Ed Review Material 3 With ANSWERSAimee100% (1)
- Training and Development, Compensation/Wages and Performance Evaluation and Employee RelationsDocument8 pagesTraining and Development, Compensation/Wages and Performance Evaluation and Employee RelationsquiroyalisonNo ratings yet
- The Value of HomeworkDocument4 pagesThe Value of HomeworkAnjelo TorresNo ratings yet
- Seven Ds of WellnessDocument1 pageSeven Ds of Wellnessapi-288526415No ratings yet
- Learning Organization and Organizational Commitment in SchoolsDocument8 pagesLearning Organization and Organizational Commitment in SchoolsNORHAZARISE BINTI BAHARUMNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Development: Assessor: Kashfiya Afrin, Lecturer, School of Business, BACDocument21 pagesHuman Resource Development: Assessor: Kashfiya Afrin, Lecturer, School of Business, BACOrbind B. ShaikatNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH Psikologi PendDocument8 pagesMAKALAH Psikologi PendFirdaus AhmadNo ratings yet
- HRM Final PDFDocument106 pagesHRM Final PDFSudhagarNo ratings yet
- Psychology Is Alive and WellDocument10 pagesPsychology Is Alive and WellRoxana MariaNo ratings yet