Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014 Skema
Uploaded by
Cikgu Faizal100%(4)100% found this document useful (4 votes)
2K views83 pagesSumber : http://iamchampion.blogspot.com/
Modul Perfect Score SBP 2014 boleh digunakan sebagai tujuan persediaan akhir. Modul Perfect Score 2014 merupakan modul tahunan yang dihasilkan oleh Panel Biologi Sekolah Berasrama Penuh sejak tahun 2008.
Selamat berjaya kepada semua calon SPM 2014
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSumber : http://iamchampion.blogspot.com/
Modul Perfect Score SBP 2014 boleh digunakan sebagai tujuan persediaan akhir. Modul Perfect Score 2014 merupakan modul tahunan yang dihasilkan oleh Panel Biologi Sekolah Berasrama Penuh sejak tahun 2008.
Selamat berjaya kepada semua calon SPM 2014
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(4)100% found this document useful (4 votes)
2K views83 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014 Skema
Uploaded by
Cikgu FaizalSumber : http://iamchampion.blogspot.com/
Modul Perfect Score SBP 2014 boleh digunakan sebagai tujuan persediaan akhir. Modul Perfect Score 2014 merupakan modul tahunan yang dihasilkan oleh Panel Biologi Sekolah Berasrama Penuh sejak tahun 2008.
Selamat berjaya kepada semua calon SPM 2014
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 83
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 1
SECTION A
[60 marks]
Answer all the questions
Jawab semua soalan dalam bahagian ini
1. Diagram 1.1 shows the structure of animal cell
Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan struktur sel haiwan
Diagram 1.1
Rajah 1.1
(a) On Diagram 1.1, label X and Y.
Pada Rajah 1.1, labelkan X dan Y
[1marks]
(b) Explain one characteristic of Y related to cell division.
Terangkan satu ciri Y berkaitan dengan pembahagian sel
Sample answer:
F: Composed of a complex arrangement of microtubules
E: Form spindle fibers during cell division (in animal cell)
[2marks]
Y: centriole
X: nucleus
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 2
(c) Explain the function of X in cell division
Terangkan fungsi X dalam pembahagian sel
Sample answer:
F: nucleus containchromosomes which carry genetic information
E: behavior of chromosome in stage of mitosis/meiosis/cell division
transfer genetic information to daughter cell
[2marks]
(d) Diagram 1.2 below shows stage of cell division in somatic cell of human.
In the box given, draw another two stage in that cell division.
Rajah 1.2 di bawah menunjukkan peringkat pembahagian sel dalam sel soma
manusia. Dalam kotak yang diberi, lukis dua peringkat dalam pembahagian tersebut
[2marks]
Diagram 1.2
Rajah 1.2
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 3
(e) If spindle fibre is not form in Diagram 1.2 (d), explain the effect on the number of
chromosome in the daughter cell.
Jika gentian gelendong tidak terbentuk dalam Rajah 1.2 (d), terangkan kesan keatas
bilangan kromosom dalam sel anak
Sample answer:
F:the number of chromosome in the daughter cell less/ extra
E: no contraction of spindle fibre to pull chromosome toward the pole
[2marks]
(f) Explain how the cell division above can be used to increase in a short time the
number of given example of the plant in the farm.
Terangkan bagaimanakah pembahagian sel di atas dapat digunakan untuk
meningkatkan bilangan dalam masa yang singkat tumbuhan yang dinamakan dalam
ladang.
Sample answer:
Example of the plant: banana/ palm oil/ any other example
F:tissue culture
E1: cut off explants / part of plant / young shoot, leaves, roots, seeds, embryos
E2: explants are sterilized and placed in cultured medium containing nutrient
such as glucose, amino acids, minerals and growth hormone/ auxin
E3:the culture medium need to be maintained at optimum pH and temperature
25 -35C
E4: explants divide by mitosis form callus// undifferentiated mass of tissues
E5: callus develop into embryoid/ somatic embryos and later into plantlets
E6: plantlets are transferred to the soil where they grow into adult plant
[3marks]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 4
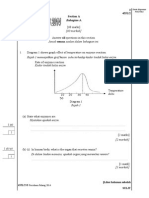
2.(a) Diagram 2.1 shows the shape of red blood cells after being immersed for 30 minutes
in three solutions with different concentration.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan bentuk sel darah merah selepas direndam selama 30 minit
dalam tiga larutan yang berbeza kepekatannya.
Based on the Diagram 2.1
Berdasarkan Rajah 2.1
(i) State the condition of the red blood cells after being immersed in
Nyatakan keadaan sel darah merah selepas direndam di dalam
Sample answer:
Solution P: Crenation / shrink / shrivel
Solution Q: Haemolysis / swell and burst
[2 marks]
Diagram 2.1
Red blood cells in Q solution
Sel darah merah dalam larutan Q
Red blood cells in P solution
Sel darah merah dalam larutan P
Red blood cells in R solution
Sel darah merah dalam larutan R
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 5
(ii) Name the type of solution R in which the red blood cells are immersed.
Namakan jenis larutan R yang mana sel darah merah direndam.
Sample answer:
Solution R is isotonic solution.
[1 mark]
(iii) Explain your answers given in a(ii)
Terangkan jawapan yang anda berikan di a(ii)
Sample answer:
P1:The cell retains its normal shape/ biconcave disc shape.
P2:The water diffuses in and out of the cells at equal rate by osmosis
P3:Solution R has the same osmotic concentration as the cytoplasmic fluid
in the red blood cells
[3 marks]
(b)
Based on the statement, explain why vinegar is suitable to be used as the natural
preservative for the preservation of garlic.
Berdasarkan pernyataan di atas ,terangkan mengapa cuka adalah sesuai digunakan
sebagai pengawet semulajadi untuk bawang putih.
Sample answer:
F1:Vinegar has a low pH/acidic
E1: Vinegar diffuses into the tissues of the garlic
E2: The tissues of the garlic becomes acidic
E3: The low pH prevents the growth of microorganisms in garlics
E4: The garlic can be preserved to last longer
[3 marks]
Food such as mushrooms, fruits, vegetables and fish can be preserved longer
by using natural preservatives such as salt, sugar and vinegar.
Makanan seperti cendawan, buah-buahan, sayur-sayuran dan ikan boleh
diawet untuk tahan lama menggunakan bahan-bahan pengawet semulajadi
seperti garam,gula dan cuka .
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 6
(c) Diagram 2.2 shows the condition of herbaceous plant due to water shortage in soil.
Rajah 2.2 menunjukkan keadaan pokok herba disebabkan oleh kekurangan air
dalam tanah.
Explain the condition of the plant in Diagram 2.2 after one week.
Terangkan keadaan pokok dalam Rajah 2.2 selepas satu minggu.
Sample answer:
F:The plant wilt
E1: The cells become flaccid / plasmolysed // both the vacuole the vacuole and
cytoplasm shrink // the plasma membrane of the root cells pull away from
the cell wall.
E2: Water molecules diffuse out from the cell sap of the root hair cell by osmosis
E3: (the remaining) soil water becomes hypertonic to the cell sap of the root hair
cell as the soil dries out.
[3 marks]
Water shortage after one week
Kekurangan air selepas satu minggu
Diagram 2.2
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 7
4. Diagram 4.1 shows the process of phagocytosis as second line of defence to destroy
the bacteria
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan proses fagositosis sebagai barisan pertahanan kedua untuk
memusnahkan bakteria.
Stage 1 Stage 2
Peringkat 1 Peringkat 2
Stage 4 Stage 3
Peringkat 4 Peringkat 3
Diagram 4.1/ Rajah 4.1
(a) (i) Name cell M involved in mechanism above.
Namakan sel M yang terlibat dalam mekanisma di atas.
Neutrophil / eosinophil / basophil / granulocyte / phagocyte
[1 mark]
(ii) Draw a diagram in stage 3
Lukis rajah dalam peringkat 3.
[1 mark]
(b) Explain the function of lisosome in mechanism above
Terangkan peranan lisosom dalam mekanisma di atas
F : digest bacteria
E : because lisosome contain hydrolytic enzymes / cellulase which digest
cellulose / by breaking down the bacteria cell wall.
[2 mark]
M
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 8
(c) Explain what happen in stage 2.
Terangkan apa yang berlaku dalam peringkat 2.
F : phagocytes surrounds / engulfs the bacteria using pseudopodia
E : forming phagocytic vacuole / fagosome /food vacuole
[2 mark]
(d) How the action of M to pathogen is different to lymphocyte?
Bagaimanakah tindakan M terhadap patogen adalah berbeza dengan limfosit?
M kill the pathogen by engulf and digest the pathogen but lymphocyte
produce antibody then antibody kill the pathogen / neutralize the toxin from
pathogen
[1 marks]
(e) Diagram below show a type of immunity occurs in human.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan jenis immuniti yang berlaku dalam manusia.
(i) Name the type of immunity shows in the diagram.
Namakan jenis immuniti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah.
Answer:
Artificial active immunity
[1 mark]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 9
(ii) Name the second injection and why the person should take second injection?
Namakan suntikan kedua dan mengapa individu ini perlu mengambil suntikan
kedua?
Sample answer:
N: booster dose // an additional administration of a vaccine
E: to stimulate lymphocyte produce more antibody until achieve immunity
level.
[2 mark]
(f) The above immunity is example of third line of defence. What make it different to the
second line of defence?
Sample answer:
P1: Third line of defence specific response to pathogen infection but
second line of defence non-specific response/generalized responses
to pathogen infection
P2: Third line of defence involved production of antibody(active immunity)/
used supply antibody (passive immunity) from leucocyte but second
line of defence involve the physical structure of leucocyte
[2 marks]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 10
Q
5. Diagram 5.1 shows the stages of the ovarian cycle in human ovary
Diagram 5.2 shows the thickness of the endometrium of uterus before the fertilisation in
the second menstrual cycle.
Rajah 5.1 menunjukkan peringkat kitaran ovary dalam ovary manusia.
Rajah 5.2 menunjukkan ketebalan endometrium dalam uterus sebelum berlaku
persenyawaan dalam kitarhaid yang kedua.
Diagram 5.1
Diagram 5.2
Y
P
Secondary
follicle
Secondary
oocyte
X
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 11
a) (i) Describe the change in the structure of follicle P into a secondary follicle.
Terangkan perubahan struktur folikel P dalam pembentukan folikel sekunder.
[2 marks]
Sample answer:
P1 : FSH concentration increases // is released (by the pituitary gland).
P2 : Stimulates the development of follicle cells. (1m)
P3 : Primary follicle developed into secondary / Graafian follicle // Primary
oocyte developed into secondary oocyte
(ii) Relate the change in (a)(i)to the thickness of the endometrium
Hubungkan perubahan dalam (a) (i) dengan ketebalan endometrium
[1 mark]
Sample answer:
P1 : The thickness of the endometrial wall increases
b) Explain the process that occurs at X.
Terangkan proses yang berlaku pada X.
[2 marks]
Sample answer:
P1 : Ovulation
P2 : The release of secondary oocyte from the (matured) secondary follicle /
Graafian follicle to the oviduct / Fallopian duct
c) Explain the effect of the change of structure Q to the thickness of the endometrium.
Terangkan kesan perubahan struktur Q keatas ketebalan dinding endometrium.
[2 marks]
Sample answer:
P1 : The thickness of the endometrial wall / uterine lining decreases.
P2 : The level of progesterone decreases.
d) (i) Fertilisation takes place in the second menstrual cycle.
Complete the graph in Diagram 5.2 to show the changes in the thickness of the
endometrium after point Y
Persenyawaan berlaku dalam kitar haid yang kedua
Lengkapkan graf dalam Rajah 5.2 untuk menunjukkan perubahan ketebalan
endometrium selepas titik Y
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 12
[1 mark]
Answer:
(ii) Explain your answer in (d)(i).
