Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Column Design Examples
Uploaded by
Santiago Andres Giron Velez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views5 pagesExamples of Metallic Design on Columns
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentExamples of Metallic Design on Columns
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views5 pagesColumn Design Examples
Uploaded by
Santiago Andres Giron VelezExamples of Metallic Design on Columns
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Dr. M.E. Haque, P.E.
Column Design Examples (Page 1 of 5)
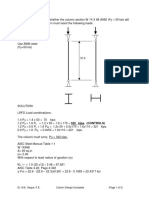
Example 1: Determine the lightest W-section for the column shown in Figure. The
column must resist the following loads:
P
D
= 50 kips
P
L
= 170 kips
P
W
= 110 kips
Use A992 steel
(Fy=50 ksi)
SOLUTION:
LRFD Load combinations:
1.4 P
D
= 1.4 x 50 = 70 kips
1.2 P
D
+ 1.6 P
L
= 1.2 x 50 + 1.6 x 170 = 332 kips. (CONTROLS)
1.2 P
D
+ 0.5 P
L
+ 1.6 P
W
= 1.2x 50 + 0.5x170 + 1.6x110 = 321 kips.
0.9 P
D
+ 1.6 P
W
= 0.9x50 + 1.6x110 = 221 kips.
The column must carry, Pu = 332 kips.
With respect to least radius of gyration (ry)
KL (y-y) = 1.0 x 20 = 20 ft
From AISC Table 4-1 (Pages 4-10 to 4-21)
For KL = 20 look horizontally and find LRFD design capacity value closest to 332 kips
(not less than 332 kips).
W 8 X 67 (347 kips)
W 10 X 49 (338 Kips)
W 12 X 53 (353 kips)
W 14 X 61 (400 kips)
W 10 X 49 is the lightest section with design compressive strength = 338 kips.
ANSWER: W 10X49
20 ft
Dr. M.E. Haque, P.E. Column Design Examples (Page 2 of 5)
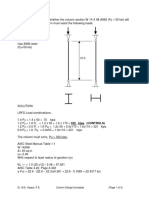
Example 2: Determine the lightest W-section for the column shown in Figure. The
column must resist the following loads:
P
D
= 50 kips
P
L
= 170 kips
P
W
= 110 kips
Use A992 steel
SOLUTION:
LRFD Load combinations:
1.4 P
D
= 1.4 x 50 = 70 kips
1.2 P
D
+ 1.6 P
L
= 1.2 x 50 + 1.6 x 170 = 332 kips. (CONTROLS)
1.2 P
D
+ 0.5 P
L
+ 1.6 P
W
= 1.2x 50 + 0.5x170 + 1.6x110 = 321 kips.
0.9 P
D
+ 1.6 P
W
= 0.9x50 + 1.6x110 = 221 kips.
The column must carry, Pu = 332 kips.
Considering an approximate ideal Fixed-Pined ends. (AISC TABLE C-C2.2)
With respect to least radius of gyration (ry)
KL (y-y) = 0.8 x 20 = 16 ft
From AISC Table 4-1 (Pages 4-10 to 4-21)
For KL = 16 look horizontally and find LRFD design capacity value closest to 332 kips
(not less than 332 kips).
W 8 X 48 (340 kips)
W 10 X 49 ( 428 kips)
W 12 X 53 ( 452 kips)
W 14 X 53 ( 338 kips)
W 8 X 48 is the lightest section with design compressive strength = 340 kips.
ANSWER: W 8X48
20 ft
Dr. M.E. Haque, P.E. Column Design Examples (Page 3 of 5)
Example 3: Determine whether the column section W 14 X 68 A992 (Fy = 50 ksi) will
be adequate. The column must resist the following loads:
P
D
= 50 kips
P
L
= 170 kips
P
W
= 110 kips
Use A992 steel
(Fy=50 ksi)
SOLUTION:
LRFD Load combinations:
1.4 P
D
= 1.4 x 50 = 70 kips
1.2 P
D
+ 1.6 P
L
= 1.2 x 50 + 1.6 x 170 = 332 kips. (CONTROLS)
1.2 P
D
+ 0.5 P
L
+ 1.6 P
W
= 1.2x 50 + 0.5x170 + 1.6x110 = 321 kips.
