Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lss 7 Transportinlivingthings
Uploaded by
wangks1980Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lss 7 Transportinlivingthings
Uploaded by
wangks1980Copyright:
Available Formats
Transport i n
Li vi ng Thi ngs
LOWER SEC SCIENCE
MASTERY LEARNI NG CENTRE
mastery learning centre
Descri be di f fusion.
Descri be osmosi s.
Expl ain the i mportance of di f fusion and osmosi s.
Descri be the ci rcul atory system i n ani mals.
Descri be the transport system i n pl ants.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
mastery learning centre
The parti cles of al l matter can move about randomly.
In sol i ds, the movement i s l i mited to vi brating about a fi xed
posi ti on.
In l i quids, the parti cles are abl e to move freely wi thi n the
boundaries of the l i quid.
In gases, the parti cles are abl e to move i n al l di rections
wi thout l i mi tations.
MOVEMENT OF PARTICLES
mastery learning centre
The movement of parti cles i s i mportant to l i vi ng cel l s.
Cel l s need water, ai r, nutrients and other useful thi ngs. These
have to be brought to them and be abl e to enter through the
cel l membrane.
At the same ti me, waste products produced by cel ls need to
be abl e to move out of the cel l s and be carri ed away and
di sposed of.
Parti cles move i n and out of the cel ls through two mai n ways:
di f fusions and osmosis.
A transport system carri es useful substances to the cel l s and
takes away harmful waste substance from the cel l s.
MOVEMENT OF PARTICLES
mastery learning centre
In di f fusion, the parti cles move from an area of hi gh
concentration to an area of l ow concentration ti l l they are
evenly di stributed (homogenous).
Di f fusion usually occurs i n sol uti ons.
No energy i s required for di f fusion.
Di f fusion can occur wi th or wi thout a parti ally permeable
membrane to separate the parti cles.
Di f fusion occurs when there i s a concentration gradient .
Di f fusion stops when the sol ution becomes homogenous.
DIFFUSION
mastery learning centre
EXAMPLE OF DIFFUSION
A bottl e of perfume i s opened at one corner of the room. Af ter
some ti me, a person standi ng on the other si de of the room i s
abl e to smel l the perfume.
Thi s shows that parti cles from the perfume have di f fused
through the ai r.
mastery learning centre
In osmosi s, water mol ecules move from a regi on of more
water mol ecules to a region of l ess water mol ecules through a
partially permeable membrane.
Osmosi s stops when the concentration of water mol ecules i s
equal on both si des of the membrane.
Osmosi s cannot occur wi thout a parti ally permeable
membrane.
No energy i s needed for osmosi s.
OSMOSIS
mastery learning centre
A di l ute sol ution has more water mol ecules than a
concentrated sol ution.
So i n osmosi s, water moves from a di l ute to a concentrated
sol uti on.
OSMOSIS
mastery learning centre
OSMOSIS IN ANIMAL CELLS
mastery learning centre
OSMOSIS IN PLANT CELLS
mastery learning centre
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS IN LIVING THINGS
mastery learning centre
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS IN LIVING THINGS
mastery learning centre
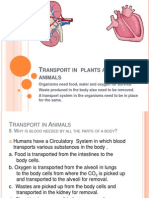
The transport of substances from one part of the ani mal to
another part takes pl ace i n the ci rculatory system.
The ci rculatory system ensures that useful materials are
brought i nto the cel l s and waste materials are carri ed away to
be di sposed of.
The ci rculatory system consi sts of the heart, bl ood vessels
and bl ood.
The heart i s a muscular pump that provi des the force that
pushes the bl ood through the bl ood vessels.
TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS
mastery learning centre
The heart keeps pumping throughout the l i fe of an ani mal.
Bl ood fl ows through the bl ood vessels i n one di rection onl y.
Bl ood vessels that carry bl ood towards the heart are cal l ed
the heart are cal l ed veins.
Bl ood vessels that carry bl ood away from the heart are cal l ed
arteries.
Vei ns and arteri es meet through capil lari es.
TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS
mastery learning centre
HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
mastery learning centre
The heart has four chambers. 2 upper chambers atria
(si ngular atri um) and 2 l ower chambers ventricles.
HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
mastery learning centre
HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
vein
right atrium
right ventricle
left ventricle
muscle
left atrium
vein
arteries
(1) De-oxygenated blood
from the body enters the
right atrium and then
into the right ventricle
(2) This blood passes
from the right ventricle,
then out to the lungs
(3) Oxygenated
blood from the
lungs enters
the left atrium
and then into
the left
ventricle
(4) This blood passes
from the left ventricle,
then out to the rest of
the body again
mastery learning centre
THE BLOOD
mastery learning centre
RED BLOOD CELLS
mastery learning centre
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
mastery learning centre
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
mastery learning centre
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
mastery learning centre
PLATELETS
mastery learning centre
PLASMA
mastery learning centre
The transport system i n pl ants consi sts of two types of ri gid
tubes that run through the stem.
Xyl em tubes carry water and mi neral sal ts from the roots to
the l eaves.
Phl oem tubes that carry food produced duri ng photosynthesis
from the l eaves to the roots.
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
mastery learning centre
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
You might also like
- Biology Essay QuestionsDocument11 pagesBiology Essay QuestionsNewton O. OchiengNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Basic Concepts in Biochemistry-HatdogDocument5 pagesAssignment 1 - Basic Concepts in Biochemistry-HatdogAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedDocument12 pagesQ4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedXyreen GalicinaoNo ratings yet
- 4.transport MechanismsDocument94 pages4.transport MechanismsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocument46 pagesBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument68 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesMara Jon Ocden CasibenNo ratings yet
- Gr9 - Movement of SubstancesDocument40 pagesGr9 - Movement of SubstancesKara NewmanNo ratings yet
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsDocument6 pagesNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEDocument37 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEJohnnie ZhangNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesCirculatory SystemDe GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Compare and Contrast of The Process of Transport and CirculationDocument27 pagesWeek 3 Compare and Contrast of The Process of Transport and CirculationRAIZA MAE MIGUELNo ratings yet
- Transport CirculationDocument39 pagesTransport CirculationClara MaeNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For OlevelDocument45 pagesBiology Notes For OlevelSaira Binte SalekNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument23 pagesCell Transport7104No ratings yet
- Group 7 Circulatory System FinalDocument51 pagesGroup 7 Circulatory System FinalAngel Faith FernandezNo ratings yet
- 7-4 Cell TransportDocument24 pages7-4 Cell Transportapi-342334216No ratings yet
- In and Out of CellsDocument3 pagesIn and Out of CellsA personNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport SystemDocument27 pagesAnimal Transport SystemcabellaNo ratings yet
- Excretory System in Invertebrates NewDocument36 pagesExcretory System in Invertebrates Newudgfusgfusfgbsufgusd100% (8)
- Chapter Two ThreeDocument50 pagesChapter Two Threerue pattinsonNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Topic 1BDocument13 pagesBiology Notes: Topic 1Blaiba amirNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome:: The Importance of Having A Transport System in Some Multicellular OrganismsDocument55 pagesLearning Outcome:: The Importance of Having A Transport System in Some Multicellular Organismsمحمد شافيقNo ratings yet
- BioCLab Mod3Document11 pagesBioCLab Mod3Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Reading and QuestionsDocument6 pagesCell Transport Reading and Questionsgualanmaikol37No ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of Circulation in Annelid, Arthopoda and MolluscsDocument4 pagesComparative Anatomy of Circulation in Annelid, Arthopoda and MolluscsNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 3 Plants and Animal Organ SystemDocument20 pagesQ4 Lesson 3 Plants and Animal Organ SystemPhan MhiveNo ratings yet