Terangkan jawapan di dalam (d)(i).
[2 marks]
Sample answer:
P1 : The corpus luteum / placenta developed.
P2 : The corpus luteum / placenta released progesterone (and oestrogen).
e) (i) State the changes in the thickness of the endometrium after point Y relating to the
secretion of hormones secreted by the ovary.
Terangkan hubungan perubahan ketebalan endometrium selepas titik Y dengan
perembesan hormon oleh ovari.
[1 mark]
Sample answer:
P1 : The thickness of the endometrial wall increases / is maintained.
(ii) State the importance of thickened endometrium to the continuity of life
Nyatakan kepentingan ketebalan endometrium dalam kesinambungan hidupan
[1 mark]
Sample answer:
P1 : Increase the chance of implantation // development of embryo /
blastocyst.
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 13
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 14
SECTION B
[40 marks]
Answer any two questions from this section
Jawab mana-mana duasoalandaripadabahagianini
6. Diagram 6.1 shows the growth and development process at the shoot tip.
Rajah 6.1 menunjukkan proses pertumbuhan dan perkembangan pada hujung pucuk.
Diagram 6.1
a) Explain the process of primary growth that shown in Diagram 6.1
Terangkan proses pertumbuhan primer yang ditunjukkandalam Rajah 6.1
[8 marks]
Sample answer:
Cell division
P1: Cell division take place by mitosis
P2: Each cell divides to become two cells which are identical to the parent cell
P3: This process repeats itself until a mass of cells consisting of many
identical cells are formed
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 15
Cell elongation
P4: Cell elongation cause by intake of water and nutrient into the cell from the
environment
P5: Water accumulates in the vacuoles of plant cells to form large central
vacuole, causing the primary wall to stretch
P6: The nutrients are used in the building up of the protoplasm// more
organelles leading to an increase in the cell size and volume
Cell differentiation
P7: Cells begin to differ from each other to form groups of specialised cells
P8: to perform new and specialised functions // Example: cell differentiation in
the epidermis of roots to form root hair to enable the cell to have a large
total surface area for absorption of water from the soil
P9: Cells differentiation causing the changes of shape and complexity of
organism
b) Explain the importance of primary growth to plant.
Terangkan kepentingan pertumbuhan primer kepada tumbuhan
[4 marks]
Sample answer:
P1: During this time the stem and roots of plant increase in length. This allows
a plant to achieve its maximum height
P2: Its bring about the formation of primary xylem that helps in the transport of
water and mineral
P3: Its bring about the formation of primary phloem that helps in the transports
organic substances
P4: Its provides support because the walls of xylem tissue are thickened with
lignin
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 16
c) Diagram 6.2 shown the tropism respond at shoot tip and root tip.
Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan gerakbalas tropisme pada hujung pucuk dan hujung akar.
Diagram 6.2
Base on diagram 6.2 explain how the tropism response occurred.
Berdasarkan rajah 6.2 terangkan bagaimana gerakbalas tropisme berlaku.
[8 marks]
Sample answer:
P1: auxins produced by shoot and root
P2: auxins diffuse into zone of elongation
P3: (Owing to gravity) auxins move to lower side of shoot and root
P4: The lower side of shoot and root has a higher concentration of auxins than
the upper side
P5: height concentration of auxins in the shoot promotes elongation of cells.
P6: the lower side of the shoot will faster than the upper side
P7: the shoot curves and grows upward (negative geotropism)
P8: height concentration of auxins in the root inhibits elongation of cells.
P9: So the upper side of the root will grow faster than the lower side
P10: the root curves and grows downwards (positive geotropism)
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 17
7. (a) Explain the interaction based on Diagram 7.1
Terangkan interaksi berdasarkan Rajah 7.1
Diagram 7.1
Rajah 7.1
[4marks]
Sample answer:
F: Commensalism
E1:relationship between two species that benefits one species/ commensal but
neither benefits nor harms the other species/ host
E2: fern has a sponge-like root mass that soaks up rain water and absorbs
nutrients released from the decaying litter.
E3: fern leaves has mesophyll cell contain chloroplast do photosynthesis
(b) Diagram 7.2 shows mechanism of photosynthesis in plant. Explain why the product
from light reaction need for dark reaction.
Rajah 7.2 menunjukkan mekanisma fotosintesis dalam tumbuhan.Terangkan
Mengapa produk dari tindakbalas cahaya diperlukan untuk tindakbalas gelap.
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 18
[6marks]
Sample answer:
F: Mechanism of photosynthesis in plant consist of light reaction
anddark reaction
E1: Chlorophyll absorbs light energy released electrons andproduce ATP
E2: Light energy is also split the water molecules intohydrogen ion(H
+
)and
hydroxyl ions(OH
-
)/Photolysis of water
E3: Hydrogen ions combine with electron from chlorophyll to form
hydrogen atoms
E4: Hydrogen atom and ATP will be used in dark reaction
E5: Each hydroxyl ion loses an electron to form hydroxyl group (the
electron is received by the chlorophyll)
E6: The hydroxyl groups then combine to form water and gaseous oxygen
E7: Hydrogen atomfit/ reduce carbon dioxide in dark reaction to form
glucose
E8: Reduction of carbon dioxide need ATP from light reaction
E9: The reaction catalysed by photosynthetic enzyme in stroma
E10: Produced glucose molecules, then glucose undergo condensation/
converted to starch for storage
Diagram 7.2
Rajah 7.2
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 19
(c) Diagram 7.3 shows the condition of the town.
Rajah 7.3 menunjukkan sebuah bandar.
Diagram 7.3
Rajah 7.3
(i) Discuss the effect of air pollution may occur in the town.
Bincangkan kesan pencemaran udaya yang mungkin berlaku dalam bandar.
[6 marks]
Sample answer:
F1: formation of haze / smog
E1: cause by fine particle matter/smoke/ soot
E2: prevents vision /reduce light intensity photosynthesis/ reduce oxygen
content
F2: acid rain
E1: cause by SO
2
/ NO
2
E2: estroy building
F3: increasetemperature
E1: cause by CO
2
E2: green house effect/ global warming
F4: depletion of ozonelayer
E1: cause by CFC gases
E4: more uv penetration
F5: respiratory problems/allergies/risk for cancer
E1: cause by CO/ SO
2
/ NO
2
E2: cause health hazards
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 20
(ii) If you are an environmental activist, suggest how you would explain to the
government about the measures needed to overcome the type of pollution.
Jika anda seorang aktivis alam sekitar, cadangkan bagaimana anda akan
menjelaskan kepada kerajaan mengenai langkah-langkah yang diperlukan untuk
mengatasi jenis pencemaran.
[4 marks]
Sample answer:
F1: implementation of laws
E1: control and prevent pollution using the environmental act
F2: use of technology
E1: using unleaded petrol for cars/ fit catalytic converter in factory
F3: education
E3: media massa/ internate/ scholl
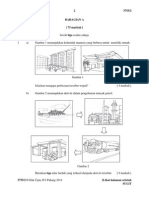
8. (a) Diagram 8.1 shows three types of neurons.
Rajah 8.1 menunjukkantigajenis neuron.
Diagram 8.1
Rajah 8.1
Name types of neurone P, Q and R and state two differences between the structure
of neurone P and neurone Q
Namakan jenis neuron P, Q dan R dan nyatakan dua perbezaan di antara struktur
bagi neuron P dan neuron Q
[4 marks]
Neurone P
Neuron P
Neurone Q
Neuron Q
Neurone R
Neuron R
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 21
Sample answer:
Neurone P is afferent neurone
Neurone Q is efferent neurone
Neurone R isinterneurone
3 = 2 marks
2 = 1 marks
Neurone P Neurone Q
P1: has a long dendron but
a short axon
Has a short dendron but a
long axon
P2: cell body is located in
the middle of the cell
Cell body is located at the
terminal / end of the cell
(b) Diagram 8.2 shows the transmission of a nerve impulse from neurone P to neurone
R.
Rajah 8.2 menunjukkan pemindahan impuls saraf dari neuron P ke neuron R.
Diagram 8.2
Rajah 8.2
Explain the transmission of a nerve impulse from neurone P to neurone R
Terangkan pemindahan impuls saraf dari neuron P ke neuron R
[6 marks]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 22
Sample answer:
P1: when impulse reaches the synaptic knob / terminal / terminal axon /
presynaptic membrane
P2: it stimulates the synaptic vesicles
P3: to release neurotransmitter
P4: mitochondrion (in the synaptic terminal) produces energy / ATP
P5: for active transport / transmission of the impulse
P6: (neurotransmitter) diffuse across / into synaptic cleft / synapse to the next
dendrite / neurone R / postsynaptic membrane
P7: transmission of impulse from neurone P to neurone R is in the form of
chemicals
(c) Diagram 8.3a shows example of voluntary action and
Diagram 8.3b shows example of involuntary action. By using pathway of transmission
of information from receptors to effectors, explain similarities and difference between
voluntary action and involuntary action.
Rajah 8.3a menunjukkan contoh tindakan terkawal dan Rajah 8.3b menunjukkan
contoh tindakan luar kawal. Dengan menggunakan laluan pemindahanmaklumat dari
reseptor kepada efektor, terangkan persamaan dan perbezaan tindakan terkawal
dan tindakan luar kawal.
Diagram 8.3a Diagram 8.3b
Rajah 8.3a Rajah 8.3b
[10 mark]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 23
Sample answer:
Pathway of transmission of information from receptors to effectors for
voluntary action
Pathway of transmission of information from receptors to effectorsfor
involuntary action
Similarities
S1: both voluntary action and involuntary action involved receptor
E1: to detect the stimulus and trigger impulse
S2: both voluntary action and involuntary action involved 3 neuron
E2: carry impulse from receptor to efector
S3: both voluntary action and involuntary action involved efector
receptor
efector
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 24
E3: contract to show the response
Differences
D1: Voluntary action is controlled by conscious thoughts but Involuntary
action occurs automatically without any conscious control
E1: because voluntary action Involves the integration and
interpretationof information in the cerebrum
but involuntary action involve spinal cord only
D2: Voluntary action are under the control of the will of the
Individual but involuntaryaction are not control by the will
E2: because voluntary action involve the action of doing
thing for activity but involuntary action involve the action to protect the
person from danger
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 25
9. (a) Diagram 9.1 and 9.2 shows the histogram about distribution of genetic variation in
human.
Rajah 9.1 dan 9.2 menunjukkan histogram mengenai taburan variasi genetik dalam
manusia.
Diagram 9.1 Diagram 9.2
(i) With a suitable example, explain the differences of two kinds of variation.
Dengan menggunakan contoh yang sesuai, terangkan perbezaan di antara kedua-
dua variasi tersebut.
[7 marks]
Sample answer:
Example of continuous variation: Height or weight
Example of discontinuous variation: ABO blood group
Differences:
Continuous variation Discontinuous variation
Graf distribution shows a normal
distribution
Graf distribution shows a discrete
distribution
The characters are quantitative /
can be measured and graded (from
one extreme to the other)
The characters are qualitative /
cannot be measured and graded
(from one extreme to the other)
Exhibits a spectrum of phenotypes
with intermediate character
Exhibits a few distinctive phenotypes
with no intermediate character
Influenced by environmental
factors
Is not Influenced by environmental
factors
Two or more genes control the
same character
A single genes determines the
differences in the traits of the
character
The phenotype is usually
controlled by many pair of alleles
The phenotype is controlled by a pair
of alleles
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 26
(ii) What is the importance of variation to organism?
Apakah kepentingan variasi kepada organisma?