0.9 P
D
+ 1.6 P
W
= 0.9x50 + 1.6x110 = 221 kips.
The column must carry, Pu = 332 kips.
AISC Steel Manual Table 1-1
W 14X68
A= 20 sq.in
ry= 2.46
With respect to least radius of gyration (ry)
KL / r = 1.0 (20 x12) / 2.46 = 97.561
AISC Table 4-22, Page 4-322
Fcr = 22.6 - (22.6 22.3)x0.561 = 22.6 - 0.1683 = 22.4317 ksi
20 ft
Dr. M.E. Haque, P.E. Column Design Examples (Page 4 of 5)
Design Compressive strength, Pn = Fcr Ag = 22.4317(20) = 448.6 kips >332 kips
Therefore, W14X68 is adequate.
OR
Use AISC TABLE 4-1 (Page 4-14)
KL with respect to least radius of gyration = 1.0(20) = 20 ft
For W14X68 with KL=20, design compressive strength = 448 kips >332 kips
Therefore, W14X68 is adequate.
Dr. M.E. Haque, P.E. Column Design Examples (Page 5 of 5)
Example 4: Calculate the design compressive strength of the column section, W 14 X
68 A992 (Fy=50 ksi).
.
SOLUTION:
AISC Steel Manual Table 1-1
W 14X68
A= 20 sq.in
ry= 2.46; rx = 6.00
For AC (Fixed-Hinge), KL/ry = 0.8(14 x 12)/2.46 = 54.63 GOVERNS
For CB (Hinge-Hinge), KL/ry = 1.0(6 x 12)/2.46 = 29.27
For AB (Fixed-Hinge), KL/rx = 0.8(20 x 12)/6.0 = 32.0
For AC, KL = 0.8 x 14 = 11.2
AISC Table 4-1 (Page 4-14),
Design Compressive strength,
c
Pn = 728 (728-700)*(11.2-11)/(12-11) = 728-5.6 = 722.4 kips
OR
For KL/r = 54.63
AISC Table 4-22, (Page 4-319)
c
Fcr = 36.4 0.3(0.63) = 36.211
Pn = Fcr Ag = 36.211 x 20 = 724 kips
20 ft
14 ft
6 ft
A
B
C
A
B
You might also like
- ColumnDesignExamples PDFDocument5 pagesColumnDesignExamples PDFArshi ParveenNo ratings yet
- ColumnDesignExamples PDFDocument5 pagesColumnDesignExamples PDFsimon petrasNo ratings yet
- ColumnDesignExamples PDFDocument5 pagesColumnDesignExamples PDFsimon petrasNo ratings yet
- ColumnDesignExamples PDFDocument5 pagesColumnDesignExamples PDFالكشكولي رضوانNo ratings yet
- Solution To Problems On Design of Machine Elements 4th Edition - Virgil M Faires, Roy M Wingren (Problem Book)Document962 pagesSolution To Problems On Design of Machine Elements 4th Edition - Virgil M Faires, Roy M Wingren (Problem Book)Ahmed Zawad Shovon89% (66)
- Design For Simple StressesDocument131 pagesDesign For Simple Stresseskhudhayer1970No ratings yet
- Machine Design by Faires (Section 1)Document64 pagesMachine Design by Faires (Section 1)Reyna Tatlonghari50% (2)
- Chapter 9Document12 pagesChapter 9Jelianne Kyla Tanpian0% (1)
- Ocbf IbcDocument3 pagesOcbf IbcNikki RobertsNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Faires PDFDocument641 pagesSolucionario Faires PDFjuan13579100% (8)
- Design of Compression MembersDocument24 pagesDesign of Compression Membersmoganna73No ratings yet
- AISC ExamI1&2&3Document11 pagesAISC ExamI1&2&3Dhurai KesavanNo ratings yet
- Steel Design - Sample QuizesDocument12 pagesSteel Design - Sample QuizesPapsi PapNo ratings yet
- Unity Check Examples (ASD Vs LFRD) PDFDocument3 pagesUnity Check Examples (ASD Vs LFRD) PDFLaurence Arcon BanalNo ratings yet
- Compression-Tension-Bending&biaxel Bending: Sharif Haji RasulDocument19 pagesCompression-Tension-Bending&biaxel Bending: Sharif Haji RasulRekan DahoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Design of Rectangular Beams and One-Way SlabsDocument9 pagesChapter - 3: Design of Rectangular Beams and One-Way SlabsMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- LRFD-Composite Beam Desing With MetaldeckDocument12 pagesLRFD-Composite Beam Desing With MetaldeckMaria FabianaNo ratings yet
- Course C-2023Document24 pagesCourse C-2023sancloudNo ratings yet