- L05 Membrane TransportDocument34 pagesL05 Membrane TransportlolNo ratings yet
- JawadDocument25 pagesJawadtik-tok worldNo ratings yet
- Quarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sDocument17 pagesQuarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sTristan Paul PagalananNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need A Transport SystemDocument2 pagesWhy Do We Need A Transport Systemkirstinrose100% (3)
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument16 pagesTransport Across The Cell MembraneJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Edexcel (9-1) H.Biology Notes: 1. Cells and TissuesDocument7 pagesIGCSE Edexcel (9-1) H.Biology Notes: 1. Cells and TissuesnaduniNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ch 11-Ans SheetDocument6 pagesAssignment-Ch 11-Ans Sheetrachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion & Osmosis LabDocument17 pagesDiffusion & Osmosis LabDee Mar0% (1)
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument2 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalNo ratings yet
- Biology Circulatory SysttemDocument5 pagesBiology Circulatory SysttemAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- B3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesDocument52 pagesB3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesMinh Hoàng ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids Compartments and ExchangeDocument21 pagesBody Fluids Compartments and ExchangeLIDIYA MOL P VNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument32 pagesDiffusionAce Mhac TeñidoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Report Physio LecDocument27 pagesGroup 3 Report Physio Lecたこ ゆきNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument26 pagesTransportBhaskar MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport System 1Document41 pagesAnimal Transport System 1Ashley JibrielleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 MedsurdgeDocument14 pagesChapter 13 MedsurdgeLaurence Angel H OrdonaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Osmosis PDFDocument17 pagesLab 2 Osmosis PDFMegan Lingo100% (1)
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocument24 pagesCell Membrane Transport NotesJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Notes - Life Processes - Transportation - C-X - PART-IIIDocument4 pagesNotes - Life Processes - Transportation - C-X - PART-IIIApoorv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Secondary II Science Chapter 10 RevisionDocument25 pagesSecondary II Science Chapter 10 RevisionASMNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Cell Content 2Document34 pagesOsmosis and Cell Content 2Ñïà ǸìæNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7Document14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7JewelNo ratings yet
- Module 11Document7 pagesModule 11Jamille Nympha C. BalasiNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument40 pagesMovement in and Out of CellslubaajamesNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 Membrane TransportDocument29 pagesLect 2 Membrane Transportramadan100% (1)
- Presentation 2Document14 pagesPresentation 2Maya TareqNo ratings yet
- Bio2 11 - 12 Q4 1102 FDDocument34 pagesBio2 11 - 12 Q4 1102 FDDIMAL, Nasiba M.No ratings yet
- Zo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaDocument20 pagesZo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaAbhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- (Original Size) Movement in and Out of CellsDocument8 pages(Original Size) Movement in and Out of CellshridanshhirparaNo ratings yet
- Lymph Health: The Key to a Strong Immune SystemFrom EverandLymph Health: The Key to a Strong Immune SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Radioactivity 1: Symbol NameDocument4 pagesRadioactivity 1: Symbol Namewangks1980No ratings yet
- Radioactivity 3Document4 pagesRadioactivity 3wangks1980No ratings yet
- How To Build Your Flying Star ChartDocument40 pagesHow To Build Your Flying Star Chartwangks1980No ratings yet
- JC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1Document13 pagesJC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1wangks1980No ratings yet
- Physics 2204 Worksheet #4 - Advanced Kinematics: 1 of 2 14 Feb 07Document2 pagesPhysics 2204 Worksheet #4 - Advanced Kinematics: 1 of 2 14 Feb 07wangks1980No ratings yet