[3 marks]
Sample answer:
P1: variation provided better adaptation for organism to survive in the
changing environment
P2: variation are essential to the survival of species / to survive more
successfully
P3: variation be able to organism explore a new habitat
P4: to ensure organism survival from predator
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 27
(b) Diagram 9.3a, 9.3b and 9.3c shows the genetic factors that affected on the variation
of organism.
Rajah 9.3a, 9.3b dan 9.3c menunjukkan faktor-faktor genetik yang member kesan
ke atas variasi pada organisma.
Diagram 9.3a
Diagram 9.3b Diagram 9.3c
Explain how these factors in the diagram above will cause the variation among the
organism.
Terangkan bagaimana faktor-faktor dalam rajah di atas akan menyebabkan variasi
dikalangan organisma. [10 marks]
Sample answer:
F1: meiosis
P1: produce varies gamete with different genetic content
P2: through homologous chromosomes random assortment during metaphase
I
Combination 4
Gabungan4
Combination 1
Gabungan 1
Combination 2
Gabungan2
Combination 3
Gabungan3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 28
F2: crossing over
P3: two homologous chromosomes are paired up / synapsis during prophase I
P3: crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids at the chiasma
P4: chromatids break and rejoin in such a way that segments of chromatids are
exchange // causing a genetic recombination
P5: genes in the chromosomes is altered and gametes with various
combinations of chromosomes are produced
F3: Fertilization
P6: random fertilization between sperm and ovum
P7: produce zygote with varies genetic material
End
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 1
SECTION A
[60 marks]
Answer all questions in this section.
Jawab semua soalan di bahagian ini
1. Diagram 1 shows a microscopic structure of a part of pancreatic cell.
Rajah 1 menunjukan struktur mikroskopik sebahagian sel pancreas.
(a) (i) Name the organelle K and organelle L
Namakan organel K dan organel L.
K: Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
L : Golgi apparatus / body
[2 marks]
(ii) Explain how the organelle K and organelle L are interrelated in their
function
Terangkan bagaimana organel K dan organel L adalah saling berkaitan dari
segi fungsi mereka.
P1 : Rough endoplasmic reticulum /K transports protein synthesized
in the ribosomes
P2 : then forms a transport vesicle which carries the protein to Golgi
body / L
P3 : Golgi body processes, modifies the protein into a functional one /
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
Note
Catatan
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 2
enzyme / hormone (before forming a secretory vesicle)
[2 marks]
(b) (i) Name one chemical substance in the structure R which is involved in the
synthesis of protien in a cell.
Namakan satu bahan kimia dalam structur R yang terlibat dalam sintesis
protien dalam suatu sel.
The chemical substance in the chromosome - DNA / Deoxyribonucleic
acid
[1 marks]
(ii) Draw the structure of the chemical compound in (b)(i) in the blank space
below.
Lukis struktur bahan kimia dalam (b)(i) dalam ruang kosong di bawah.
DNA structure:
Nitrogenous base
DNA strand
comprises phosphate and pentose sugar
[2 marks]
(c) (i) Based on the diagram, describe the synthesis of a specific pancreatic
hormone in the cell.
Berdasarkan gambarajah itu, huraikan bagaimana suatu hormon tertentu
disintesiskan dalam sel itu
The synthesis of hormone in the pancreas cell:
P1 : The genetic information for the synthesis of the protein/ hormone
(eg. Insulin contained in the DNA) is copied to RNA / messenger
RNA
P2: (RNA) carries the information to ribosome
P3: (Ribosome) synthesize the protein and
Drawing = 1 mark
2 correct labels = 1 mark
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 3
P4 : (Protein) is transfer to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
P5: then protein is transported to Golgi Apparatus
P6: (In Golgi Apparatus) protein is modified to hormone // processed
/packed and sorted / transport to plasma membrane
[3 marks]
(ii) The structure R in Diagram 1 undergoes some changes due to exposure to
radioactive rays. Explain the possible effect to the synthesis of the
hormone.
Struktur R dalam Rajah 1 mengalami perubahan akibat pendedahan
kepada sinaran radioaktif. Terangkan kemungkinan kesanya ke atas
sintesis hormon itu.
Effect of changes of the structure R / chromosome on hormone
synthesis:
P1: there will be some changes in the gene / base sequence / gene
mutation responsible for the synthesis of the hormone
P2: protein synthesis changes , a different protein / not the original
hormone is synthesized or no hormone is being synthesized
[2 marks]
2. Diagram 2.1 shows two individual, P and Q in two different situations. P is in a
vigorous activity while Q is at rest. Processes of R and S occurs in a human muscle
cell.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan dua individu, P dan Q dalam dua situasi yang berbeza. P
sedang melakukan satu aktiviti cergas manakala Q berada dalam keadaan rehat.
Proses R dan S berlaku dalam satu sel otot manusia.
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 4
(a) Based on Diagram 2.1, name the processes R and S.
Berdasarkan Rajah 2.1, namakan proses R dan S.
Process R/ Proses R : Anaerobic respiration
Process S/ Proses S : Aerobic respiration
[2 marks]
(b) Write the equation of process S.
Tuliskan persamaan bagi proses S.
[1 marks]
(c)
State two differences between process R and process S.
Nyatakan perbezaan diantara proses R dan proses S.
Process R/ Anaerobic respiration Process S/ Aerobic respiration
Glucose + Water Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
Diagram 2.1
Rajah 2.1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 5
Glucose is broken down partially Glucose is broken down completely
ATP produced 2 ATP ATP produces 38 ATP
Product Lactic acid and energy Product Carbon dioxide , water
and energy
Occurs in the absence of oxygen Occurs in the presence of oxygen
[2 marks]
(d)
Diagram 2.2(a) shows fish respiratory structure and Diagram 2.2(b) shows
human respiratory structure.
Rajah 2.2(a) menunjukkan struktur respirasi ikan dan Rajah 2.2(b)
menunjukkan struktur respirasi manusia.
(i) What is X?
Apakah X?
Answer : Gills
[1 mark]
(ii) Structure X has adaptation for good gases exchange in fish.
Explain one adaptation of X.
Answer: 1. A :(Gills ) have lamellae
E :to increase total surface area (for gases exchange)
Diagram 2.2(a)
Rajah 2.2(a)
Diagram 2.2(b)
Rajah 2.2(b)
X
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 6
2. A : (Gills) have network of blood capillary
E : to transport gases rapidly
3. A : Counter current of blood and water
E: increase diffusion of gases in and out of the gills
4: A :Numerous in number
E: to increase total surface area (for gases exchange)
[2 marks]
(e) A man is a heavy smoker.
Explain how this habit affect the efficiency of gases exchange on the
respiratory structure in Diagram 2.2(b).
Seorang lelaki adalah seorang perokok tegar.
Terangkan bagaimana tabiat ini mempengaruhi kecekapan pertukaran gas
pada struktur respirasi dalam Diagram 2.2(b).
Answer:
P1: Tobacco smoke contain tar
P2: (Tar) deposit on the surface of alveolus
P3 : Tobacco smoke contain heat
P4 : reduce moisture on the surface of alveolus
P5 : Tobacco smoke contain NO
2
P6 : increase acidity / corrode the surface of alveolus
[4 marks]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 7
3. Diagram 3.1 shows the sequence of hydrolysis of starch to molecules P and molecule Q
by enzymes.
Rajah 3.1 menunjukkan urutan hidrolisis kanji kepada molekul P dan molekul Q oleh enzim.
(a) (i) Complete Table 3.1.
Lengkapkan Jadual 3.1
Molecule
Molekul
Name of molecule
Nama molekul
Name the enzyme
involved in hydrolysis
Namakan enzim yang
terlibat dalam hidrolisiss
P Maltose Amylase
Q Glucose Maltase
[4 marks]
(ii) Based on your biological knowledge, explain the effect of consuming food that
Enzyme
Enzim
Starch
Kanji
+ water
air
+ water
air
Molecule P
Molekul P
Enzyme
Enzim
Molecule Q
Molekul Q
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
Table 3.1 / Jadual 3.1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 8
contain excessive of starch on health.
Berdasarkan pengetahuan biologi anda, terangkan kesan pengambilan
makanan yang mengandungi kanji berlebihan keatas kesihatan.
Answer :
P1 : Glucose level in blood increase/ hyperglycemia
P2 : Starch (finally) is digested into glucose
P3 : Glucose is absorbed into blood (capillary)
P4 : causes diabetes mellitus / obesity
[2 marks]
(b) Table 3.2 shows the energy value and nutrient content in a few types of food taken by
student.
Jadual 3.2 menunjukkan nilai tenaga dan kandungan nutrient di dalam beberapa jenis
makanan yang diambil oleh seorang pelajar.
Food
Makanan
(/100g)
Energy
Tenaga
(kJ)
Carbohydrate
Karbohidrat
(g)
Fats
Lemak
(g)
Protein
Protein
(g)
Vitamin C
Vitamin C
(g)
Rice
Nasi
1530 86.8 1.0 6.4 0.0
Fish
Ikan
320 0.0 0.5 17.5 0.0
Egg
Telur
612 0.0 10.9 12.4 0.0
Orange
Oren
150 8.5 0.0 0.8 50
(i) Based on Table 3.2, which type of food supplies the most energy?
Table 3.2/ Jadual 3.2
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 9
Berdasarkan Jadual 3.2, jenis makanan manakah yang membekalkan paling
banyak tenaga?
Answer: Rice
[1 mark]
(ii) Which type of food should be taken regularly to prevent scurvy?
Jenis makanan manakah yang perlu kerap diambil untuk mengelakkan
penyakit skurvi?
Answer: Orange
[1 mark]
(iii) Calculate the amount of energy obtained by the student if he eats a meal which
contain 200 g rice and 150g fish.
Kirakan jumlah tenaga yang diperolehi oleh pelajar tersebut jika dia mengambil
200 g nasi dan 150 g ikan.
Answer:
Rice - 1530 kJ x 2 = 3060 kJ
Fish - 320 kJ x 1.5 = 480 kJ
Total : 3060 + 480 = 3540 kJ
[3 marks]
(c) Why does an egg produces double amount of energy compared to a fish?
Mengapakah sebiji telur menghasilkan jumlah tenaga dua kali ganda berbanding
seekor ikan?
Answer:
Egg contain more fat/lipid than fish
[1 mark]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 10
4.
Diagram 4.1 shows a longitudinal section of the reproductive parts of a flower during
fertilization.
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan keratan memanjang bahagian pembiakan bunga semasa
persenyawaan.
(a) (i) In Diagram 4.1, label P,Q, R and S
Pada Rajah 4.1, labelkan P, Q, R dan S
[2 marks]
(ii) In the space below, draw a section through the ovule showing all the cells in S.
Label the cells involved in fertilization.
Dalam ruang di bawah , lukiskan keratan melalui ovul menunjukkan semua sel-
sel dalam S. Labelkan sel-sel yang terlibat dalam persenyawaan
Pollen tube
Male gamete nucleus
Embryo sac
Ovary
Diagram 4.1
Rajah 4.1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 11
Drawing: clear diagram with 8 nucleus 1 mark
Label : 2 label =1 mark
(iii) Describe the fertilization process that occurs.
Huraikan proses persenyawaan yang berlaku .
[2marks]
P1 :One of the Q/ male nucleus fertilizes an egg to form the diploid zygote
P2:One of the Q/ male nucleus fertilizes 2 polar nuclei to form the triploid
endosperm
(b) (i) In Diagram 4.1, the structure Y has to be kept dormant for future research
purposes.
Explain how Y can be prevented from germinating.
Dalam Rajah 4.1, struktur Y perlu disimpan tidak aktif untuk tujuan penyelidikan
pada masa hadapan.