- LRFD Axially Loaded Compression MembersDocument4 pagesLRFD Axially Loaded Compression Membersالكشكولي رضوانNo ratings yet
- Strength ReductionDocument2 pagesStrength ReductionJadrien Mark ImperialNo ratings yet
- Beam Bearing PlatesDocument23 pagesBeam Bearing PlatesShah Jehan HanifNo ratings yet
- Basement Column Supporting Lateral Resisting Frame Based On ACI 318-11 Input Data & Design SummaryDocument46 pagesBasement Column Supporting Lateral Resisting Frame Based On ACI 318-11 Input Data & Design SummaryHizbar ArsjadNo ratings yet
- Slab On Metal Deck AnalysisDocument5 pagesSlab On Metal Deck Analysismaris_sasecNo ratings yet
- Time Saving Design AidsDocument86 pagesTime Saving Design AidsPurvish Joshi50% (2)
- 5 1 (Compression Members)Document30 pages5 1 (Compression Members)yugoingNo ratings yet
- ColumnsDocument83 pagesColumnsKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- Steel and TimberDocument17 pagesSteel and TimberDiecon Irish ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Ce 03024Document211 pagesCe 03024kimchhoungNo ratings yet
- 3rd Edition LRFD - 2nd Printing ErrataDocument79 pages3rd Edition LRFD - 2nd Printing ErratarilopiyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Elemen Mesin Problem SolvingDocument11 pagesTugas Elemen Mesin Problem SolvingDeandra DenidauliaNo ratings yet
- 2 ULS - Bending With or Without Axial Force (2014) PDFDocument15 pages2 ULS - Bending With or Without Axial Force (2014) PDFLuke LdhNo ratings yet
- Unbraced Column ExampleDocument9 pagesUnbraced Column ExampleAJA14No ratings yet
- Steel Final Project: Prepared By: Siva Soran Supervised By: Mr. Shuaaib A. MohammedDocument25 pagesSteel Final Project: Prepared By: Siva Soran Supervised By: Mr. Shuaaib A. Mohammedsiva soranNo ratings yet
- SCBF Parallel NewDocument156 pagesSCBF Parallel NewZarna ModiNo ratings yet
- New ProjDocument30 pagesNew ProjHueyNo ratings yet
- C 2021 PDFDocument18 pagesC 2021 PDFDenise Koh Chin HuiNo ratings yet
- Post-Tensioned Slab Design ExampleDocument9 pagesPost-Tensioned Slab Design ExampleLaura ManolacheNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design A Practice Oriented Approach 2nd Edition Aghayere Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesStructural Steel Design A Practice Oriented Approach 2nd Edition Aghayere Solutions Manualmediandorsadwl5z100% (23)
- PS9Soln 2014Document13 pagesPS9Soln 2014Eddz Del Rosario RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Test Prep Physics CHP 9-13Document6 pagesAnswer Key To Test Prep Physics CHP 9-13linlinyc686450% (2)
- Circ BaseDocument8 pagesCirc BaseMario Sajulga Dela Cuadra100% (1)
- ColumnsDocument83 pagesColumnsAbdurrahman Asim100% (1)
- Solucionariofaires 141109154231 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument641 pagesSolucionariofaires 141109154231 Conversion Gate02 PDFjersonNo ratings yet
- армирование колонаDocument25 pagesармирование колонаtangerineNo ratings yet
- Chapter - (C) NewDocument32 pagesChapter - (C) NewMeza DhayanNo ratings yet
- Ce408 Chap.cDocument21 pagesCe408 Chap.cmadafaca13100% (1)
- Lecture 8 - Compression Axial OnlyDocument9 pagesLecture 8 - Compression Axial OnlyHumberto EstevezNo ratings yet
- Steel Column DesignDocument18 pagesSteel Column Designmr740111No ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tables of Normalized Associated Legendre Polynomials: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Normalized Associated Legendre Polynomials: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsFrom EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNo ratings yet