- 3CC - Properties of Metals - Notes 13Document6 pages3CC - Properties of Metals - Notes 13wangks1980No ratings yet
- Answer All Questions. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in The Table BelowDocument4 pagesAnswer All Questions. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in The Table Belowwangks1980No ratings yet
- Sec 2 Normal AcademicDocument2 pagesSec 2 Normal Academicwangks1980No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesChapter 5 Lesson Planwangks1980No ratings yet
- SAJC Prospectus 2014Document68 pagesSAJC Prospectus 2014wangks1980No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AnswersDocument10 pagesChapter 5 Answerswangks1980No ratings yet
- Learner Guide HDB Resale Procedure and Financial Plan - V2Document0 pagesLearner Guide HDB Resale Procedure and Financial Plan - V2wangks1980No ratings yet
- Geometrical Proof SolutionDocument1 pageGeometrical Proof Solutionwangks1980No ratings yet
- TPFF T4Q2Document1 pageTPFF T4Q2wangks1980No ratings yet
- SoundsDocument61 pagesSoundsJemabel RosarioNo ratings yet
- Swot Matrix Strengths WeaknessesDocument6 pagesSwot Matrix Strengths Weaknessestaehyung trash100% (1)
- Swenson 1 Dan Swenson Printing Press: Part One (Timeline)Document6 pagesSwenson 1 Dan Swenson Printing Press: Part One (Timeline)Dan SwensonNo ratings yet
- Powering Laser Diode SystemsDocument134 pagesPowering Laser Diode SystemsNick100% (1)
- NiftDocument3 pagesNiftMegha Nair PillaiNo ratings yet
- Handbook On National Spectrum Management 2015Document333 pagesHandbook On National Spectrum Management 2015Marisela AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Moc3040 MotorolaDocument3 pagesMoc3040 MotorolaBryanTipánNo ratings yet
- Kunst 1600 Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesKunst 1600 Case AnalysisrakeshNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Medieval MuslimDocument16 pagesContribution of Medieval Muslimannur osmanNo ratings yet
- ERP Solution in Hospital: Yangyang Shao TTU 2013Document25 pagesERP Solution in Hospital: Yangyang Shao TTU 2013Vishakh SubbayyanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE ™: Combined ScienceDocument11 pagesCambridge IGCSE ™: Combined ScienceAhmed Jomaa Salem0% (1)
- Lab 3 Report Fins RedoDocument3 pagesLab 3 Report Fins RedoWestley GomezNo ratings yet
- Basic Approach To The Audit of Electronically Processed DataDocument2 pagesBasic Approach To The Audit of Electronically Processed DataJestell Ann ArzagaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronDocument2 pagesEffect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronsachinguptachdNo ratings yet
- TinkerPlots Help PDFDocument104 pagesTinkerPlots Help PDFJames 23fNo ratings yet
- Number CardsDocument21 pagesNumber CardsCachipún Lab CreativoNo ratings yet
- Paper Ed Mid TermDocument2 pagesPaper Ed Mid Termarun7sharma78No ratings yet
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2000 Paper IDocument17 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2000 Paper Itom stuartNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering & Processing: Process Intensi Fication: ArticleinfoDocument9 pagesChemical Engineering & Processing: Process Intensi Fication: Articleinfomiza adlinNo ratings yet
- DLL Drafting 7Document4 pagesDLL Drafting 7Ram Dacz100% (3)
- Chomsky's Universal GrammarDocument4 pagesChomsky's Universal GrammarFina Felisa L. AlcudiaNo ratings yet
- SQL - Day 2: Structured Query LanguageDocument10 pagesSQL - Day 2: Structured Query LanguageNight KingNo ratings yet
- Hume 100 ReviewerDocument7 pagesHume 100 ReviewerShai GaviñoNo ratings yet
- 2011 Burris CatalogDocument56 pages2011 Burris CatalogMario Lopez100% (1)
- Credit Card Authorization Form WoffordDocument1 pageCredit Card Authorization Form WoffordRaúl Enmanuel Capellan PeñaNo ratings yet
- Combinational Logic-Part-2 PDFDocument25 pagesCombinational Logic-Part-2 PDFSAKSHI PALIWALNo ratings yet
- OB Case Study Care by Volvo UK 2020Document1 pageOB Case Study Care by Volvo UK 2020Anima AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Class Routine Final 13.12.18Document7 pagesClass Routine Final 13.12.18RakibNo ratings yet
- Learning Plans in The Context of The 21 ST CenturyDocument29 pagesLearning Plans in The Context of The 21 ST CenturyHaidee F. PatalinghugNo ratings yet
- Solar-range-brochure-all-in-one-Gen 2Document8 pagesSolar-range-brochure-all-in-one-Gen 2sibasish patelNo ratings yet