Terangkan bagaimana Y boleh dihalang daripada bercambah .
[2 marks]
P1 : Keep Y in dry place/ low temperature
P2 : Because moisture initiate germination// enzyme is in inactive state
(ii) Suggest one method to stimulate the germination of Y
Cadangkan satu kaedah untuk merangsang percambahan Y.
[1mark]
Dropping/ spraying sucrose / sugary solution on Y
(e)
Diagram 4.2 shows a watermelon with seed and watermelon without seed..
Rajah 4.2 menunjukkan buah tembikai dengan biji dan buah tembikai tanpa biji.
Polar cell
Egg cell
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 12
Nowadays, it is more easier
to find seedless watermelon in market. Shoppers also can find varieties of
seedless oranges, grapes, and cucumbers.
Explain how to produce varieties of fruits without seed.
Pada masa kini, adalah lebih lebih untuk mencari tembikai tanpa biji di pasaran.
Pembeli juga boleh mendapatkan buah limau , anggur dan timun tanpa biji .
Terangkan bagaimana untuk menghasilkan buah tanpa biji . [3marks]
P1 : Parthenocarpy
P2 : Spraying flower with auxin,
P3 : stigma and anther becomes degenerate
P4 : auxin diffuse into ovary and stimulate ovary to develop.
5 Diagram 5.1 shows a uriniferous tubule and its associated blood vessels.
Diagram 5.2 shows cells from structure P as seen through an electron microscope.
Gambarajah 5.1 menunjukkan tubul uriniferus dan salurdarah yang berkaitan.
Gambarajah 5.2 menunjukkan struktur sel P seperti yang dilihat di bawah mikroskop
elektron.
Diagram 4.2 / Rajah 4.2
Diagram 5.1
Rajah 5.1
Y
P
X
Q
Blood
Darah
Blood
Darah
Blood vessel
Salur darah
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 13
(a) State the difference in the urea composition between the blood vessel X and Y.
Nyatakan perbezaan kandungan urea antara salur darah X dan Y.
Urea concentration is lowest in Y but higher in X.
[1 mark]
(b) Based on the Diagram 5.2 explain how the cells are structured for reabsorption of
substances.
Berdasarkan Gambarajah 5.2, terangkan bagaimana sel distrukturkan untuk
penyerapan semula bahan.
P1 :They have many/abundant mitochondria
P2 : Produce a lot of energy needed for active transport
or
P1 :Numerous/many microvilli
P2 : Increase total surface area for reabsorption
[2 marks]
(c) Table 5.1 shows the concentration of certain substances found in structure Q.
Diagram 5.1
Rajah 5.1
Diagram 5.2
Rajah 5.2
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 14
Jadual 5.1 menunjukkan kepekatan beberapa bahan yang terdapat di dalam struktur
Q.
Substances
Bahan
Water
Air
Protein
Protein
Glucose
Glukosa
Urea
Urea
Salts
Garam
Concentration
Kepekatan
(%)
95.0 0.00 0.00 2.00 1.50
Explain how the concentration of the substances present in Q would change after
eating meat and eggs.
Terangkan bagaimana kepekatan bahan-bahan yang terdapat dalam Q akan berubah
selepas memakan daging dan telur.
P1 :meat and eggs contains high protein/ main source of amino acid
P2:(Excess) amino acids are deaminated / converted into ammonia / urea in
the liver
P3 :The urea is transported to the kidneys and removed as urine
P4 :The concentration of urea in the urine would increase then 2.00
[3 marks]
(d)
Diagram 5.2 shows the flow of blood and dialysis fluid through a dialysis machine.
Rajah 5.2 menunjukkan aliran darah dan bendalir dialisis melalui suatu mesin dialisis.
Table 5.1 / Jadual 5.1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 15
DIAGRAM 5.2/ RAJAH 5.2
Tube P contain more nitrogenous waste compared to tube Q. Explain why.
Tiub P mengandungi banyak bahan kumuh bernitrogen berbanding tiub Q.
Terangkan mengapa.
P1 - The concentration of dialysis fluid is maintained at a concentration
similar to the blood plasma of healthy person
P2 - the concentration of nitrogenous waste / urea / salt in P higher than
dialysis fluid
P3 - urea / salt diffused out into dialysis fluid
P4 - through semi-permeable tubing
(Any 3)
[3 marks]
(e) Explain the importance of kidney in maintaining human health.
Terangkan kepentingan ginjal dalam mengekalkan kesihatan manusia.
To eliminate waste materials / urea / toxics / excess water / salts
from the blood.
Maintaining normal osmotic pressure in the blood / constant
internal environment.
Ensure an optimal physical / chemical condition (in the internal
environment).
[3 marks]
Section B
Bahagian B
[40 markah]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 16
Answer all question from this section
Jawab semua soalan dalam bahagian ini.
6(a) Diagram 6.1 shows a forearm of humans.
Rajah 6.1 menunjukkan lengan atas manusia.
SKEMA JAWAPAN
6(a) Similarities:
S1 : Both joint has cavity filled with synovial fluid// lines with synovial membrane
S2 : (synovial fluid) act as lubricant to reduce friction between two bones.
S3 :The end surface of bone are covered with cartilage
A joint is the location at which bones connect. They are constructed to allow
movement and provide mechanical support.
Explain the similarity and difference between joint S and T?
Sendi adalah tempat di mana tulang-tulang bertemu. Sendi dibina untuk membolehkan
pergerakan dan member sokongan mekanikal berlaku.
Terangkan persamaan dan perbezaan antara sendi S dan T?
[6 marks/6 markah]
Joint S
Sendi S
Joint S
Sendi S
Diagram 6.1
Rajah 6.1
Joint T
Sendi T
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 17
S4 : (Cartilage) to protect the bone /reduce friction between the bones
S5 : Both joint are connected with ligament
S6 : (Ligament) allow movement/ avoid dislocation of bone during movement
Differences:
Joint S Joint T
D1 Hinge joint /Elbow joint Ball and socket joint/Shoulder joint
D2 Allow the movement in
one plane
Allow rotation movement // all direction
movement
D3 Articulation between
humerus, ulna and radius
Articulation between humerus,scapula
and clavicle.
(b)
Based on your biological knowledge, discuss the statement above.
Dengan menggunakan pengetahuan biologi anda, bincangkan pernyataan di atas.
[6 marks/6 markah]
SKEMA JAWAPAN
(b) P1 : problem / disease : arthritis/gout
P2 : (diet high protein intake) cause accumulation of uric acid in the joint
P3: inflammation at joint // joint become stiff and pain
P4 : Lack of exercise
P5 : Diet lack of calcium / vitamin D
P6 : reduce the mass of bone //bone become lighter
P7: practice wrong posture during activity
A man has swollen ankle and is painful during movement after having a
habit of taking high protein diet and practicing unhealthy lifestyle.
Seorang lelaki mengalami bengkak pada buku lali dan berasa sakit ketika
bergerak setelah mengamalkan pengambilan diet yang tinggi kandungan
yang protein dan tidak mengamalkan gaya hidup sihat.
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 18
(c) Diagram 6.2 show an earthworm and structure in its body.
Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan seekor cacing tanah dan struktur pada badannya.
Explain how the structure in the earthworm involve in their movement .
Terangkan bagaimana struktur pada cacing tanah terlibat dengan pergerakannya.
[4 marks/4 markah]
SKEMA PEMARKAHAN
(c) P1 : Hydrostatic skeleton
P2 : fluid in the body cavity helps the earthworm to move / give support
P3 : muscle at the body wall are longitudinal and circular muscle //antagonistic muscle
P4 : contraction of circular muscle( and relaxation of longitudinal muscle) cause
segment of body extended/longer/thinner
P5 : contraction of longitudinal muscle (and relaxation of circular muscle) cause
segment of body shorten/ thicken
P6 : (The presence of) chaetae
P7 : secure/anchor the shorted segment on the ground
[4 marks]
P8 : give pressure to skeleton system
[6 marks]
Diagram 6.2 /Rajah 6.2
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 19
(d)
Diagram 6.3 shows flight muscle of a bird.
Rajah 6.3 menunjukkan otot penerbangan seekor burung.
Explain the effect to locomotion of bird if structure W is torn.
Terangkan kesan terhadap pergerakan burung kastuktur W terkoyak.
[4 marks/4 mark]
SKEMA PEMARKAHAN:
(d) P1: W is tendon
P2 : Tendon is inelastic /strong/ tough
P3 : Function of tendon is to connect (pectoralis minor) muscle to bone
(/humerus)
P4 : Contarction of (pectoralis minor) muscle produces (pulling) force
P5 : (If tendon is torn), (pulling) force (that produced by contraction of
muscle)
Diagram 6.3
Rajah 6.3
W
Pectoralis minor muscle
Ototpektoralis minor
Humerus
Humerus
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 20
cannot be transferred to the bone
P5 : the bone/humerus is not pulled upward
P6 : no movement of wing
[4 marks]
7 Diagram 7.1 shows part of the blood circulatory system and the lymphatic system in
the human body.
Rajah 7.1 menunjukkan system peredaran darah dan sistem limfa dalam badan
manusia.
Diagram 7.1
Rajah 7.1
(i) Explain the differences between the composition of fluid P and fluid Q
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 21
Terangkan perbezaan antara komposisi bendalir P dan bendalir Q.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
(a) (i) Able to explain the diffrences of composition fluid P and fluid Q
Sample answer:
F1: Fluid Q/lymph has a larger numbers of lymphocyte compare
to fluid P/blood
P1: lymphocyte is produced by the lymph nodes in lymph system
F2: Fluid Q/lymph has lower contents of oxygen compare to fluid
P/blood
P2: oxygen has been used up by the cell
1
1
1
1
4
(ii) Describe how the fluid Q is formed from blood until it is incorporated back into the
blood circulatory system.
Huraikan bagaimana bendalir Q terbentuk daripada darah sehingga bendalir
tersebut masuk semula ke dalam sistem peredaran darah.
(a) (ii)
Able to describe how lymph is formed from blood until it is brought
back into the blood circulatory system.
Sample Answer :
P1: (When the blood flows from arteries into capillaries) there is
higher hydrostatic pressure at the arterial end of the
capillaries
P2: (This high pressure) forces some plasma to pass through the
capillary walls into the intercellular spaces (between the cells)
P3: Once the fluid leaves the capillary walls, it is called
interstitial/tissue fluid // The interstitial fluid fills the spaces
between the cells and constantly bathes the cells
P4: 90% of the interstitial fluid diffuses back into blood capillary
P5: 10% of the interstitial fluid that has not been reabsorbed into
the bloodstream goes into the lymph capillaries.(Once inside
the lymph capillaries) the fluid is known as lymph.
1
1
1
1
1
1
6
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 22
[6 marks][6 markah]
(c) (i) Describe how are lacteals in the villi related with the lymphatic system?
Huraikan bagaimana lakteal di dalam vilus dapat dikaitkan dengan sistem limfa?
(c) (i) Able to describe the how are lacteals related with the lymphatic
P6: The lymph capillaries unite to form larger lymphatic vessels.
P7: From the lymphatic vessels, lymph eventually passes into the
thoracic duct/the right lymphatic duct.
P8:The thoracic duct empties its lymph into the right subclavian
vein. (Hence, lymph drains back into the blood).
Any 6 P
1
1
Max 6
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 23
system.
Sample answer:
P1: A lacteal is a lymphatic capillary
P2: absorbs fatty acids and glycerol in the villi of the small
intestine
P3: lacteals merge to form larger lymphatic vessels
P4: that transport the fats to the thoracic duct which empties into
the left subclavian vein.
1
1
1
1
4
(ii) Helmie takes fried chicken at lunch.
