Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applied Physics Question Paper 59
Uploaded by
RA.......VAOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Applied Physics Question Paper 59
Uploaded by
RA.......VACopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Hydrogen bond is an example for
(a) Electrostatic bond
(b) Secondary bond
(c) Primary bond
(d) Dispersion bond
2. The element which has covalently bonded crystal structure is
(a) tin
(b) sodium chloride
(c) aluminum
(d) germanium
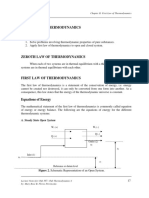
3. The condition for minimum potential energy between two atoms, is
(a) n > m
(b) n+m = 0
(c) m > n
(d) n = m
4. If the atoms or molecules in a solid are periodically at regular spacings in three dimensions then that solid is known
as
(a) metallic solid
(b) non-metallic solid
(c) Amorphous solid
(d) Crystalline solid
5. For mono-clinic crystal system, the lattice parameters are
(a) a = b = c; α = β = γ = 90o
(b) a 6= b 6= c; α = β = 90o 6= g
(c) a 6= b = c; α = β = γ = 90o
(d) a = b = c; α = β = γ 6= 90o
6. There is only one Bravias lattice for the crystal system of
(a) Monoclinic
(b) Cubic
(c) Tetragonal
(d) Triclinic
7. The crystal structure which has the highest packing factor is
(a) BCC
(b) Diamond
(c) SC
(d) FCC
8. The lattice parameter of a simple cubie structure is 3.6 nm. The radius of the atoms with which the crystal is
composed, is equal to
(a) 3.6 nm
(b) 1.8 nm
(c) 7.2 nm
(d) 0.9 nm
9. If the lattice parameter a = 1.25 nm for a BCC structure, the nearest neighbour distance, is
(a) 0.44 nm
(b) 0.88 nm
(c) 1.08 nm
(d) 0.54 nm
10. If the lattice parameter a = 3.2 nm, for an FCC structure, the atomic radius is
(a) 0.44 nm
(b) 4.53 nm
(c) 1.13 nm
(d) 2.26 nm
11. If ‘x’ is the lattice parameter of a diamond structure, the number of atoms per unit volume is
(a) 4/x3
(b) 2/x3
(c) 8/x3
(d) 1/x3
12. Zinc blende structure is almost identical to
(a) NaCl structure
(b) KCl structure
(c) diamond structure
(d) CsC1 structure
13. The bond energy of NaCl molecule is
(a) 6.5 eV
(b) 5.5 eV
(c) 3.5 eV
(d) 4.5 eV
14. The coordinates of chlorine ion in CsCl structure are
(a) 1/2, 1/2, 1/2
(b) 1, 1, 1
(c) 2, 2, 2
(d) 0, 0, 1
15. Miller indices of the plane parallel to Z axis is
(a) (001)
(b) (101)
(c) (111)
(d) (110)
16. The direction opposite to [102] is
(a) [2 0 1]
(b) [1 0 2]
(c) [2 0 1]
(d) [2 0 4]
17. In a simple cubic lattice d100 : d110 : d111 is
(a) 61/2 : 31/2 : 21/2
(b) 61/2 : 31/2 : 41/2
(c) 6: 3: 2
(d) 6: 3: 21/2
18. The velocity of X-rays is equal to
(a) The velocity of sound at 100o C in air
(b) The velocity of sound at 0o C in air
(c) The velocity of sound at 30o C in air
(d) The velocity of light
19. The Bragg’s law for constructive interference is
(a) nλ = 2d sin θ
(b) 2d = nλ sin θ
(c) d = 2λ
(d) nd = 2 λ sin θ
20. Using X-ray powder diffraction the can be determined
(a) Size of atom
(b) Size of crystal
(c) Interatomic distance
(d) Interplanar distance
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hot-Finishedcelsius Rectangular Hollow Sections: BS 5950-1: 2000 BS EN 10210-2: 1997Document6 pagesHot-Finishedcelsius Rectangular Hollow Sections: BS 5950-1: 2000 BS EN 10210-2: 1997maeglin_elendilNo ratings yet
- Equivalences Between Different Designations: Chemical CompositionDocument2 pagesEquivalences Between Different Designations: Chemical CompositionSuleman KhanNo ratings yet
- Jmep - Review - Comments Embedded in The ManuscriptDocument15 pagesJmep - Review - Comments Embedded in The ManuscriptAnish KarmakarNo ratings yet