- Company in India" DTDC Constantly Endeavours To Meet & Exceed Customers'Document7 pagesCompany in India" DTDC Constantly Endeavours To Meet & Exceed Customers'Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Cooperative Communication For Wireless NetworksDocument164 pagesPerformance Analysis of Cooperative Communication For Wireless NetworksIhtesham JadoonNo ratings yet
- Sap BarcodesDocument59 pagesSap BarcodesDarmin MemiševićNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Erp Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Is An Integrated Computer-Based SystemDocument51 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Erp Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Is An Integrated Computer-Based Systemchandru5g100% (4)
- Wedding Show Proposal BaliDocument10 pagesWedding Show Proposal BaliGirie d'PrayogaNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiDocument26 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiSK BeharNo ratings yet
- 1169a AopDocument12 pages1169a AopBAYARD BernardNo ratings yet
- Mach Oil BrochureDocument44 pagesMach Oil BrochureIntan DavidNo ratings yet
- (ENG) C&T Catalog Hydrelio® Technology 2021Document24 pages(ENG) C&T Catalog Hydrelio® Technology 2021ReenNo ratings yet
- 651Document26 pages651riskraj1984No ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Measuring Machines & It's Applications: Introduction ToDocument65 pagesCo-Ordinate Measuring Machines & It's Applications: Introduction Toshiva dNo ratings yet
- Priorities For Access To HealthDocument25 pagesPriorities For Access To HealthsvpadillaNo ratings yet
- BTD-Final Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesBTD-Final Lesson PlanSunil BajantriNo ratings yet
- Ricardo R4105ZD-61kW Genset Spec SheetDocument2 pagesRicardo R4105ZD-61kW Genset Spec SheetRonald Booc100% (3)
- Section: Engine MechanicalDocument76 pagesSection: Engine MechanicalcesarNo ratings yet
- ASH ReportDocument3 pagesASH ReportChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Heidegger Midterm DissDocument72 pagesHeidegger Midterm Dissrhoda mae a. paquinolNo ratings yet
- PLSQL TutorialspointDocument22 pagesPLSQL TutorialspointSatanu MaityNo ratings yet
- SFTP Certificate Handling in BISDocument18 pagesSFTP Certificate Handling in BISkemoT1990TM100% (1)
- Adobe Transaction No 0991059129 20190125Document2 pagesAdobe Transaction No 0991059129 20190125Mohamed WinnēriNo ratings yet
- Sony Blitz h36 - ManualDocument212 pagesSony Blitz h36 - ManualBohorc Ivica JerryNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Petroleum Engineering BookDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Petroleum Engineering BookRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 - Analisis SinyalDocument17 pagesMateri 1 - Analisis SinyalUsmanNo ratings yet
- About Indian Institute of Technology KanpurDocument54 pagesAbout Indian Institute of Technology KanpurPooja PundeerNo ratings yet
- ANTENASDocument10 pagesANTENASGreo HernandezNo ratings yet
- 816D Specalog (Small)Document2 pages816D Specalog (Small)Arvind HarryNo ratings yet
- Passport Appointment PDFDocument5 pagesPassport Appointment PDFRitu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Transport ModellingDocument37 pagesTransport ModellingRiza Atiq Abdullah Rahmat100% (6)
- Anern Integrated Solar Garden Light-201604Document1 pageAnern Integrated Solar Garden Light-201604Godofredo VillenaNo ratings yet
- KampasDocument1 pageKampasSamer aneNo ratings yet