Explain the absorption and assimilation process of lipid content in the fried chicken.
Helmie mengambil ayam goreng semasa makan tengah hari.
Huraikan proses penyerapan dan asimilasi lemak yang terkandung dalam ayam
goreng tersebut.
[6 marks]
(c) (i) Able to explain the absorption and assimilation of lipid
Absorption
P1: Digestion of lipid produce fatty acid and glyserol
P2: Absorption of lipid occur at ileum
P3: At ileum there are villi which have lacteal
P4: Fatty acid and glyserol are absorbed into lacteal
P5: In the lacteal condensation of fatty acid and glyserol forms
lipid
P6: The lipids then transported via the subclavian vein into the
blood steam
Assimilation
P7: In the cells lipid is use as a main component of plasma
membrane
P8: lipid also is use as a main component of some hormone and
vitamin
P9: Excess lipid will be stored underneath the skin as adipose
tissue
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
max
6
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 24
8(a) Diagram 8.1 shows the process of colonisation and succession in a habitat.
Rajah 8.1 menunjukkan proses pengkolonian dan penyesaran dalarn suatu habitat.
Diagram 8.1
What is meant by "colonisation and succession in a habitat?
Based on Diagram 8.1 .explain how colonisation and succession bring about the formation of the
primary forest.
[10 marks]
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan "pengkolonian dan penyesaran dalam suatu habitat"?
Berdasarkan Rajah 8.1, terangkan bagaimana pengkolonian dan penyesaran membawa kepada
pembentukan hutan primer dalam suatu habitat. [ 10 markah]
8.0 F1: COLONISATION The process whereby living organisms move into
this newly formed area which is completely devoid of life.
1
Rhizophora sp
Sonneratia sp
Bruguiera sp
Low
tidal
High tidal
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 25
F2: SUCCESSION The gradual process where one community changes
its environment so that it is replaced by another community.
Zone 1 / Avicennia sp. and Sonneratia sp.
P1: The pioneer species in a mangrove swamp are the Avicennia sp.
and Sonneratia sp.
P2: The Avicennia sp. grows in the part of the mangrove swamp that
faces the sea while Sonneratia sp. grows at the mouth of the river
which is sheltered.
P3: A root system that spreads out widely to give support to the trees in
the soft muddy soil
P4: The Avicennia sp. and Sonneratia sp. have asparagus-shaped
pneumatophores that grow vertically upwards from the main roots
through the mud into the air.
P5: The widely spread roots of the Avicennia sp. and Sonneratia sp. trap
mud.
P6: As more and more mud accumulate, the bank is slowly raised and
would then contain less water.
P7: The mangrove swamp is now more suitable for another mangrove
tree which is the Rhizophora sp. Hence the Rhizophora sp. as the
successor will slowly replace the pioneer species.
Zone 2 / Rhizophora sp. zone
P8: This zone is higher and less waterlogged.
P9: The Rhizophora sp. has prop roots to support and anchor the tree in
the soft muddy soil.
P10: The Rhizophora sp. has viviparity seeds to ensure that the
seedlings can grow and are not carried away by the seawater.
P11: The prop roots of the Rhizophora sp. are able to trap mud. The pioneer
species and the Rhizophora sp. that are old, will die and decay, adding
humus to the soil.
P12: The banks are raised up even higher. The soil becomes more
solid/compact, more fertile and less saline.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 26
(b) Diagram 8.2 shows sources of greenhouse gases arising from human activities and natural
processes.
Rajah 8.2, menunjukan sumber-sumber gas rumah hijau yang dihasilkan daripada aktiviti
manusia dan proses-proses semulajadi.
P13: The soil that is harder and drier now is not suitable for the Rhizophora
sp. Hence, the Rhizophora sp. is replaced by the Bruguiera sp.
Zone 3 / Bruguiera sp. zone
P14: Trees of Bruguiera sp. grow well in hard clay soil that subjects to
flooding during high tide.
P15: Trees of Bruguiera sp. have buttress roots for support and knee-
shaped pneumatophores for gaseous exchange (Figure 8.24(c)).
P16: As more sedimentation of decayed substances occur, new mud banks
are being built up seawards while the old banks move further inland,
away from the sea.
P17 : The soil becomes harder and dry land is formed.
P18: Bruguiera sp. are replaced by other types of plants such as coconut
trees, palm trees and Pandanus sp.
P19: These are later replaced by other land plants.
P20: Finally, after a few hundred years, the process of succession stops and
a tropical rain forest, which is the climax community, is formed.
At least one point in each zone.
[10 marks]
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 10
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 27
Diagram 8.2 Rajah 8.2
Based on Diagram 8.2, Explain the green house effectand global warming as a result of
human activities.
Berdasarkan Rajah 8.2, terangkan kesan rumah hijau dan pemanasan global akibat aktiviti-
aktiviti manusia
[5 marks].
b) The formation of greenhouse effect caused by;
P1: Solar radiation , containing uv rays penetrate earth atmosphere and
reaches the earth surface
P2: Part of uv rays is reflected back by earth's surface to atmosphere in
the form of infrared radiation / light which contains heat
P3: Heat (energy) is trapped by greenhouse gases (such as carbon
dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, methane)
P4: Human activities such as combustion of fossil fuel by factories and
vehicles increase the amount of greenhouse gases
P5: Higher concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere results
in more heat being absorbed / trapped
P6: Extensive forest burning, burning of fossil fuel and higher rate of
evaporation worldwide causes accumulation of great amount of water
vapour in the air
P7: which also contribute to the increase in the earth's temperature /
causes global warming
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 5
8 (c)
Diagram 8.3 shows the emission of gases from factories.
Rajah 8.3 menunjukkan pelepasan gas daripada kilang.
Nitrogen oxide (NO) ,sulphur dioxide (SO
2
)
Nitrogen oksida(NO), sulfur dioksida (SO
2
)
Pond
Kolam
Forest
Hutan
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 28
(i) Explain the effects of the emission of the gases to the ecosystem.
Terangkan kesan pembebasan gas tersebut kepada ekosistem.
[5 marks]
SKEMA PEMARKAHAN
8(c)
P1: (The release of nitrogen oxides / sulphur dioxides) leads to the formation of
acid rain
P2 : the gases dissolve in the rain water
P3 : Acid rain causes damage on the leaves / chloroplast
P3 : Lower rate of photosynthesis
P4 : Leads to stunted growth / death of plants//population reduced
P5 : Acid rain lowers pH of the pond// more acidic
P6 : causes death to aquatic organisms /fishes
P7 : pH of soil lower//more acidic
P8 : crop yield decrease [max : 5 marks]
9.(a) Diabetics do not correctly produce or use their insulin hormone. The insulin hormone
helps control how much sugar is in your bloodstream. Millions of diabetics need to take
insulin. Insulin from cows and pigs has been used since the early 1900s to treat diabetes.
Now human insulin hormone can be mass-produced through genetic engineering
processes.
Pesakit kencing manis tidak dapat menghasilkan atau menggunakan insulin dengan
betul. Hormone insulin membantu mengawal kandungan gula dalam aliran darah .
Berjuta-juta pesakit kencing manis perlu mengambil insulin. Insulin daripada lembu dan
babi telah digunakan seja kawal 1900-an untuk merawat kencing manis. Sekarang
hormon insulin manusia boleh dihasilkan secarabesar-besaran melalui proses
kejuruteraan genetik.
Diagram 9.1shows a few stage that involves in the production of insulin hormone through
genetic engineering technology.
Rajah 9.1 menunjukkan sebahagian daripada peringkat yang terlibat dalam proses
penghasilan hormon insulin melalui teknologi kejuruteraan genetik.
Diagram 8.3/Rajah 8.3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 29
By using your knowledge , explain how this technology can be used in insulin hormone
production.
Berdasarkan pengetahuan biologi anda huraikan bagaimana teknologi ini dijalankan bagi
menghasilkan hormone insulin.
[6 marks/ 6 markah]
SKEMA JAWAPAN
9(a) P1 -The gene for the insulin is isolated from human pancreas cell
P2 - The bacterial plasmid is isolated (DNA found in bacteria)
P3 - The bacterial plasmid is cut by using enzyme
P4 - The enzyme used to incorporate gene for insulin production into the
plasmid
P5 - the bacteria are cultured in bioreactor
P6 - the plasmid replicate as a bacteria divide asexually .
P7 - the bacteria can produce insulin in large quantity, purified and isolate.
(b)
Genetic engineering (GE) is the manipulation of genetic material (DNA or genes) in a
cell or an organism in order to produce desired characteristics and to eliminate
unwanted ones. GE includes a range of different techniques with many different uses,
Diagram 9.1
Rajah 9.1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 30
and can be applied to plants, animals and humans.
For example, the genetic modification of food is a form of GE that involves manipulating
the cells of plants.
Kejuruteraan genetik (GE) adalah manipulasi bahan genetik (DNA atau gen) di dalam
selatau organism untuk menghasilkan ciri-ciri yang dikehendaki dan untuk
menghapuskan organisma yang tidak diingini. GE termasuk pelbagai teknik yang
berbeza dengan kegunaan yang berbeza, dan boleh digunakan untuk tumbuh-
tumbuhan, haiwan dan manusia. Sebagai contoh, pengubahsuaian genetic makanan
adalah satubentuk GE yang melibatkan memanipulasi sel-sel tumbuh-tumbuhan.
Diagram 9.2 shows twotoma to leaves which have been exposed to a bacterial
pathogen, Pseudomonas syringae. Leaf A is the normal leaf show disease when
infected with the bacteria while Leaf B, the genetically engineered leaf shows
practically no signs of damage.
Rajah 9.2 menunjukkan dua helai daun tomato yang telah didedahkan kepada sejenis
pathogen bacteria ,Pseudomonas syringae. Daun A adalah daun bias yang
menunjukkan tanda-tanda penyakit setelah dijangkiti oleh bacteria tersebut,
manakala daun B yang telah mengalami pengubahsuaian kandungan genetiknya tidak
menunjukkan tanda kerosakan.
Discuss the benefits and the risks of using the genetically engineered organisms in
agriculture and food production.
Bincangkan faedah dan risiko menggunakan organism yang terubah suai kandungan
genetiknya dalam pertanian dan penghasilan makanan.
[10 marks/10 markah]
Diagram 9.2/ Rajah 9.2
Leaf A /Daun A Leaf B /Daun B
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 31
SKEMA PEMARKAHAN
9(b) The benefit:
P1: Genetic engineering used to produce disease resistant /pest resistant plant.
P2 : Less pesticide are used
P3 : Less pollution to the environment //better health for consumer
P4: Increase crop yield
P5 : help to solve problem of insufficient food
P6 :better livehood for farmer
P7 : Increase resistance to herbicide
P8 : which allow weeds to be killed without affecting the crop plant
P9 : Able to survive on poorer quality grassland
P10 : can resist drought // climatic changes
P11 : create crops with better nutrition value
P12 : with high vitamin A / protein content
P13 : help to solve problems of malnutrition
P14: create crops with longer shelf live
P15: less food wastage
P16: genetically modified livestock (eg :cow)
P17: produce meat with less fat / more milk
[Max : 6 marks]
The risk:
K1 : Pest resistant genes may be transferred to weed
K2 : may be difficult to control the growth of weed
K3: some transgenic crops may have animal genes
K4: this may not be acceptable to certain groups for religious reasons
K5: genetically modified food may be harmful to health
K6: may activate human genes to cause cancer
K7: transgenic organism may affected the survival of other organism in the
ecosystem
K8: may cause the imbalance of nature / ecosystem
K9 : decrease biodiversity
K10: certain cultivar are being planted to the exclusion of others
K11: this will less the genetic variation in environment.