- The Dual Nature of LightDocument12 pagesThe Dual Nature of LightrkukgNo ratings yet
- A New Fatigue Damage Accumulation Rating Life Model of Ball Bearings Under Vibration LoadDocument11 pagesA New Fatigue Damage Accumulation Rating Life Model of Ball Bearings Under Vibration LoadAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Refraction: Tagaban, Mark Adrian U. Bsme-1 BDocument5 pagesRefraction: Tagaban, Mark Adrian U. Bsme-1 BMark Adrian TagabanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 1Document6 pagesMechanics 1Ahmed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Glass Composition Types Fracture Patterns Sample Collection and AnalysisDocument36 pagesGlass Composition Types Fracture Patterns Sample Collection and AnalysisThea Marie SantarinNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MtechDocument8 pagesSyllabus MtechYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Annie Fang - Research PosterDocument1 pageAnnie Fang - Research PosterAnnie FangNo ratings yet
- Part I Refrigeration Chapter 1Document43 pagesPart I Refrigeration Chapter 1eskewt0% (1)
- Lec 1-Vapor Liquid Equilibrium-Part 1Document30 pagesLec 1-Vapor Liquid Equilibrium-Part 1DianaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Contact Angle Hysteresis in Liquid Bridges: Graphical AbstractDocument25 pagesDynamic Contact Angle Hysteresis in Liquid Bridges: Graphical AbstractMaja VuckovacNo ratings yet
- RCD RulDocument54 pagesRCD RulCj GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechanics DEM Simulation HartDocument9 pagesRock Mechanics DEM Simulation Hartj_brug571No ratings yet
- Invar PRDocument2 pagesInvar PRZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- C Purlin Design Calculation: y 2 3 3 3 3 3 6 4 Y-Y X-XDocument6 pagesC Purlin Design Calculation: y 2 3 3 3 3 3 6 4 Y-Y X-XSalvatore ShwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Teacher S Guide 2009Document33 pagesChapter 4 Teacher S Guide 2009Chen ShyanNo ratings yet
- PH Diagram PDFDocument4 pagesPH Diagram PDFMay Salvi Rosa D0% (1)
- A Novel High Sensitivity Optical Fiber LSPR SARS-CoV-2 Sensor Based On Triangular Gold NanosheetsDocument15 pagesA Novel High Sensitivity Optical Fiber LSPR SARS-CoV-2 Sensor Based On Triangular Gold Nanosheetsirving tarnNo ratings yet
- NDT Anfd Failure AnalysisDocument65 pagesNDT Anfd Failure AnalysisAgung SudrajatNo ratings yet
- NREL Thin Film Overview-2008Document7 pagesNREL Thin Film Overview-2008eitanc369No ratings yet
- ENSC 461 Tutorial, Week#4 - IC EnginesDocument8 pagesENSC 461 Tutorial, Week#4 - IC Enginesandres179No ratings yet
- RT Relevant DiscontinuitiesDocument70 pagesRT Relevant Discontinuitiesabdo50% (2)
- Borehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangDocument7 pagesBorehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangJose Leo MissionNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - QBDocument13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - QBInduPalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2SelNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompositesDocument30 pagesCarbon CompositesVIbhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For Metals 50Cr4V2Document3 pagesDatasheet For Metals 50Cr4V2vamsi patnalaNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of A Coil SpringDocument7 pagesFailure Analysis of A Coil SpringCiobanu MihaiNo ratings yet