[Max: 4 marks]
(c)
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j. Diagram 9.3 shows a cloning process of a plant.
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN AKADEMIK SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 | MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 32
k. Rajah 9.3 menunjukkan proses pengklonan satu tumbuhan.
Explain the characteristic of cloned plant.
Terangkan ciri-ciri tumbuhan yang diklon.
[4 marks]
SKEMA PEMARKAHAN
9(C) P1: Clones are genetically identical to the parent cell
P2: no exchange of genetic materials
P3: Clones have the same chromosomal number as the parent cell
P4: no reduction in the chromosomal number
P5: Clones easily get disease // shorter life span
P6: Clones have the same body resistance against disease
End ..
Leaf cells form calluses in culture medium
Sel daun membentuk kalus di dalam
medium kultur
Calluses develop into tiny plantlets
Kalus berkembang menjadi anak pokok kecil
Cloned plants
Tumbuhan klon
Leaf cells are taken from the parent plant
Sel daun diambil dari tumbuhan induk
Diagram 9.3
Rajah 9.3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 1
QUESTION 1:
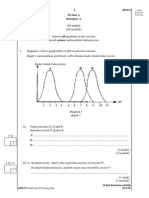
1. A group of students carried out an experiment to study the effect of intraspecific
competition on the growth of maize seedlings.
Sekumpulan pelajar menjalankan satu eksperimen untuk mengkaji kesan persaingan
intraspesifik ke atas pertumbuhan biji benih jagung.
Diagram 1 shows the apparatus set-up of the experiment
Rajah 1 menunjukkan susunan radas untuk eksperimen tersebut
Step 1 : Three seedlinging trays are filled with 4 kg of garden soil.
Langkah 1 : Tiga kotak semaian diisikan dengan 4 kg tanah kebun.
Step 2 : The trays are labeled as P, Q and R.
Langkah 2 : Kotak-kotak semaian dilabelkan P, Q dan R.
Step 3 : In tray P, 50 maize seedlings are seedlinged at a distance of 15 cm
intervals.
In tray Q, 50 maize seedlings are seedlinged at a distance of 10 cm
intervals.
In tray R, 50 maize seedlings are seedlinged at a distance of 5 cm
intervals.
Langkah 3 : Dalam kotak P, 50 anak benih jagung ditanam pada jarak 15 cm
berselang seli.
Dalam kotak Q, 50 anak benih jagung ditanam pada jarak 10 cm berselang seli.
Dalam kotak R, 50 anak benih jagung ditanam pada jarak 5 cm berselang seli.
Step 4 : Each tray is watered daily with the same amount of water for 30 days.
Langkah 4 : Setiap kotak semaian disiram tiap-tiap hari dengan jumlah air yang
sama banyak untuk 30 hari.
Step 5 : After 30 days, remove 30 maize seedlings randomly from tray P, tray Q and tray R.
The root of seedlings are washed and wipedry.
Langkah 5 : Selepas 30 hari, 30 anak benih jagung secara rawak dari kotak P, kotak Q dan
kotak R. Akar anak benih dibersihkan dan dilapkan sehingga kering.
Step 6 : The dry weight of the maize seedlings is recorded in Table 1.
Langkah 6 : Berat kering anak benih jagung dicatatkan dalam Jadual 1.
O 0 0
O 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
Tray P/kotak P Tray Q /kotak Q Tray R/kotak R
Diagram 1/rajah 1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 2
Distance
between
maize
seedlings /
jarak antara
anak benih
jagung (cm)
Dry weight of 30 maize seedlings (g) /
berat kering 30 anak benih jagung (g)
15
10
200
150
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 3
5
Table 1/Jadual 1
(a) Record the dry weight of the maize seedlings in the boxes provided in Table 1
Rekodkan berat kering anak benih jagung di dalam kotak yang disediakan dalam
jadual 1.
(b) (i) Based on the results in Table 1 , state two observations that can be made from
this experiment.
Berdasarkan keputusan di dalam Jadual 1, nyatakan dua pemerhatian yang dapat
dibuat daripada eksperimen ini
Observation 1/pemerhatian 1:
At distance 15 cm, the dry weight of 30 paddy seedlings is 200g
Observation 2/pemerhatian 2:
At distance 5 cm, the dry weight of 30 paddy seedlings is 100g
[3 marks]
(ii) State the inference from the observations in (b) (i).
Nyatakan inferens berdasarkan pemerhatian di (b) (i)
Inference from observation 1/inferen dari pemerhatian 1:
(At distance 15 cm), there is low intraspecific competition so the growth rate of
maize plant is high
Inference from observation 2/inferen dari pemerhatian 2:
(At distance 5 cm), there is highintraspecific competition so the growth rate of
maize plant is low
[3 marks]
100
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 4
(c) Complete table 2 based on the experiment.
Berdasarkan eksperimen, lengkapkan jadual 2 di bawah
[3 marks]
(d) State the hypothesis for this experiment.
Nyatakan hipotesis bagi eksperimen ini
The further the distance between the maize seedlings, the higher the growth rate
of/dry weight of maize plant//vice versa
[3 marks]
(e) Construct a table and record all your data collected in the experiment which include the
following aspects :
Bina satu jadual untuk merekodkan semua keputusan eksperimen meliputi aspek
berikut :
Distance between maize seedlings/jarak antara anak benih jagung
Dry weight of 30 maize seedlings/berat kering 30 anak benih jagung
Growth rate of maize seedling/kadar pertumbuhan anak benih jagung
Growth rate = Dry weight of maize seedlings
Number of days
Kadar pertumbuhan = Berat kering anak benih jagung
Bilangan hari
Variable
Pembolehubah
Particulars to be implemented
Cara mengendalikan pembolehubah
Manipulated/
manipulasi:
Distance between
maize seedlings
Used different distance between maize seedling//used
the distances at 15cm, 10cm and 5cm
Responding /
bergerakbalas:
Dry weight of maize
seedlings//
growth rate
Record dry weight of maize seedlings by using a
weight balance // calculate the growth rate using
formula
Growth = Dry weight of 30 maize plant
30 days
Controlled/ dimalarkan
Volume garden soil //
type of maize plant //
size of tray
Fix the volume of garden soil at 4kg // fix the same
type of maize plant // fix the same size of tray
Table 2// Jadual 2
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 5
Distance between maize
seedlings (cm)
Dry weght of 30 maize
seedlings (g)
Growth rate (g/days)
15 200 6.67
10 150 5.00
5 100 3.33
[3 marks]
(f) Use the graph paper provided on page 55 to answer this question. Using the data in 1
(e)draw a graph of the growth rate of maize seedlings against the distance between the
maize seedlings.
Dengan menggunakan kertas graf yang dibekalkan pada muka surat 55 untuk menjawab
soalan ini. Dengan menggunakan data di dalam 1 (e), lukiskan graf kadar pertumbuhan
anak benih jagung melawan jarak di antara anak benih jagung
[3 marks]
(g) Based on graph in 1 (f), explain the relationship between the growth rate of maize
seedlings and distance between seedling
Berdasarkan graf di 1 (f), terangkan hubungan di antara kadar pertumbuhan anak
benih jagung dan jarak antara anak benih.
P1: As the distance between maize increases, the growth rate of maize
seedlings increases.
P2: This is because there is lower intraspecific competition
P3: causes the dry weight of maize seedlings increase
[3 marks]
(h) If the experiment is repeated by increasing the distance between the maize seedlings to
20 cm, predict the observation . Explain your prediction..
Jika eksperimen diulang dengan meningkatkan jarak di antara anak benih jagung pada
20 cm,ramalkanpemerhatian. Terangkan ramalan anda.
P1: The dry weight more than 200g
P2: because longer distance give more water/ nutrient / space to the maize
seedling,
P3: so the growth rate of maize seedlings increases
[3 marks]
(i) Based on this experiment, what can you deduce about intraspecific competition?
Berdasarkan eksperimen ini, apakah yang dapat anda rumuskan tentang persaingan
intraspesifik?
P1: Intraspecific competition is the growth maize plants when it compete
between themselves
P2: and shown by the dry weight of maize seedling.
P3: The growth rate of maize is affected by the distance between the seedlings
[3 marks]
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 6
(j) When resources are limited supply, organisms living in the same habitat will compete for
the same resources. The following is a list of the resources.
Apabila sumber-sumber menjadi terhad, organisma hidup di habitat yang sama akan
bersaing untuk sumber yang sama. Berikut ialah senarai sumber-sumber tersebut.
In Table 3, classify the resources given according to what are the resources competed
by animals and resources compete by plants.
Dalam Jadual 3, klasifikasikan sumber-sumber yang diberi mengikut apakah sumber-
sumber yang dsaingi oleh haiwan dan sumber-sumber yang disaingi oleh tumbuhan.
The resources competed by animals/
Sumber-sumber yang dsaingi oleh haiwan
Resources compete by plants/
Sumber-sumber yang disaingi oleh
tumbuhan
Food
Space
Breedingmate
Nutrien
Water
Light
[3 marks]
Food/makananSpace/ruang Breedingmate/pasangan mengawan
Nutrient/nutrien Water/air Light/cahaya
Table 3/Jadual 3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 7
Distance between
maize seedlings (cm)
0 5 10 15
6
5
4
3
2
1
Growth rate
Of maize
seedlings
(g/days)
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 8
QUESTION 2
Score Explanation
01 Identified the problem
3 Able to state problem statement correctly
P1 light intensity
P2 rate of transpiration
Sample answer:
Is the light intensity increase the rate of transpiration of plant?
2 Able to state problem statement but slightly incorrect
1 Able to state idea only (not in question)//Hypothesis form.
0 No response or wrong response.
Objective of study/Aim
Able to state the objective of study correctly
Sample answer:
To investigate the effects of light intensity on the rate of transpiration of a
balsam plant.
Variables
Able to state any one item for each variable given.
Manipulated Variable : distance light sources// ligh intensity
Responding Variable : Time taken for the air bubble move// rate of
transpiration
Fixed / Controlled Variable: temperature//type of plant
02 Statement of hypothesis
P1 light intensity
P2 rate of transpiration
P3 The rate transpiration / air bubble movement / is influence by light
intensity
3 Able to state the hypothesis correctly by relating two variable correctly.
Sample answer:
The higher the light intensity, the rate of transpiration of a balsam plant
increase.
2 Able to state hypothesis but slightly incorrect.
1 Able to state idea only.
0 No response or wrong response.
05
List of apparatus
Photometer, stopwatch, cutter (knife), beaker, fluorescent lamp, meter
ruler
List of materials
Balsam plant, Vaseline, water, tissue
3 Able to list down 4 apparatus and 3 material.
2 Able to list down 2 apparatus and 2 material.
1 Able to list down 1 apparatus and 1 material.
0 No response or wrong response.
B1 1
Technique used
Measure and record the time taken for the air bubble to move in a
distance for 10 cm by (B1-1).
04
Experimental procedure
1. A suitable balsam plant is selected (K1) and is cut using a sharp
knife (K1). The cut end is immediately immersed in a beaker filled
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 9
with distilled water. (K1)
2. The cut plant is then fixed onto a photometer (K1) and the joints
between the plant and the photometer are sealed using Vaseline to
make them airtight (K5).
3. The laboratory curtains and doors are pulled and closed so that
outside lightning will not affect the outcome of the experiment (K1).
4. A 40W(K2) fluorescent lamp is set 30 cm (K3) away from the edge
of the (K3) photometer with a meter rule placed to measure the
distance.
5. The air bubble in the photometer is set to 0 cm (K4). The lamp is
switched on and the stopwatch is started (K4) when the air bubble
cross the X mark .
6. The movement of air bubble is observed and the stopwatch is
stopped when the bubble reaches Y mark, that is 10 cm (K2).
7. Record the time taken into a table(K4) .
8. Steps 4 to 7 are repeated, with the distance of the lamp are put at
40 cm(K3), 50 cm(K3), 60 cm (K3) away from the photometer.
9. All the findings are recorded into the table(K4).
3 All 5Kcriteria correct
K1 any three criteria
K2 any one criteria
K3 any three criteria
K4 any two criteria
K5 any one criteria
2 3K 4Kcriteria correct.
1 At least 2Kcriteria correct.
0 No response or wrong response.
B2 1
Presentation of data
Data is present in a table with right unit for rate of transpiraton (for B2 1
cm/second or cm second
-1
)
If without the unit for the rate of transpiration, give no an idea (x) and B2 -
0.
Conclusion
Write the hypothesis or another hypothesis.
Sample answer:
The higher the light intensity the higher the rate of transpiration.
Hypothesis is accepted.
03 Report writing
3 Score 3 = 7-9
2 Score 2 = 4-6
Distance of lamp
from the edge of
the photometer
(cm)
Time taken for
the air bubble
to travel for X
to Y (s)
Rate of
Transpiration
(cm/second)
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP 10
1 Score 1 = 1-3
0 No response or wrong response.
Question 1: 33 Marks
Question 2: 17 Marks
(Total = 50 marks)
END OF THE SCHEME MARKING
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
1
SKEMA BIOLOGI KERTAS 3
Question Criteria Score
1 (a) Able to record all the data for volume of the urine collected and
average of urine produce correctly.
Sample answers
Type of
Vegetables
Amount of Filtrate needed to decolorize
DCPIP solution (ml)
Cauliflower 4.2
Broccoli 2.5
Lime 3.6
Ascorbic
Acid
1.0
3
Able to record 3 data correctly 2
Able to record 2 data correctly 1
Able to record only 1 data / wrong response 0
(b) (i) Able to state two different observation correctly base on the
criteria:
C1 Type of vegetables
C2 Amount of Filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP solution
(ml)
Sample answers
1. The amount of Cauliflower/ Broccoli/ Lime/ Ascorbic Acid
filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP solution is 4.2 ml/ 2.5 ml/
3.6ml/ 1.0ml
2. The amount of Cauliflower filtrate needed to decolorize
DCPIP solution is higher than the amount of Broccoli filtrate.
3
Able to state one correct observation and one inaccurate
observation.
Sample answer (inaccurate)
1. The amount of cauliflower filtrate needed to decolorize
DCPIP solution the highest
2
Able to state only one correct observation or two observations at
idea level.
Sample answer (idea)
1. The amount of vegetables filtrate needed to decolorize
DCPIP solution is different
1
No response or incorrect response or inaccurate observation or
one idea only.
0
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
2
Question Criteria Score
(b) (ii) Able to make two accurate inferences base on two criteria:
C1 amount of vegetable filtrate
C2 content of vitamin C
Sample answer
1. Amount of vegetable filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP
solution is high, the content of vitamin C in the vegetables
filtrate is low.
2. Amount of vegetable filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP
solution is low, the content of vitamin C in the vegetables
filtrate is high.
3
Able to make one correct inference and one inaccurate
inference or able to state two inaccurate inferences.
Sample answer (inaccurate)
1. More / high / much (amount) of vegetable filtrate.
2. Low/ high content of Vitamin C
2
Able to sate one correct inference or two inferences at idea
level.
Sample answer (idea level)
1. The content of vitamin C is different
1
No response or inaccurate response 0
Summary of scoring for 1(b)(i) and 1(b)(ii)
Score Correct Inaccurate Idea Wrong
3 2 - - -
2
1 1 - -
- 2 - -
1
1 - 1 -
- - 2 -
- 1 1 -
0
- 1 - 1
- - 1 1
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
3
Question Criteria Score
(c) Able to state all variables and methods to handle each variable
correctly.
Sample answer
Variable Method
Manipulated variable:
Types of Filtrate
Use different type of filtrate
Responding variable:
Volume of filtrate needed
to decolorize DCPIP
solution
Measure and record the
volume of vegetable filtrate
needed to decolorize
DCPIP solution using
syringe
Calculate and record the
percentage of Vitamin C
using the formula :
Amount of Ascorbic Acid
needed to decolorize
DCPIP solution(ml) x 0.1%
Amount of Filtrate needed to
decolorize DCPIP solution(ml)
Initial volume of filtrate/
volume of DCPIP solution
Fix the initial volume of filtrate
which is 5ml / volume of
DCPIP solution which is 1ml
Able to state 4 5 ticks 2
Able to state 2 3 ticks 1
No response or incorrect response or 1 tick only 0
(d)
Able to state the hypothesis relating the manipulated variable
and the responding variable correctly based on three criteria:
P1 : Manipulated variable (volume of water intake)
P2 : Responding variable ( volume of urine collected)
H : Relationship of the variables.
Sample answer
1. Broccoli has the highest amount of Vitamin C compared to
3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
4
Cauliflower, and Spinach.
P1 + P2 + H
Able to state the hypothesis based on any two criteria.
Sample answer
1. The amount of filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP solution
affects the content of Vitamin C.
2. Different amount of filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP
solution, different content of Vitamin C.
P1 + P2 // P1/P2 + H
2
Able to state the hypothesis based on any one criteria or idea
level.
Sample answer
1. The content of Vitamin C is different.
1
Question Criteria Score
(e) (i) Able to construct a table correctly with the following aspects:
T : Title with correct unit - 1 mark
D : Data - 1 mark
C : Percentage of Vitamin C - 1 mark
Sample answer
Type of filtrate The amount of
filtrate needed to
decolorize DCPIP
solution (ml)
Percentage of
Vitamin C (%)
Cauliflower 4.2 0.02//0.022
Broccoli 2.5 0.04
Lime 3.6 0.03//0.027
Ascorbic Acid 1.0 0.1
3
Any two aspect correct 2
Any one aspect correct 1
Incorrect response 0
(ii) Able to draw the graph of volume of water reabsorb against
volume of water intake based on the following aspects:
P (Paksi): Title of x-axis and y-axis with unit - 1 mark
Title (Title) : Four points plotted correctly - 1 mark
B (Bentuk) : All points connected smoothly - 1 mark
All three aspect correct
3
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
5
Any two aspect correct 2
Any one aspect correct 1
No response or Incorrect response 0
(f) Able to explain the relationship between the amount of
vegetable filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP solution and type
of filtrate base on the following criteria.
R1 : Relationship -
R2 : the amount of vegetable filtrate to decolorize DCPIP
R3 : the concentration of vitamin C
Sample answer
Broccoli has the highest amount of vitamin C compared to
cauliflower and Lime. This is because the amount of vegetable
filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP is low, thus the
concentration of vitamin C is high enough which needed only
small amount of flitrate to reduce DCPIP solution.
3
Able to explain the relationship using any two aspects 2
Able to explain the relationship using any one aspect only 1
No response or Incorrect response 0
Question Criteria Score
(g) Able to predict and explain the volume of urine produced based
on the following criteria :
P1 : Prediction - More than 4.5 ml
P2 : Explanation - denaturation of vitamin C
P3 : Concentration of filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP
solution
Sample answer
Volume of filtrate needed to decolorize DCPIP solution is more/
higher than 4.5ml. This is because boiling causes Vitamin C to
denature. Thus there is less/ no vitamin C concentration in
filtrate to decolorize DCPIP solution
Able to predict and explain the volume of urine produced based
on any two criteria
2
Able to predict and explain the volume of urine produced based
on any one criteria
1
No response or Incorrect response
0
(h) Able to define Vitamin C operationally based on the following
criteria.
D1 :
D2 :
D3 :
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
6
Sample answer
3
Any two criteria stated 2
Any one criteria stated 1
No response or Incorrect response 0
Question Criteria Score
(i) Able to classify apparatus and materials into their respective
variables.
Sample answer
Materials Apparatus
Ascorbic Acid
Fruit Juices
DCPIP Solution
Syringe with needle
Specimen Tube
Measuring Cylinder
All 6 corrects in its appropriate correct.
3
5 4 correct 2
3- 2correct 1
1 0 No response or Incorrect response 0
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
7
Paper 3 No 2 (Scheme)
Item Criteria Marks
Problem statement
Able to state the problem statement of the experiment correctly
based on three criteria:
Manipulated variables (different) water sources/ samples (P1)
Responding variables time taken to decolourise methylene
blue solution
// level of polution (P2)
Relationship in question form and question symbol [?] (H)
Sample Answer
1. What is the time taken to decolourise methylene blue solution//
level of pollution of different water sources/samples ?
2. Does different water sources/samples has different time taken to
decolourise methylene blue solution// level of pollution ?
3 marks
Able to state the problem statement of the experiment correctly
based on any two criteria.
Sample Answer
1. What is the time taken to decolourise methylene blue solution//
level of pollution of different water sources/ samples.
2 marks
Able to state the problem statement of the experiment correctly
based on only one criteria.
Sample Answer
1. What is the time taken to decolourise methylene blue
solution / level of pollution of water sources/ sample.
2. Water sources/ samples have different level of pollution.
1 mark
Wrong or no response
0 mark
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
8
Item Criteria Marks
Hypothesis
Able to state the hypothesis of the experiment correctly based on
three criteria:
Manipulated variables different water sources/ samples (P1)
Responding variables time taken to decolourise methylene
blue solution
/level of pollution (P2)
Relationship more/less than//higher/lower than // shortest//most
(H)
Sample Answer
1. Water sample A/ drain water took the shortest time to
decolourise methylene blue solution compared to water sample B,
C and D.
2. Drain water /water sample A is the most polluted samples of
water collected.
3 marks
Able to state the hypothesis of the experiment correctly based on
two criteria:
Sample Answer
1. Different sources of water samples affect the time taken for the
methylene blue solution to decolourise .
2 marks
Able to state the hypothesis of the experiment correctly based on
one criteria:
Sample Answer
1. The drain water is polluted
1 mark
Wrong or no response 0 mark
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
9
Item Criteria Marks
Variables
Able to state the variables of the experiment correctly that include
three criteria:
Manipulated : different water sources/ samples
Responding : time taken to decolourise methylene blue solution
// level of polution
Constant : volume of water samples// volume of methylene blue
solution
3
marks
Able to state the variables of the experiment correctly that include
two criteria.
2
marks
Able to state the variables of the experiment correctly that include
one criteria
1 mark
Wrong or no response
0 mark
Item Criteria Marks
Materials
Methylene blue solution, water samples from A, B, C and D
Apparatus
Syringe with needle, stop watch, Reagent bottle, stopper and beaker
3
marks
2M +
5A
Materials
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
10
Two materials
Apparatus
Any three apparatus (syringe and stop watch are compulsory )
2
marks
2M +
3A
Materials
Two materials
Apparatus
Two apparatus ( syringe and stop watch )
1 mark
2M +
2A
Cannot state the functional materials and apparatus
0 mark
Item Criteria Marks
Procedure
Able to state five Ks correctly.
K1 : Preparation of materials & apparatus (3K1)
K2 : Operating fixed variable (1K2)
K3 : Operating responding variable (1K3)
K4: Operating manipulated variable (1K4)
K5 : Precaution (1K5)
3
marks
Able to state any three Ks correctly
2
marks
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
11
Able to state any two Ks correctly
1
marks
Able to state only one K correctly or no response
0
marks
Example for procedure
K1: Preparation of materials & apparatus
1. Water samples are collected from four different sources A,B,C
and D
2. The reagent bottles are labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4
3. The reagent bottles are closed with the stopper immediately
4. The stopwatch is activated
5. The bottles are examined from time to time
6. The results are tabulate.
K2: Operating fixes variable
1. Measure 250 ml of water sample from A, B, C and D
separately and pour into the reagent bottle labelled 1, 2, 3 and
4 respectively
2. 1 ml of methylene blue solution is added to each water
sample using a syringe
K3: Operating responding variable
1. The time taken for the methylene blue solution to decolourise is
measured and recorded in the table using stop watch.
K4: Operating manipulated variable
1. Measure 250 ml of water samples from A, B, C and D
separately and pour into the reagent bottle labeled 1, 2, 3 and
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
12
4 respectively
Item Criteria Marks
K5: Precaution
1. 1 ml of methylene blue solution is added to the base of each
water sample using a syringe with needle
2. The reagent bottles are closed with stopper immediately
3. The contents of the bottles cannot be shaken.
4. All the reagent bottles are kept in a dark cupboard
Sample answer:
Method / procedure :
1. Water samples are collected (K1) from 4 different water
resources (K3)
*(A,B,C and D).
2. The reagent bottles are labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4
3. 250 ml of water samples (K2) is measured (K1) from 4
different water
Resources (A, B, C and D) separately and pour (K1) into the
reagent bottle labeled 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively.
4. 1 ml (K2) of methylene blue solution is added (K1) to the base
(K5) of each water sample using a syringe with needle.
5. The reagent bottles are closed with stopper immediately. (K5)
6. The content of the bottles cannot be shaken. (K5)
7. All the reagent bottles are kept in a dark cupboard. (K5)
8. The stop watch is activated. (K1)
9. The bottles are examined (K1) at one hour interval.
10. The time taken for the methylene blue solution to decolourise is
measured and recorded for all the water samples using stop
watch. (K3)
11. The result is tabulated. (K1)
*Tap,
drain,
river,
pond.
PROGRAM KECEMERLANGAN SPM SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH, KPM 2014
BIOLOGY 4551 MODUL PERFECT SCORE SBP
13
Presentation of data
1. Able to state all the titles correctly with units.
2. Able to state 4 water samples.
Water samples Time taken for methylene
blue solution to decolourise
(hour )
Tap water
Drain water
River water
Pond water
2
marks
Able to state any one criteria only 1 mark
END OF MARKING SCHEME
You might also like
- SPM 4551 2009 Biology k2Document20 pagesSPM 4551 2009 Biology k2pss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- SPM 2011 4551 Biology k2Document24 pagesSPM 2011 4551 Biology k2pss smk selandar50% (2)
- Biologi k2 Bab 5Document29 pagesBiologi k2 Bab 5Joseph Adinkz100% (1)
- Modul Cemerlang Kimia Melaka Gemilang SPM 2014Document33 pagesModul Cemerlang Kimia Melaka Gemilang SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal50% (2)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2014 - Modul Pecutan - Modul X A PlusDocument219 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2014 - Modul Pecutan - Modul X A PlusCikgu Faizal100% (3)
- SPM 4541 2007 Chemistry k1Document15 pagesSPM 4541 2007 Chemistry k1pss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2Document18 pagesSains Tingkatan 2nazatulfirdausNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Document56 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (4)
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 1 ExerciseDocument31 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 1 ExerciseDennis Ling100% (9)
- Pat Fiz 2018 K2Document32 pagesPat Fiz 2018 K2Syikin ZainalNo ratings yet
- SPM 2008 Biology K2Document23 pagesSPM 2008 Biology K2pss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Soalan Bio Kertas 2 f4Document14 pagesSoalan Bio Kertas 2 f4unieezzNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 4 (BL)Document10 pagesIT Chem F5 Topical Test 4 (BL)Hajar Norasyikin Abu Bakar0% (1)
- Percubaan SPM 2016 Biologi Kertas 3Document14 pagesPercubaan SPM 2016 Biologi Kertas 3kiongocNo ratings yet
- QS016-1 Sem1 2010-2011Document15 pagesQS016-1 Sem1 2010-2011pusatsumberkmtphNo ratings yet
- Ujian Setara Matematik Tingkatan 2 2019 SMK PamolDocument16 pagesUjian Setara Matematik Tingkatan 2 2019 SMK PamolAinul Syahirah Omar50% (2)
- Modul SEBATIAN KARBONDocument18 pagesModul SEBATIAN KARBONNorliyana Ali100% (9)
- SPM 4531 2010 Physics k2Document40 pagesSPM 4531 2010 Physics k2pss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Bab Jirim Dan Bahan Ting 4 LatihanDocument2 pagesBab Jirim Dan Bahan Ting 4 Latihantumirah86No ratings yet
- BAB 4 - Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument64 pagesBAB 4 - Jadual Berkala UnsurNini Asnini Ismail0% (1)
- JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPM K1 Set ADocument26 pagesJUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPM K1 Set ACikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Bab 2 Jirim Dan Struktur AtomDocument27 pagesBab 2 Jirim Dan Struktur AtomAZMIRA100% (1)
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Biology Paper 2Document37 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Biology Paper 2ChinWynn.com100% (25)
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap2Document17 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 Chap2PK ChunNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score Dan Pecutan Kimia Serta Xa Plus SBP 2014 With SkemaDocument229 pagesModul Perfect Score Dan Pecutan Kimia Serta Xa Plus SBP 2014 With SkemaRohana AsranNo ratings yet
- Ujian MacDocument7 pagesUjian MacMUHAMMAD FIRDAUS BIN MOHD FAUZAI MoeNo ratings yet
- Lines and Angles II & Polygons IIDocument9 pagesLines and Angles II & Polygons IIHelen PappuNo ratings yet
- Kuiz Kimia Kebangsaan Malaysia PDFDocument1 pageKuiz Kimia Kebangsaan Malaysia PDFShay LeehinNo ratings yet
- Ujian Matematik Tingkatan 4Document8 pagesUjian Matematik Tingkatan 4Waheeda Wahee33% (3)
- Bio P3 PPT F4 2018Document10 pagesBio P3 PPT F4 2018veronica francisNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 K1Document29 pagesTrial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 K1Cikgu Faizal86% (7)
- Kimia Tingkatan 4 Bab 2Document6 pagesKimia Tingkatan 4 Bab 2Vicknesh Ramanaidu100% (1)
- JUJ Pahang 2014 Biology SPM K2 Set 1 SkemaDocument15 pagesJUJ Pahang 2014 Biology SPM K2 Set 1 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (3)
- Ujian 1 - F4 - Sains - 2020 - SkemaDocument5 pagesUjian 1 - F4 - Sains - 2020 - SkemareetajesuNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Rumus Algebra Latihan TambahanDocument3 pagesModul 3 Rumus Algebra Latihan TambahanEmilyNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry Paper 2Document19 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry Paper 2ChinWynn.com100% (10)
- SPM 4541 2007 Chemistry k2Document24 pagesSPM 4541 2007 Chemistry k2pss smk selandar0% (1)
- SPM 2008 Chemistry k1Document29 pagesSPM 2008 Chemistry k1pss smk selandar100% (1)
- 2016 Soalan P3 Trial BiologyDocument26 pages2016 Soalan P3 Trial BiologyPoziah Md Yusoff100% (1)
- 2012 PSPM Kedah Fizik 2 W AnsDocument34 pages2012 PSPM Kedah Fizik 2 W Ansjee2kk100% (1)
- Bio k2Document19 pagesBio k2Zainurain Zainal Abidin0% (1)
- Midyer Bio Paper2 (Repaired)Document17 pagesMidyer Bio Paper2 (Repaired)hanafizaNo ratings yet
- Trial SBP SPM 2013 Biology K1Document32 pagesTrial SBP SPM 2013 Biology K1Cikgu Faizal100% (4)
- Perbengkelanbiologi2015 150511050145 Lva1 App6892Document170 pagesPerbengkelanbiologi2015 150511050145 Lva1 App6892zul100% (1)
- Biology Paper 2,3 Trial SPM 2013 MRSM GRDocument45 pagesBiology Paper 2,3 Trial SPM 2013 MRSM GRJessica MasonNo ratings yet
- Q Kertas 1Document30 pagesQ Kertas 1mohd nazrul nizamNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2Document23 pagesTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Bio k2Document19 pagesBio k2Sivam DhanabalNo ratings yet
- Matematik LatihanDocument17 pagesMatematik LatihandmvksytbvzNo ratings yet
- Trial Penang SPM 2013 BIOLOGY K2 K3 (SCAN)Document0 pagesTrial Penang SPM 2013 BIOLOGY K2 K3 (SCAN)Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- SPM Bio1 Q&A (MLK)Document33 pagesSPM Bio1 Q&A (MLK)SimPor100% (2)
- Pptbiot4.2015.kertas 2Document15 pagesPptbiot4.2015.kertas 2Nang Maizana Megat YahyaNo ratings yet
- Myschoolchildren Bio k23 Trial SPM 2012 SelangorDocument36 pagesMyschoolchildren Bio k23 Trial SPM 2012 SelangorArvinth Guna SegaranNo ratings yet
- PERCUBAAN SPM KEDAH Kertas 1 BIOLOGIDocument33 pagesPERCUBAAN SPM KEDAH Kertas 1 BIOLOGIZambrisaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- 4551-1 Bio Trial SPM 2015Document28 pages4551-1 Bio Trial SPM 2015zulkarnain100% (2)
- SPMC Bio Perlis k1 2016Document28 pagesSPMC Bio Perlis k1 2016zulkarnainNo ratings yet
- BIO - Modul CemerlangDocument84 pagesBIO - Modul Cemerlangmustaqil90% (21)
- Bio T4 2022 Kertas 1Document17 pagesBio T4 2022 Kertas 1syahiddasabriNo ratings yet
- Biologi K123 F4 2010Document92 pagesBiologi K123 F4 2010Roxus ThamNo ratings yet
- Kedah SPM Trial 2011 Biology (W Ans) PDFDocument95 pagesKedah SPM Trial 2011 Biology (W Ans) PDFrickysuNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2Document22 pagesTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2 SkemaDocument12 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Tahun Tingkatan 1Document14 pagesPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun Tahun Tingkatan 1Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K1Document30 pagesTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K1Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Modul Prinsip Perakaunan Penyata Pengeluaran SPM 2014Document6 pagesModul Prinsip Perakaunan Penyata Pengeluaran SPM 2014Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K1Document22 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K1Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Menyelesaikan Maslah P & P Fizik DGN Menggunakan Reso-EqDocument6 pagesMenyelesaikan Maslah P & P Fizik DGN Menggunakan Reso-EqPhysics MGCM100% (1)
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM Skema K1 K2Document14 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM Skema K1 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2Document23 pagesTrial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument18 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2Document19 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K2Document14 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K2Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K1 Modul 2Document24 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K1 Modul 2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014Document58 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (7)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument16 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah Trial SPM 2014 B.tamil (2BFC891C)Document13 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah Trial SPM 2014 B.tamil (2BFC891C)gunaNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang Matematik SPM 2014 K2Document31 pagesTrial Pahang Matematik SPM 2014 K2Cikgu Faizal100% (8)
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Document25 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Sejarah-Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Kertas 3 SPM 2014 (Bahagian B)Document47 pagesSejarah-Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Kertas 3 SPM 2014 (Bahagian B)Dyieba LatifNo ratings yet
- Contoh 1 - Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Open Book Test Kertas 3 Sejarah SPM 2014 PPD Kuala LangatDocument17 pagesContoh 1 - Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Open Book Test Kertas 3 Sejarah SPM 2014 PPD Kuala LangatCikgu Faizal75% (4)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument19 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument19 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument40 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument47 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument42 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal75% (4)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument39 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument41 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument46 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Document56 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (4)